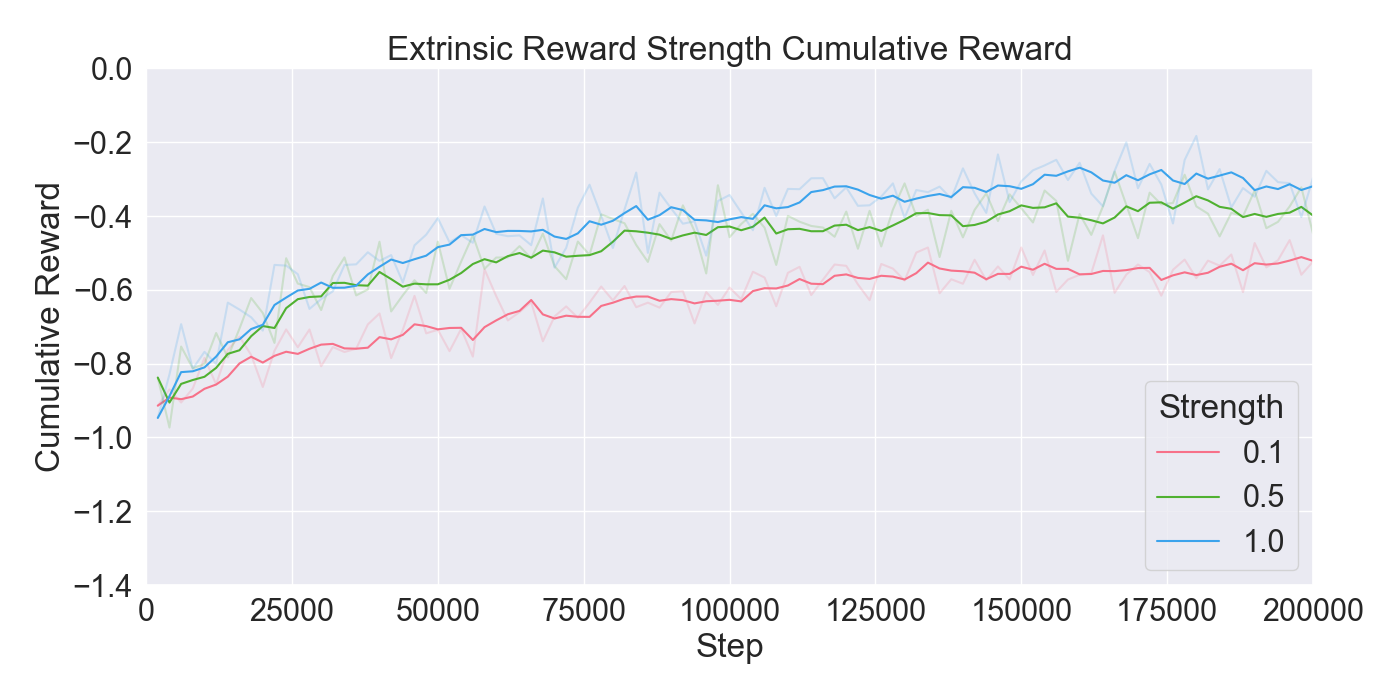
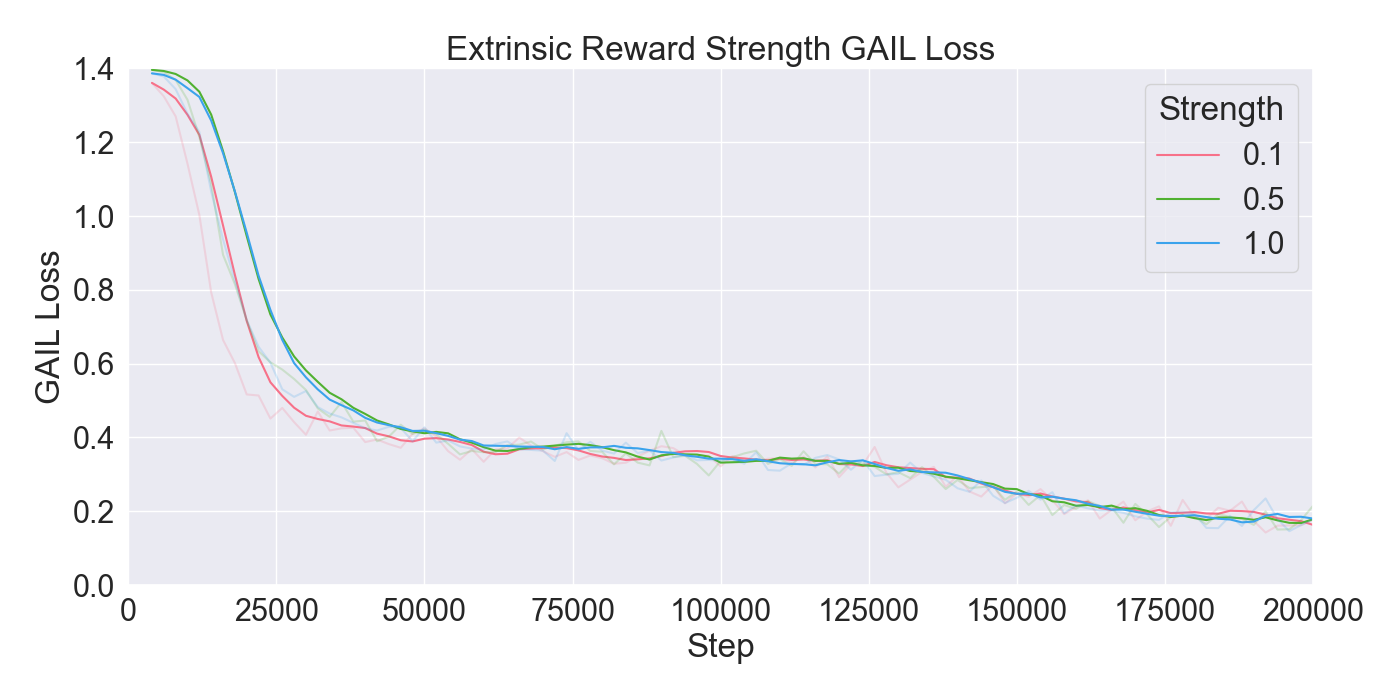
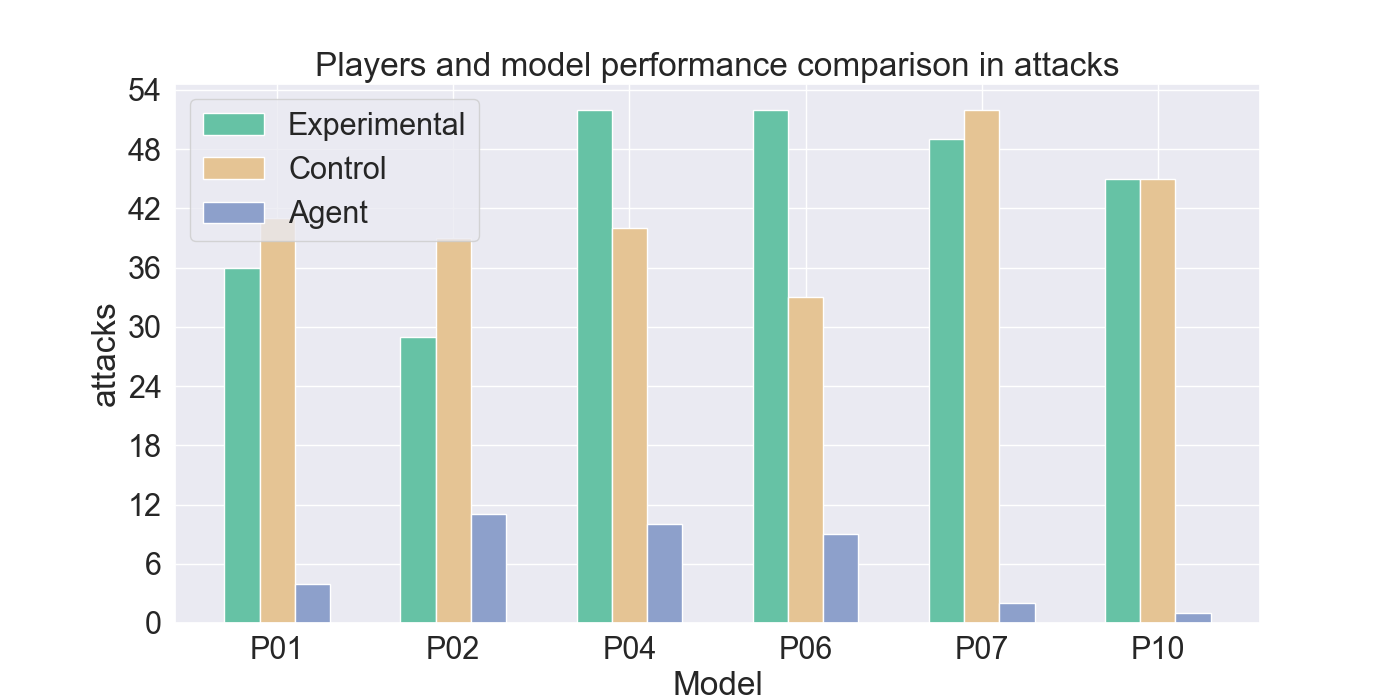
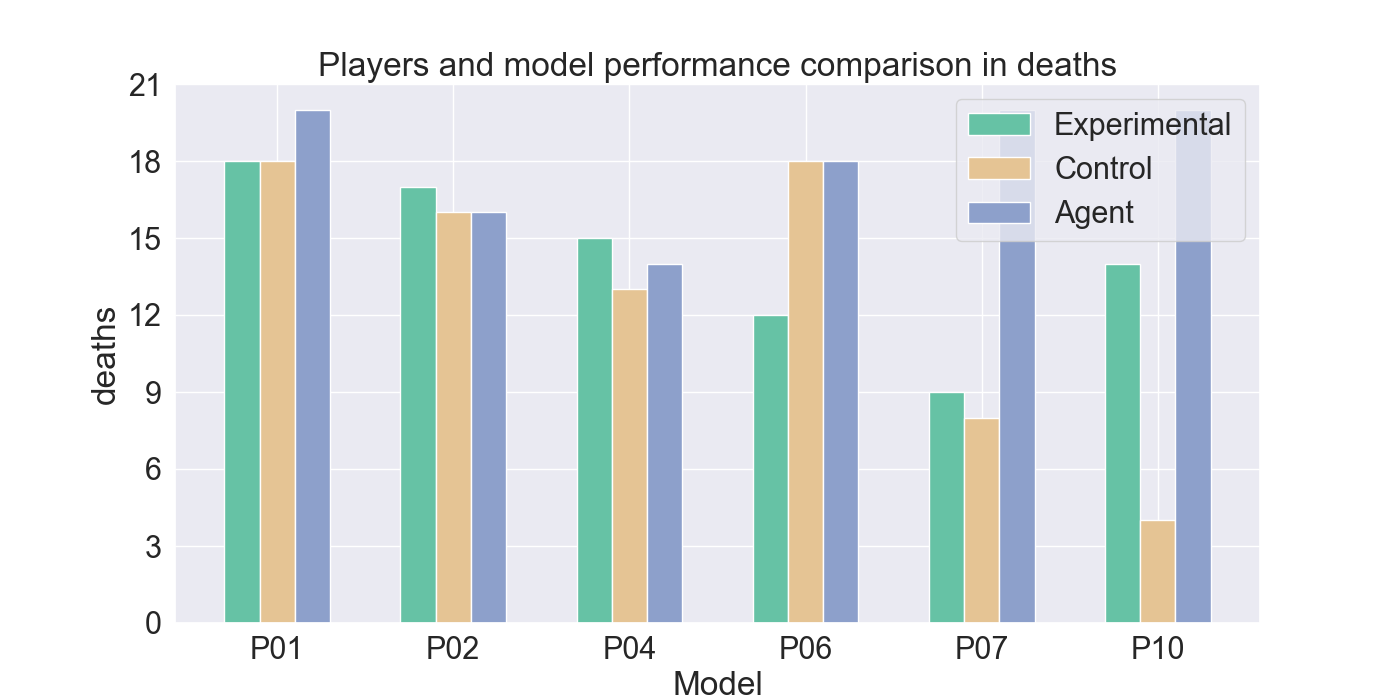
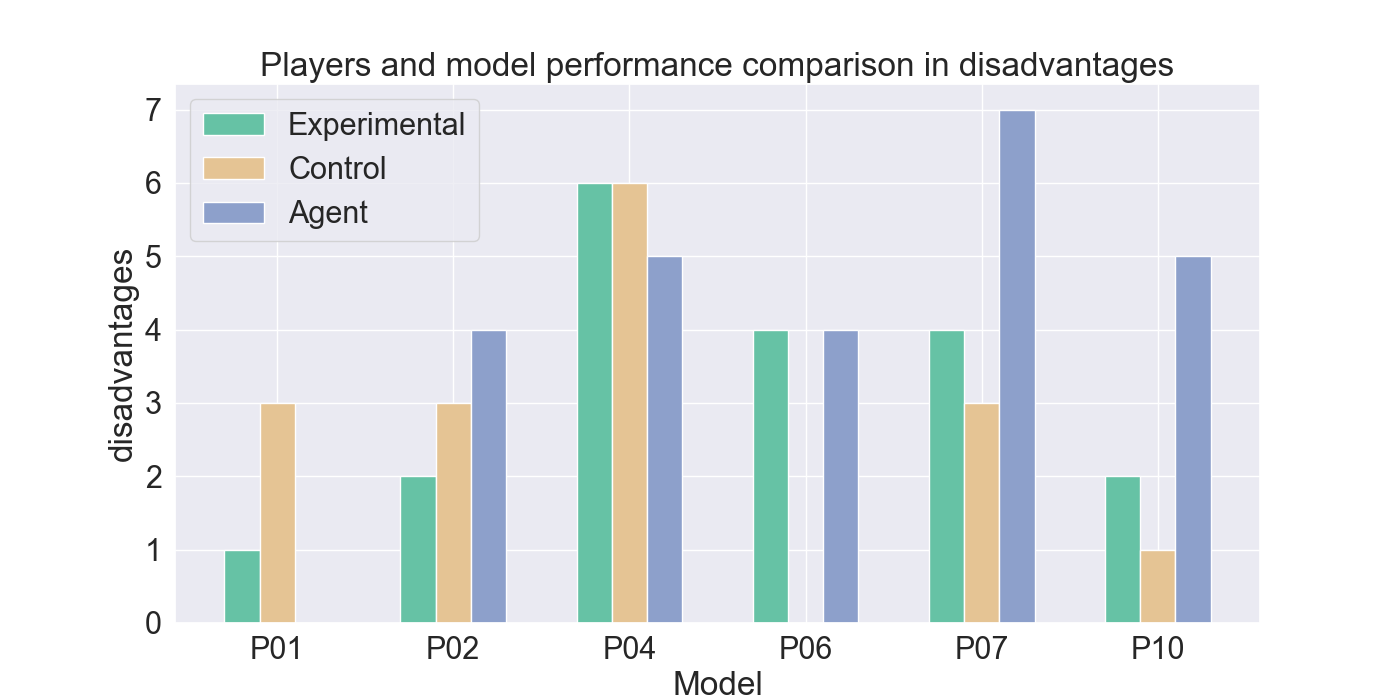
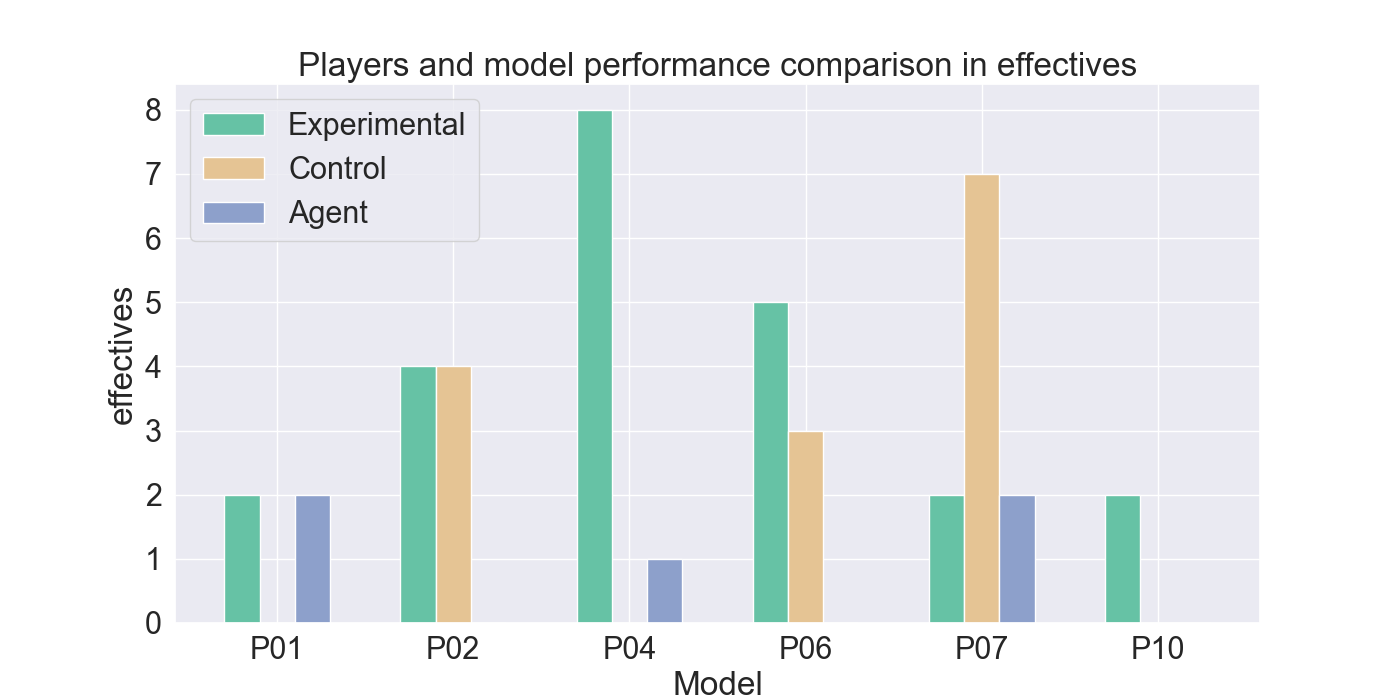
📝 Original Info Title: Mirror Mode in Fire Emblem: Beating Players at their own Game with Imitation and Reinforcement LearningArXiv ID: 2512.11902Date: 2025-12-10Authors: Yanna Elizabeth Smid, Peter van der Putten, Aske Plaat📝 Abstract Enemy strategies in turn-based games should be surprising and unpredictable. This study introduces Mirror Mode, a new game mode where the enemy AI mimics the personal strategy of a player to challenge them to keep changing their gameplay. A simplified version of the Nintendo strategy video game Fire Emblem Heroes has been built in Unity, with a Standard Mode and a Mirror Mode. Our first set of experiments find a suitable model for the task to imitate player demonstrations, using Reinforcement Learning and Imitation Learning: combining Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning, Behavioral Cloning, and Proximal Policy Optimization. The second set of experiments evaluates the constructed model with player tests, where models are trained on demonstrations provided by participants. The gameplay of the participants indicates good imitation in defensive behavior, but not in offensive strategies. Participant's surveys indicated that they recognized their own retreating tactics, and resulted in an overall higher player-satisfaction for Mirror Mode. Refining the model further may improve imitation quality and increase player's satisfaction, especially when players face their own strategies. The full code and survey results are stored at: https://github.com/YannaSmid/MirrorMode
💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content Mirror Mode in Fire Emblem:
Beating Players at their own Game
with Imitation and Reinforcement Learning
Yanna Elizabeth Smid
yanna.e.smid@gmail.com
LIACS, Leiden University
Leiden, The Netherlands
Peter van der Putten
p.w.h.van.der.putten@liacs.leidenuniv.nl
LIACS, Leiden University
Leiden, The Netherlands
Aske Plaat
a.plaat@liacs.leidenuniv.nl
LIACS, Leiden University
Leiden, The Netherlands
Abstract
Enemy strategies in turn-based games should be surprising and
unpredictable. This study introduces Mirror Mode, a new game
mode where the enemy AI mimics the personal strategy of a player
to challenge them to keep changing their gameplay. A simplified
version of the Nintendo strategy video game Fire Emblem Heroes
has been built in Unity, with a Standard Mode and a Mirror Mode.
