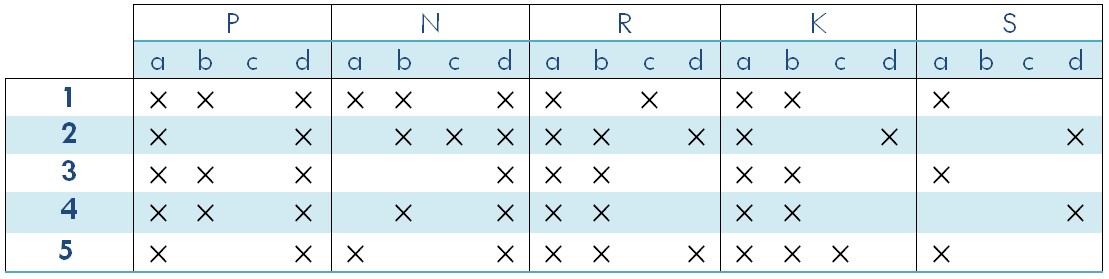
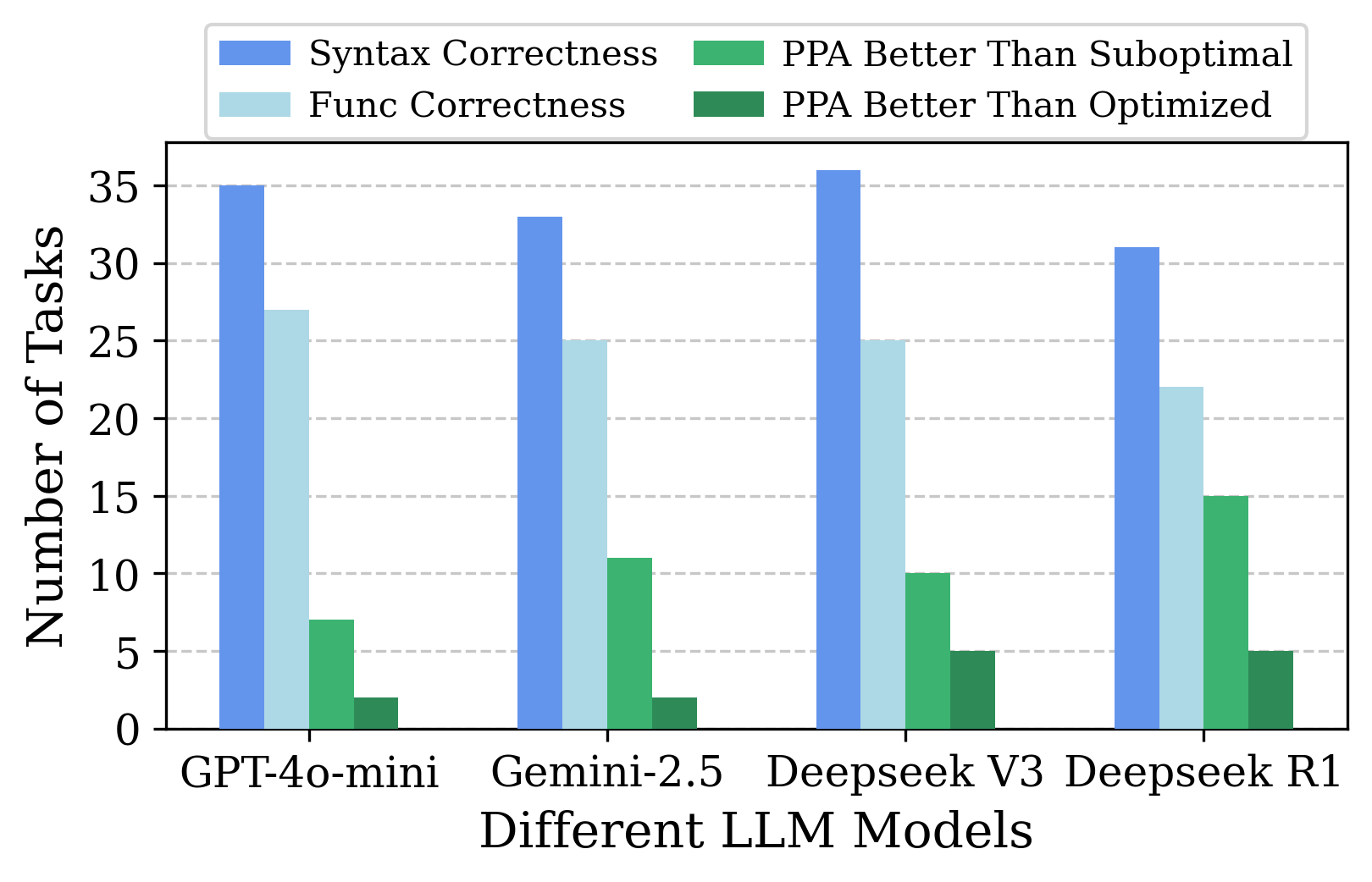
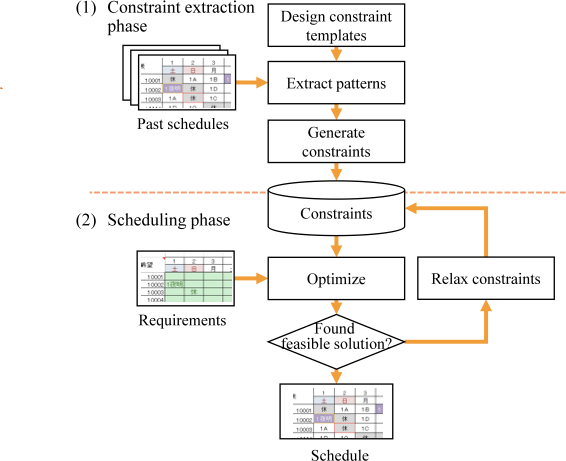
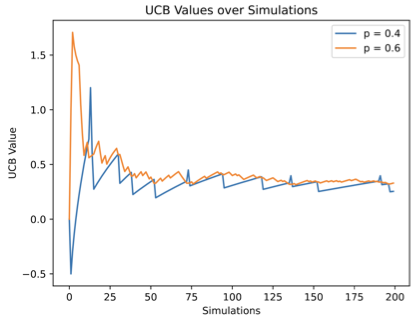
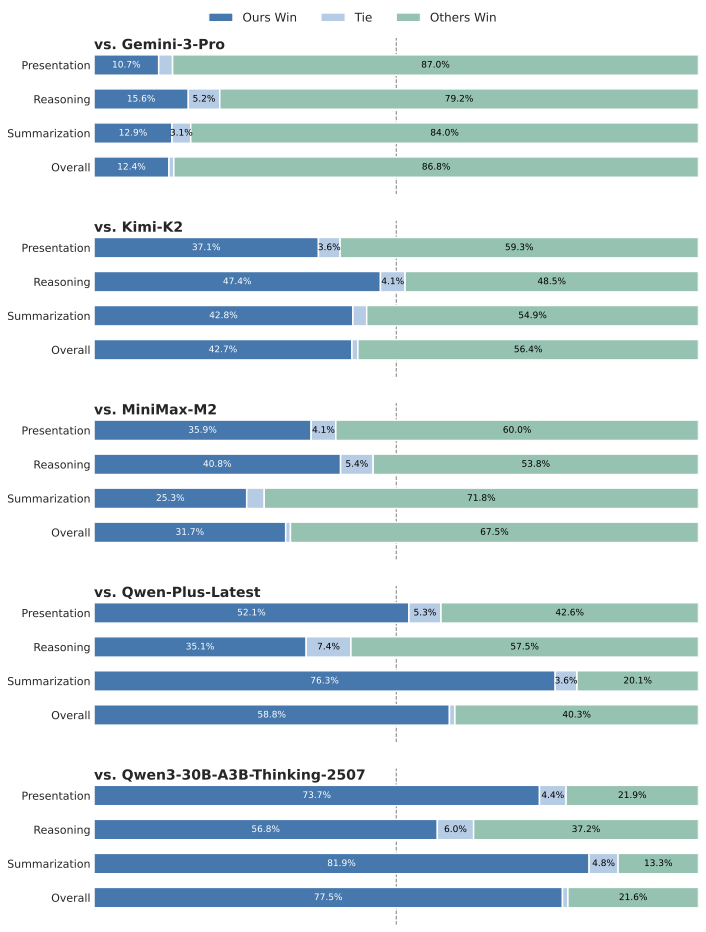
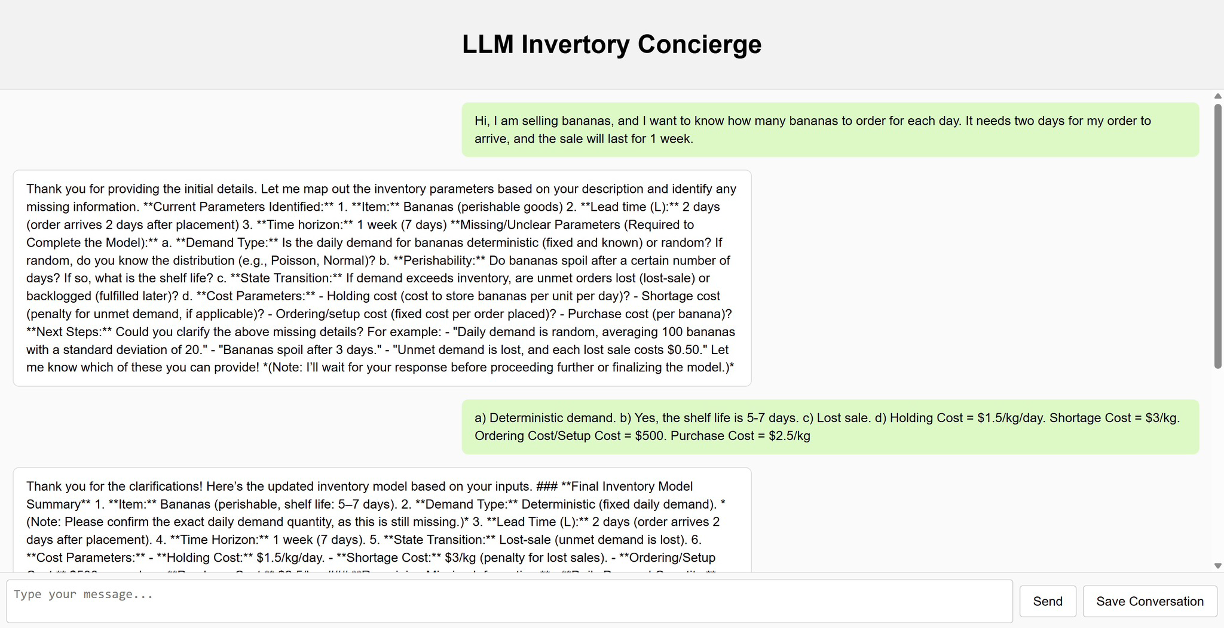
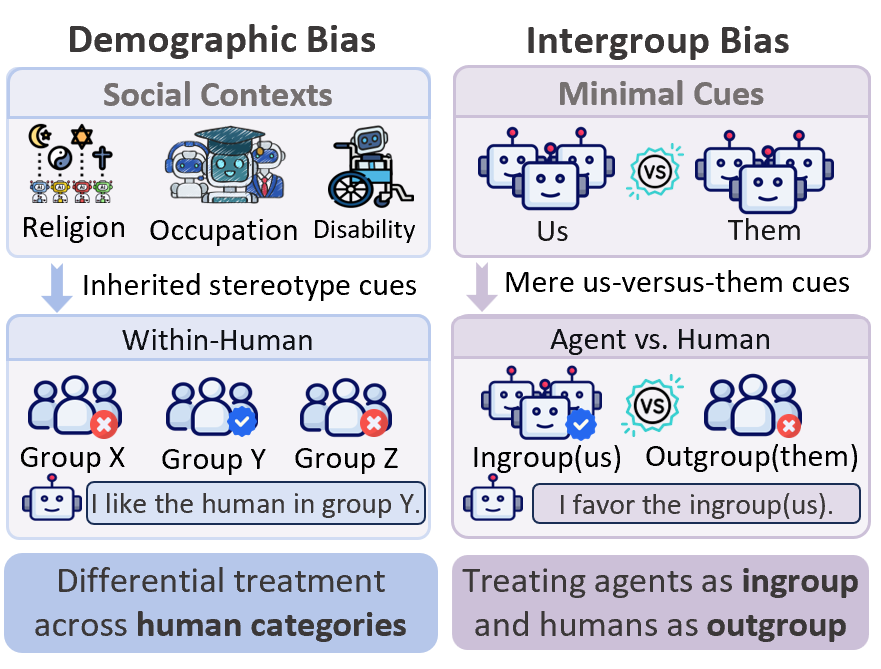
