📝 Original Info Title: Leveraging Lightweight Entity Extraction for Scalable Event-Based Image RetrievalArXiv ID: 2512.21221Date: 2025-12-24Authors: Dao Sy Duy Minh, Huynh Trung Kiet, Nguyen Lam Phu Quy, Phu-Hoa Pham, Tran Chi Nguyen📝 Abstract Retrieving images from natural language descriptions is a core task at the intersection of computer vision and natural language processing, with wide-ranging applications in search engines, media archiving, and digital content management. However, real-world image-text retrieval remains challenging due to vague or context-dependent queries, linguistic variability, and the need for scalable solutions. In this work, we propose a lightweight two-stage retrieval pipeline that leverages event-centric entity extraction to incorporate temporal and contextual signals from real-world captions. The first stage performs efficient candidate filtering using BM25 based on salient entities, while the second stage applies BEiT-3 models to capture deep multimodal semantics and rerank the results. Evaluated on the OpenEvents v1 benchmark, our method achieves a mean average precision of 0.559, substantially outperforming prior baselines. These results highlight the effectiveness of combining event-guided filtering with long-text vision-language modeling for accurate and efficient retrieval in complex, real-world scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/PhamPhuHoa-23/Event-Based-Image-Retrieval
💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content Leveraging Lightweight Entity Extraction for Scalable
Event-Based Image Retrieval
Dao Sy Duy Minh∗
23122041@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Huynh Trung Kiet∗
23132039@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Nguyen Lam Phu Quy†
23122048@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Phu-Hoa Pham†
23122030@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Tran Chi Nguyen†
23122044@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
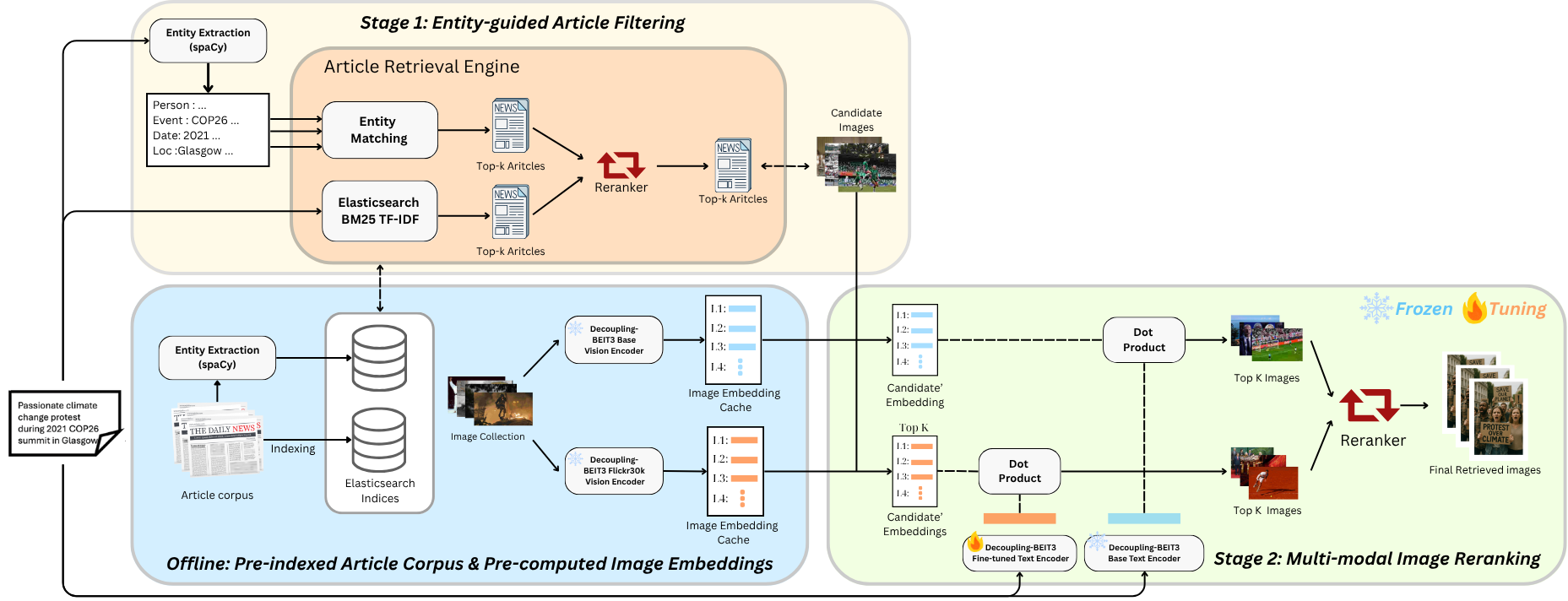
Figure 1: System Architecture for Lightweight Entity-Guided Event-Based Image Retrieval
Abstract
Retrieving images from natural language descriptions is a core task
at the intersection of computer vision and natural language pro-
cessing, with wide-ranging applications in search engines, media
archiving, and digital content management. However, real-world
image-text retrieval remains challenging due to vague or context-
dependent queries, linguistic variability, and the need for scalable
solutions. In this work, we propose a lightweight two-stage retrieval
∗The first two authors contributed equally as lead authors.
