DeepFake face swapping enables highly realistic identity forgeries, posing serious privacy and security risks. A common defence embeds invisible perturbations into images, but these are fragile and often destroyed by basic transformations such as compression or resizing. In this paper, we first conduct a systematic analysis of 30 transformations across six categories and show that protection robustness is highly sensitive to the choice of training transformations, making the standard Expectation over Transformation (EOT) with uniform sampling fundamentally suboptimal. Motivated by this, we propose Expectation Over Learned distribution of Transformation (EOLT), the framework to treat transformation distribution as a learnable component rather than a fixed design choice. Specifically, EOLT employs a policy network that learns to automatically prioritize critical transformations and adaptively generate instance-specific perturbations via reinforcement learning, enabling explicit modeling of defensive bottlenecks while maintaining broad transferability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves substantial improvements over state-of-the-art approaches, with 26% higher average robustness and up to 30% gains on challenging transformation categories.
DeepFake [12,16,20,29,37]-synthetic media created using advanced generative models-have rapidly advanced in both realism and accessibility, enabling seamless manipulation of visual and auditory content. Among various forms The protective perturbation generated by the naive PGD algorithm [28] loses its effectiveness after the perturbed image undergoes box blur transformation, whereas our method maintains its protective effect and continues to disrupt the face-swapping output. Note that naive PGD achieves a similar protective effect as ours when no transformation is applied.
of DeepFake, face swapping [5,6,19] is one of the most widespread and impactful, allowing a person’s facial identity to be replaced with another’s while maintaining expressions, pose, and scene context. While this technology has enabled creative applications in entertainment and data augmentation, it also raises serious ethical and security concerns, such as identity theft, misinformation, and the erosion of digital trust.
