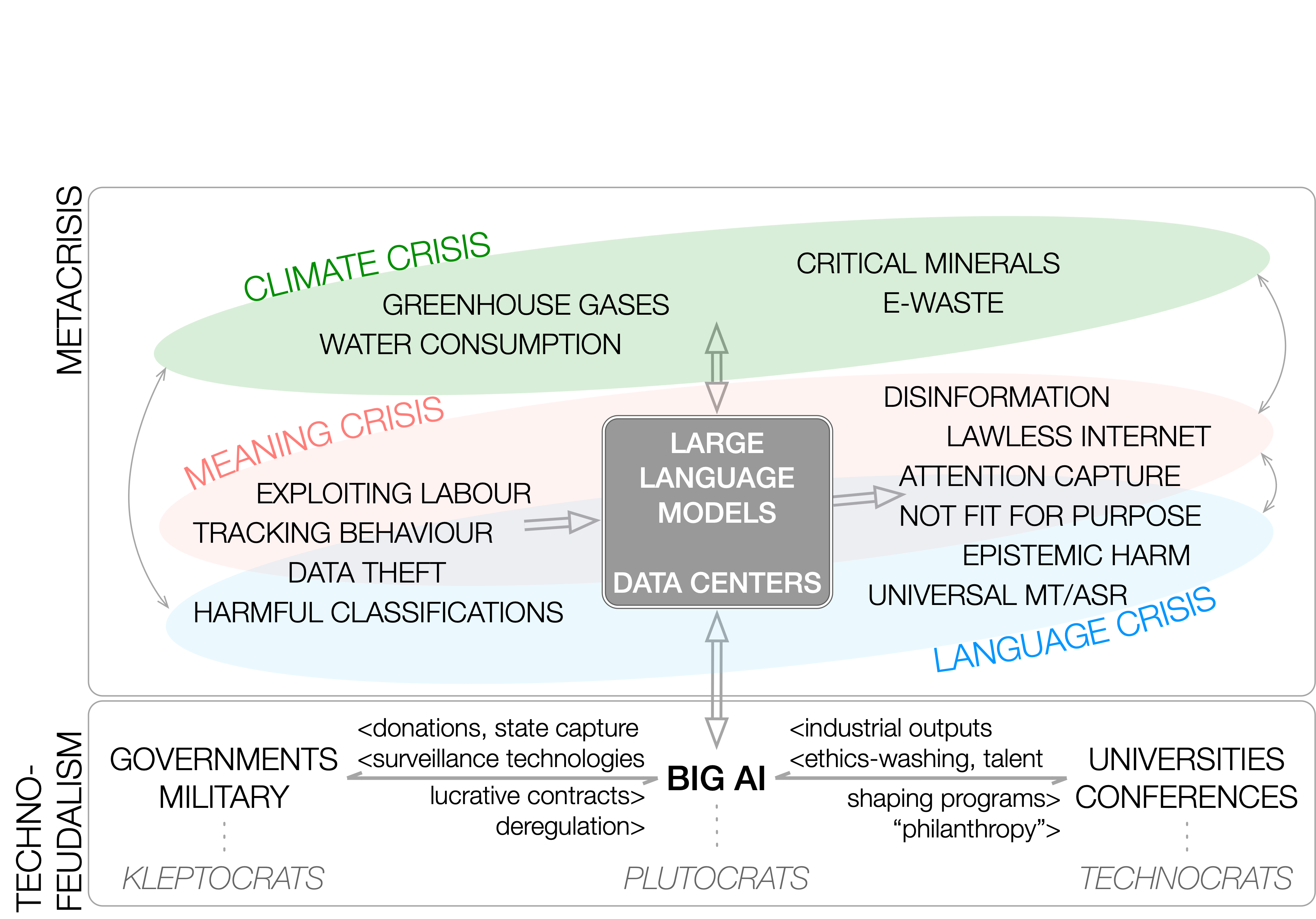
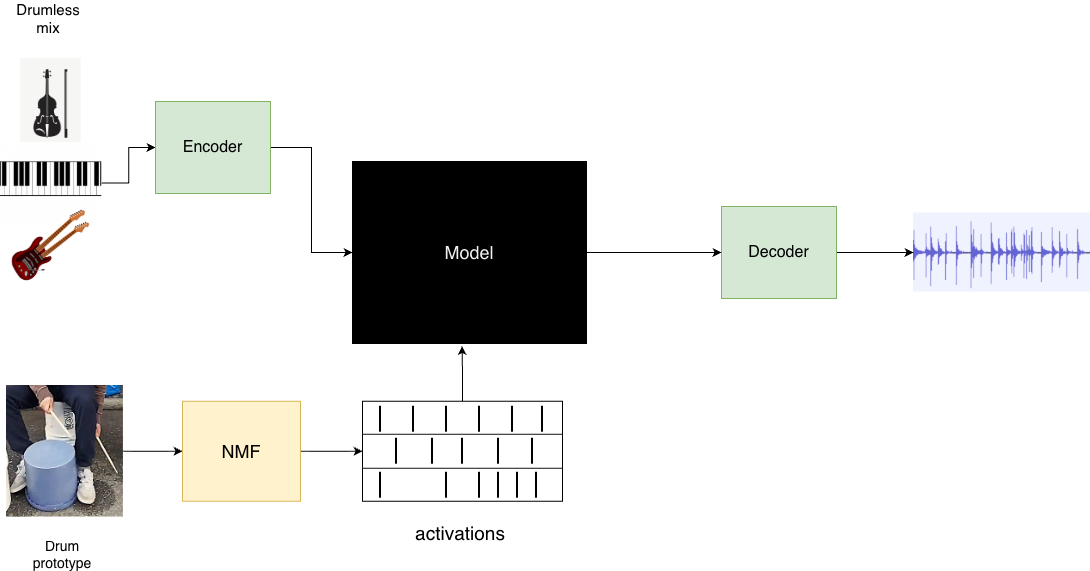
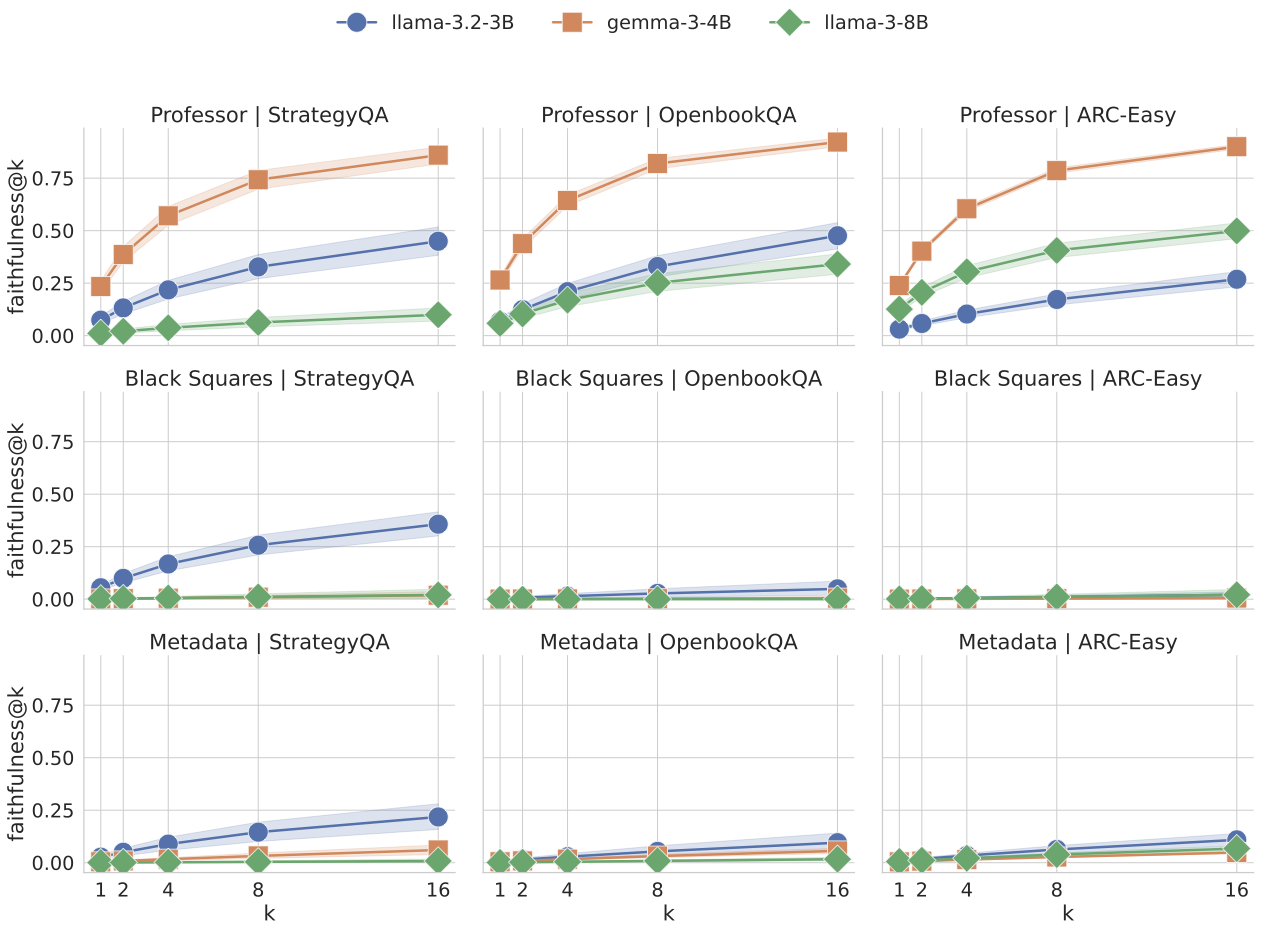
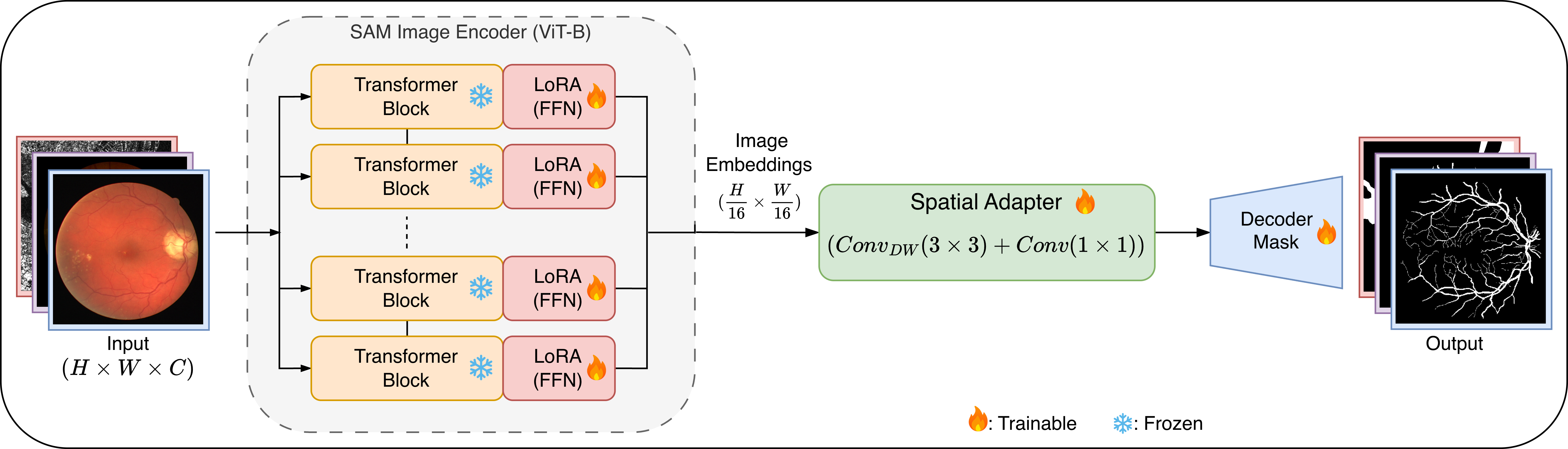
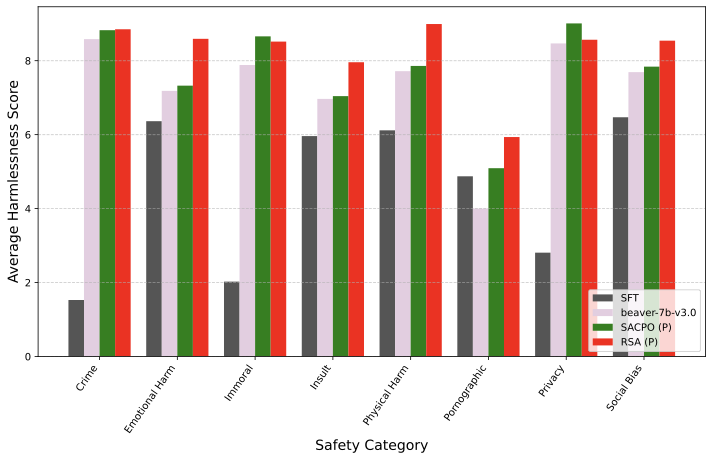
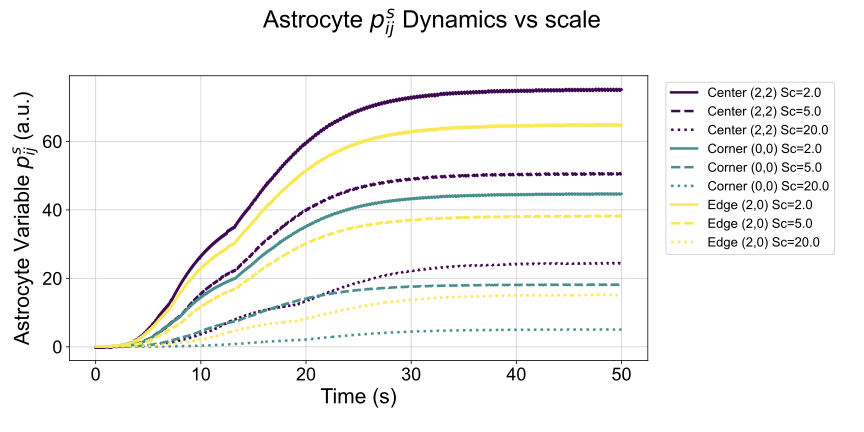
Lower Bounds for Function Inversion with Quantum Advice
Function inversion is the problem that given a random function $f [M] to [N]$, we want to find pre-image of any image $f^{-1}(y)$ in time $T$. In this work, we revisit this problem under the preprocessing model where we can compute some auxiliary information or advice of size $S$ that only depends on $f$ but not on $y$. It is a well-studied problem in the classical settings, however, it is not clear how quantum algorithms can solve this task any better besides invoking Grover s algorithm, which does not leverage the power of preprocessing. Nayebi et al. proved a lower bound $ST^2 ge tilde Omega(N)$ for quantum algorithms inverting permutations, however, they only consider algorithms with classical advice. Hhan et al. subsequently extended this lower bound to fully quantum algorithms for inverting permutations. In this work, we give the same asymptotic lower bound to fully quantum algorithms for inverting functions for fully quantum algorithms under the regime where $M = O(N)$. In order to prove these bounds, we generalize the notion of quantum random access code, originally introduced by Ambainis et al., to the setting where we are given a list of (not necessarily independent) random variables, and we wish to compress them into a variable-length encoding such that we can retrieve a random element just using the encoding with high probability. As our main technical contribution, we give a nearly tight lower bound (for a wide parameter range) for this generalized notion of quantum random access codes, which may be of independent interest.