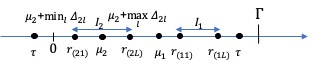
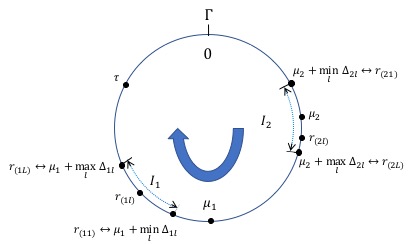
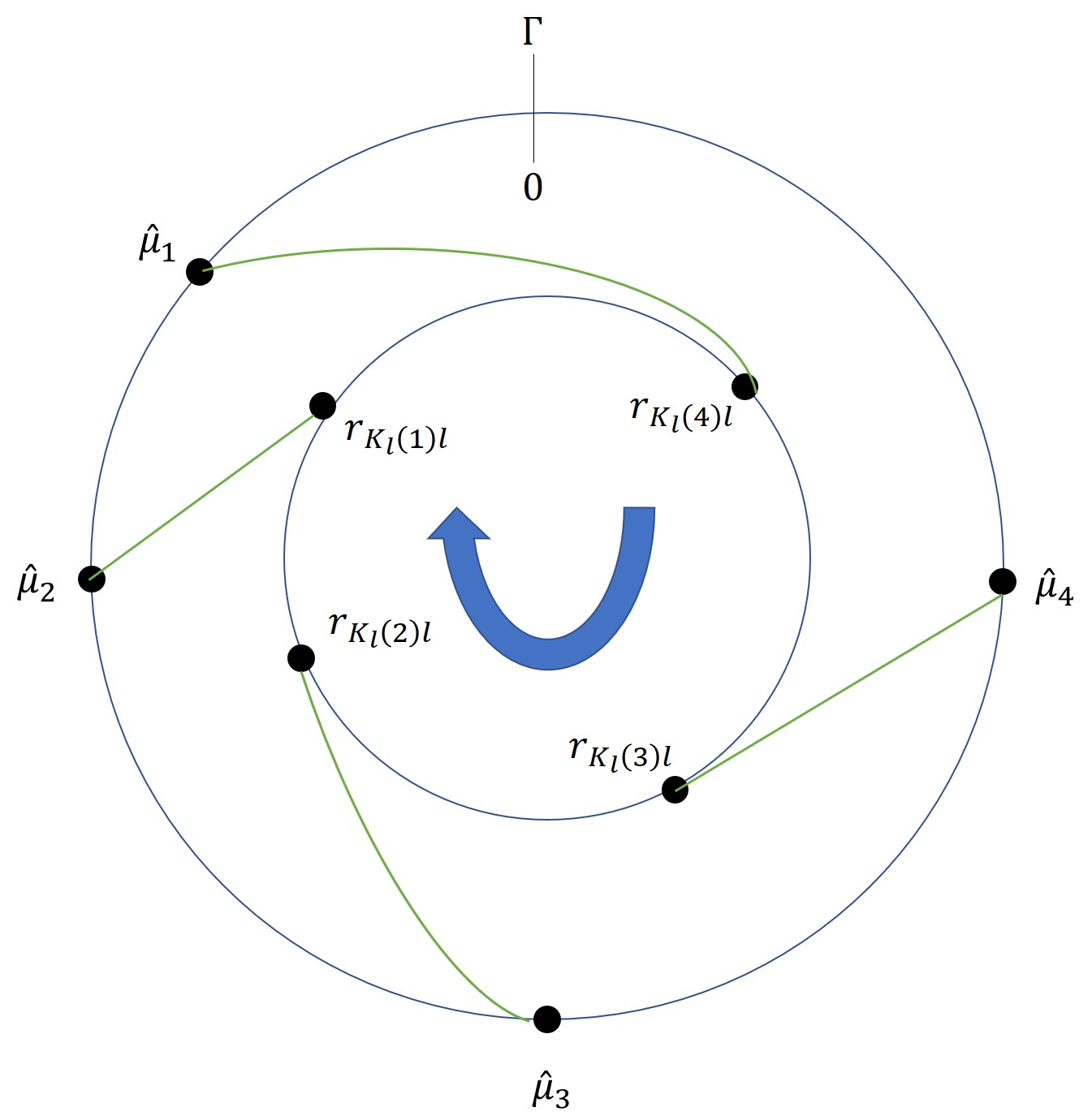
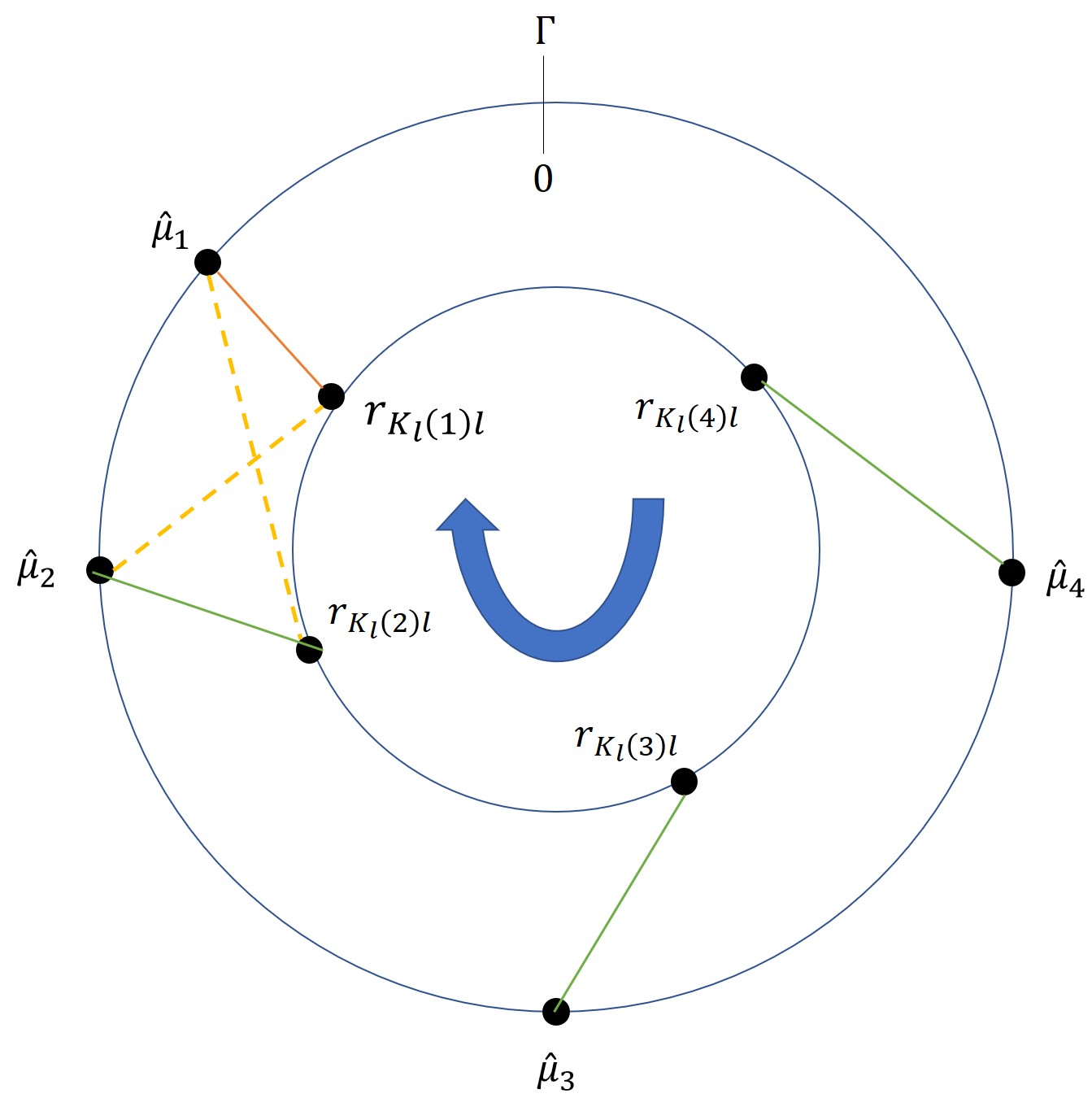
Statistical Robustness in Chinese Remainder Theorem for Multiple Numbers
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Statistical Robust Chinese Remainder Theorem for Multiple Numbers- ArXiv ID: 1909.00225
- Date: 2019-09-04
- Authors: Hanshen Xiao, Nan Du, Zhikang T. Wang and Guoqiang Xiao
📝 Abstract
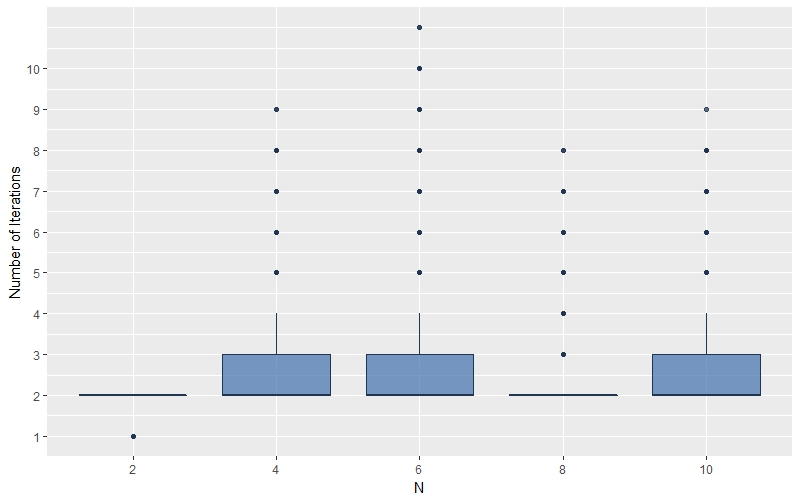
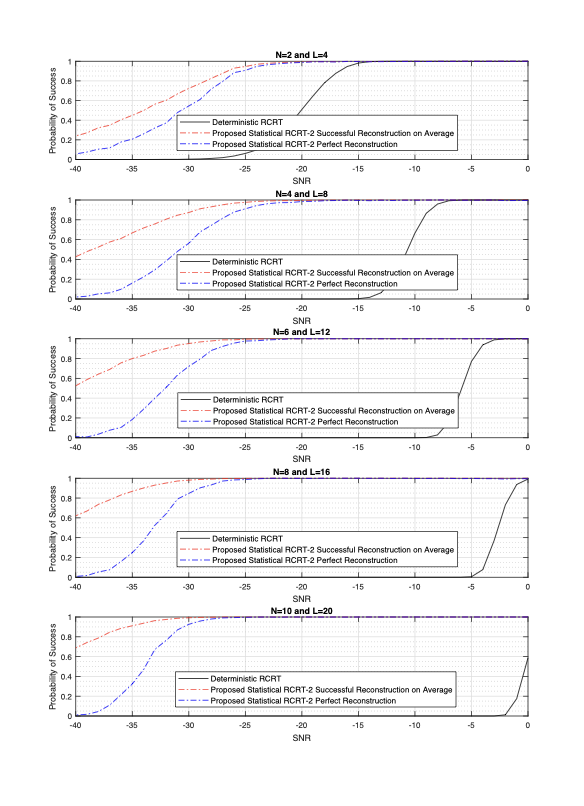
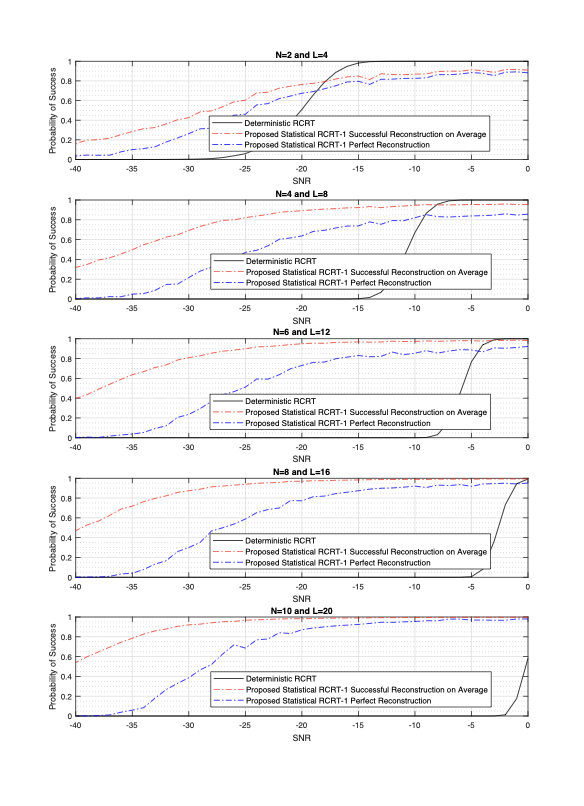
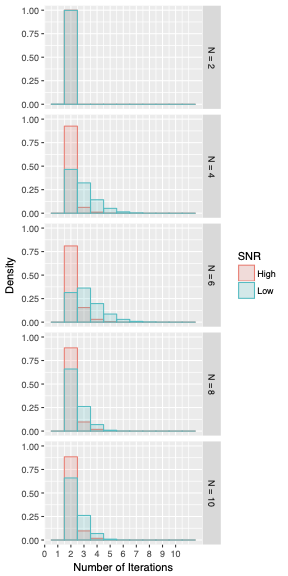
Generalized Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT) is a well-known approach to solve ambiguity resolution related problems. In this paper, we study the robust CRT reconstruction for multiple numbers from a view of statistics. