실시간 비디오 기반 2D 동작 모방을 통한 다중 캐릭터 제어 학습
Reading time: 4 minute
...
📝 Original Info
- Title: 실시간 비디오 기반 2D 동작 모방을 통한 다중 캐릭터 제어 학습
- ArXiv ID: 2512.08500
- Date: Pending
- Authors: ** - Jianan Li¹ - Xiao Chen¹ - Tao Huang²³ - Tien‑Tsin Wong⁴ ¹ The Chinese University of Hong Kong ² Shanghai AI Laboratory ³ Shanghai Jiao Tong University ⁴ Monash University **
📝 Abstract
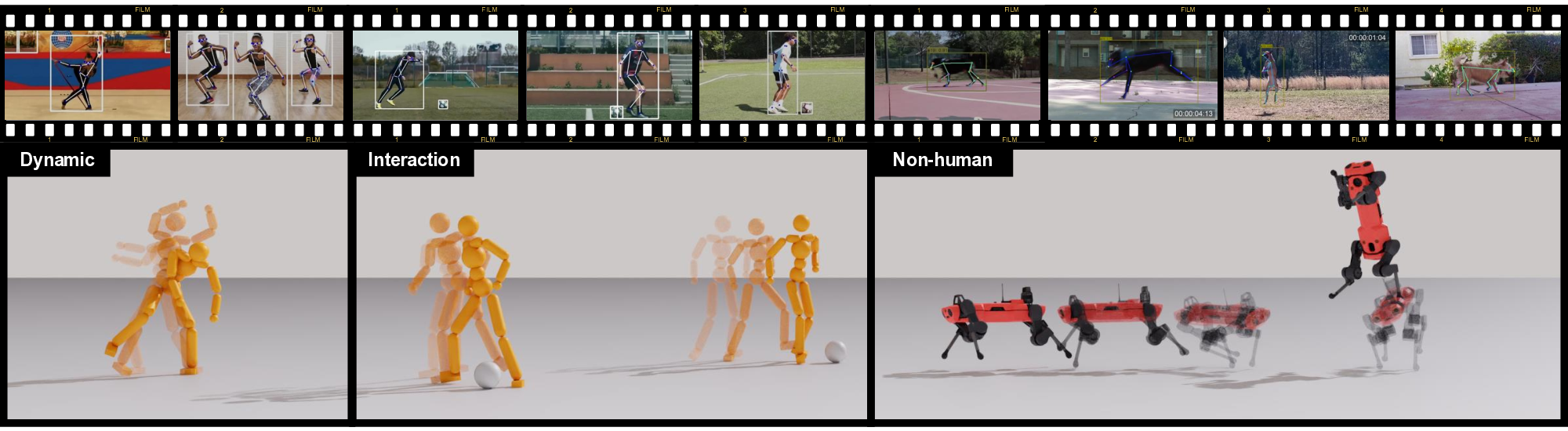
Figure 1. The proposed Mimic2DM effectively learns character controllers for diverse motion types, including dynamic human dancing, complex ball interactions, and agile animal movements, by directly imitating 2D motion sequences extracted from in-the-wild videos.💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
Learning to Control Physically-simulated 3D Characters via Generating and
Mimicking 2D Motions
Jianan Li1
Xiao Chen1
Tao Huang2,3
Tien-Tsin Wong4
1 The Chinese University of Hong Kong
2 Shanghai AI Laboratory
3 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
4 Monash University
Non-human
2
FILM
2
FILM
1
FILM
1
FILM
2
FILM
2
FILM
3
FILM
3
FILM
2
FILM
2
FILM
3
FILM
3
FILM
4
FILM
4
FILM
1
FILM
1
FILM
Dynamic
Interaction
1
FILM
1
FILM
Figure 1. The proposed Mimic2DM effectively learns character controllers for diverse motion types, including dynamic human dancing,
complex ball interactions, and agile animal movements, by directly imitating 2D motion sequences extracted from in-the-wild videos.
Abstract
Video data is more cost-effective than motion capture data
for learning 3D character motion controllers, yet synthe-
sizing realistic and diverse behaviors directly from videos
remains challenging.