Our first set of experiments find a suitable model for the task to
imitate player demonstrations, using Reinforcement Learning and
Imitation Learning: combining Generative Adversarial Imitation
Learning, Behavioral Cloning, and Proximal Policy Optimization.
The second set of experiments evaluates the constructed model
with player tests, where models are trained on demonstrations pro-
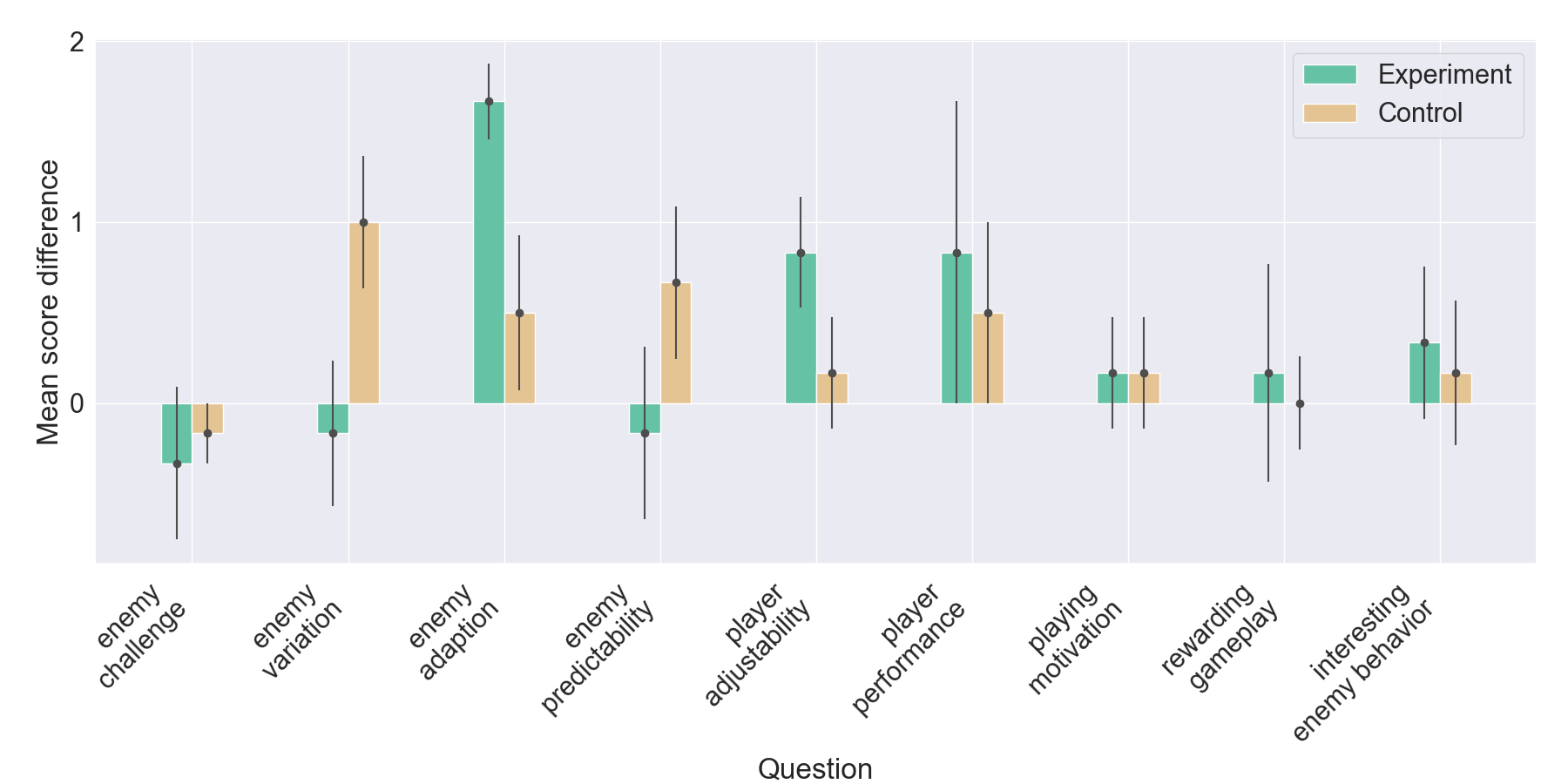
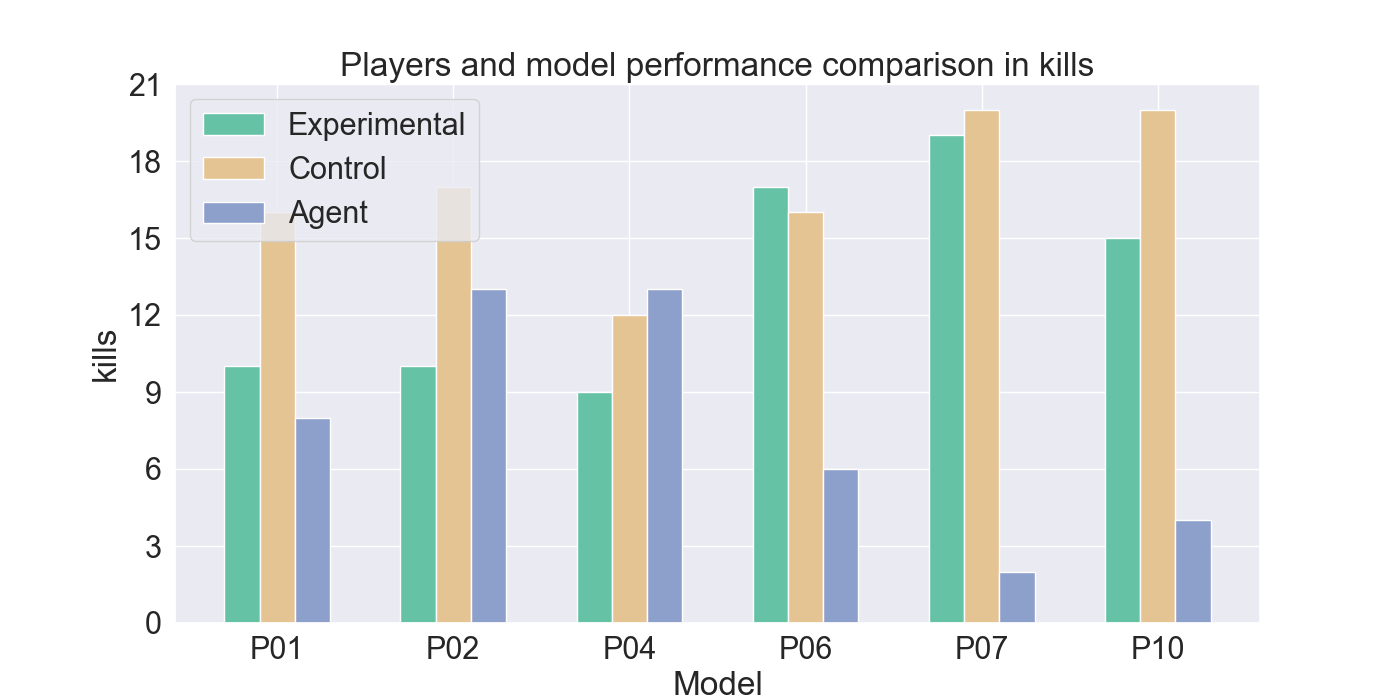
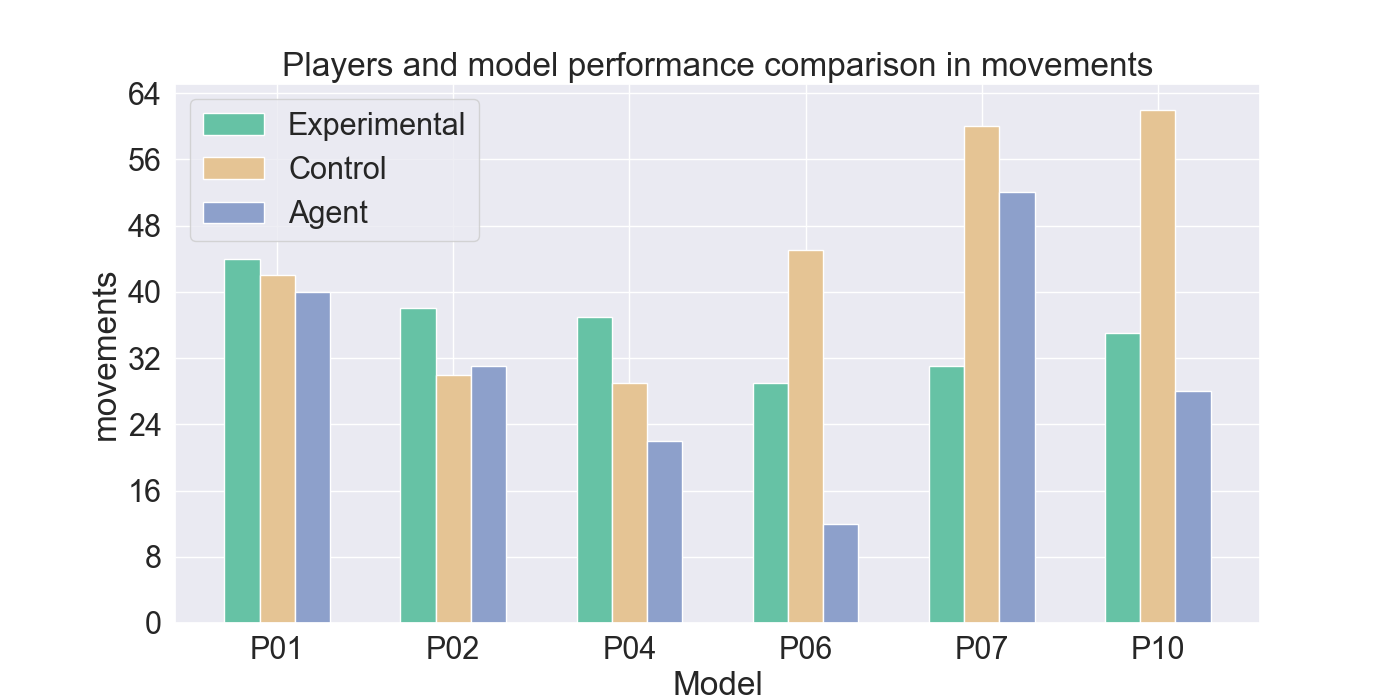
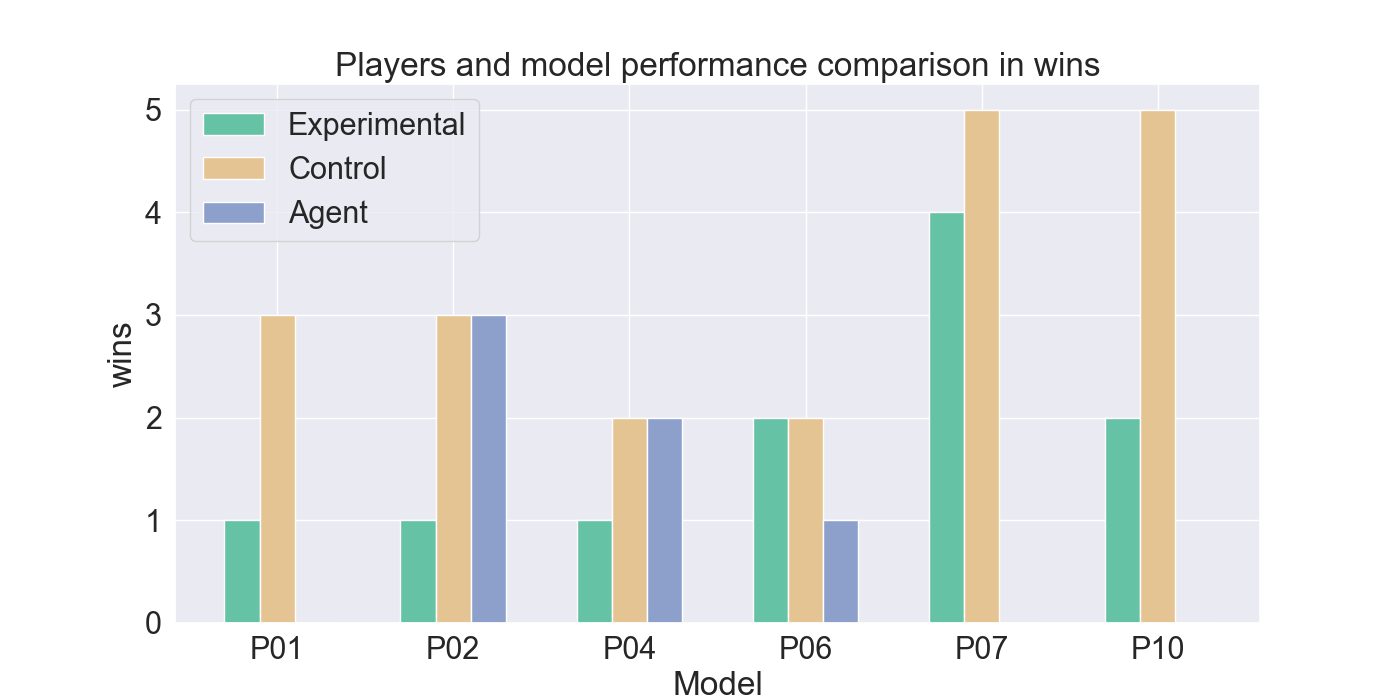
vided by participants. The gameplay of the participants indicates
good imitation in defensive behavior, but not in offensive strategies.
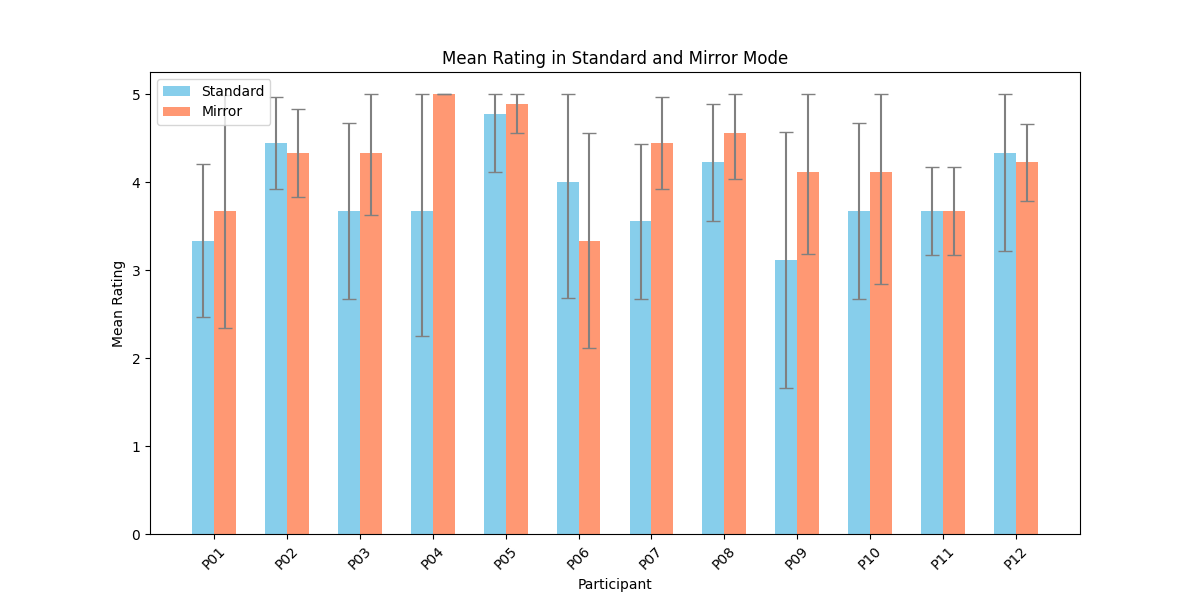
Participant’s surveys indicated that they recognized their own re-
treating tactics, and resulted in an overall higher player-satisfaction
for Mirror Mode. Refining the model further may improve imitation
quality and increase player’s satisfaction, especially when players
face their own strategies. The full code and survey results are stored
at: https://github.com/YannaSmid/MirrorMode.
Keywords
Imitation Learning, Reinforcement Learning, Game AI, Strategy
Games
ACM Reference Format:
Yanna Elizabeth Smid, Peter van der Putten, and Aske Plaat. 2025. Mirror
Mode in Fire Emblem: Beating Players at their own Game with Imitation
and Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of LIACS. ACM, New York, NY,
USA, 14 pages.
1
Introduction
In video games, non-playable character (NPC) behavior has relied
on artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms for decades [23]. Now, with
the quick advancements made in AI, new possibilities are found to
enhance the behavior of NPCs, to increase the quality of a video
game. NPC behavior refers to how characters in games should act
and react to certain events in the game environment. Realistic NPC
behavior contributes significantly to the player immersion and
satisfaction of the game [16]. Traditionally, these behavior types
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
LIACS, Leiden
© 2025 Copyright held by the owner/author(s).
are handled by Finite State Machines (FSM) or Behavior Trees (BT),
where each character follows a set of predefined heuristics and
transitions between states based on game events [8]. Nevertheless,
this method of programmable behavior can result in repetitive
behavior that makes NPCs predictable in their actions [1, 17].
In strategy games, predictability in enemy tactics can have a
major influence on player experience. Strategy games require tac-
tical thinking to defeat a team of opponents, while keeping your
own team alive. Statistics in 2024 have shown that the popularity
of strategy games has drastically decreased in the past 9 years [28].
This may be linked to the predictability of the enemy’s action as it
makes games easier to play, possibly reducing the engagement of
more experienced players [1]. In addition to this, it is found that
playing several repetitive games can cause boredom [5].
