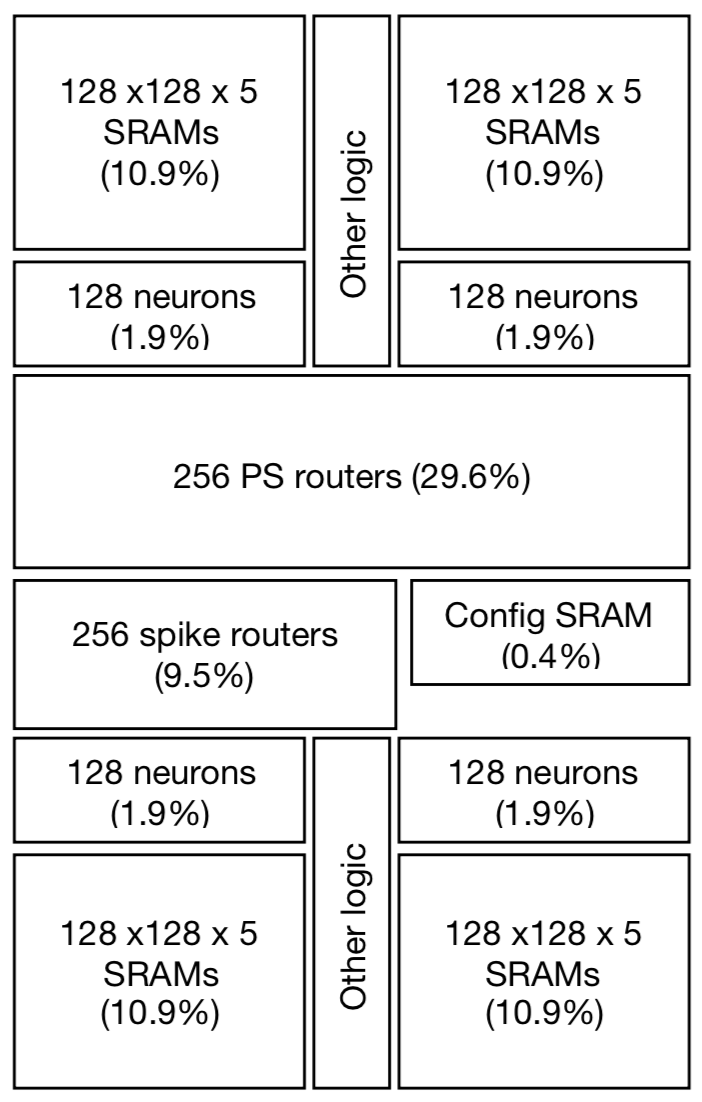
Channel Characterization for 1D Molecular Communication with Two Absorbing Receivers
This letter develops a one-dimensional (1D) diffusion-based molecular communication system to analyze channel responses between a single transmitter (TX) and two fully-absorbing receivers (RXs). Incorporating molecular degradation in the environment, rigorous analytical formulas for i) the fraction of molecules absorbed, ii) the corresponding hitting rate, and iii) the asymptotic fraction of absorbed molecules as time approaches infinity at each RX are derived when an impulse of molecules are released at the TX. By using particle-based simulations, the derived analytical expressions are validated. Simulations also present the distance ranges of two RXs that do not impact molecular absorption of each other, and demonstrate that the mutual imfluence of two active RXs reduces with the increase in the degradation rate.