Person re-identification (ReID) is an extremely important area in both surveillance and mobile applications, requiring strong accuracy with minimal computational cost. State-ofthe-art methods give good accuracy but with high computational budgets. To remedy this, this paper proposes VisNet, a computationally efficient and effective re-identification model suitable for real-world scenarios. It is the culmination of conceptual contributions, including feature fusion at multiple scales with automatic attention on each, semantic clustering with anatomical body partitioning, a dynamic weight averaging technique to balance classification semantic regularization, and the use of loss function FIDI for improved metric learning tasks. The multiple scales fuse ResNet50's stages 1 through 4 without the use of parallel paths, with semantic clustering introducing spatial constraints through the use of rule-based pseudo-labeling. VisNet achieves 87.05% Rank-1 and 77.65% mAP on the Market-1501 dataset, having 32.41M parameters and 4.601 GFLOPs, hence, proposing a practical approach for real-time deployment in surveillance and mobile applications where computational resources are limited.
The advent of intelligent video analytics has enabled the development of large-scale surveillance networks for applications like retail analytics, forensic investigation, and public safety. At the core of these systems is Person Re-identification (re-ID), the task of matching an individual's appearance across non-overlapping camera views. While crucial for scalable analytics, achieving robustness remains difficult due to significant appearance variations across disparate views. The visual signature of an identity is frequently compromised by dramatic changes in camera angles and body poses (viewpoint variation), or by crowded scenes that obscure discriminative cues (occlusion). Furthermore, photometric inconsistencies from lighting changes, scale variations due to differing camera distances, and temporal gaps significantly alter appearance. Traditional hand-crafted features, such as color histograms and edge-based descriptors [1], fail to capture the semantic richness required to overcome such variations, necessitating more robust feature learning approaches.
