Exploring World Maps in Virtual Reality Comparing 3D Exocentric Globes, Flat Maps, Egocentric 3D Globes, and Curved Maps
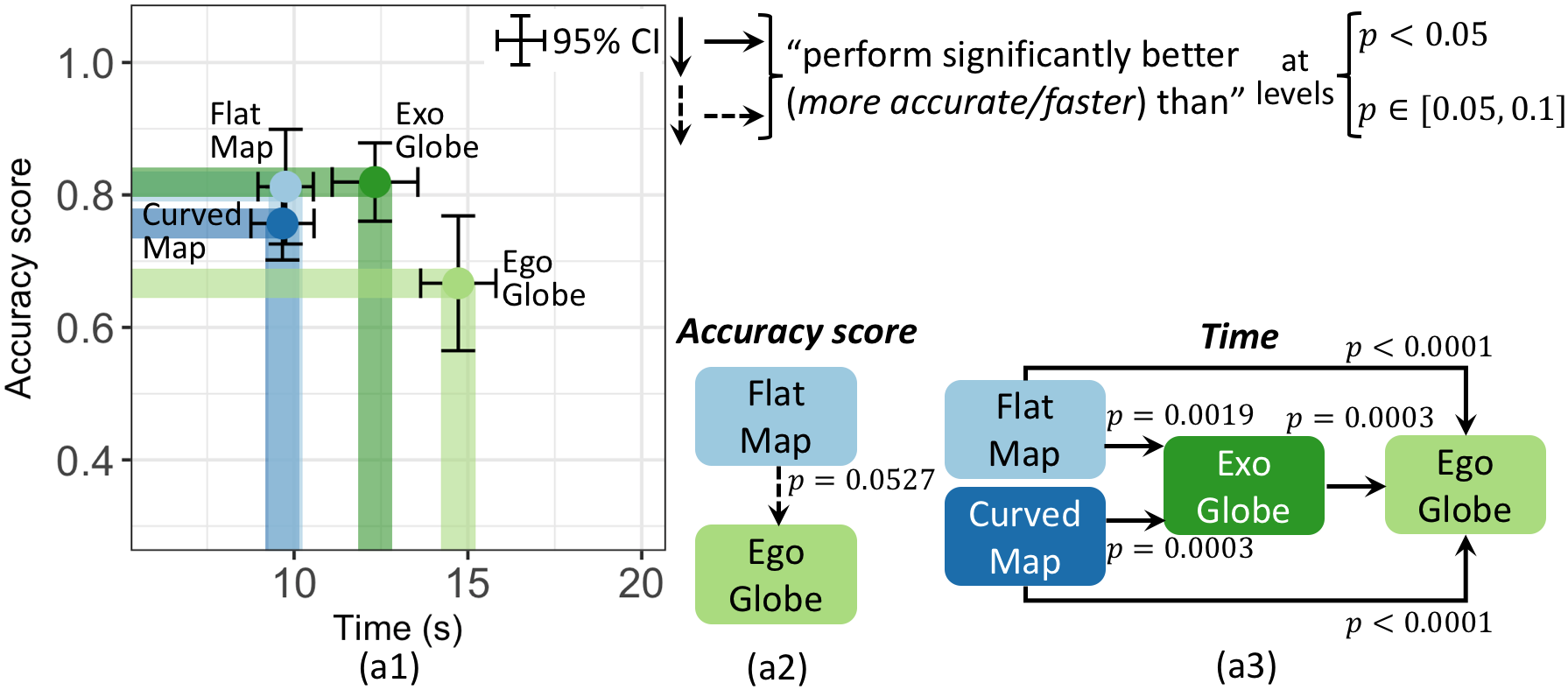
This paper explores different ways to render world-wide geographic maps in virtual reality (VR). We compare (a) a 3D exocentric globe, where the user s viewpoint is outside the globe; (b) a flat map (rendered to a plane in VR); (c) an egocentric 3D globe, with the viewpoint inside the globe; and (d) a curved map, created by projecting the map onto a section of a sphere which curves around the user. In all four visualisations the geographic centre can be smoothly adjusted with a standard handheld VR controller and the user, through a head-tracked headset, can physically move around the visualisation. For distance comparison, exocentric globe is more accurate than egocentric globe and flat map. For area comparison, more time is required with exocentric and egocentric globes than with flat and curved maps. For direction estimation, the exocentric globe is more accurate and faster than the other visual presentations. Our study participants had a weak preference for the exocentric globe. Generally, the curved map had benefits over the flat map. In almost all cases the egocentric globe was found to be the least effective visualisation. Overall, our results provide support for the use of exocentric globes for geographic visualisation in mixed-reality.