Previous approaches typically rely
on off-the-shelf motion reconstruction techniques to obtain
3D trajectories for physics-based imitation. These recon-
struction methods struggle with generalizability, as they ei-
ther require 3D training data (potentially scarce) or fail to
produce physically plausible poses, hindering their appli-
cation to challenging scenarios like human-object interac-
tion (HOI) or non-human characters. We tackle this chal-
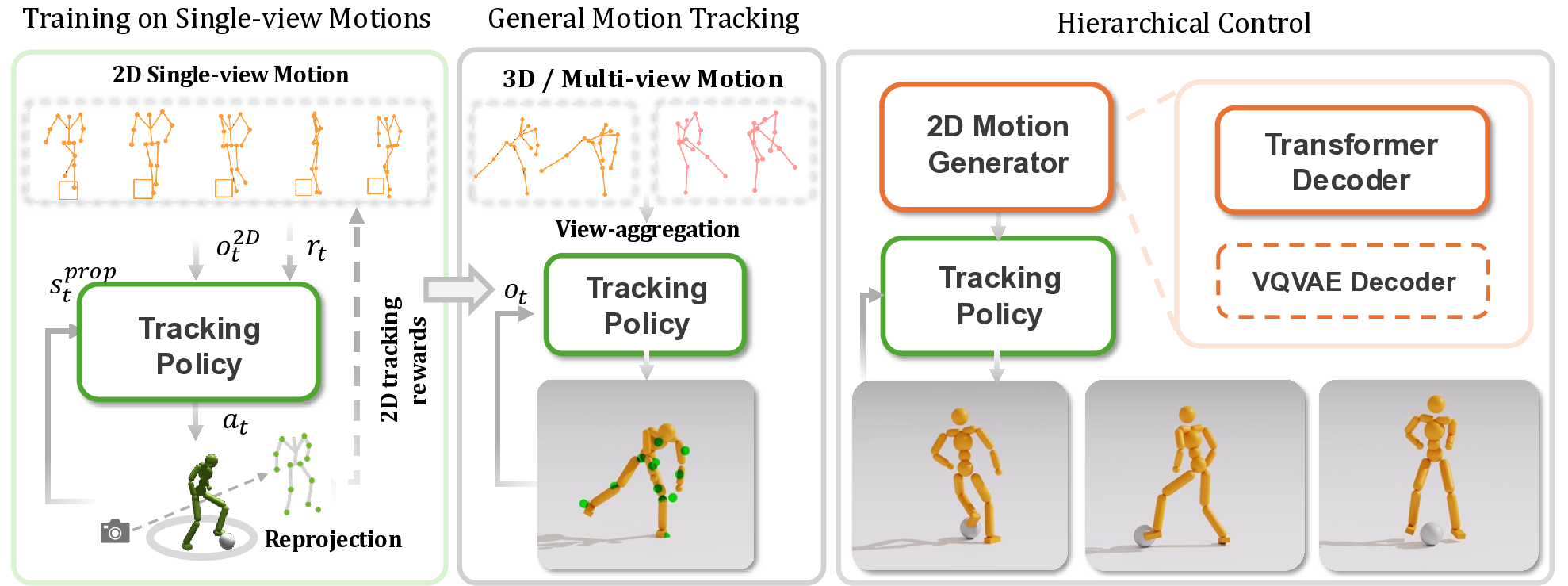
lenge by introducing Mimic2DM, a novel motion imita-
tion framework that learns the control policy directly and
solely from widely available 2D keypoint trajectories ex-
tracted from videos.
By minimizing the reprojection er-
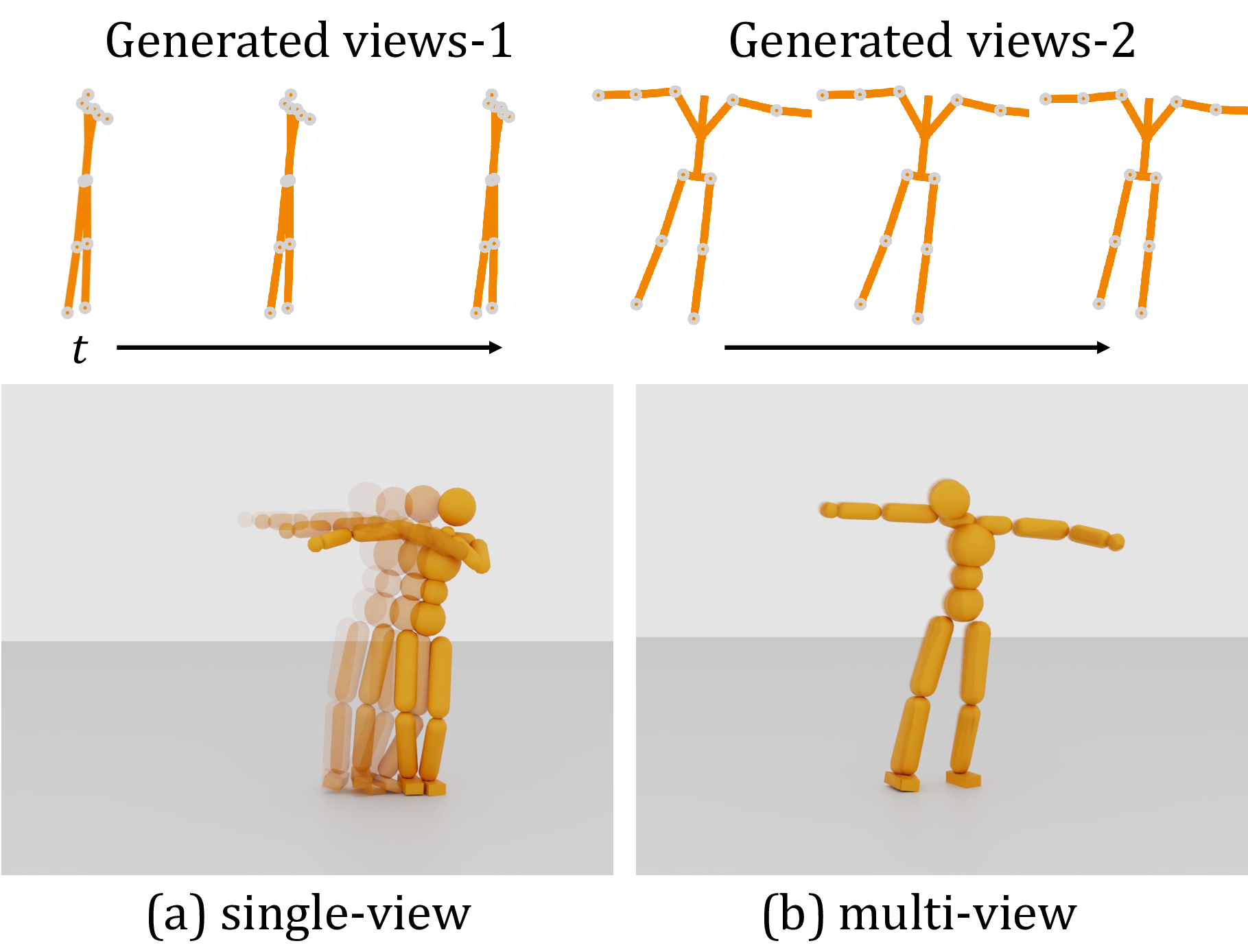
ror, we train a general single-view 2D motion tracking pol-
icy capable of following arbitrary 2D reference motions in
physics simulation, using only 2D motion data. The pol-
icy, when trained on diverse 2D motions captured from dif-
ferent or slightly different viewpoints, can further acquire
3D motion tracking capabilities by aggregating multiple
views. Moreover, we develop a transformer-based autore-
gressive 2D motion generator and integrate it into a hier-
archical control framework, where the generator produces
high-quality 2D reference trajectories to guide the tracking
policy. We show that the proposed approach is versatile
and can effectively learn to synthesize physically plausible
and diverse motions across a range of domains, including
dancing, soccer dribbling, and animal movements, without
any reliance on explicit 3D motion data. Project Website:
https://jiann-li.github.io/mimic2dm/
1. Introduction
Controlling physically simulated characters to perform real-
istic motion and plausible object interactions remains a fun-
damental yet challenging problem in computer animation
and robotics. Recently, motion imitation techniques have
leveraged motion capture (MoCap) data to train physics-
based character controllers, achieving impressive results in
producing highly dynamic and physically realistic motions
on the simulated virtual character [7, 12, 13, 29, 35, 52].