With the advent of deep learning, spatial partition strategies and CNN-based methods offered a radical improvement. Meth- ods like PCB and AANet captured local semantic structure by partitioning feature maps or introducing adaptive attention, achieving 76-92% Rank-1 accuracy [2] [3]. However, these approaches remained inherently limited by their reliance on predefined spatial regions. Consequently, recent works have moved their focus towards Transformer architectures [4] and vision-language models to capture global semantic context. Solutions such as TransReID [5] and CLIP-ReID [6] report higher accuracy (greater than 88% Rank-1) but are computationally prohibitive. For instance, TransReID introduces approximately 17.8 GFLOPs and 86M parameters, making its deployment on edge devices infeasible. This explicitly establishes an efficiency-accuracy trade-off that lightweight CNN-based methods remain computationally efficient but lack the semantic reasoning of Transformers, while Transformerbased models advance accuracy at a computational cost that prohibits deployment in resource-constrained environments.
To address this trade-off, a method is required that retains the spatial efficiency of CNNs while mimicking the semantic capture of Transformers. While multi-scale feature learning is well-known in computer vision, where spatial pyramid pooling and feature pyramid networks [7] improve object detection, it remains underutilized in re-ID. Furthermore, while attention mechanisms like SE-Net [8] and CBAM [9] operate on channel or spatial dimensions, the scale dimension remains an underexplored design space about determining which multi-scale feature representation is most informative for a given image.
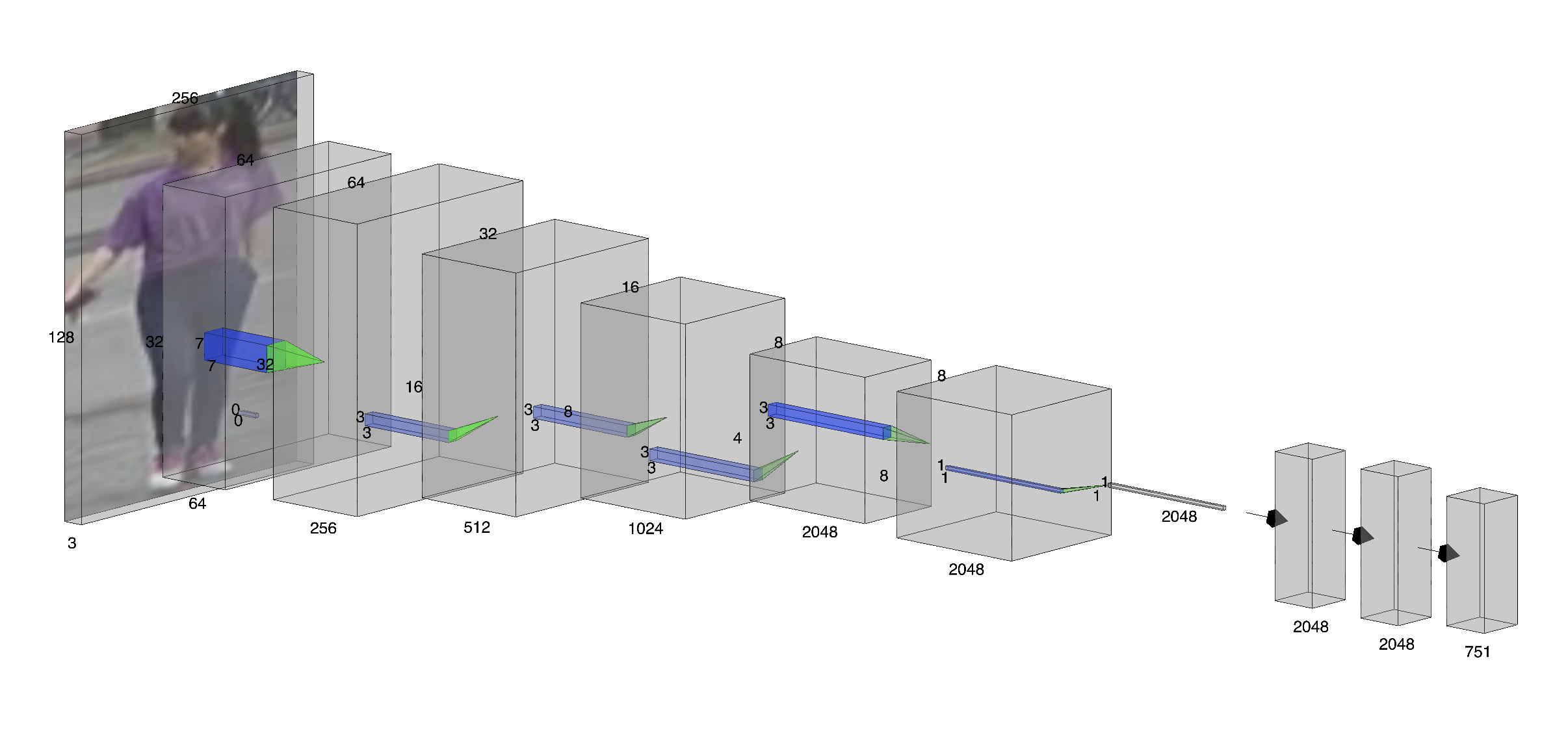
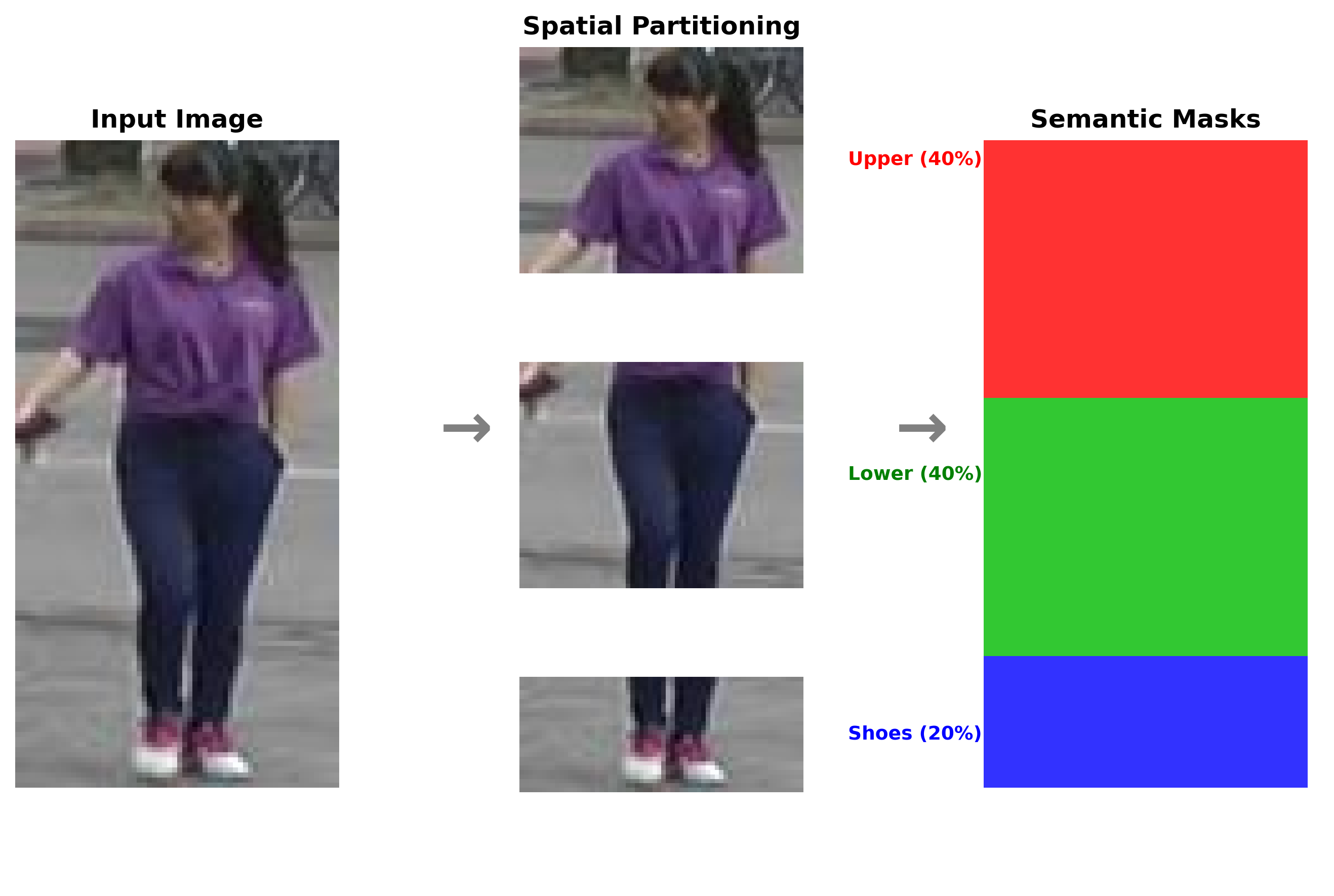