Therefore, this study aims to address the risk of boredom in strat-
egy video games by introducing Mirror Mode, a new game mode
where the enemy NPCs learn a strategy based on the player’s strat-
egy through Imitation Learning (IL) [20]. A simplified version of the
mobile strategy game Fire Emblem Heroes [21] was developed, to
apply combinations of Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning
(GAIL), Behavioral Cloning (BC), and Proximal Policy Optimization
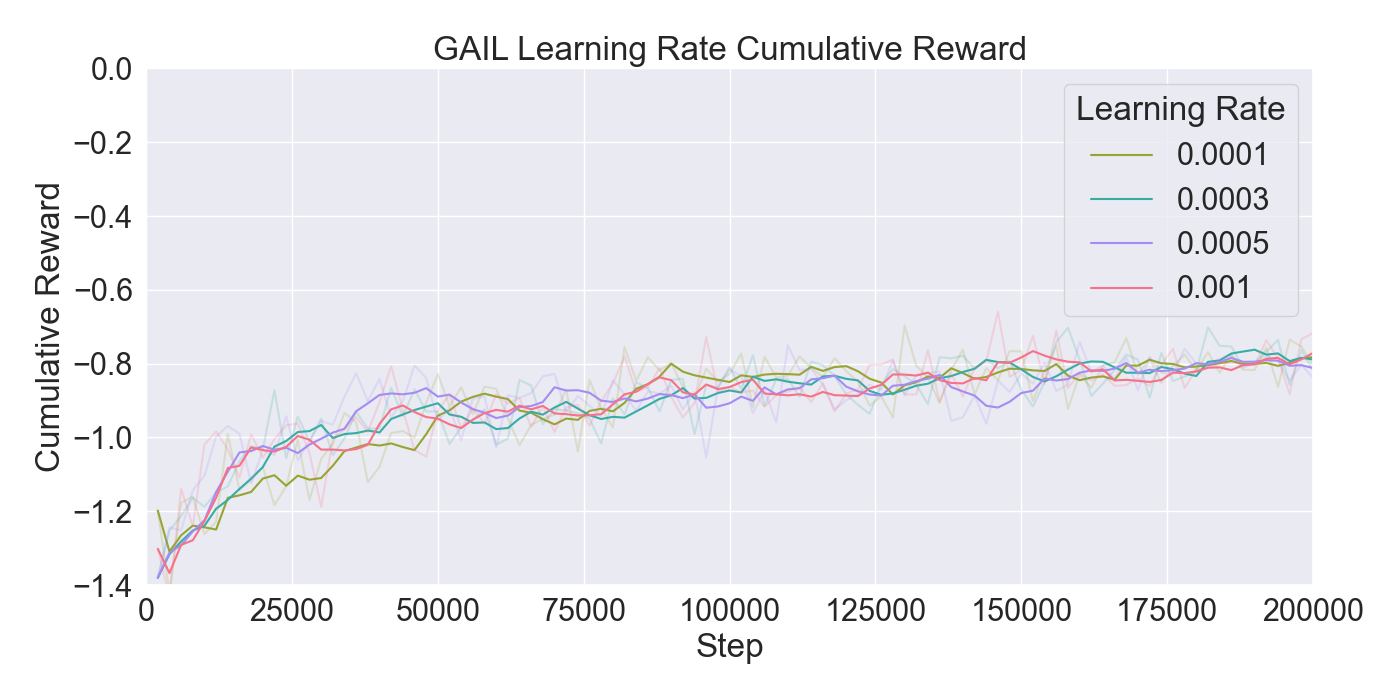
