Large language models (LLMs) are post-trained through reinforcement learning (RL) to evolve into Reasoning Language Models (RLMs), where the hallmark of this advanced reasoning is ``aha'' moments when they start to perform strategies, such as self-reflection and deep thinking, within chain of thoughts (CoTs). Motivated by this, this paper proposes a novel reinforced strategy injection mechanism (rSIM), that enables any LLM to become an RLM by employing a small planner to guide the LLM's CoT through the adaptive injection of reasoning strategies. To achieve this, the planner (leader agent) is jointly trained with an LLM (follower agent) using multi-agent RL (MARL), based on a leader-follower framework and straightforward rule-based rewards. Experimental results show that rSIM enables Qwen2.5-0.5B to become an RLM and significantly outperform Qwen2.5-14B. Moreover, the planner is generalizable: it only needs to be trained once and can be applied as a plug-in to substantially improve the reasoning capabilities of existing LLMs. In addition, the planner supports continual learning across various tasks, allowing its planning abilities to gradually improve and generalize to a wider range of problems.
Large language models (LLMs) have been enhanced with advanced reasoning capabilities, evolving into Reasoning Language Models (RLMs) (Besta et al., 2025) that solve problems through step-by-step reasoning, commonly referred to as chain-of-thought (CoT) (Wei et al., 2022). A key advancement in RLMs is their ability to integrate reasoning strategies, such as self-reflection, decomposition, and deliberative thinking, into the CoT process, contributing to improved problem-solving accuracy.
