Sabrina Modeling and Visualizing Economic Data with Incremental Domain Knowledge
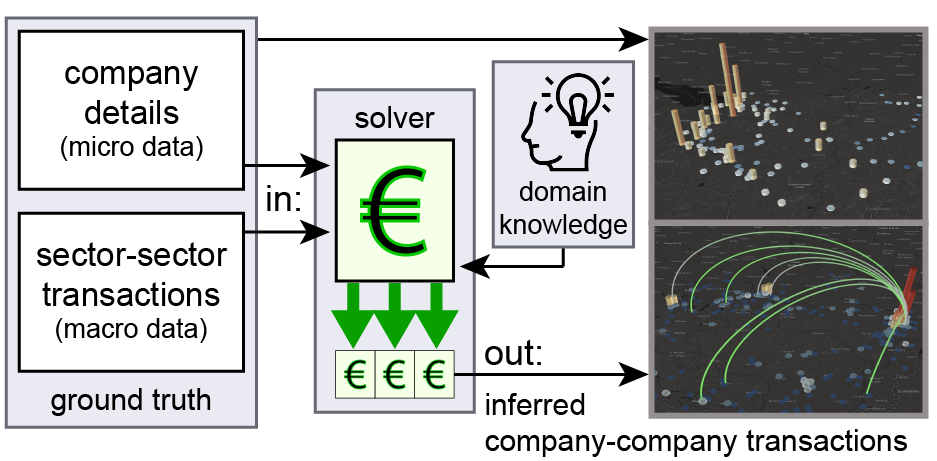
Investment planning requires knowledge of the financial landscape on a large scale, both in terms of geo-spatial and industry sector distribution. There is plenty of data available, but it is scattered across heterogeneous sources (newspapers, open data, etc.), which makes it difficult for financial analysts to understand the big picture. In this paper, we present Sabrina, a financial data analysis and visualization approach that incorporates a pipeline for the generation of firm-to-firm financial transaction networks. The pipeline is capable of fusing the ground truth on individual firms in a region with (incremental) domain knowledge on general macroscopic aspects of the economy. Sabrina unites these heterogeneous data sources within a uniform visual interface that enables the visual analysis process. In a user study with three domain experts, we illustrate the usefulness of Sabrina, which eases their analysis process.