1
arXiv:2512.08500v1 [cs.GR] 9 Dec 2025
However, collecting high-quality 3D MoCap data is costly
and labor-intensive, as it requires numerous skilled per-
formers and specialized capture systems.
To address the scarcity of high-quality MoCap 3D data,
recent studies have explored exploiting videos as an alter-
native data source. Most existing methods [24, 30, 59, 62]
leverage off-the-shelf human motion reconstruction tech-
niques to estimate 3D motions from videos for learning
physics-based skills. While advanced training-based esti-
mation methods can achieve remarkable accuracy and re-
alism in reconstructing human motions, their performance
heavily depends on extensive high-quality 3D data for train-
ing, limiting their applicability in domains with scarce 3D
data, such as human–object interactions or non-human mo-
tions. Moreover, these methods often result in physically
implausible motions due to a lack of physics constraints,
which in turn hinders subsequent motion imitation.
In contrast to training on unreliable 3D motions esti-
mated from videos, some studies have demonstrated the
possibility of directly utilizing 2D motions extracted from
the video footage as supervision, achieving success across
various 3D tasks [3, 11, 16, 33, 44].
This 2D data is
highly accessible and can be easily extracted from videos
for a wide range of skeletons, including object interac-
tions and non-human (animal) movements. Additionally,
2D keypoint motion detected in videos provides unbiased
2D evidence that accurately reflects the original movements
present in the footage. The key challenge when employing
2D data is the missing depth information. While 2D priors
combined with geometrical constraints can yield visually
plausible 3D poses, the resulting motions are often physi-
cally limited and cannot be directly utilized as high-quality
data for motion imitation.
In this paper, we present Mimic2DM, a generic imitation
learning framework capable of acquiring a wide range of
complex, physics-based skills, including
📸 Image Gallery

Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.