To mitigate these threats, researchers have explored two main defense paradigms: passive and proactive defenses. Passive defenses [4,26,26,30,33,35,36] aim to detect forged content after creation by identifying spatial, temporal, or frequency inconsistencies, but they often struggle with generalization and are vulnerable to unseen manipulation methods. In contrast, proactive defenses [1,15,32,40] act preemptively by embedding protective perturbations into original images to prevent malicious manipulation. This approach is related to the longstanding challenge of adversarial examples in deep neural networks [13,21,28], though with a different attack objective. A key limitation of passive defenses is that, in most cases, the harm has already occurred by the time manipulated images are detected. In comparison, protective perturbations secure the content at its source, helping to prevent negative consequences from arising.
However, existing proactive defenses face a severe limitation: their effectiveness often degrades under input transformations [11,25,31] such as compression, resizing, and color adjustment, which naturally occur during real-world data sharing or may be intentionally applied by malicious actors as countermeasures. Despite its importance for realworld deployment, this issue has been largely underexplored, and the community’s understanding remains limited. So far, the most effective approach to improving the robustness of protective perturbations is Expectation Over Transformation (EOT) [2], which integrates a uniform distribution of transformations and aggregates perturbations generated from randomly sampled transformations.
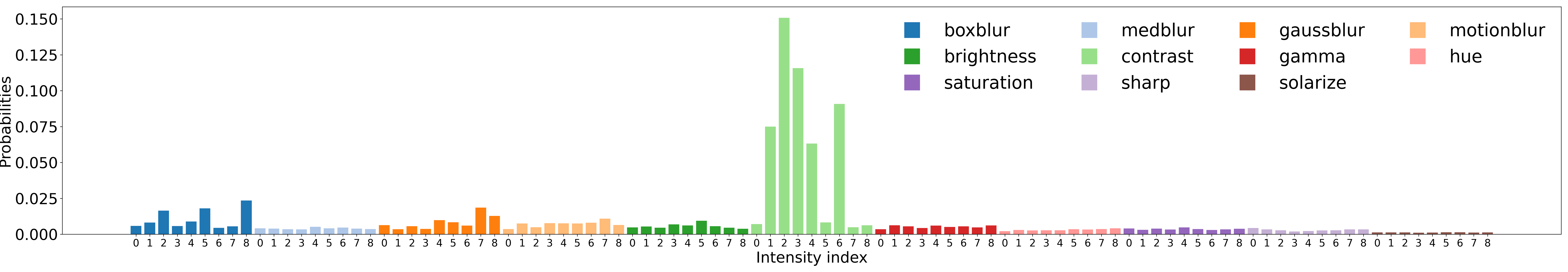
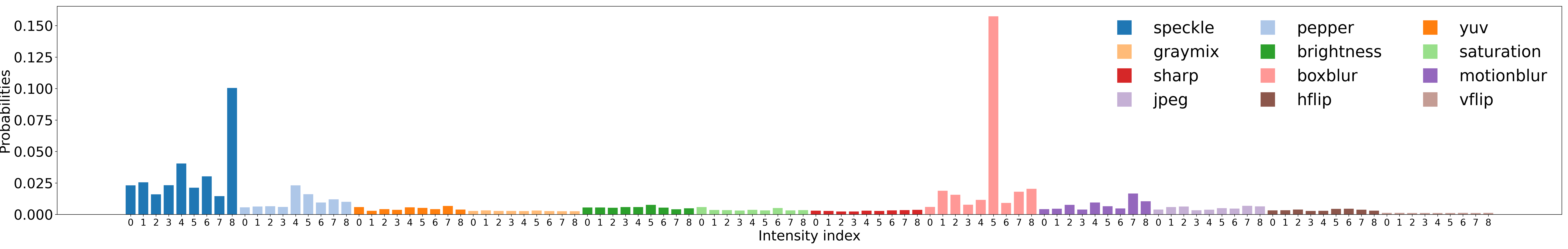
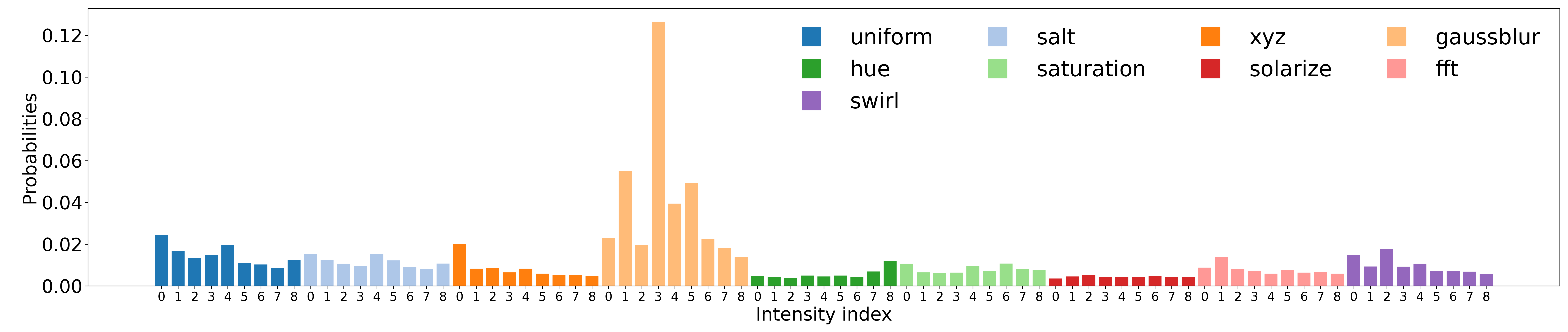
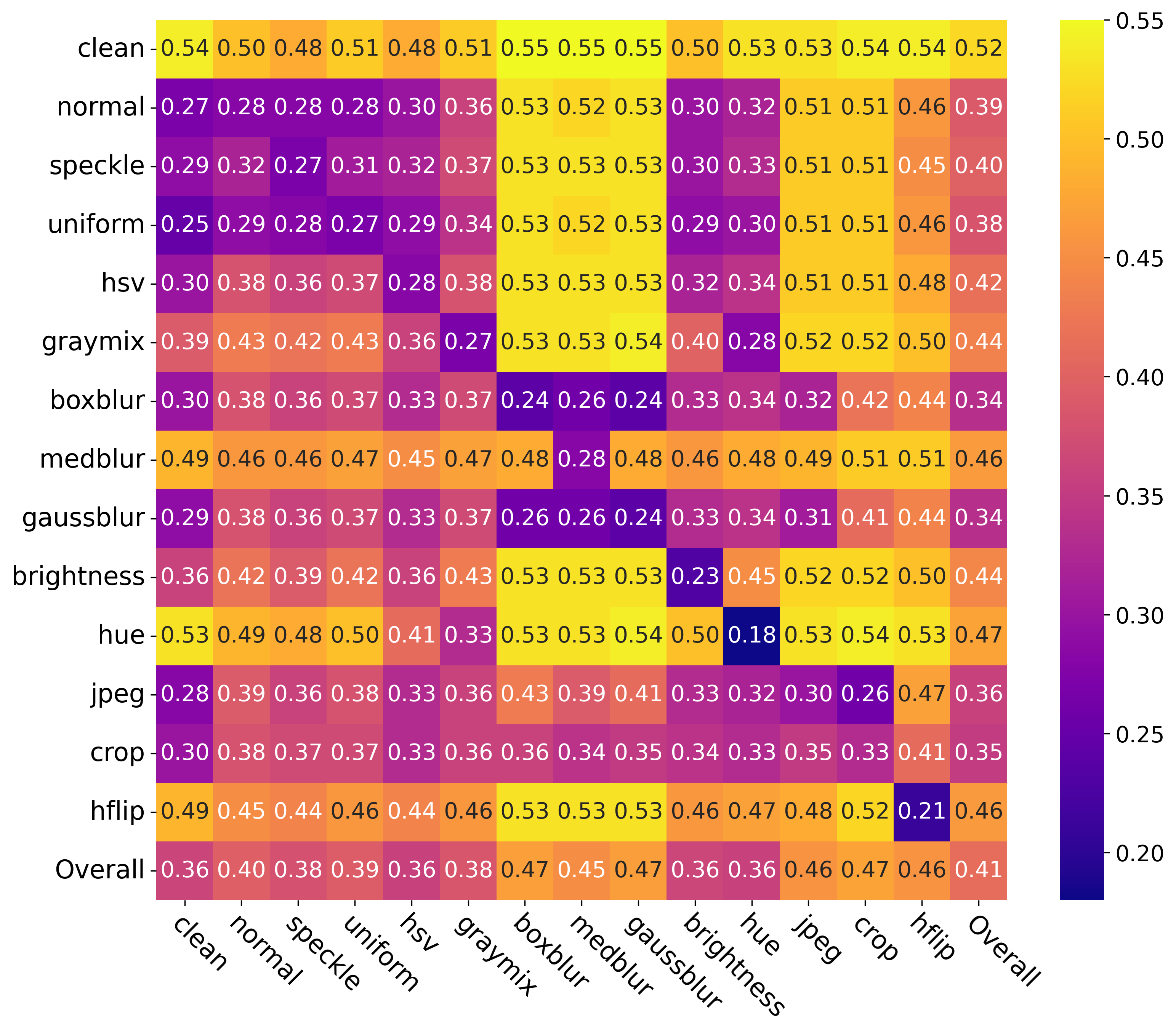
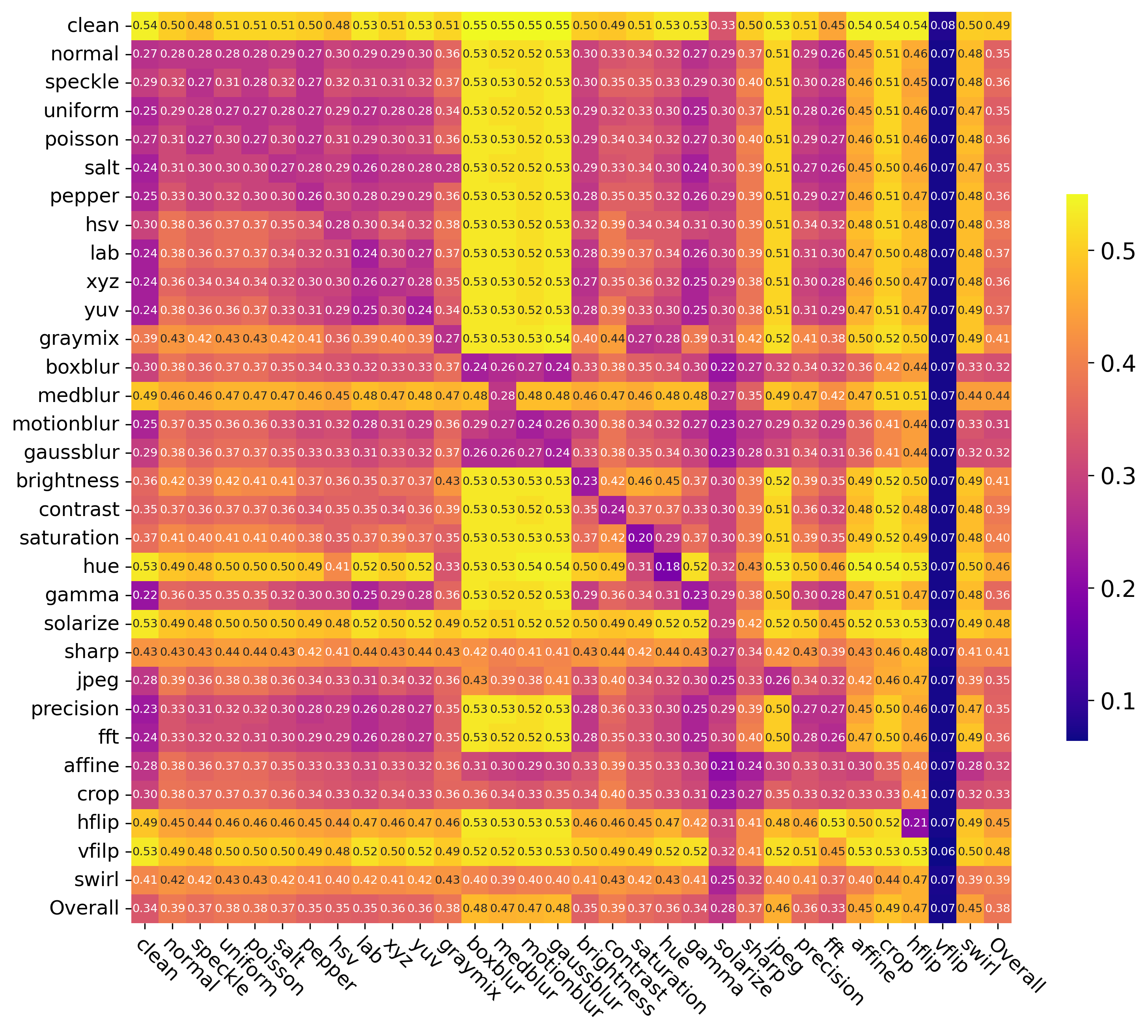
In this work, we take a step toward addressing this limitation by conducting the first comprehensive investigation into the generalization of protective perturbations across 30 transformations. Our analysis reveals two critical findings:
(1) Transformations vary widely in generalization. Some produce perturbations that transfer robustly across different categories of transformation, while others lead to severe overfitting or even reduce overall effectiveness. (2) Certain transformations act as defensive bottlenecks. Some cannot be adequately defended against through transfer from other transformation types and must be explicitly included during perturbation generation. These findings expose a fundamental flaw in the uniform random sampling approach used in EOT: it treats all transformations equally, overlooking their highly variable impact on robustness and failing to prioritize critical defensive bottlenecks.
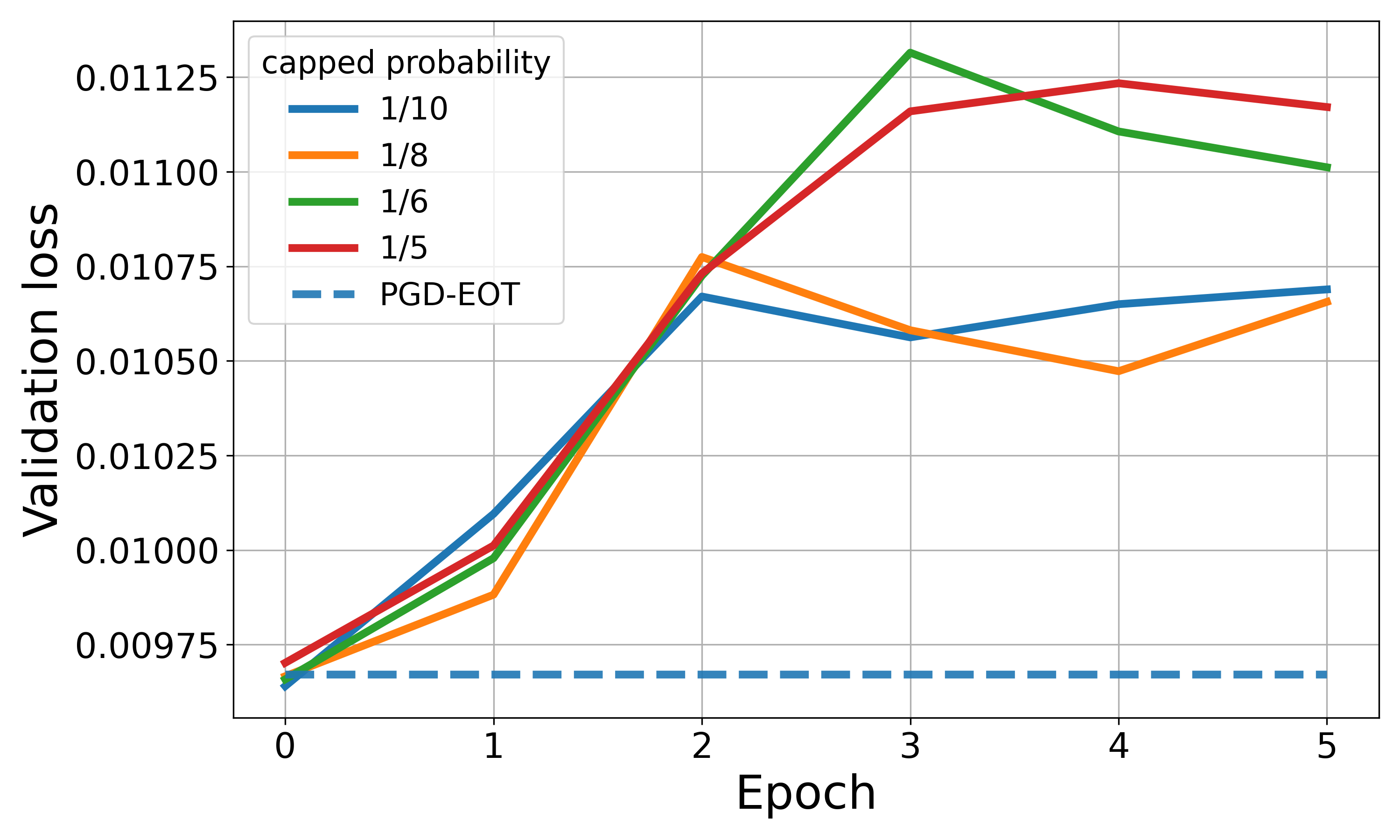
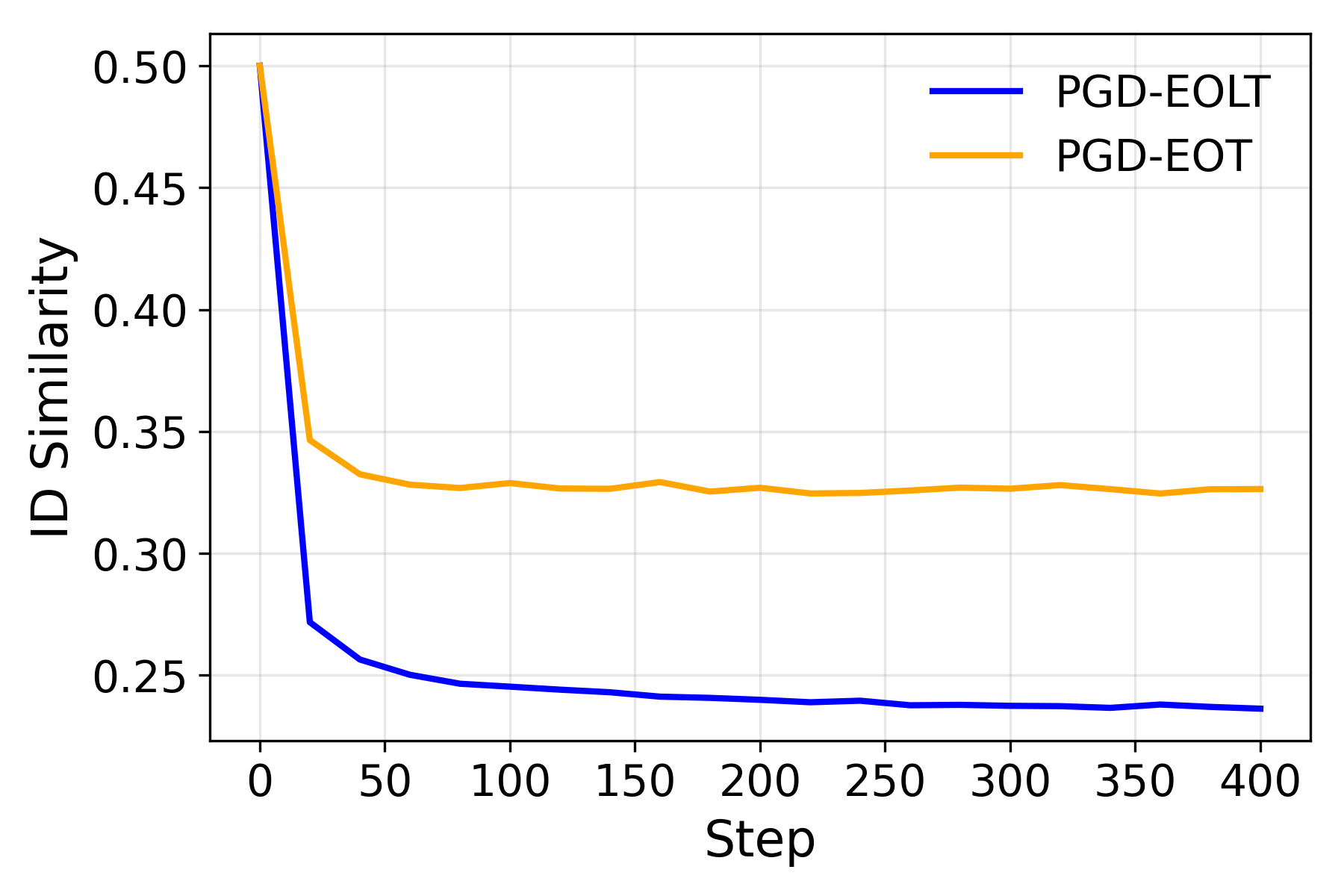
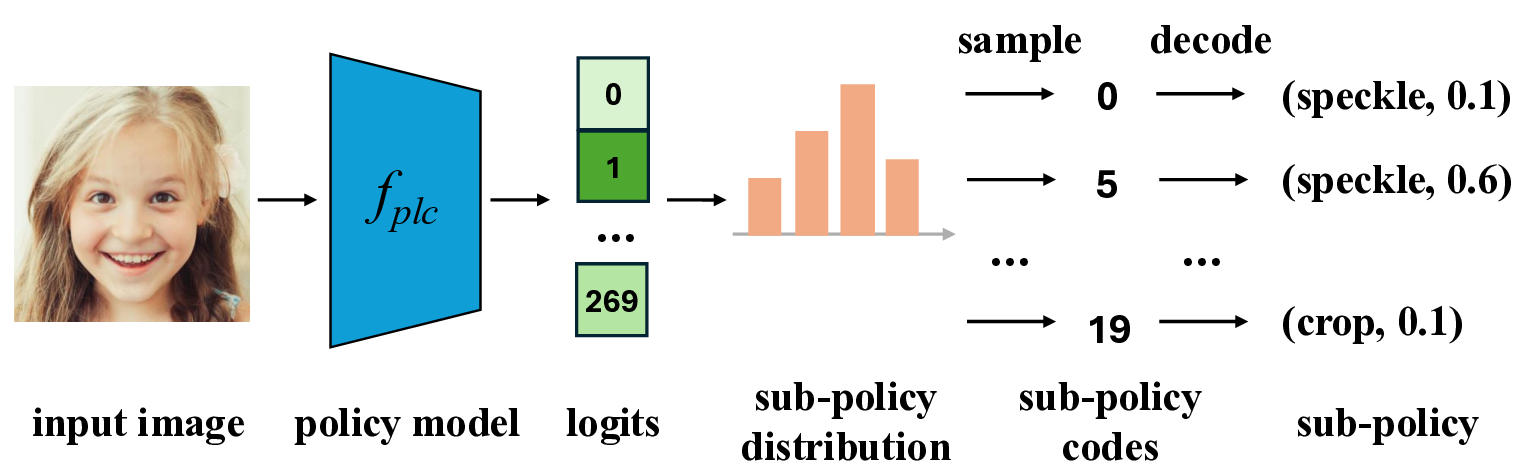
Motivated by the above insights, we propose a new approach, named Expectation Over Learned distribution of Transformation (EOLT), to enhance the robustness of protective perturbations. EOLT replaces the uniform prior over transformations in EOT with an optimized transformation distribution. This distribution is modeled by a deep neural network, referred to as the policy model, and is optimized by learning the policy model parameters to maximize the robustness of protective perturbations generated using sampled transformations against a target set of transformations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves substantial improvements over state-of-the-art approaches, with 26% higher average robustness and up to 30% gains on challenging transformation categories.
Overall, our contributions are twofold: • We present a comprehensive analysis of proactive defense robustness under 30 common input transformations, systematically examining their cross-transformation generalization behaviors. This analysis reveals several practical insights into how different transformations interact and impact protection effectiveness. • We propose a novel method for generating robust protective perturbations against DeepFake face swapping.
Our approach achieves state-of-the-art robustness across a wide range of input transformations, supporting the practical deployment of proactiv
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.