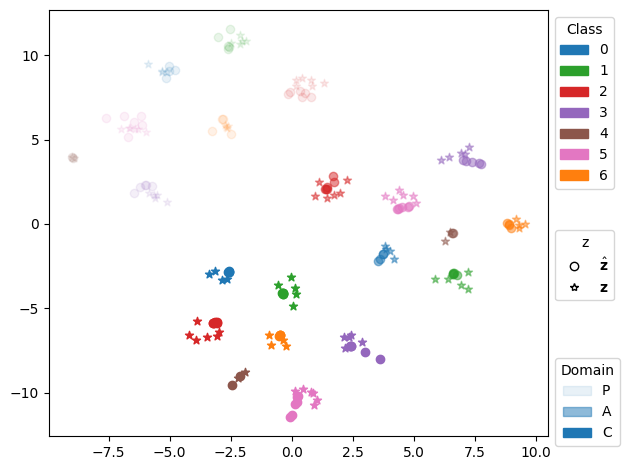
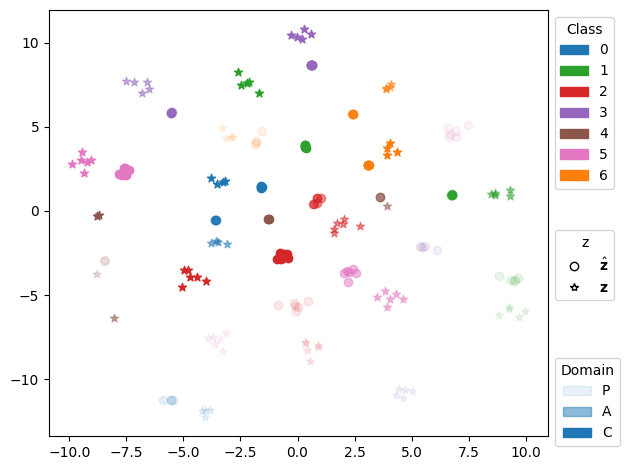
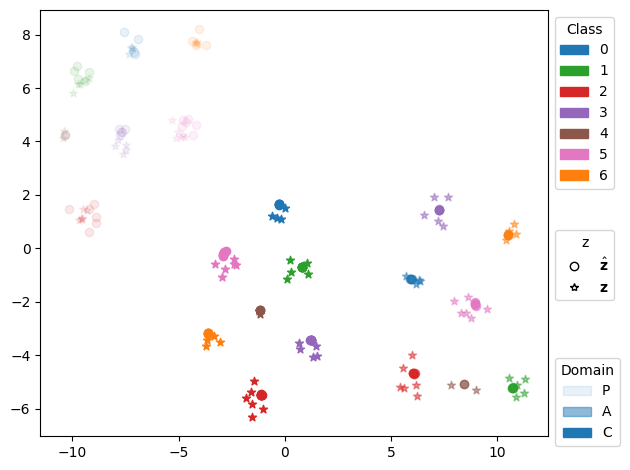
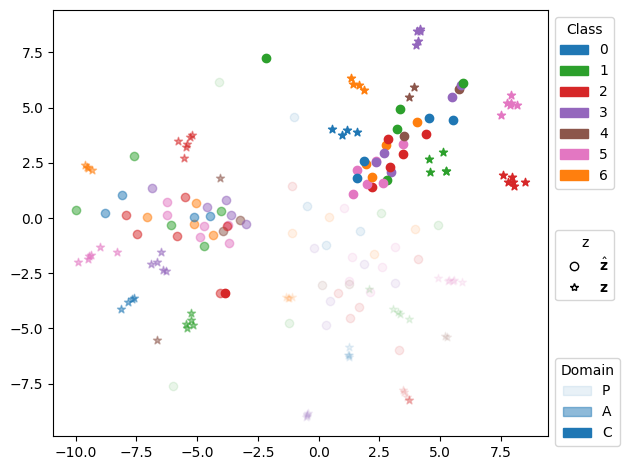
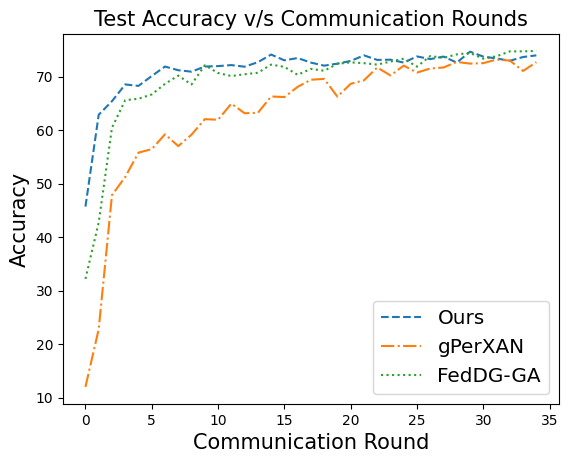
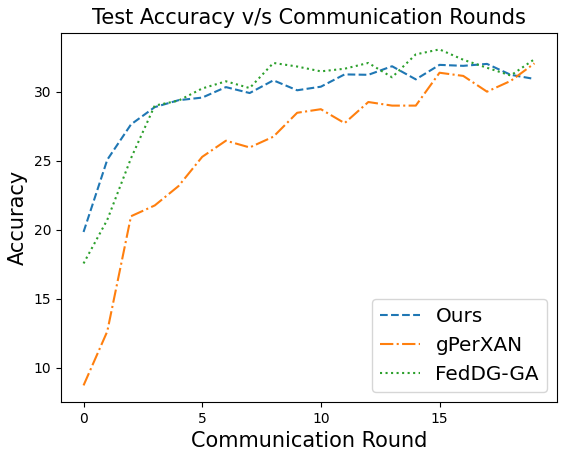
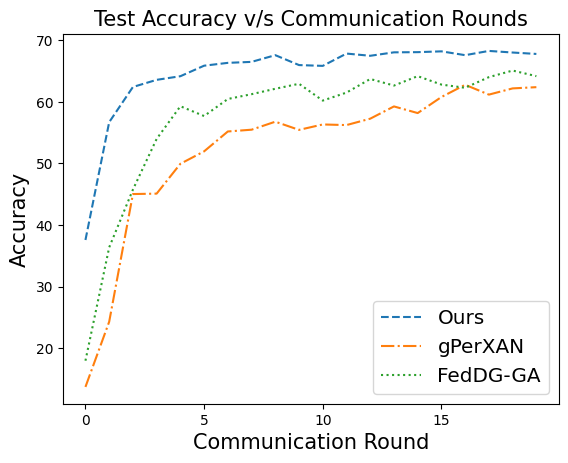
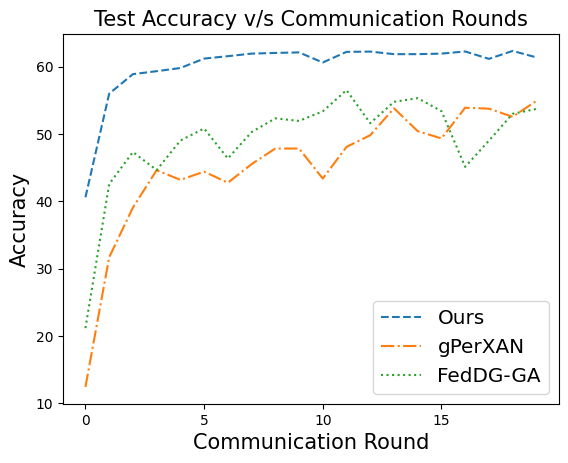
📝 Original Info Title: Federated Domain Generalization with Latent Space InversionArXiv ID: 2512.10224Date: 2025-12-11Authors: Ragja Palakkadavath, Hung Le, Thanh Nguyen-Tang, Svetha Venkatesh, Sunil Gupta📝 Abstract Federated domain generalization (FedDG) addresses distribution shifts among clients in a federated learning framework. FedDG methods aggregate the parameters of locally trained client models to form a global model that generalizes to unseen clients while preserving data privacy. While improving the generalization capability of the global model, many existing approaches in FedDG jeopardize privacy by sharing statistics of client data between themselves. Our solution addresses this problem by contributing new ways to perform local client training and model aggregation. To improve local client training, we enforce (domain) invariance across local models with the help of a novel technique, \textbf{latent space inversion}, which enables better client privacy. When clients are not \emph{i.i.d}, aggregating their local models may discard certain local adaptations. To overcome this, we propose an \textbf{important weight} aggregation strategy to prioritize parameters that significantly influence predictions of local models during aggregation. Our extensive experiments show that our approach achieves superior results over state-of-the-art methods with less communication overhead.
💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content Federated Domain Generalization with
Latent Space Inversion
Ragja Palakkadavath‡, Hung Le‡, Thanh Nguyen-Tang†, Svetha Venkatesh‡ and Sunil Gupta‡
‡Deakin Applied Artificial Intelligence Initiative, Deakin University, Australia
Email: {s222101652, thai.le, svetha.venkatesh, sunil.gupta}@deakin.edu.au
†Ying Wu College of Computing, New Jersey Institute of Technology, USA
Email: thanh.nguyen@njit.edu
©2025 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including
reprinting/republishing this material for advertising or promotional purposes, creating new collective works, for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or
reuse of any copyrighted component of this work in other works. DOI: ¡DOI No.¿
Abstract—Federated domain generalization (FedDG) addresses
distribution shifts among clients in a federated learning frame-
work. FedDG methods aggregate the parameters of locally
trained client models to form a global model that generalizes
to unseen clients while preserving data privacy. While improving
the generalization capability of the global model, many existing
approaches in FedDG jeopardize privacy by sharing statistics
of client data between themselves. Our solution addresses this
problem by contributing new ways to perform local client
training and model aggregation. To improve local client training,
we enforce (domain) invariance across local models with the help
of a novel technique, latent space inversion, which enables better
client privacy. When clients are not i.i.d, aggregating their local
models may discard certain local adaptations. To overcome this,
we propose an important weight aggregation strategy to prioritize
parameters that significantly influence predictions of local models
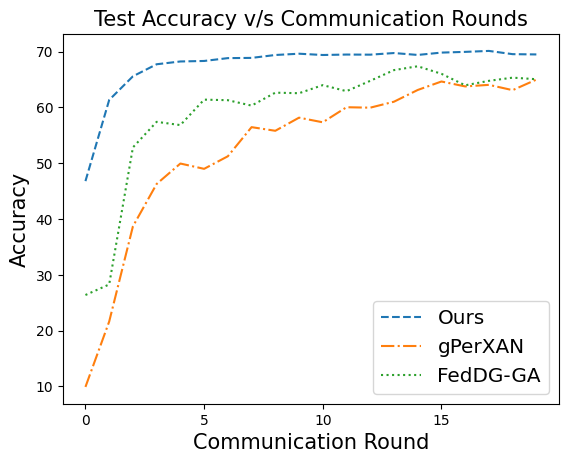
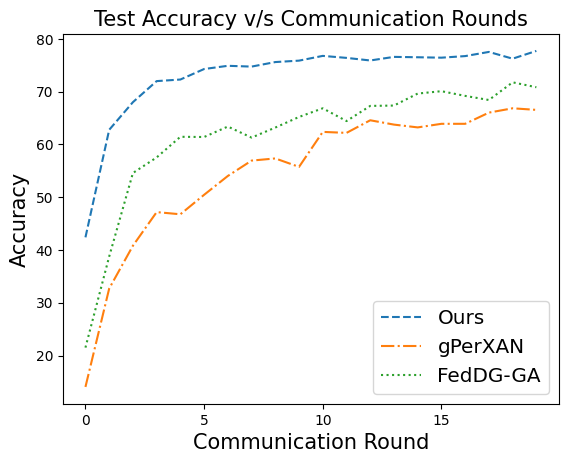
during aggregation. Our extensive experiments show that our
approach achieves superior results over state-of-the-art methods
with less communication overhead. Our code is available here.
Index Terms—latent representations, model inversion, feder-
ated domain generalization
I. INTRODUCTION
In many real-world applications, when developing predictive
models, restrictions in data sharing make it challenging to
train a single model in a distributed setup. For example,
when developing a model to analyze healthcare data from
multiple sources, healthcare providers face restrictions on
sharing patient information among themselves or storing it
in a central repository because it contains sensitive informa-
tion. Federated learning (FL) [1] allows multiple distributed
clients to collaboratively train a global model by sharing the
parameters of their local models with a central server while
keeping their local data private. The central server aggregates
the model parameters to compute the global model. However,
differences in data distribution across local client data can
degrade the global model performance in standard federated
learning methods.
Meanwhile, domain generalization (DG) [2] techniques
leverage data from source domains with potentially different
distributions to extract a domain-agnostic model that general-
izes predictive performance from these domains to an unseen
domain. DG enables the model to generalize across source and
unseen domains, but it assumes a centralized setting where
data from all source domains is available in one place.
1. Train local
models
= Aggregate ( ,......, )
2. Aggregate
local model
parameters
1. Train model by aggregating
data from all source domains.
2. Use to predict on target
domain data.
3. Repeat 1. (with as initialization) and 2.
until convergence.
= Aggregate ( ,......, )
4. Use to predict on both
unseen and existing
clients.
FEDERATED LEARNING
DOMAIN GENERALIZATION
FEDERATED DOMAIN GENERALIZATION
2.
4. Use to predict on existing clients.
Client 1
Client
1. Train local
models in
isolation.
Client 1
Client
3. Repeat steps 1. and 2. until convergence.
Unseen Client
Source Domains
Unseen
Domain
Fig. 1: Illustration of a model F trained in federated learning,
domain generalization, and federated domain generalization.
A key challenge in the deployment of DG algorithms in real-
world settings arises when data providers (such as hospitals
or financial institutions) do not share raw data due to privacy,
legal, or infrastructural constraints. This precludes training a
single model using centralized data, which is often required
to establish domain invariance between data from different
domains. Federated domain generalization (FedDG) bridges
this gap by incorporating generalization techniques into the
federated learning framework. Each client in FedDG may
have a potentially different data distribution from the others.
FedDG techniques are expected to capture domain invariance
between clients and generalize the global model to an unseen
client without violating client data privacy. In this work, we
consider that each federated
📸 Image Gallery
Reference This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.