📝 Original Info Title: Beyond Vision: Contextually Enriched Image Captioning with Multi-Modal RetrievalArXiv ID: 2512.20042Date: 2025-12-23Authors: ** - Nguyen Lam Phu Quy* (23122048@student.hcmus.edu.vn ) – University of Science, VNUHCM, Vietnam - Pham Phu Hoa* (23122030@student.hcmus.edu.vn ) – University of Science, VNUHCM, Vietnam - Tran Chi Nguyen* (23122044@student.hcmus.edu.vn ) – University of Science, VNUHCM, Vietnam - Dao Sy Duy Minh† (23122041@student.hcmus.edu.vn ) – University of Science, VNUHCM, Vietnam - Nguyen Hoang Minh Ngoc† (ng0005oc@e.ntu.edu.sg ) – Nanyang Technological University, Singapore - Huynh Trung Kiet† (23132039@student.hcmus.edu.vn ) – University of Science, VNUHCM, Vietnam * 첫 세 저자는 동등한 기여를 함. † 마지막 세 저자는 보조 역할을 수행함. — **📝 Abstract Real-world image captions often lack contextual depth, omitting crucial details such as event background, temporal cues, outcomes, and named entities that are not visually discernible. This gap limits the effectiveness of image understanding in domains like journalism, education, and digital archives, where richer, more informative descriptions are essential. To address this, we propose a multimodal pipeline that augments visual input with external textual knowledge. Our system retrieves semantically similar images using BEIT-3 (Flickr30k-384 and COCO-384) and SigLIP So-384, reranks them using ORB and SIFT for geometric alignment, and extracts contextual information from related articles via semantic search. A fine-tuned Qwen3 model with QLoRA then integrates this context with base captions generated by Instruct BLIP (Vicuna-7B) to produce event-enriched, context-aware descriptions. Evaluated on the OpenEvents v1 dataset, our approach generates significantly more informative captions compared to traditional methods, showing strong potential for real-world applications requiring deeper visual-textual understanding
💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content Beyond Vision: Contextually Enriched Image Captioning with
Multi-Modal Retrieval
Nguyen Lam Phu Quy∗
23122048@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Pham Phu Hoa∗
23122030@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Vietnam
Tran Chi Nguyen∗
23122044@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Dao Sy Duy Minh†
23122041@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, State B, Vietnam
Nguyen Hoang Minh Ngoc†
ng0005oc@e.ntu.edu.sg
Nanyang Technological University
Singapore
Huynh Trung Kiet†
23132039@student.hcmus.edu.vn
University of Science - VNUHCM
Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
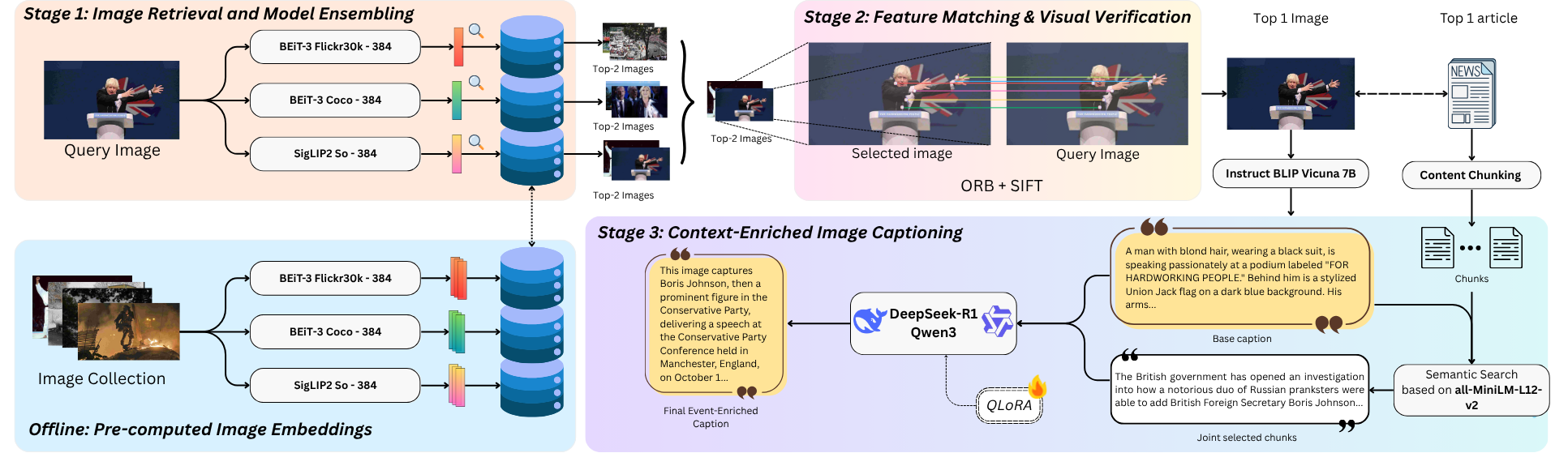
Figure 1: System Architecture of the Multimodal Caption Generation Framework
Abstract
Real-world image captions often lack contextual depth, omitting
crucial details such as event background, temporal cues, outcomes,
and named entities that are not visually discernible. This gap limits
the effectiveness of image understanding in domains like journal-
ism, education, and digital archives, where richer, more informative
descriptions are essential. To address this, we propose a multimodal
pipeline that augments visual input with external textual knowl-
edge. Our system retrieves semantically similar images using BEIT-3
(Flickr30k-384 and COCO-384) and SigLIP So-384, reranks them us-
ing ORB and SIFT for geometric alignment, and extracts contextual
information from related articles via semantic search. A fine-tuned