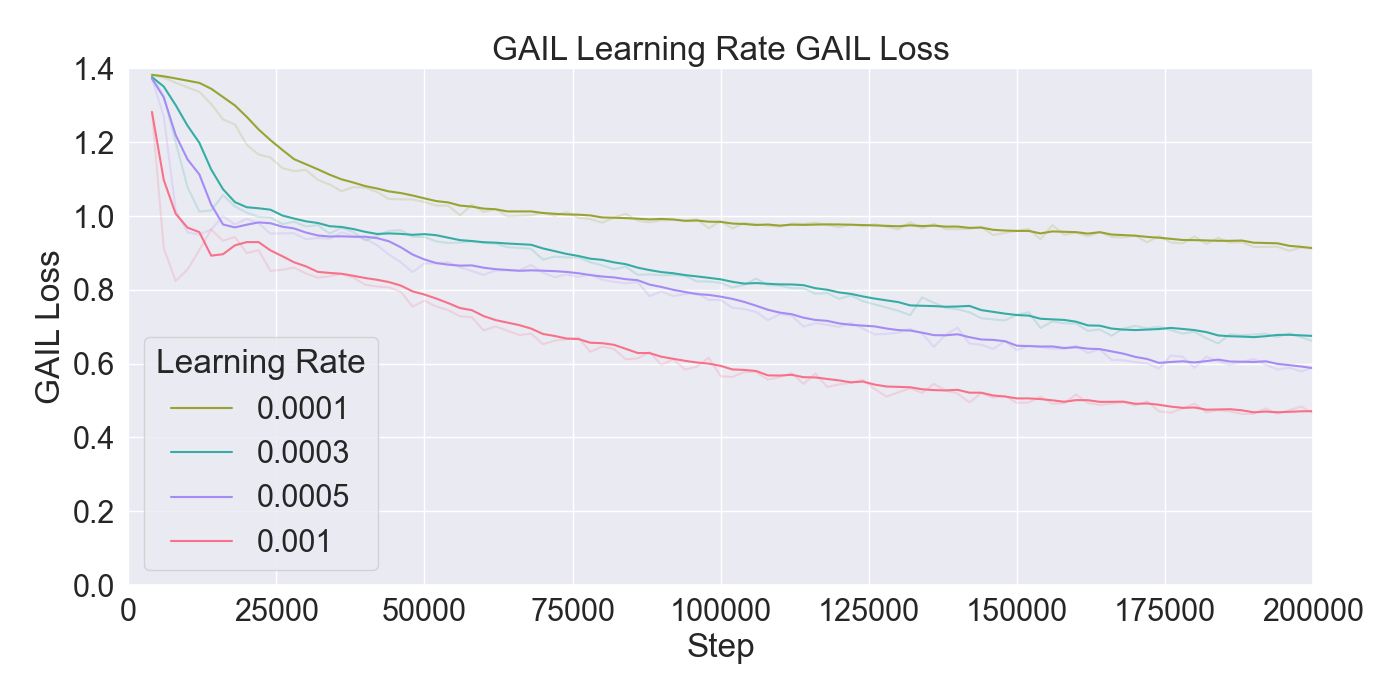
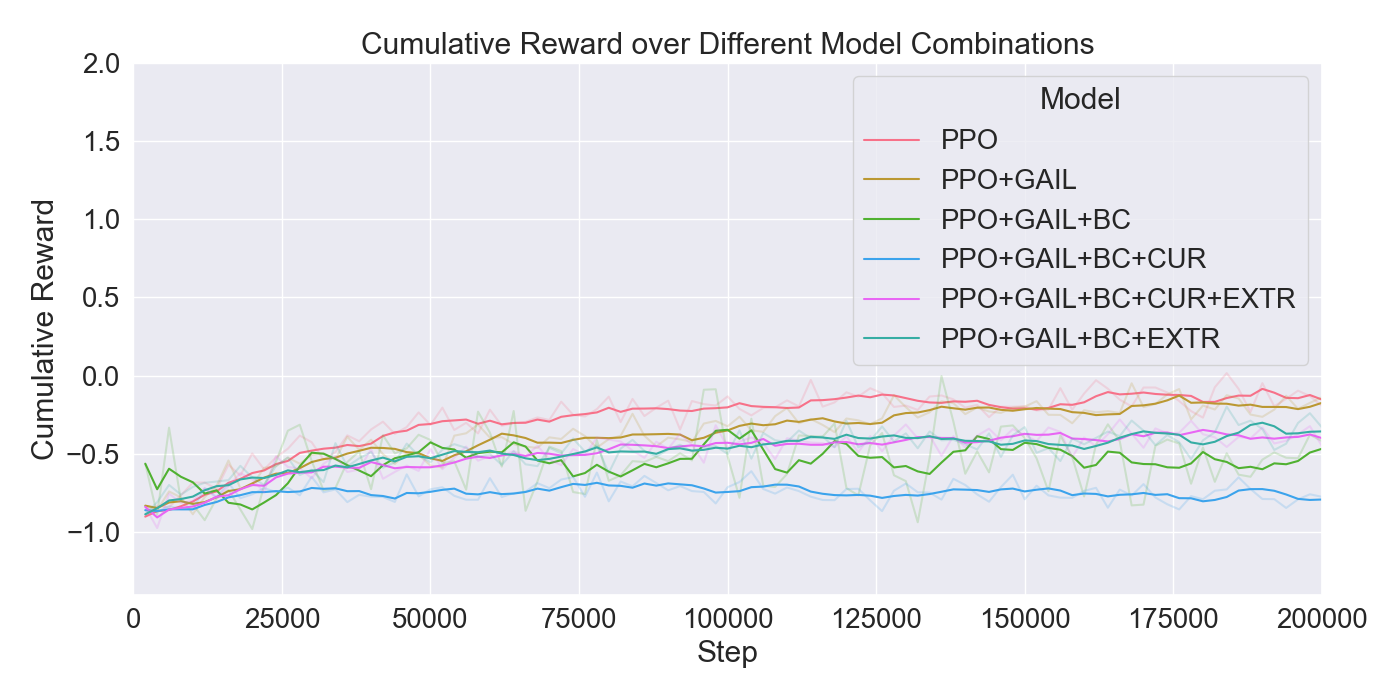
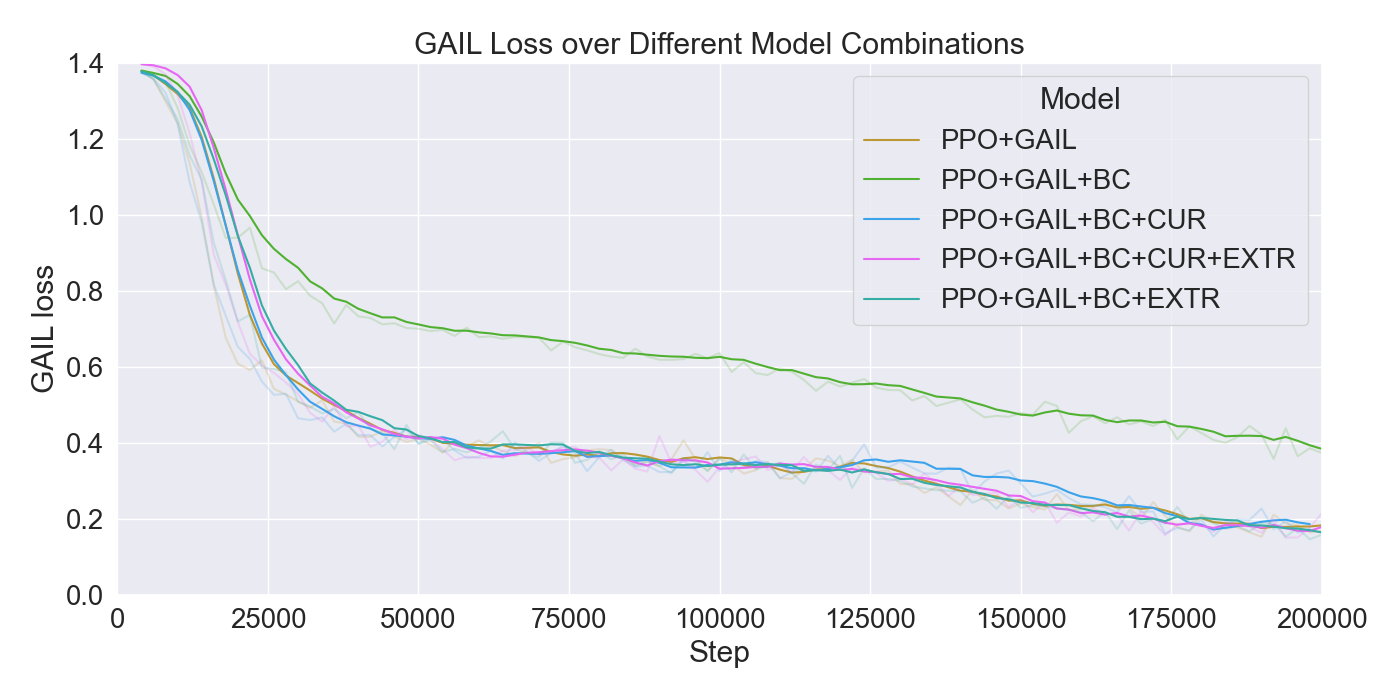
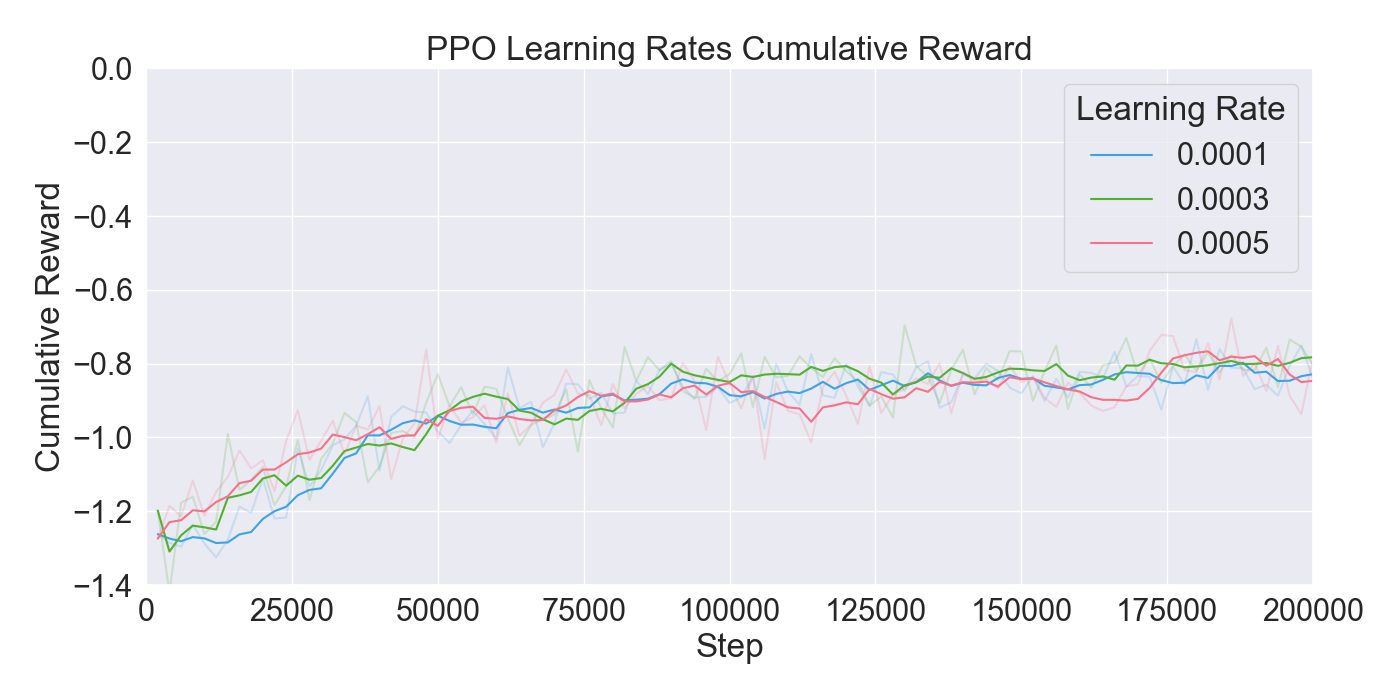
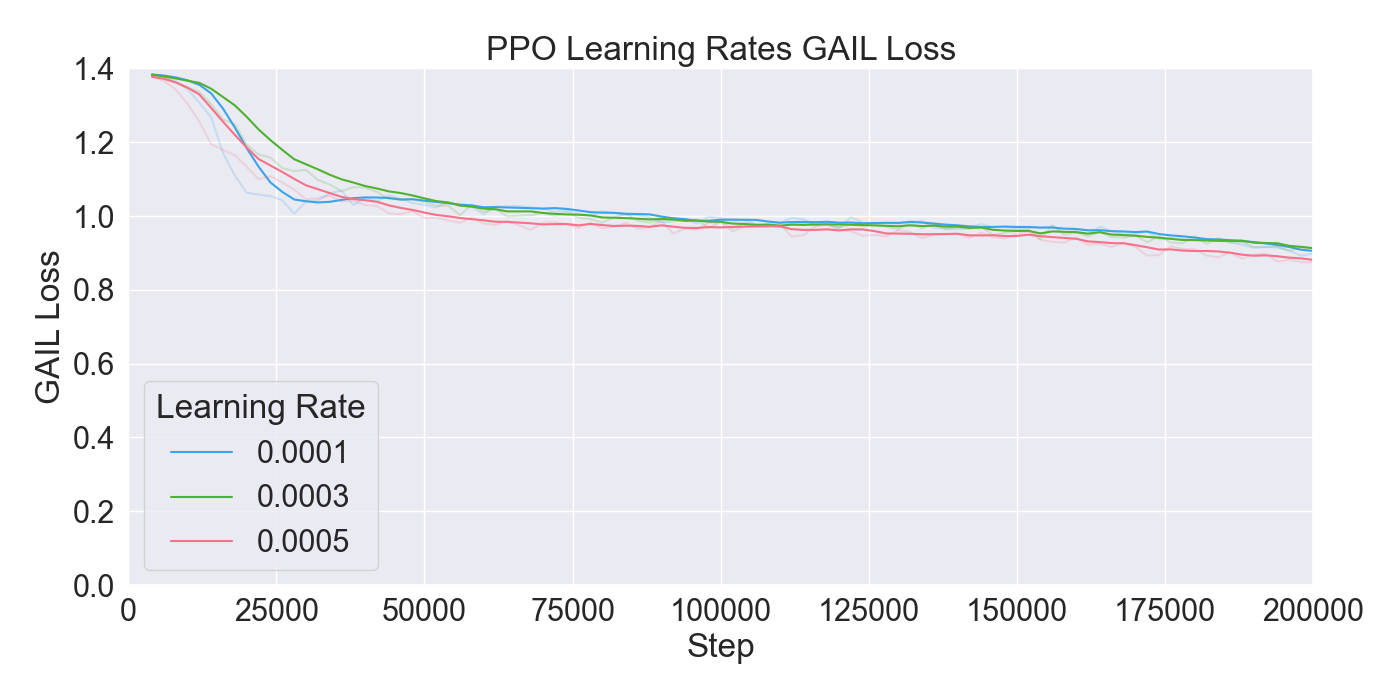
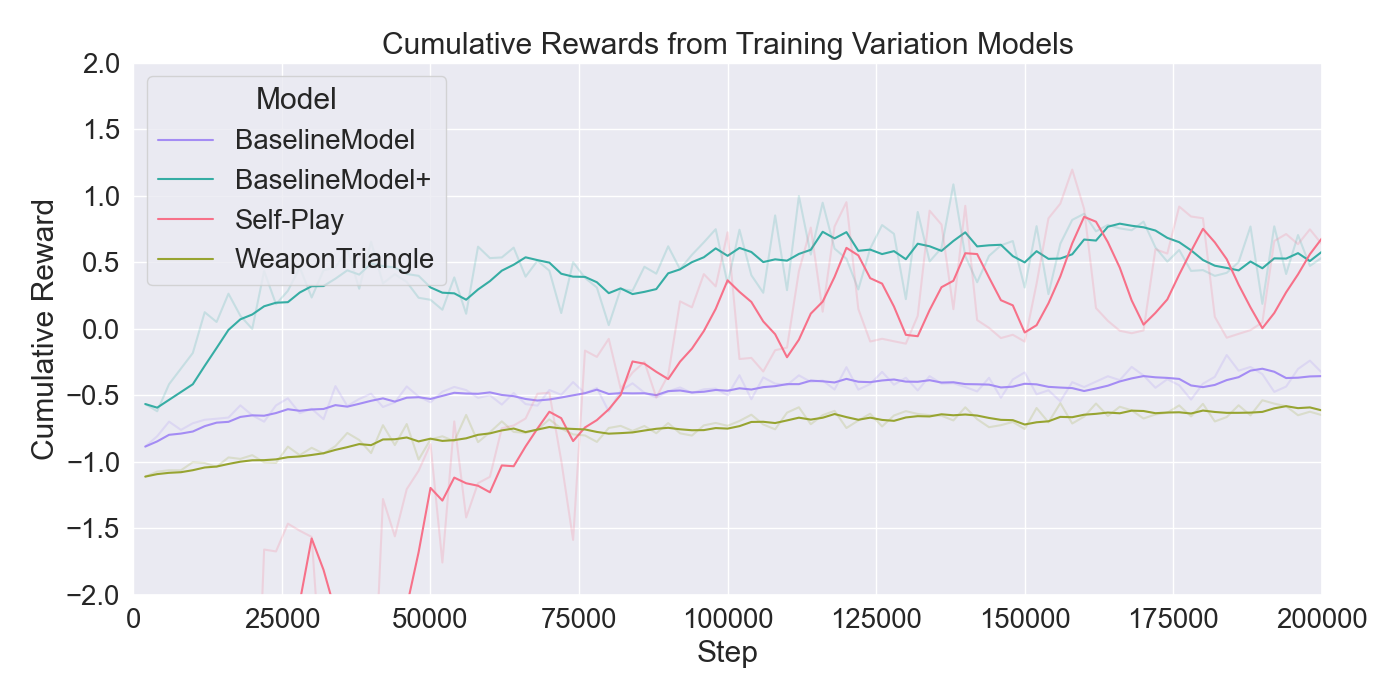
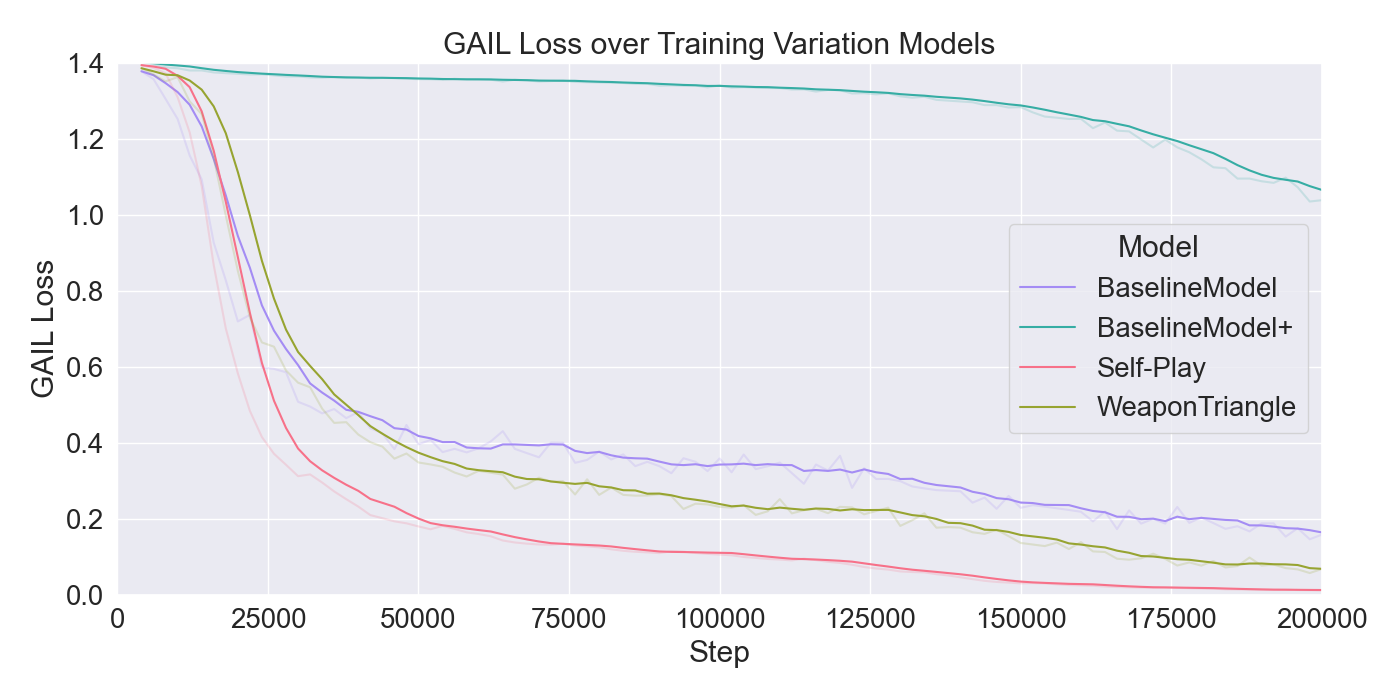
(PPO), in order to train agents. The performance of the algorithms
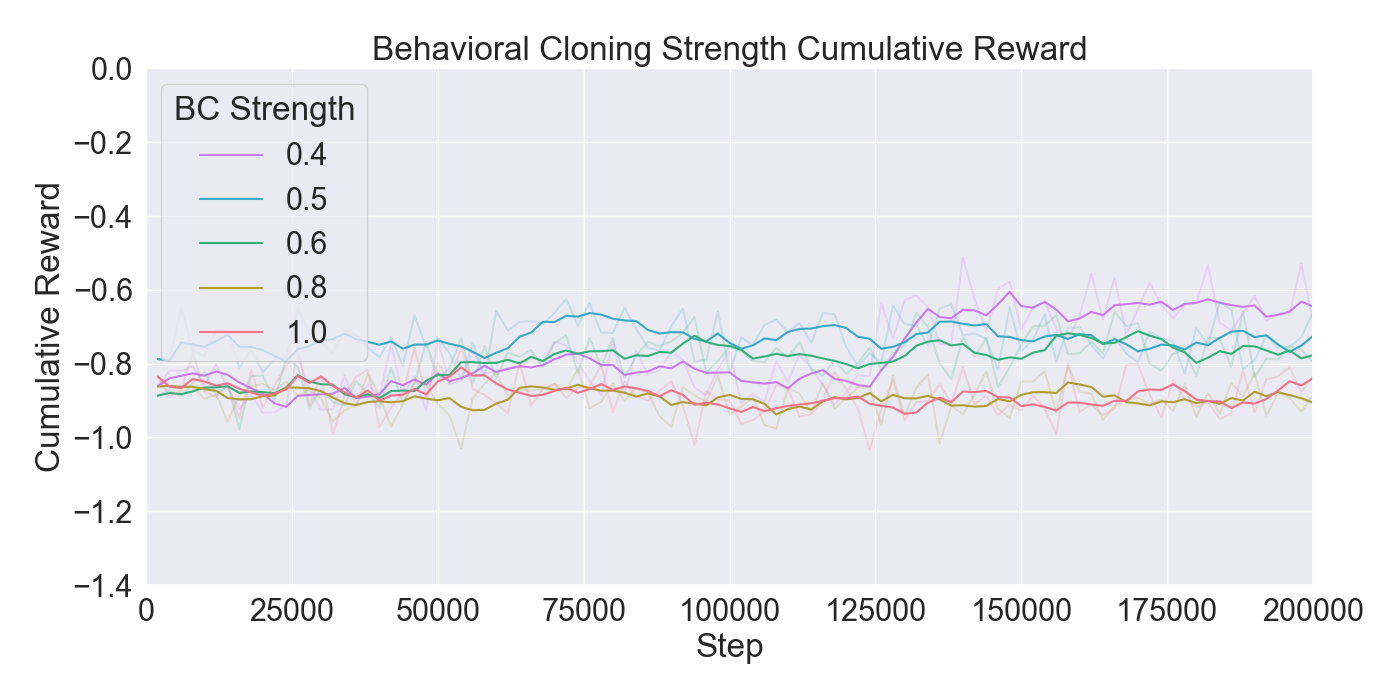
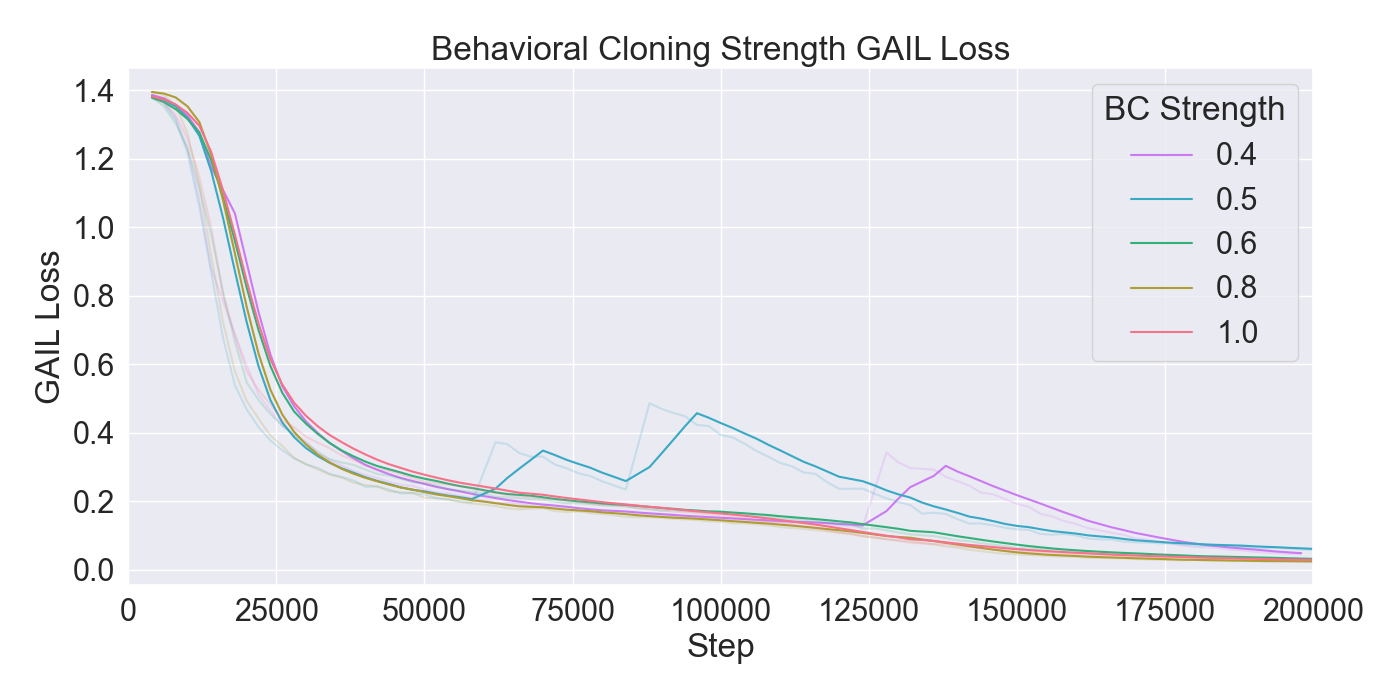
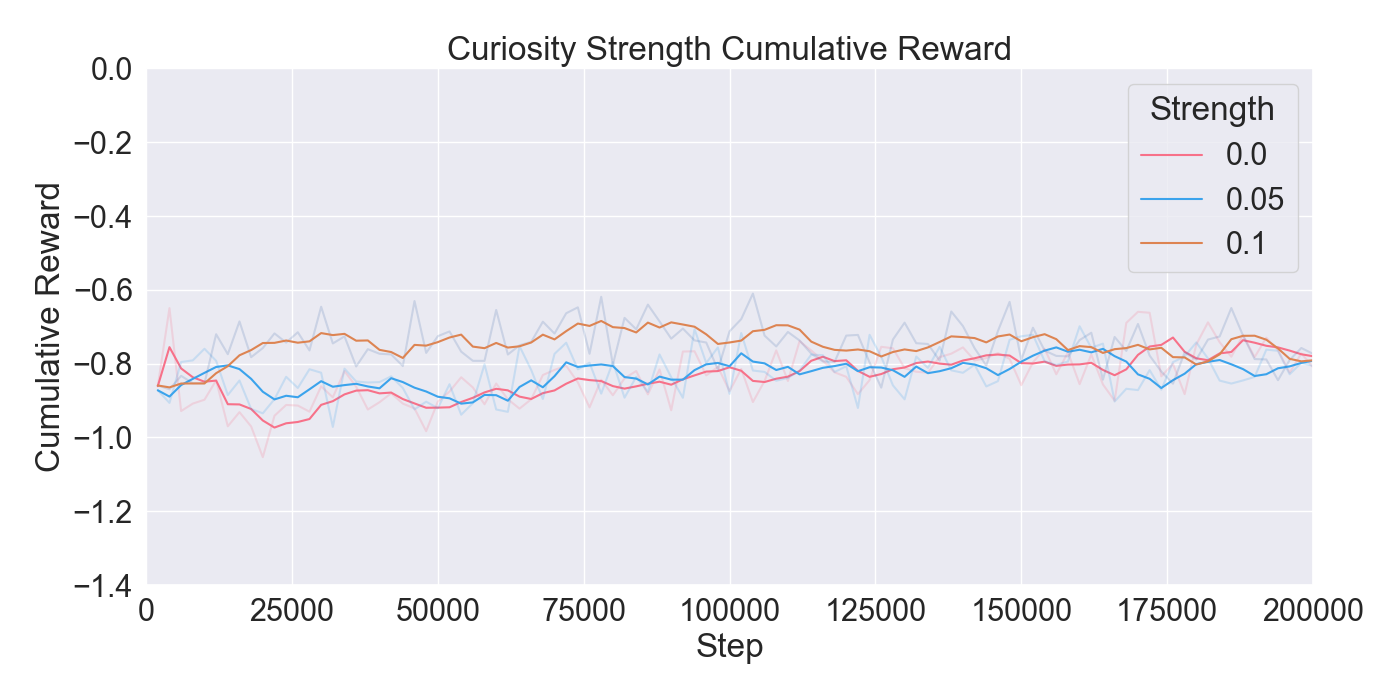
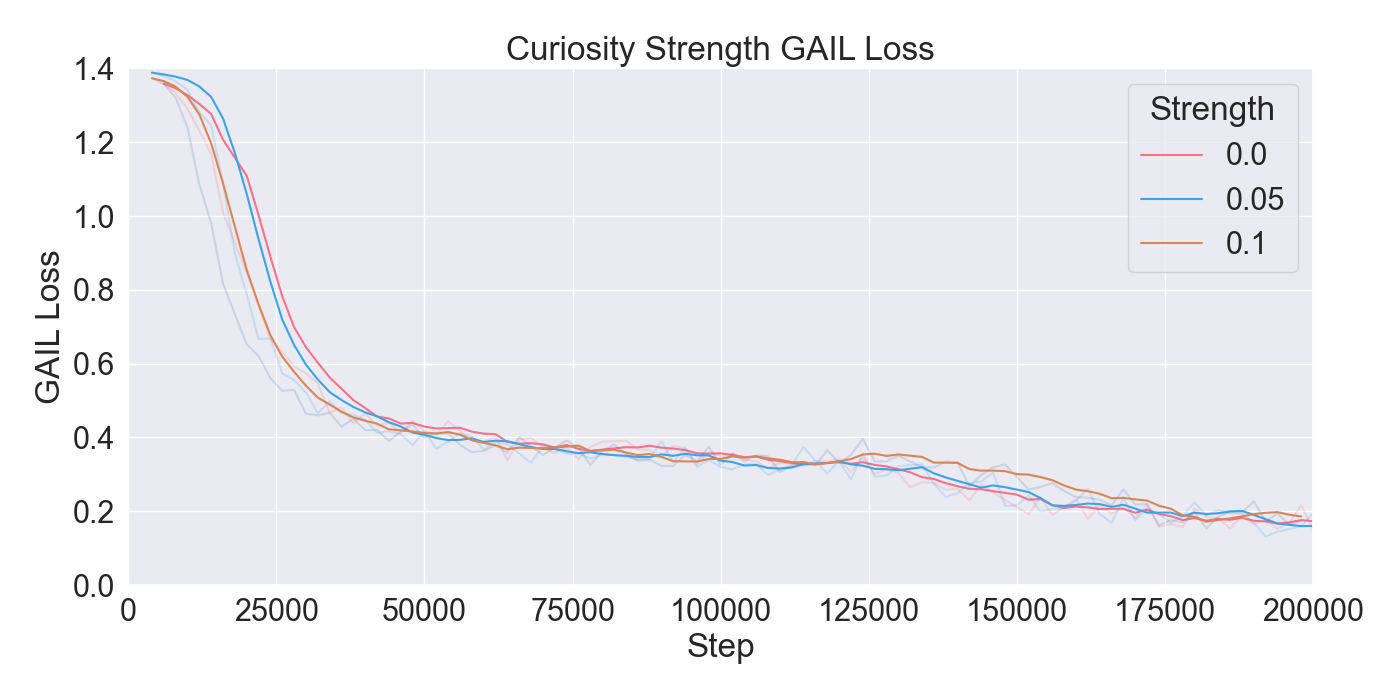