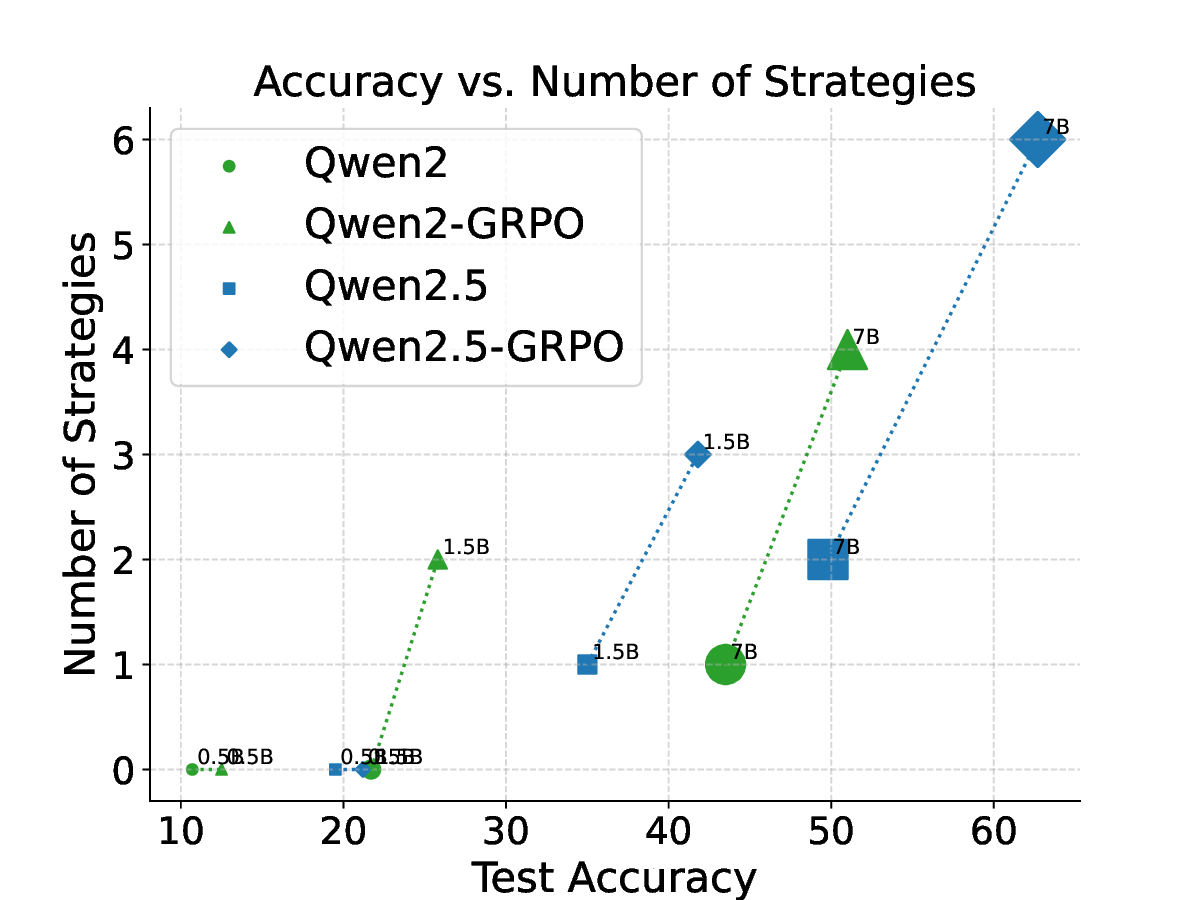
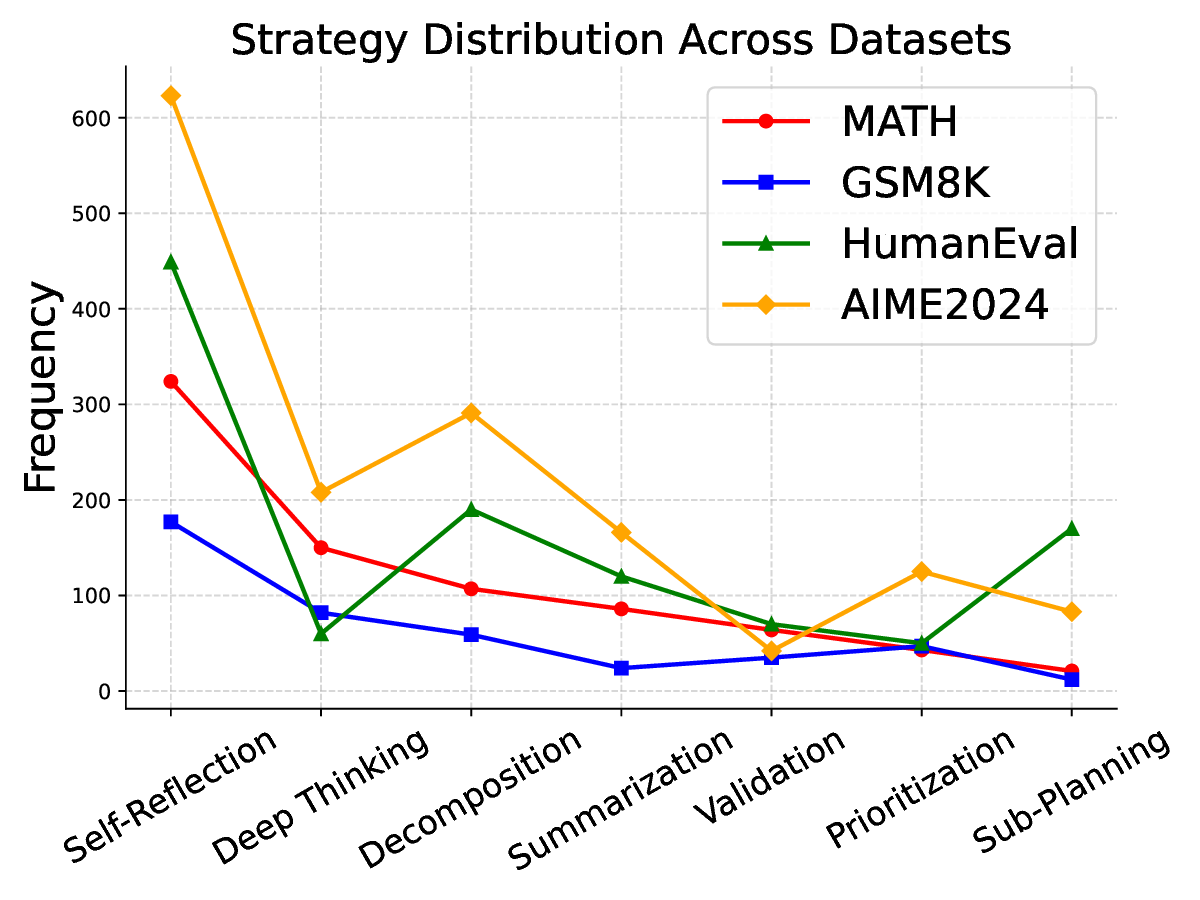
Existing literature (Trung et al., 2024;Havrilla et al., 2024), especially the recent Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) (Guo et al., 2025), primarily post-trains LLMs to evolve into RLMs purely through reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms. A hallmark of this evolution is the emergence of the “aha moment” where LLMs start to perform strategies such as self-reflection within CoTs. We empirically found that the better performance of evolved RLMs correlates with the higher appearance frequency and more appropriate positions of these strategies compared to those in LLMs. However, our findings also indicate that when LLMs, particularly smaller ones, inherently lack the capacity to perform basic reasoning strategies, RL-based post-training is unable to transform them into capable RLMs.
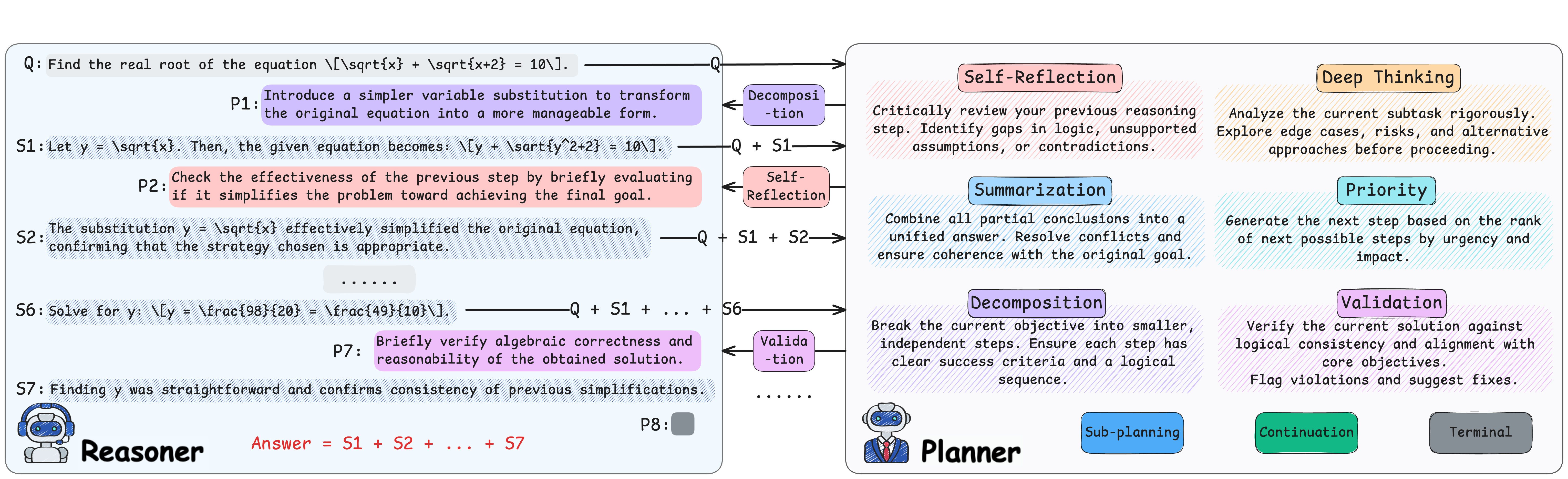
Therefore, this paper proposes a reinforced strategy injection mechanism (rSIM), which enables any LLM, in particular those as small as 0.5B, to evolve into an RLM with minimal or even no additional training. To achieve this, rSIM introduces only an auxiliary planner that, at each reasoning step of an LLM, adaptively selects an appropriate strategy from a predefined set such as self-reflection, decomposition, and others, and injects it into the chain of thought (CoT) to guide the next step generation. Specifically, the rSIM offers the following four key contributions:
• Injecting reasoning strategies adaptively into the CoT process of any LLM, including small and large ones, via a planner enables the LLM to directly gain the advanced reasoning ability like RLMs.
