Pretrained Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across diverse domains, with education and research emerging as particularly impactful areas. Among current state-of-the-art LLMs, ChatGPT and DeepSeek exhibit strong capabilities in mathematics, science, medicine, literature, and programming. In this study, we present a comprehensive evaluation of these two LLMs through background technology analysis, empirical experiments, and a real-world user survey. The evaluation explores trade-offs among model accuracy, computational efficiency, and user experience in educational and research affairs. We benchmarked these LLMs performance in text generation, programming, and specialized problem-solving. Experimental results show that ChatGPT excels in general language understanding and text generation, while DeepSeek demonstrates superior performance in programming tasks due to its efficiency-focused design. Moreover, both models deliver medically accurate diagnostic outputs and effectively solve complex mathematical problems. Complementing these quantitative findings, a survey of students, educators, and researchers highlights the practical benefits and limitations of these models, offering deeper insights into their role in advancing education and research.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has rapidly evolved into one of the most influential areas of artificial intelligence (AI), driving progress in applications such as speech recognition, named entity recognition, machine translation, question answering, text summarization, and program code generation. Early advances were shaped by recurrent neural networks (RNNs), whose sequential arXiv:2512.08057v1 [cs.AI] 8 Dec 2025 structure enabled them to capture dependencies across tokens. Variants such as long short-term memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent units (GRU) [24] alleviated the vanishing gradient problem and improved context modeling. Nevertheless, RNN-based architectures struggled to scale to extremely long-range dependencies [25], leading to inefficiencies in training and difficulty in modeling global semantic relationships. The emergence of the Transformer [21] architecture marked a paradigm shift in NLP by overcoming the fundamental limitations of RNNs. Transformers utilize a self-attention mechanism that enables efficient modeling of dependencies across all tokens in a sequence, regardless of their positional distance [31]. This breakthrough became the foundation of modern large language models (LLMs), enabling unprecedented fluency and contextual reasoning in text generation.
The development of ChatGPT by OpenAI, launched in 2022, marks a significant milestone in the evolution of LLMs. Initially based on the GPT-3 architecture and later enhanced with GPT-4, ChatGPT employs a combination of supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) [23]. This training approach was developed to address the unpredictable and undesirable outputs common in earlier models, including responses that lacked coherence, contained harmful or biased language, or presented inaccurate information [11]. By integrating human feedback into its learning process, ChatGPT effectively improved the safety, reliability, and contextual coherence of its responses. Since its release, ChatGPT has become a widely adopted conversational AI capable of generating fluent, human-like dialogue across an extensive range of topics and applications.
In contrast, DeepSeek emerges in the NLP domain with a specific emphasis on knowledge retrieval, semantic search, and structured question answering. Initially introduced as an effort to design efficient yet powerful Transformer-based models and employs a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture that dynamically activates specialized sub-models for different tasks, reducing redundant computations and improving scalability [20]. This design not only lowers the hardware requirements compared to conventional large-scale models but also enhances efficiency in training and inference. DeepSeek focuses on precise and context-aware information retrieval and is well-suited for domain-specific applications that require accuracy and efficient access to relevant data [22]. Furthermore, DeepSeek leverages advanced techniques such as reinforcement learning to automate and refine human feedback and achieves competitive performance on complex reasoning and mathematical tasks while keeping computational costs significantly lower than those of larger generalist models.
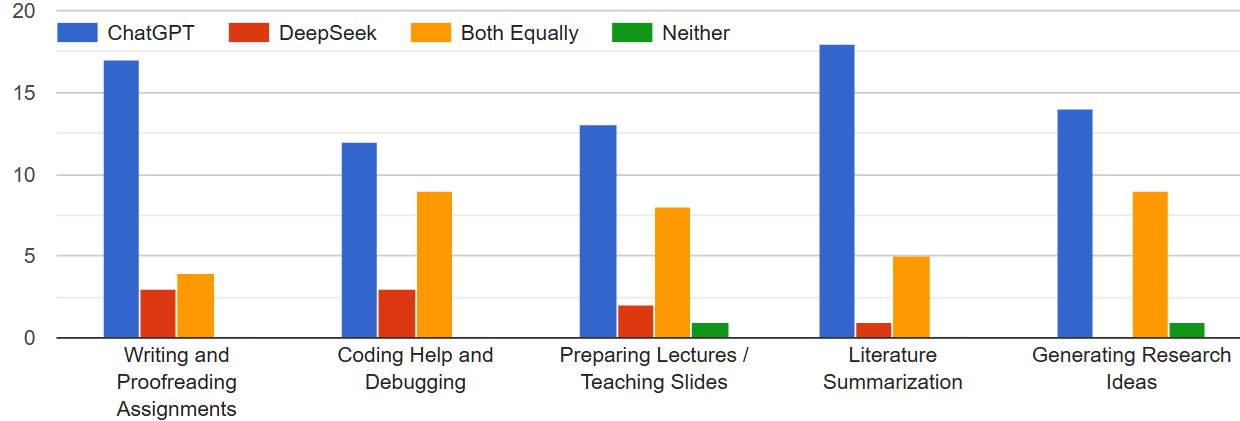
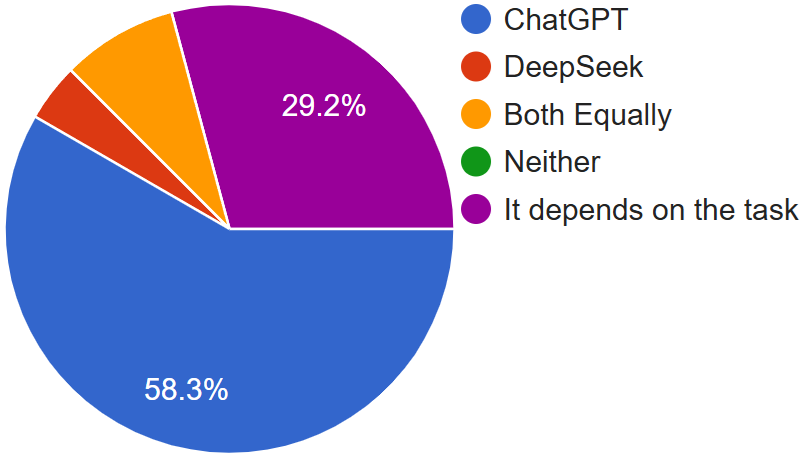
Although both ChatGPT and DeepSeek are based on Transformer architectures, they are optimized for different objectives. ChatGPT excels in conversational text generation, enabling applications such as creative writing, code generation, tutoring, and interactive learning, while DeepSeek prioritizes highprecision knowledge access, making it valuable for research assistance, information retrieval, and technical question answering. Together, they complement each other: ChatGPT provides conversational adaptability, and DeepSeek en-sures factual accuracy, offering a combined toolkit for enhancing educational and research environments. Both models are increasingly applied in education and research. ChatGPT supports students and educators by generating lecture materials, presentations, and problem sets, while DeepSeek improves efficiency in literature reviews, structured knowledge extraction, and specialized query responses. These technologies highlight both opportunities, including accessibility, personalization, and efficiency, and risks, such as misinformation, academic dishonesty, and over-reliance on AI.
To the best of our knowledge, no comprehensive study has systematically compared ChatGPT and DeepSeek across the dual dimensions of technical performance and user perception in education and research contexts. Existing evaluations largely focus on single-model case studies or narrowly defined application domains. This paper addresses that gap by presenting a comprehensive comparative analysis of ChatGPT and DeepSeek. We benchmark their effectiveness in programming education, research, and academic tasks; complement these results with a user survey of students, educators, and researchers; and provide a balanced discus
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.