In this work, we propose VisNet, a systematically designed person re-ID model that achieves competitive accuracy while maintaining practical computational efficiency. Instead of utilizing computationally expensive Transformer architectures, VisNet leverages a strategic combination of proven CNNbased techniques. It extracts features from multiple ResNet50 residual blocks [10] and projects them to a unified dimension. These are combined via a novel custom scale attention mechanism, a lightweight module that learns adaptive perscale weighting to capture semantic information at multiple levels of abstraction. To further regularize semantic learning without expensive teacher-student frameworks like SOLIDER [11], we introduce spatial semantic clustering with rule-based pseudo-labels (classifying upper body, lower body, and shoes). Finally, to ensure robust metric learning, we employ FIDI loss, Semantic Loss and Cross Entropy Loss with dynamic weight averaging [12], which balances the convergence rates of identity classification, metric learning, and semantic regularization tasks.
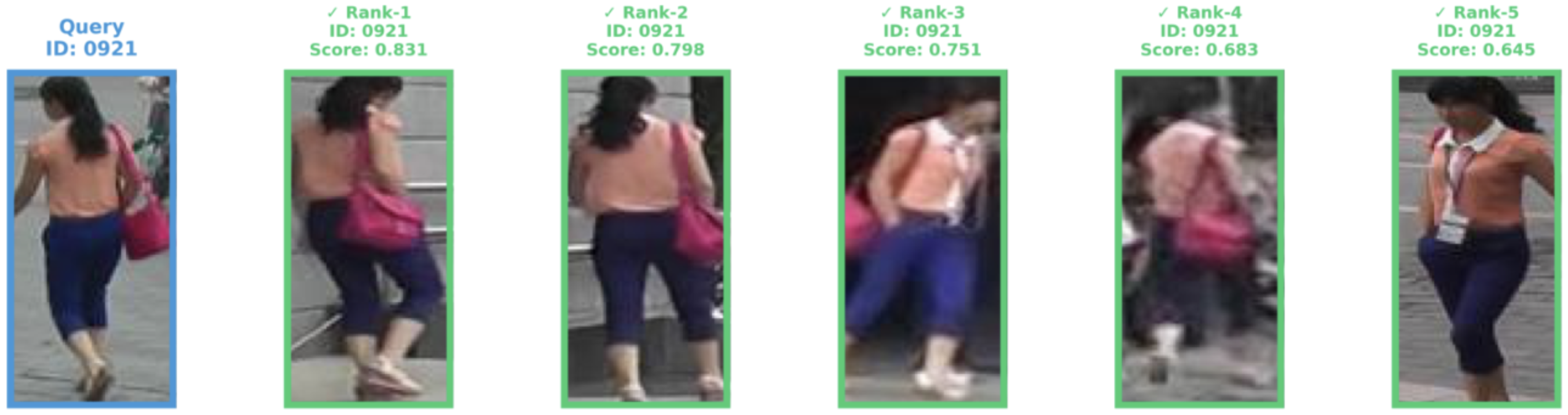
The proposed scheme is validated on the Market-1501 benchmark [13], achieving 87.05% Rank-1 accuracy and 77.65% mAP with only 4.601G FLOPs and 31.08M parameters (0.36× the size of TransReID). The main contributions of this paper are listed as follows:
• A lightweight, yet accurate CNN-based person re-ID model utilizing customized scale attention mechanism for learning adaptive per-scale weighting towards multi-scale feature fusion • Demonstration of the approach that rule-based spatial pseudo-labels effectively regularize semantic learning without expensive teacher-student frameworks and serve as a competitive, simpler alternative to recent complex methods. • Extensive empirical validation quantifying the contribution of each component, efficiency-accuracy trade-off analysis, and qualitative analysis of results. • A semantic-aware augmentation framework that enforces background invariance by explicitly decoupling foreground identity from environmental clutter.
The paper is organized as follows: Section II covers the proposed VisNet architecture. Section III describes the evaluation pe
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.