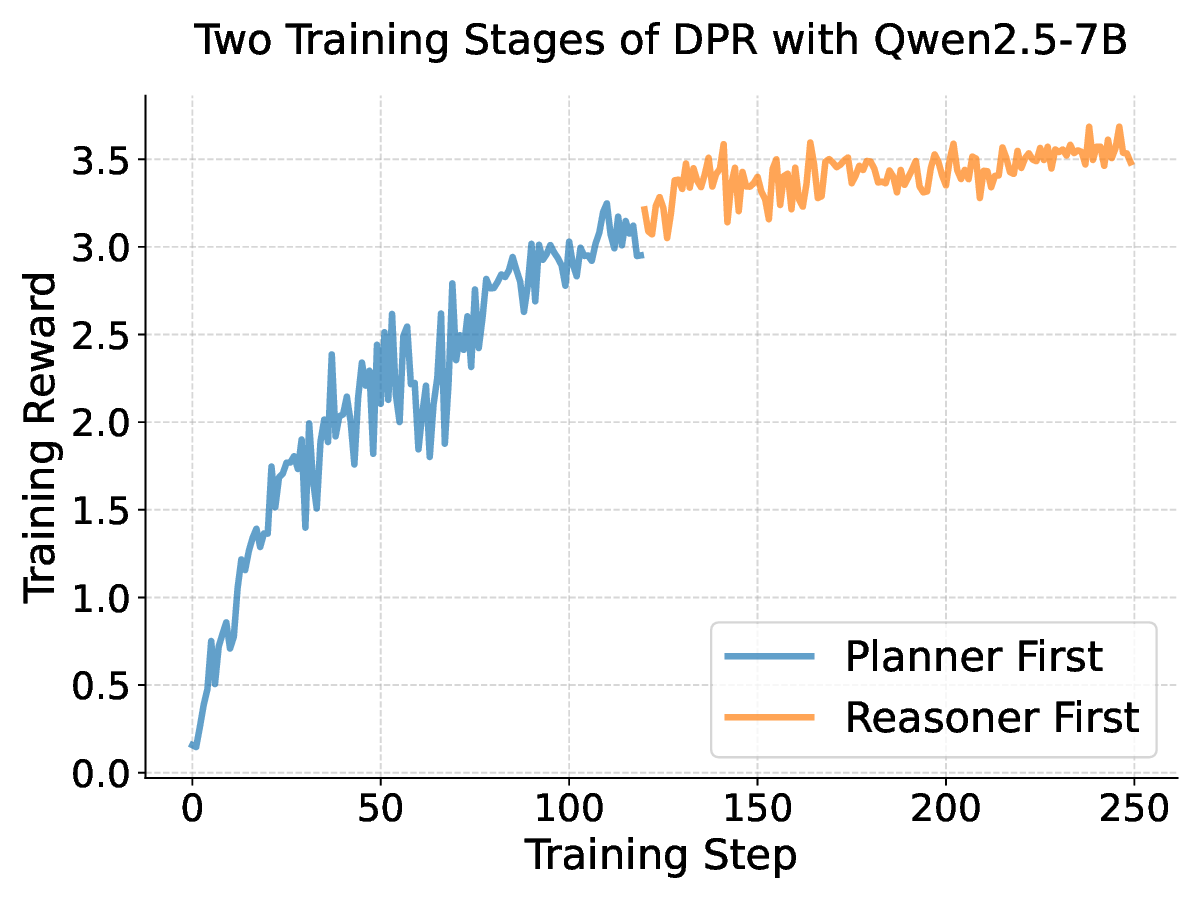
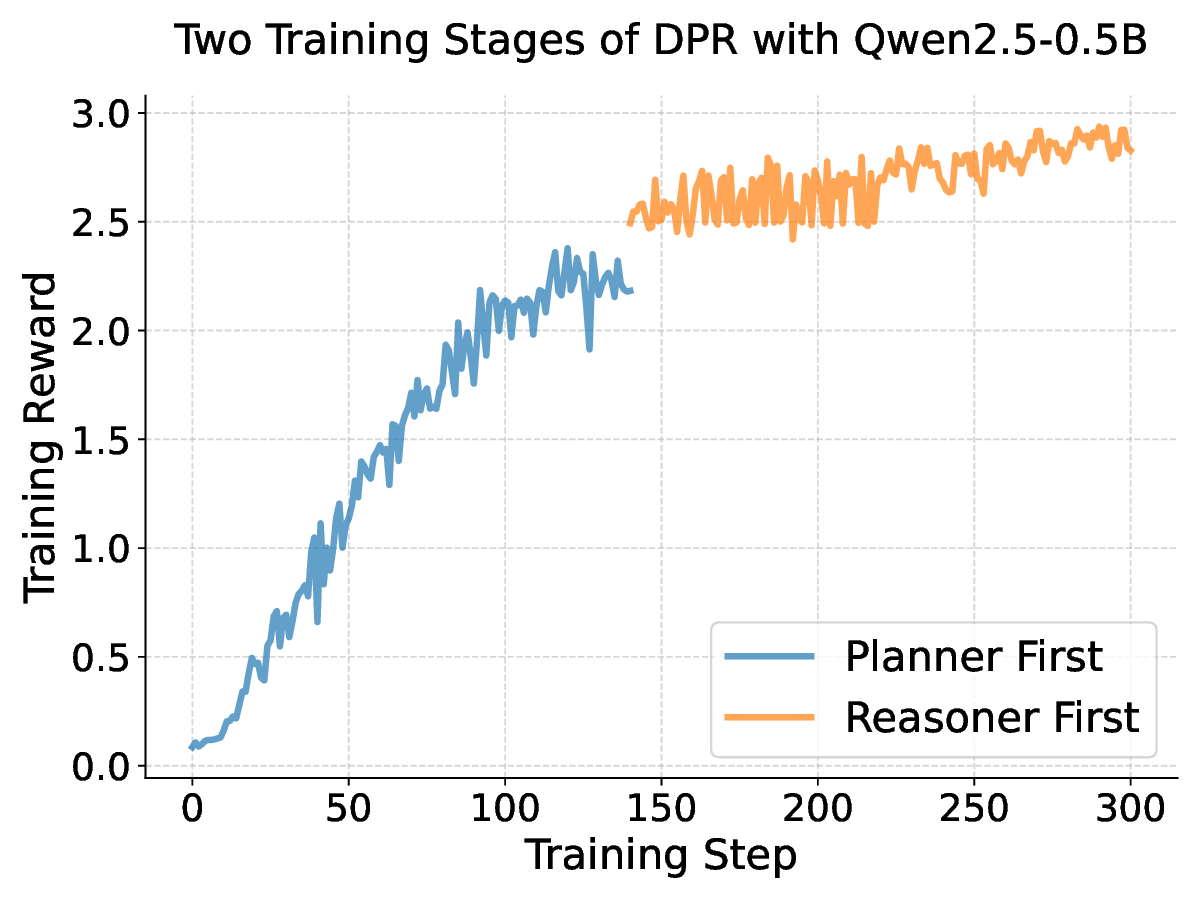
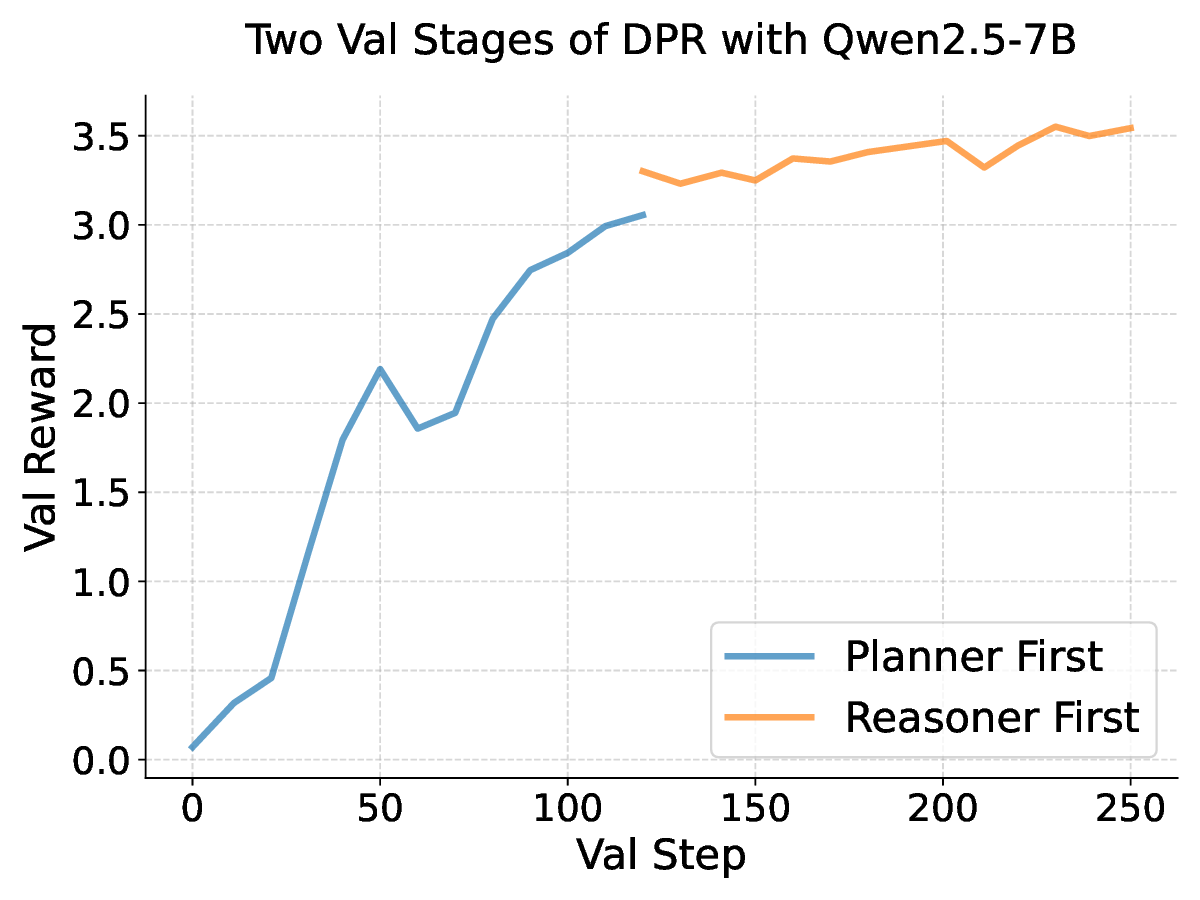
• Training the planner and LLM jointly as two agents under multi-agent RL (MARL) with the leader-follower algorithm (Gerstgrasser and Parkes, 2023) reinforces the planner’s ability to inject strategies.