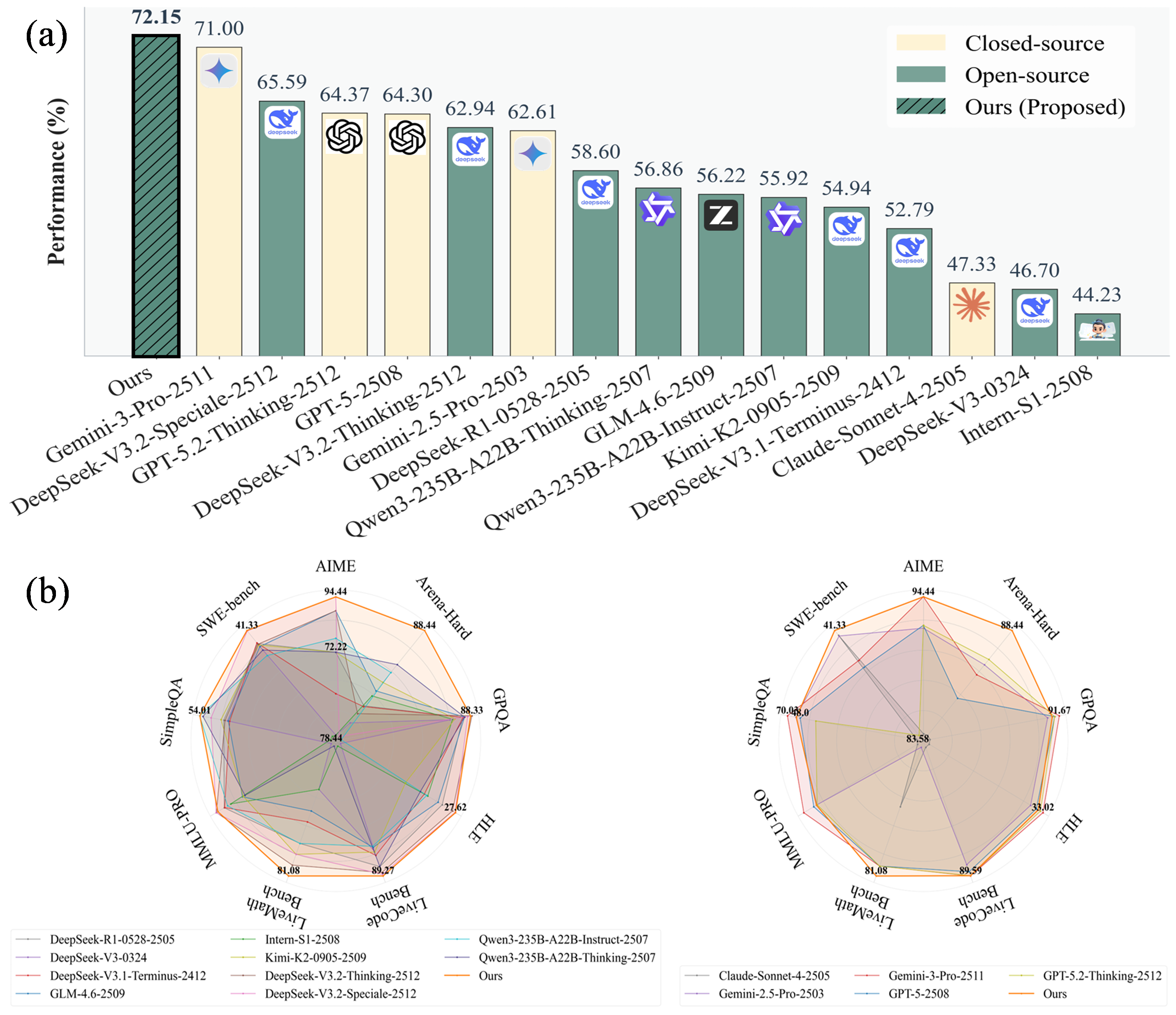
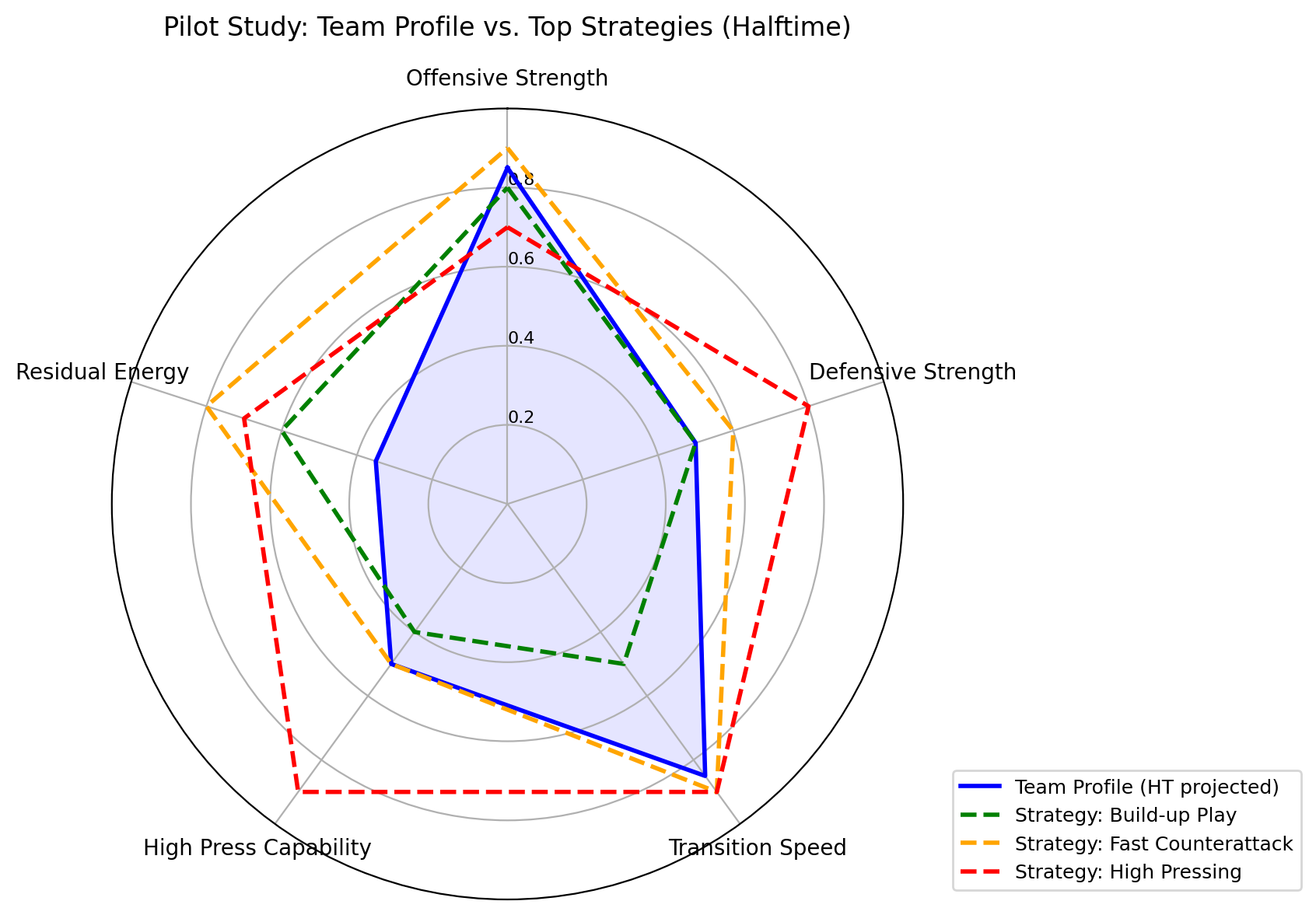
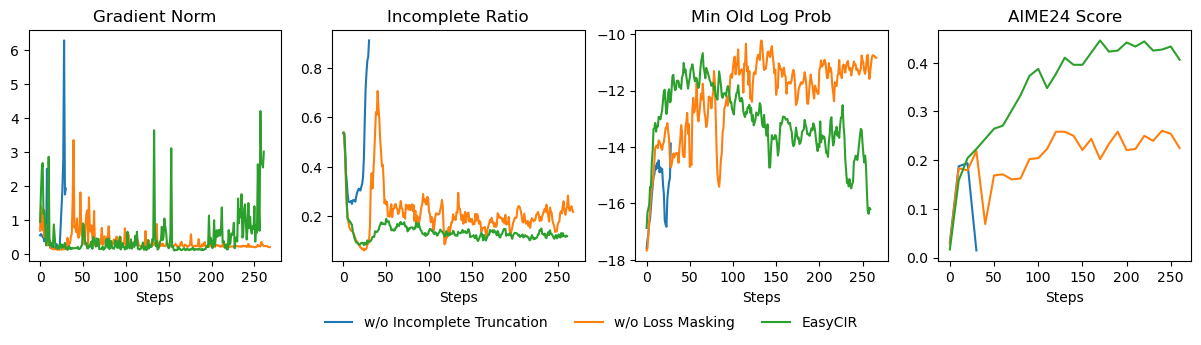
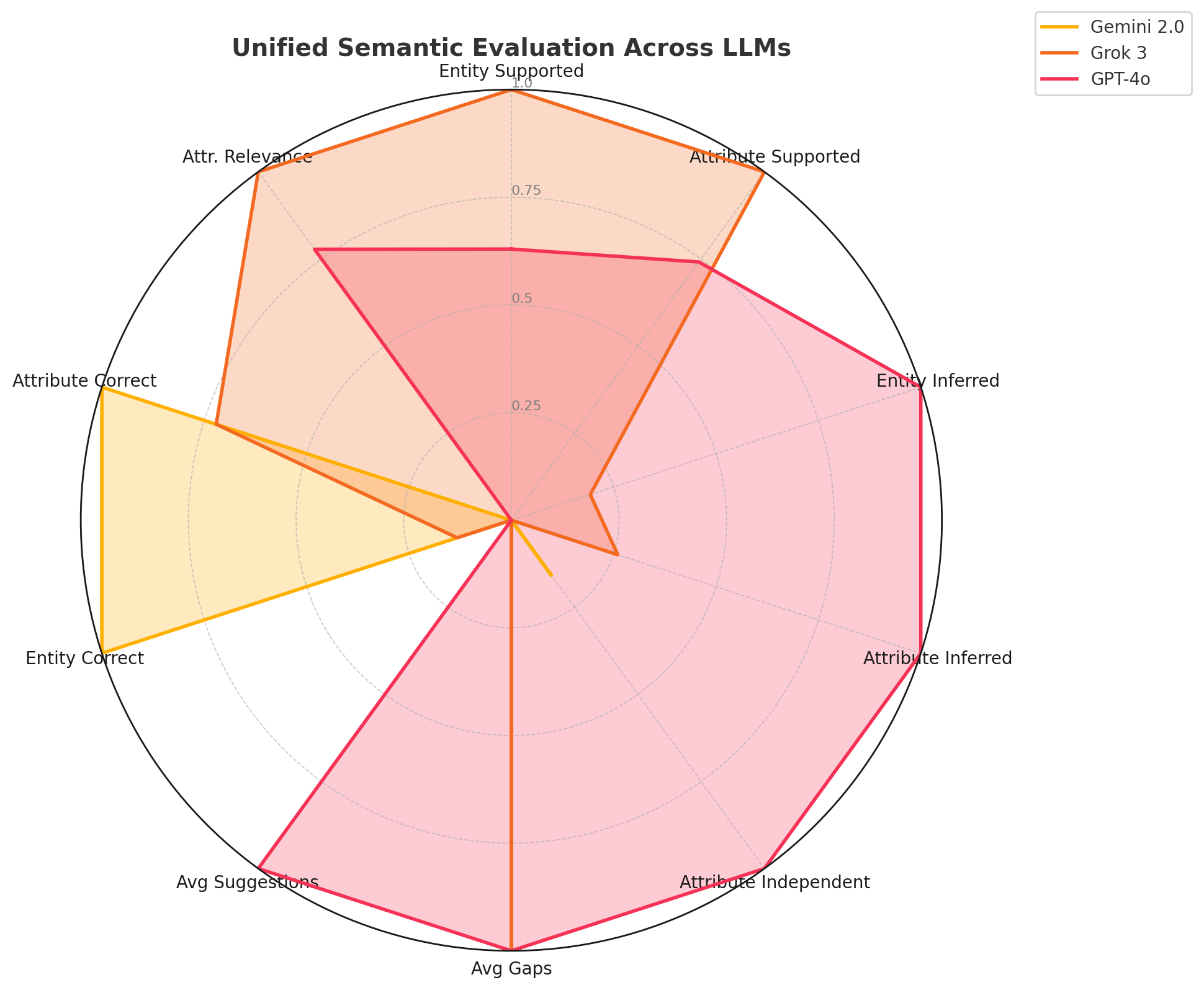
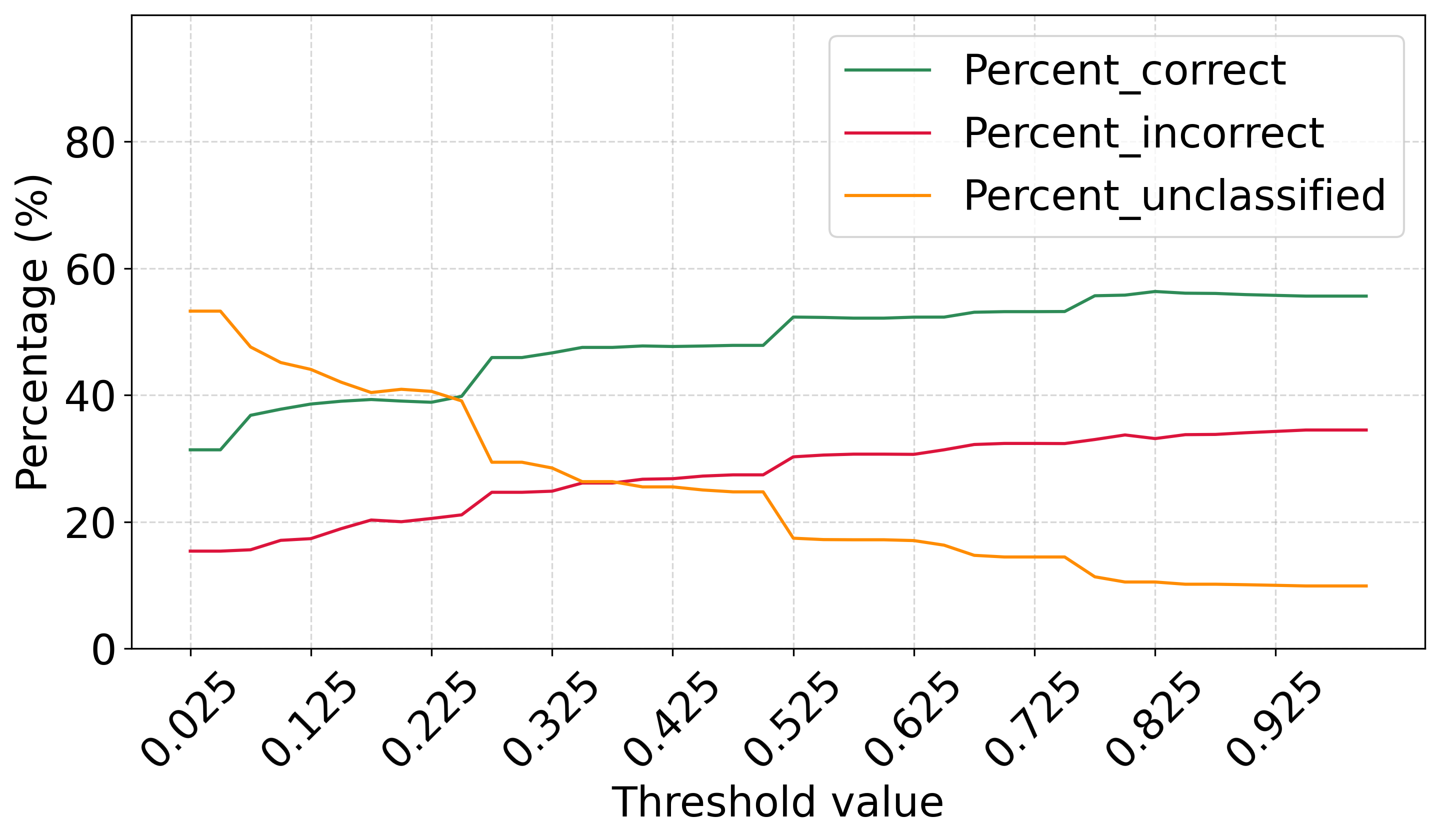
AI Agent Systems Architectures, Applications, and Evaluation
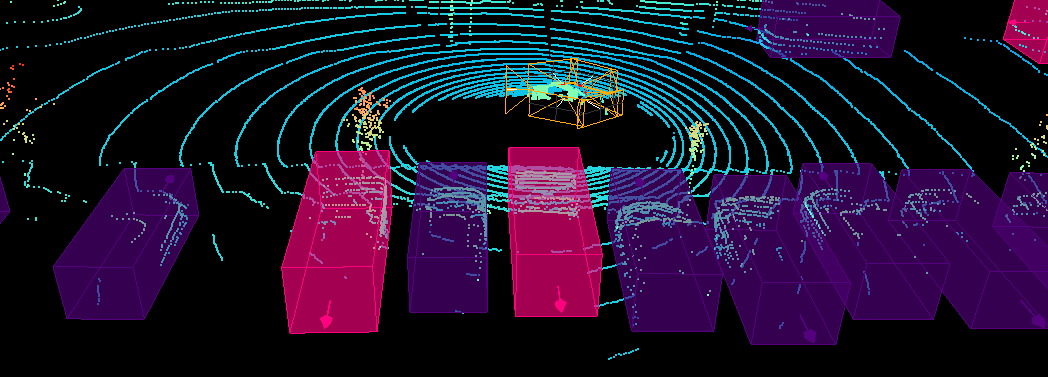