†The last three authors contributed equally as supporting roles.
Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or
classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed
for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation
on the first page. Copyrights for components of this work owned by others than the
author(s) must be honored. Abstracting with credit is permitted. To copy otherwise, or
republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission
and/or a fee. Request permissions from permissions@acm.org.
MM ’25, Dublin, Ireland
© 2018 Copyright held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights licensed to ACM.
ACM ISBN 978-1-4503-XXXX-X/2018/06
https://doi.org/XXXXXXX.XXXXXXX
pipeline that leverages event-centric entity extraction to incorpo-
rate temporal and contextual signals from real-world captions. The
first stage performs efficient candidate filtering using BM25 based
on salient entities, while the second stage applies BEiT-3 models
to capture deep multimodal semantics and rerank the results. Eval-
uated on the OpenEvents v1 benchmark, our method achieves a
mean average precision of 0.559, substantially outperforming prior
baselines. These results highlight the effectiveness of combining
event-guided filtering with long-text vision-language modeling for
accurate and efficient retrieval in complex, real-world scenarios.
Our code is available at https://github.com/PhamPhuHoa-23/Event-
Based-Image-Retrieval
CCS Concepts
• Computing methodologies →Visual content-based index-
ing and retrieval.
Keywords
image retrieval, multimodal dataset, real-world events, event-centric
vision-language
arXiv:2512.21221v1 [cs.CV] 24 Dec 2025
MM ’25, October 27–31, 2025, Dublin, Ireland
Dao Sy Duy Minh, Huynh Trung Kiet, Nguyen Lam Phu Quy, Phu-Hoa Pham, and Tran Chi Nguyen
ACM Reference Format:
Dao Sy Duy Minh, Huynh Trung Kiet, Nguyen Lam Phu Quy, Phu-Hoa
Pham, and Tran Chi Nguyen. 2018. Leveraging Lightweight Entity Ex-
traction for Scalable Event-Based Image Retrieval. In Proceedings of 2025
ACM Multimedia Conference (MM ’25). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 6 pages.
https://doi.org/XXXXXXX.XXXXXXX
1
Introduction
Retrieving images from natural language descriptions plays a cen-
tral role in various applications such as web search, news archiving,
e-commerce, and media curation. As the volume of multimodal
content continues to grow rapidly, effective cross-modal retrieval
systems are becoming increasingly important for organizing and
accessing relevant visual information from textual inputs.
Most existing models, such as CLIP [12] and its variants, are
trained primarily on clean visual descriptions—typically short im-
age captions sourced from large-scale web datasets like LAION-
400M [14]. While effective for general-purpose retrieval, these cap-
tions often lack the complexity, entity density, and contextual vari-
ability present in real-world queries. As a result, such models strug-
gle when applied to domains like news or event retrieval, where
queries are significantly more complex: they may involve multi-
ple named entities, temporal references, or require event-centric
grounding.
Furthermore, in many practical scenarios, captions are embed-
ded within broader news content, rather than standing alone as
purely visual descriptions. This mixing of modalities introduces
noise and ambiguity, making it difficult for conventional text-to-
image retrieval models—optimized for literal, surface-level visual
alignment—to perform effectively. In addition, natural queries are
frequently truncated due to token limits in transformer-based mod-
els, leading to semantic misalignment between the i
📸 Image Gallery
Reference This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.