• Planners are pluggable, meaning that a planner trained on one task can be directly integrated with arXiv:2512.08300v1 [cs.AI] 9 Dec 2025
another LLM to enhance its reasoning ability on similar tasks.
• Planners support continual learning, as a planner in our rSIM can be continuously trained across tasks to enhance its planning ability over a broader range of problems.
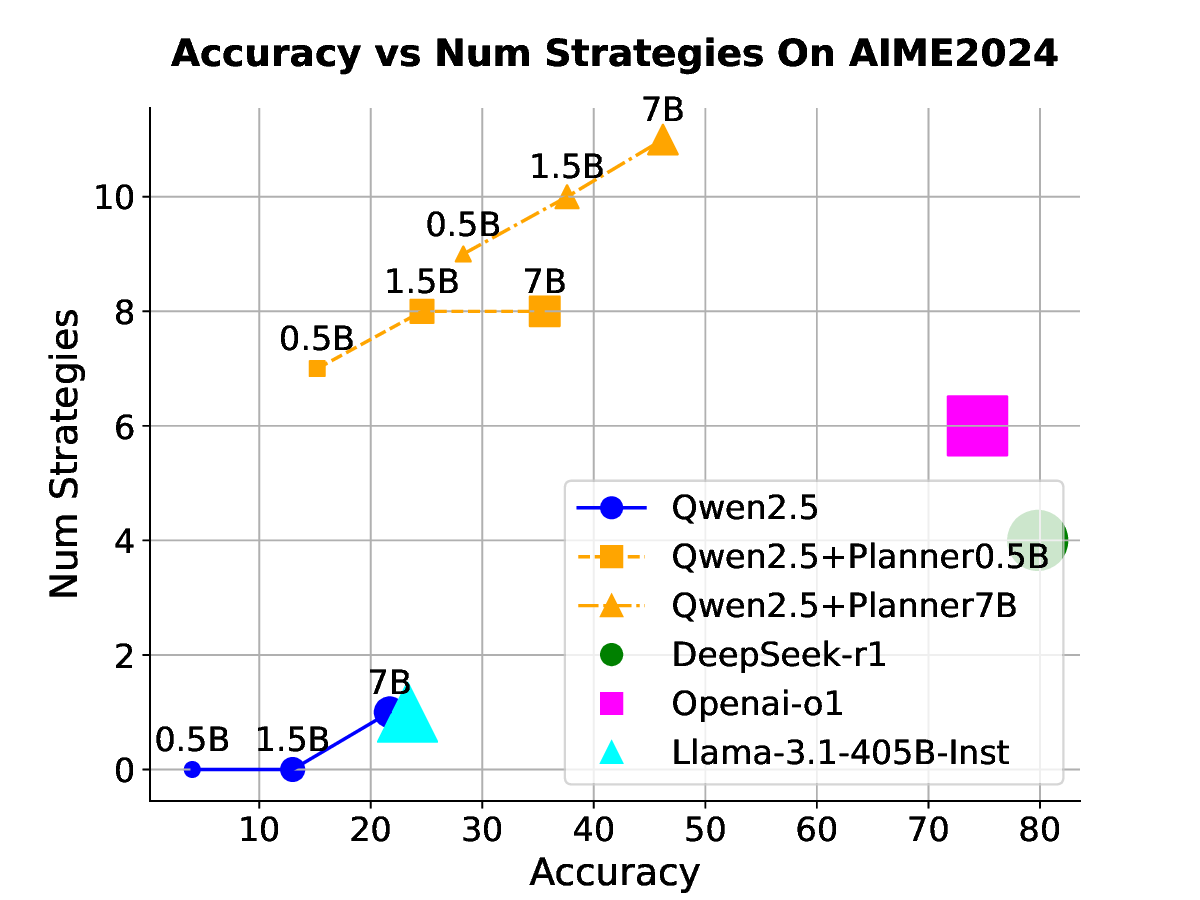
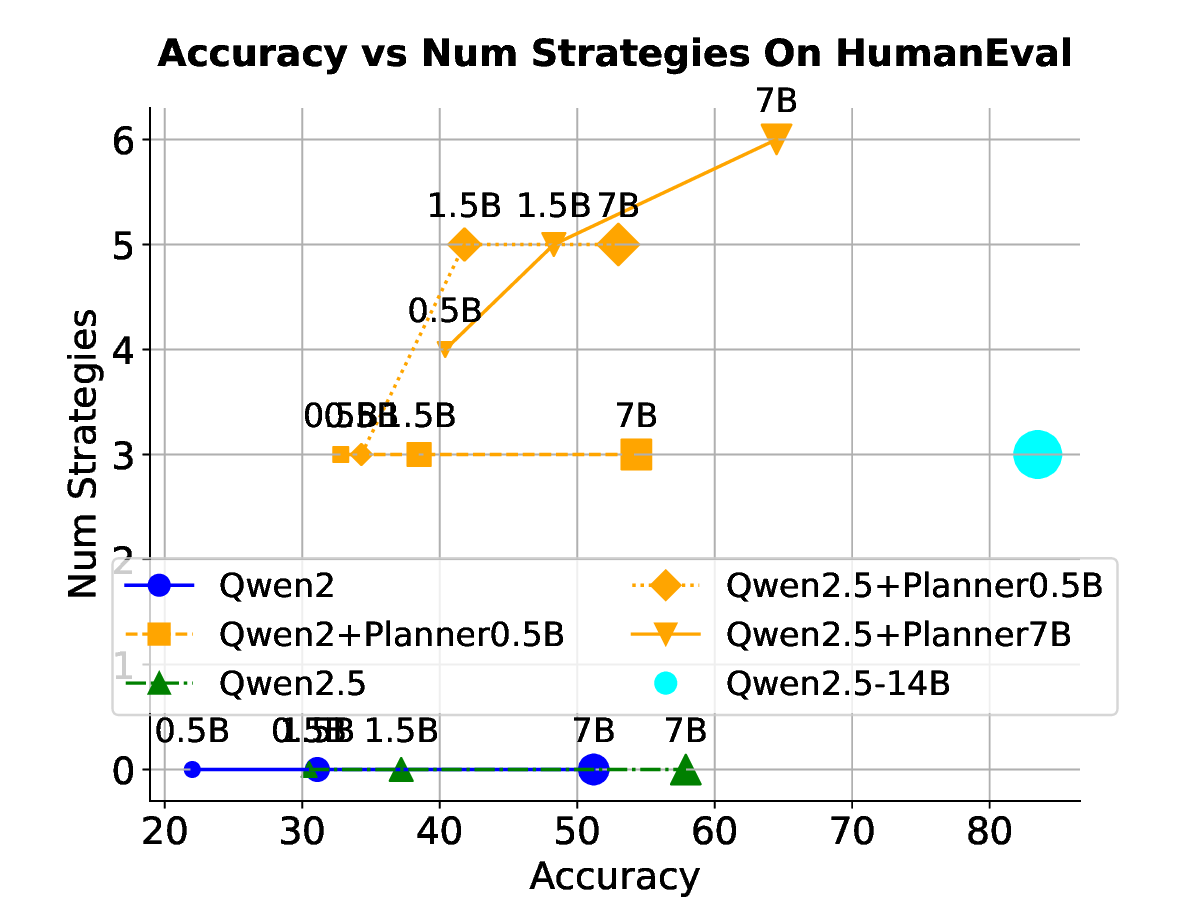
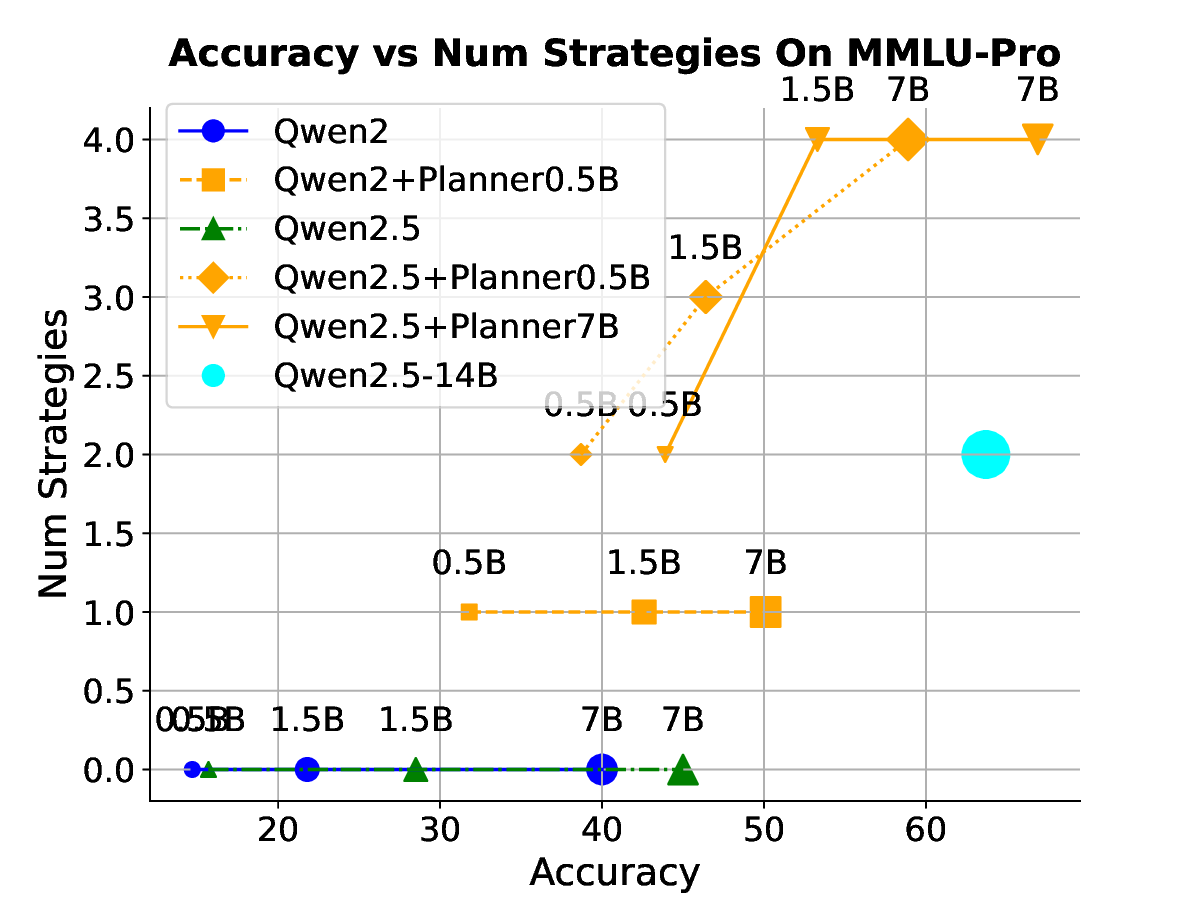
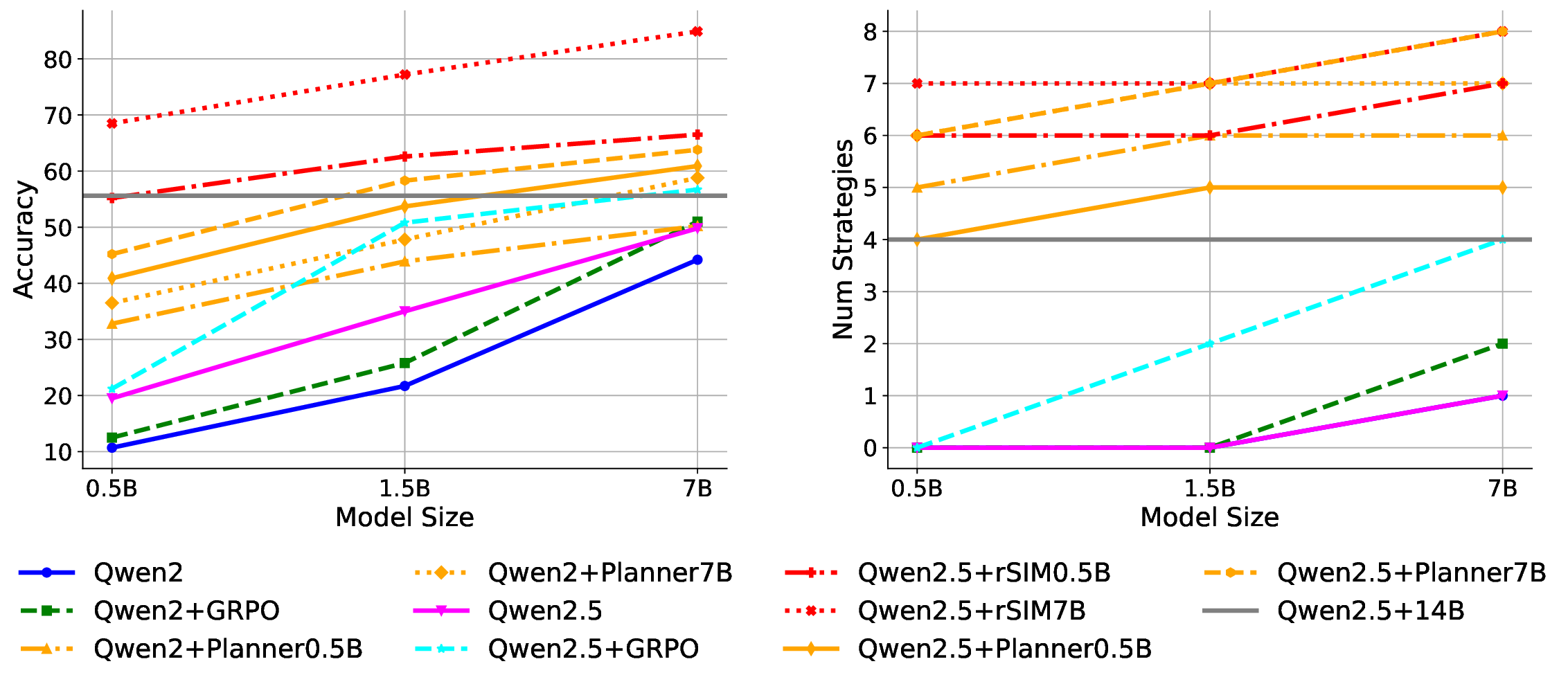
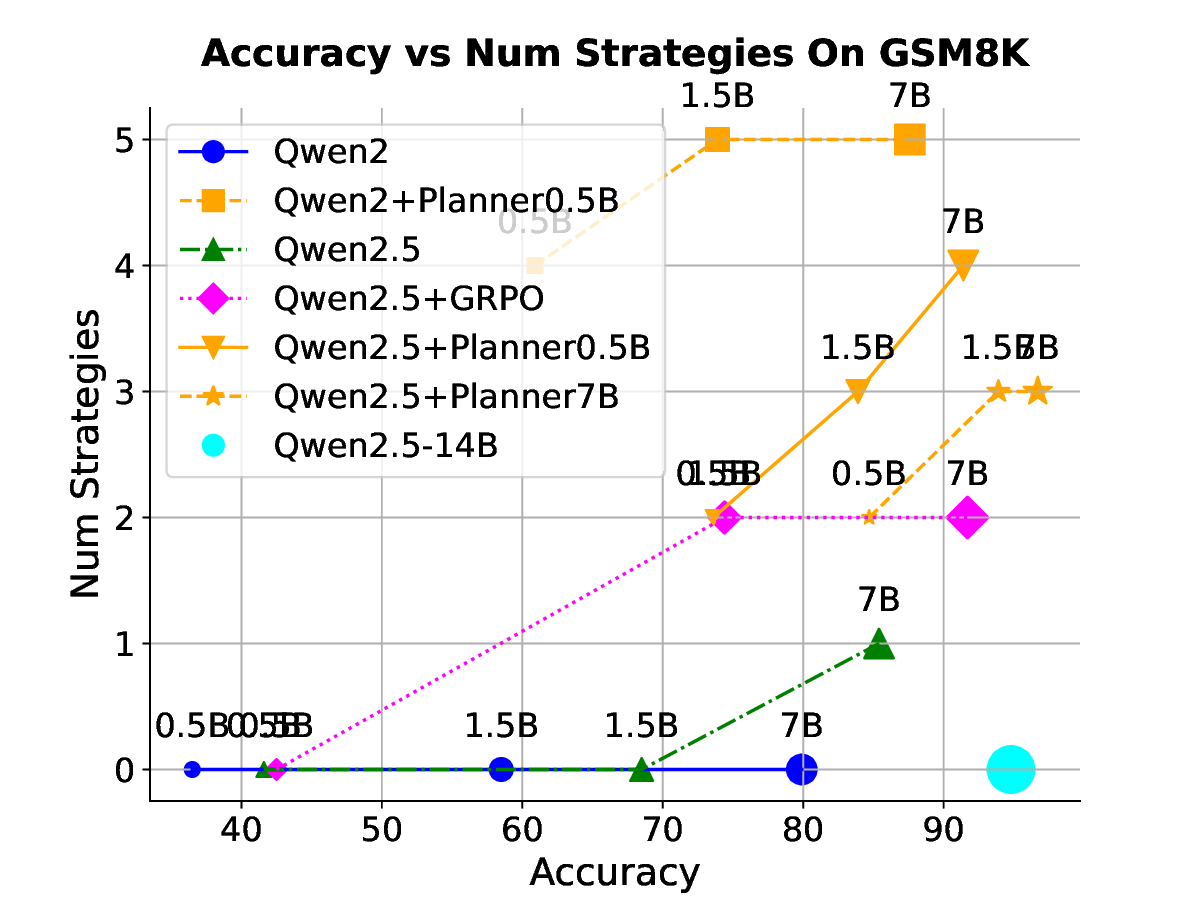
Our results across seven datasets covering mathematics, multi-task reasoning, and code generation verify the benefits of rSIM. First, even small LLMs such as Qwen2.5-0.5B, when