An Adaptive, Disentangled Representation Method for Multidimensional MRI Reconstruction
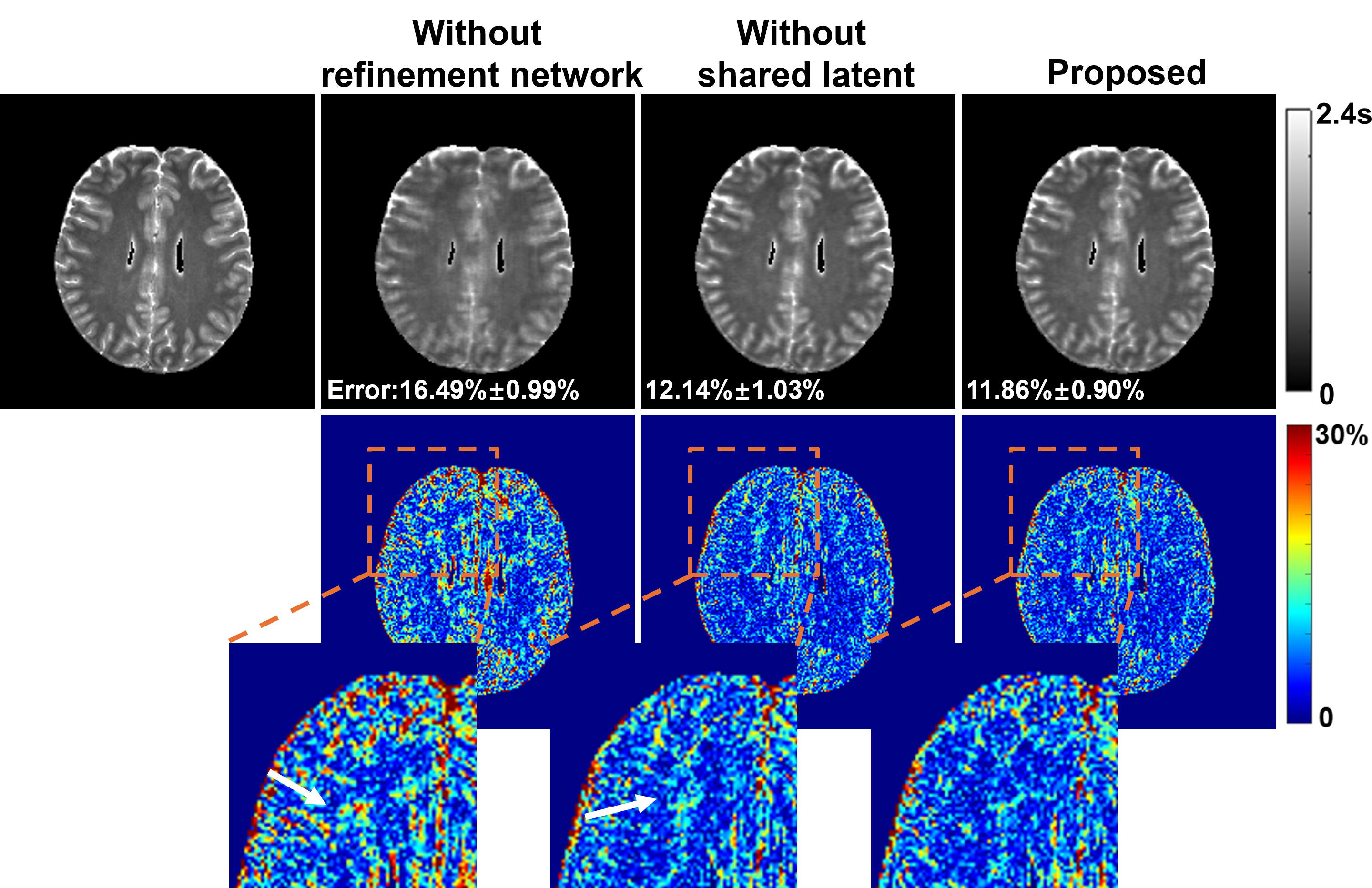
We present a new approach for representing and reconstructing multidimensional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. Our method builds on a novel, learned feature-based image representation that disentangles different types of features, such as geometry and contrast, into distinct low-dimensional latent spaces, enabling better exploitation of feature correlations in multidimensional images and incorporation of pre-learned priors specific to different feature types for reconstruction. More specifically, the disentanglement was achieved via an encoderdecoder network and image transfer training using large public data, enhanced by a style-based decoder design. A latent diffusion model was introduced to impose stronger constraints on distinct feature spaces. New reconstruction formulations and algorithms were developed to integrate the learned representation with a zero-shot selfsupervised learning adaptation and subspace modeling. The proposed method has been evaluated on accelerated T1 and T2 parameter mapping, achieving improved performance over state-of-the-art reconstruction methods, without task-specific supervised training or fine-tuning. This work offers a new strategy for learning-based multidimensional image reconstruction where only limited data are available for problem-specific or task-specific training.