Qwen3 model with QLoRA then integrates this context with base
∗The first three authors contributed equally as lead authors.
†The last three authors contributed equally in a supporting role.
Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or
classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed
for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation
on the first page. Copyrights for components of this work owned by others than the
author(s) must be honored. Abstracting with credit is permitted. To copy otherwise, or
republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission
and/or a fee. Request permissions from permissions@acm.org.
MM ’25, Dublin, Ireland
© 2025 Copyright held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights licensed to ACM.
ACM ISBN 978-1-4503-XXXX-X/2018/06
https://doi.org/XXXXXXX.XXXXXXX
captions generated by Instruct BLIP (Vicuna-7B) to produce event-
enriched, context-aware descriptions. Evaluated on the OpenEvents
v1 dataset, our approach generates significantly more informative
captions compared to traditional methods, showing strong potential
for real-world applications requiring deeper visual-textual under-
standing. Our code is available at https://github.com/PhamPhuHoa-
23/Event-Enriched-Image-Captioning-ReZeroSlavery
CCS Concepts
• Computing methodologies;
Keywords
event-enriching captioning, image-caption retrieval, image-caption
generation, visual analysis
ACM Reference Format:
Nguyen Lam Phu Quy, Pham Phu Hoa, Tran Chi Nguyen, Dao Sy Duy Minh,
Nguyen Hoang Minh Ngoc, and Huynh Trung Kiet. 2025. Beyond Vision:
Contextually Enriched Image Captioning with Multi-Modal Retrieval. In
Proceedings of 2025 ACM Multimedia Conference (MM ’25). ACM, New York,
NY, USA, 7 pages. https://doi.org/XXXXXXX.XXXXXXX
1
Introduction
Image captioning has evolved from simple object recognition to
sophisticated multimodal understanding, yet current approaches
remain limited by their reliance on purely visual information [14,
arXiv:2512.20042v2 [cs.CV] 1 Feb 2026
MM ’25, October 27–31, 2025, Dublin, Ireland
Nguyen Lam Phu Quy, Pham Phu Hoa, Tran Chi Nguyen, Dao Sy Duy Minh, Nguyen Hoang Minh Ngoc, and Huynh Trung Kiet
15]. While state-of-the-art models can accurately describe visible
elements, they fail to capture crucial contextual details such as
event background, temporal dynamics, named entities, and real-
world significance that extend beyond what is directly observable
in the image.
Several recent works have attempted to incorporate external
knowledge into image captioning [5, 25, 39]. However, these ap-
proaches typically generate brief, sentence-level descriptions that
focus on immediate visual-textual alignment rather than compre-
hensive event understanding. For instance, knowledge-enhanced
models may correctly identify "President Biden" in an image but fail
to provide the rich contextual narrative about the specific meeting,
its outcomes, or broader implications, producing captions of 10-20
words instead of the detailed, paragraph-length descriptions needed
for meaningful event documentation.
This limitation is particularly problematic in domains like jour-
nalism and digital archives, where images serve as visual docu-
mentation of significant events requiring rich, contextually-aware
descriptions. A photograph of officials at a conference table may
appear visually similar across diff
📸 Image Gallery
Reference This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.