jointly trained with a planner (Qwen2.5-0.5B), can evolve into an RLM, achieving accuracy on par with Qwen2.5-14B on MATH (Hendrycks et al., 2021). Second, using the trained planner as a plugin enables another LLM to outperform larger models by a significant margin without any additional training. Third, a planner trained on mathematics can be continuously finetuned on coding tasks such as CodeAlpaca-20k (Chaudhary, 2023) to further guide an LLM like Qwen2.5-0.5B, achieving 17% higher accuracy on code generation.
Data distillation. Knowledge distilled from large language models (LLMs) can be transferred to smaller models to enhance their performance (Xu et al., 2024). In particular, (Guo et al., 2025) verifies that larger LLMs can transfer their step-by-step reasoning abilities to smaller models by distilling chain-of-thought (CoT) (Wei et al., 2022) samples, where LLM-generated reasoning traces serve as additional fine-tuning data. Fine-tuning with teachergenerated CoT outputs (Magister et al., 2022;Yu et al., 2024;Dai et al., 2024), rationalizations (Li et al., 2023a), specialized reasoning skills (Liao et al., 2025), CoT and Program of Thought (PoT) (Chenglin et al., 2024), or even incorrect CoT samples (Huang et al., 2022;Hosseini et al., 2024) can significantly improve the reasoning abilities of smaller models. In this paper, using the planner from our DPR framework as a plugin to improve the reasoning of smaller models can be viewed as transferring a human-level planning chain to them.
Reinforcement learning. Reinforcement learning (RL) (Thrun and Littman, 2000) has been widely applied to decision-making tasks, as demonstrated by AlphaGo (Silver et al., 2016) and Alp-haZero (Silver et al., 2017). RLHF (Ouyang et al., 2022) first leveraged PPO (Schulman et al., 2017) to align models with human preferences. ReFT (Trung et al., 2024) pioneered the use of RL as a fine-tuning paradigm to enhance LLM reasoning performance. Building on this progress, DeepSeek-R1-Zero (Guo et al., 2025) made a breakthrough by demonstrating that self-verification, reflection, and the ability to generate long CoTs in LLMs can be incentivized purely through
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.