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first rigorous analysis on the underlying statistical model of CRT-based multiple parameter estimation. To address the problem, two novel approaches are established. One is to directly calculate a conditional maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) estimation of the residue clustering, and the other is based on a generalized wrapped Gaussian mixture model to iteratively search for MAP of both estimands and clustering. Residue error correcting codes are introduced to improve the robustness further. Experimental results show that the statistical schemes achieve much stronger robustness compared to state-of-the-art deterministic schemes, especially in heavy-noise scenarios.💡 Summary & Analysis
This paper introduces a statistical approach to robustly reconstruct multiple numbers using the Generalized Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT). It addresses ambiguity resolution issues in CRT-based estimation and presents two innovative methods: one for directly calculating conditional maximum a posteriori probability (MAP) estimates of residue clustering, and another based on a generalized wrapped Gaussian mixture model to iteratively find MAPs. These techniques are particularly effective under high-noise conditions, outperforming traditional deterministic schemes.Core Summary: The paper proposes new statistical approaches using CRT to reconstruct multiple numbers with robustness, especially under noisy conditions. Problem Statement: Traditional CRT-based methods face challenges in resolving ambiguities and maintaining performance under heavy noise. Solutions (Key Technologies): Two main techniques are introduced:
- Direct calculation of MAP estimates for residue clustering.
- Iterative search using a generalized wrapped Gaussian mixture model to find MAPs. Major Achievements: Experimental results show that the proposed statistical schemes perform significantly better than existing deterministic methods, particularly in high-noise environments. Significance and Applications: This research provides a pioneering statistical framework for CRT-based multiple parameter estimation, enhancing robustness under noisy conditions. It can be applied in signal processing, cryptography, and complex system monitoring.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)