Control of the Painlevé Paradox in a Robotic System
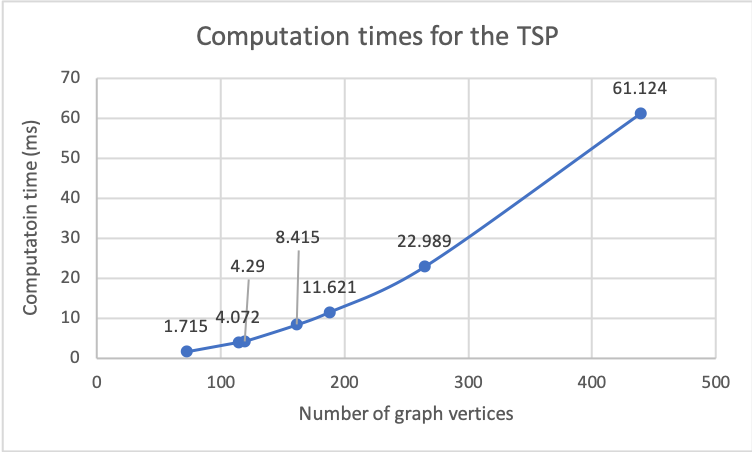
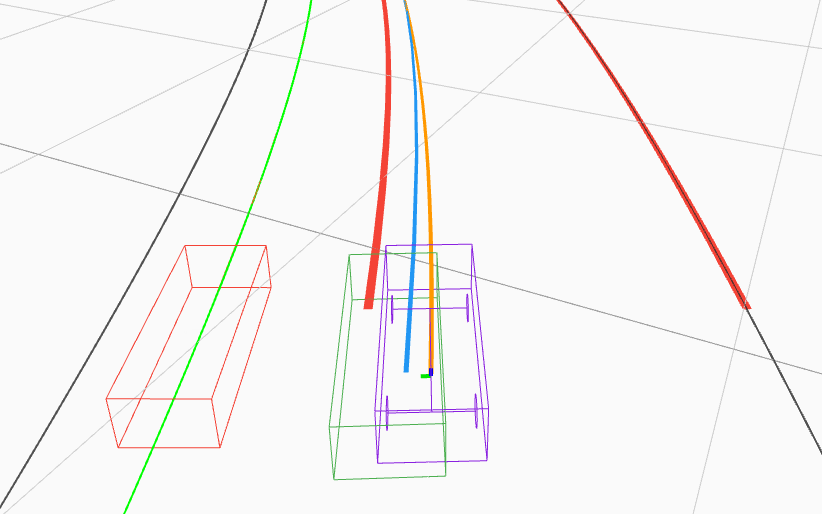
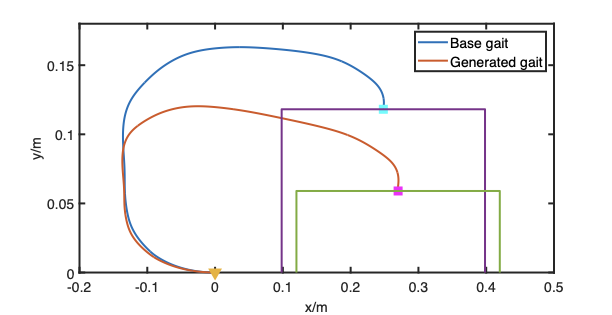
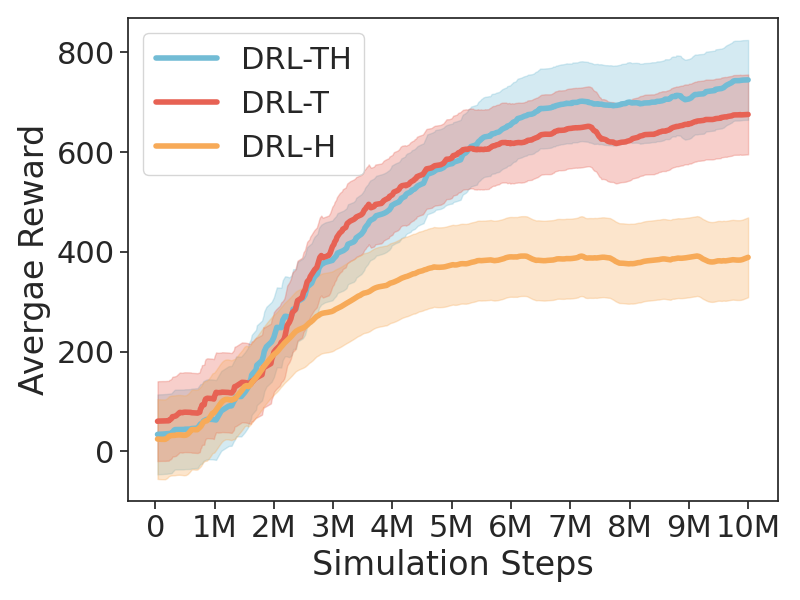
The Painlev e paradox is a phenomenon that causes instability in mechanical systems subjects to unilateral constraints. While earlier studies were mostly focused on abstract theoretical settings, recent work confirmed the occurrence of the paradox in realistic set-ups. In this paper, we investigate the dynamics and presence of the Painlev e phenomenon in a twolinks robot in contact with a moving belt, through a bifurcation study. Then, we use the results of this analysis to inform the design of control strategies able to keep the robot sliding on the belt and avoid the onset of undesired lift-off. To this aim, through numerical simulations, we synthesise and compare a PID strategy and a hybrid force/motion control scheme, finding that the latter is able to guarantee better performance and avoid the onset of bouncing motion due to the Painlev e phenomenon.