are assessed through ablation and optimization experiments, where
the best configuration of algorithms and their hyperparameters
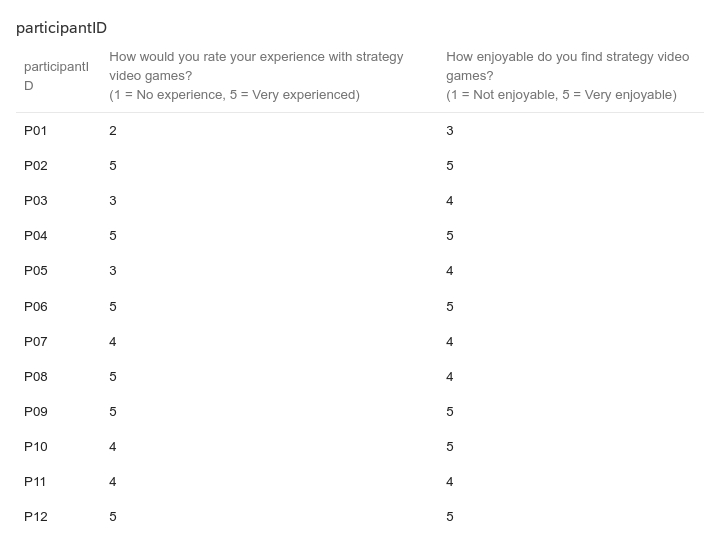
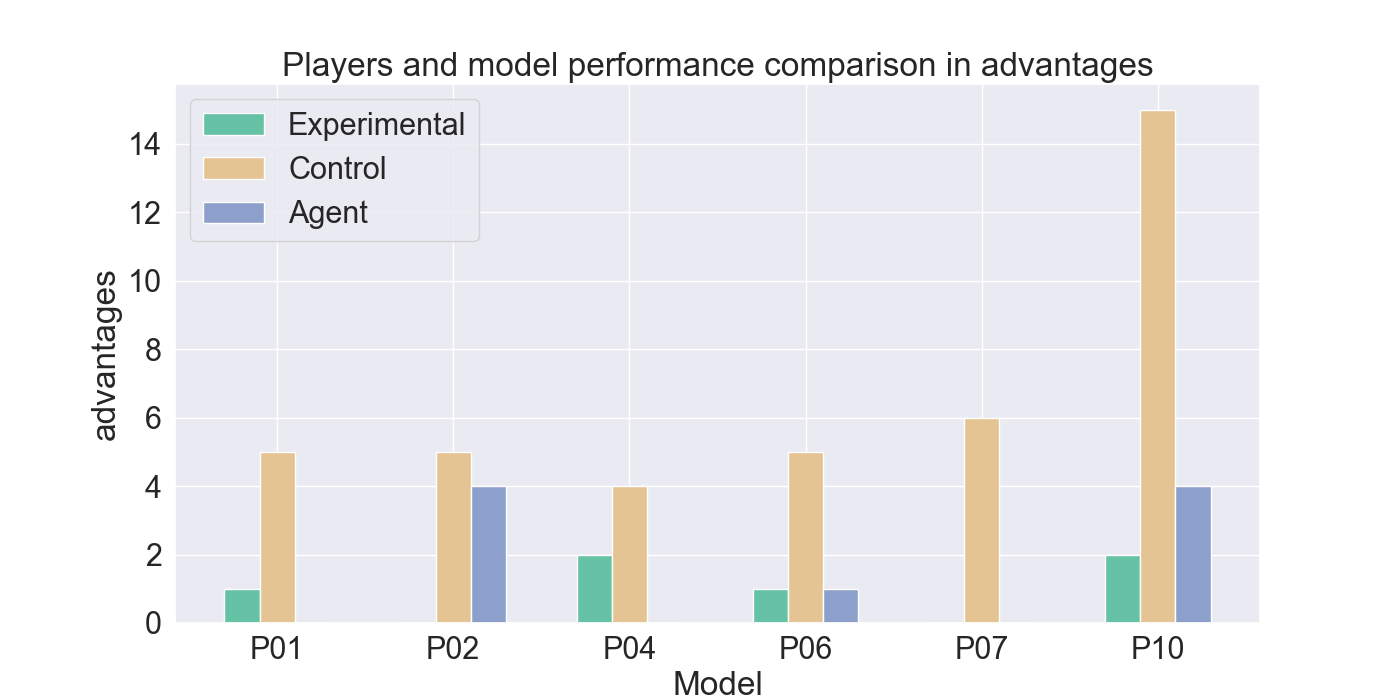
were used for further evaluations through user studies. The con-
ducted user studies evaluated the performance of the trained agents
and their imitation quality. The research aims to answer the central
research question: How will a player’s game experience be influenced
when NPCs imitate their strategy in a turn-based strategy game?
With the results of the finetuning experiments the study aims to
further explore the sub-question: “To what extent can reinforcement
learning (RL) and imitation learning (IL) be applied to teach NPCs
the strategy of a player in a turn-based strategy game?”
Altogether, the study provides an innovative method of playing
strategy games, and offers insights into the effectiveness of IL a
📸 Image Gallery
Reference This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.