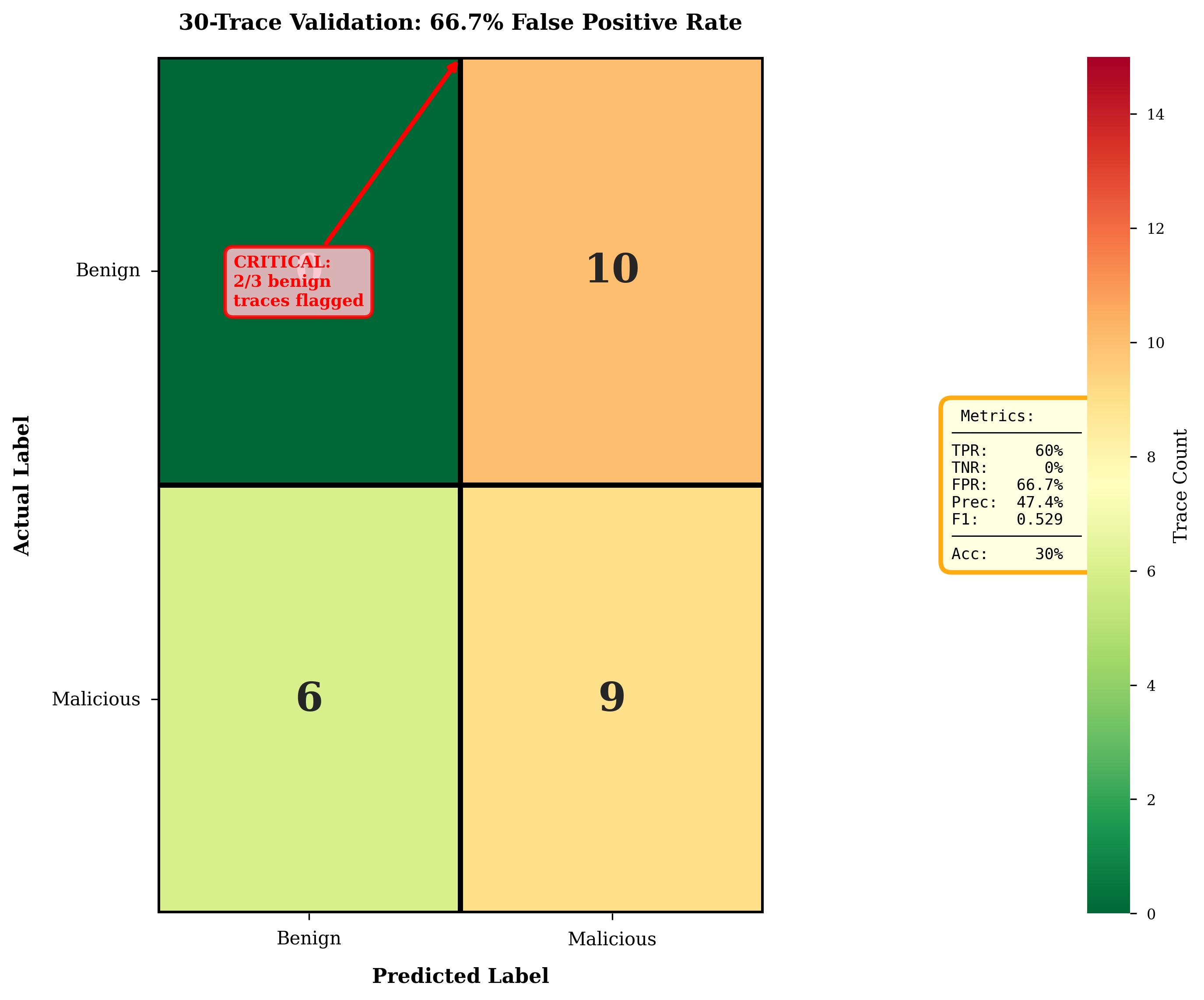
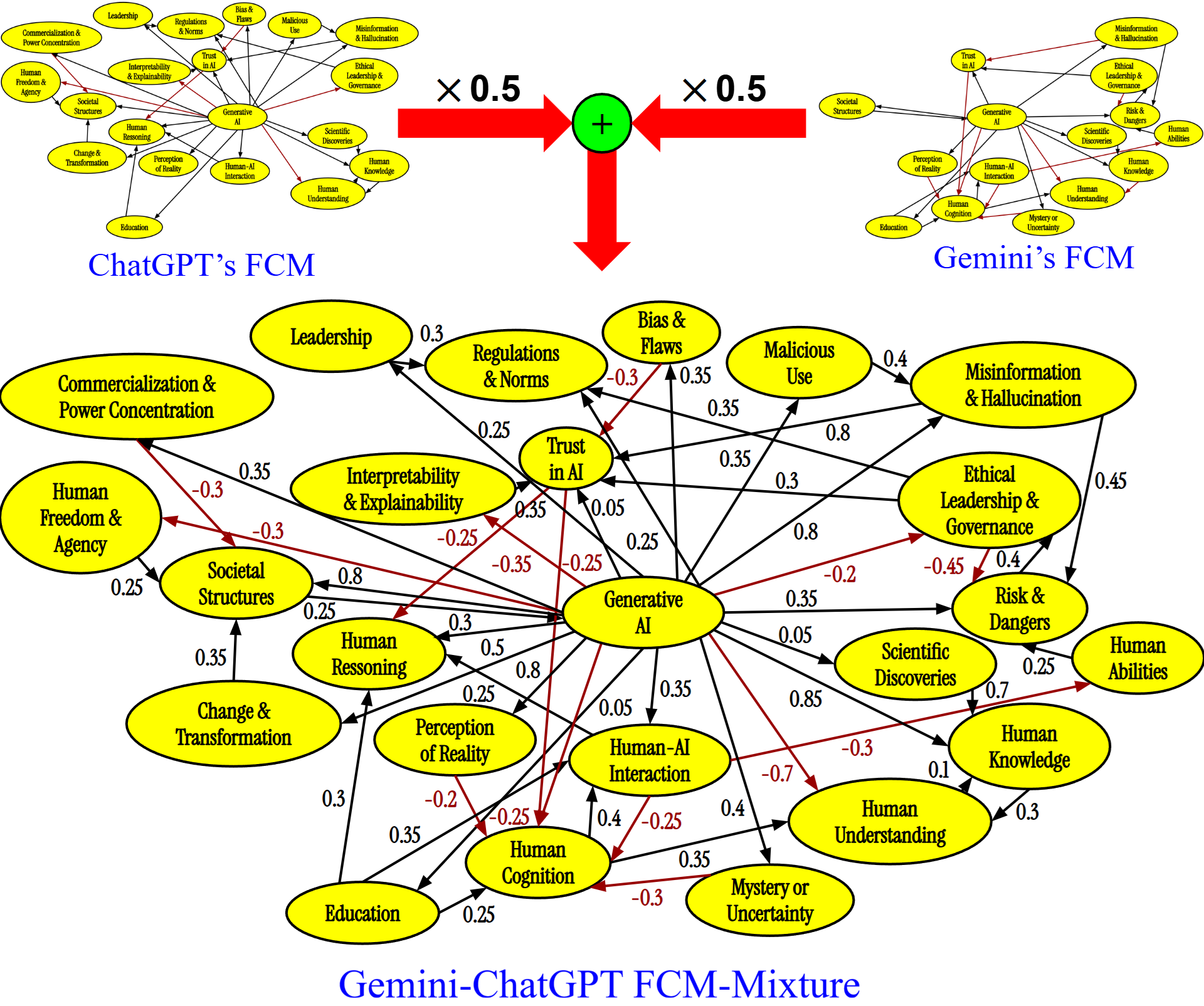
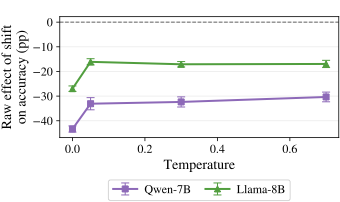
AI agents -- systems that combine foundation models with reasoning, planning, memory, and tool use -- are rapidly becoming a practical interface between natural-language intent and real-world computation. This survey synthesizes the emerging landscape of AI agent architectures across (i) deliberation and reasoning (e.g., chain-of-thought-style decomposition, self-reflection and verification, and constraint-aware decision making), (ii) planning and control (from reactive policies to hierarchical and multi-step planners), and (iii) tool calling and environment interaction (retrieval, code execution, APIs, and multimodal perception). We organize prior work into a unified taxonomy spanning agent components (policy/LLM core, memory, world models, planners, tool routers, and critics), orchestration patterns (single-agent vs. multi-agent; centralized vs. decentralized coordination), and deployment settings (offline analysis vs. online interactive assistance; safety-critical vs. open-ended tasks). We discuss key design trade-offs -- latency vs. accuracy, autonomy vs. controllability, and capability vs. reliability -- and highlight how evaluation is complicated by non-determinism, long-horizon credit assignment, tool and environment variability, and hidden costs such as retries and context growth. Finally, we summarize measurement and benchmarking practices (task suites, human preference and utility metrics, success under constraints, robustness and security) and identify open challenges including verification and guardrails for tool actions, scalable memory and context management, interpretability of agent decisions, and reproducible evaluation under realistic workloads.