Although persona prompting in large language models appears to trigger different styles of generated text, it is unclear whether these translate into measurable behavioral differences, much less whether they affect decision-making in an adversarial strategic environment that we provide as open-source. We investigate the impact of persona prompting on strategic performance in PERIL, a world-domination board game. Specifically, we compare the effectiveness of persona-derived heuristic strategies to those chosen manually. Our findings reveal that certain personas associated with strategic thinking improve game performance, but only when a mediator is used to translate personas into heuristic values. We introduce this mediator as a structured translation process, inspired by exploratory factor analysis, that maps LLM-generated inventory responses into heuristics. Results indicate our method enhances heuristic reliability and face validity compared to directly inferred heuristics, allowing us to better study the effect of persona types on decision making. These insights advance our understanding of how persona prompting influences LLM-based decision-making and propose a heuristic generation method that applies psychometric principles to LLMs.
"If you would read a [person's] Disposition, see him Game, you will then learn more of him in one hour, than in seven Years Conversation," according to a letter of advice written over 300 years ago (Lingard and Erb, 1907). If this advice is correct, perhaps nowhere is one's personality more apparent than in strategic adversarial games, where individual behavioral tendencies such as aggression, patience, caution, and others dictate the heuristics that guide players' decision-making. Such settings present a unique opportunity to study the relationship between how modern large language models (LLMs) relate personality descriptions (often called personas) and decision-making in strategic environments.
In this paper, we investigate whether personality traits inferred from prompts reliably translate into actionable heuristics in a strategy board game. Strategic reasoning is a critical capability for advancing AI in decision-making and humanmachine collaboration. Beyond gaming, the findings have broader implications for simulation, training, and the development of automated systems requiring strategic adaptability. Such work contributes to advancing AI’s role in team-based environments, military simulations, and other domains where human-like variability and strategic decisionmaking are essential.
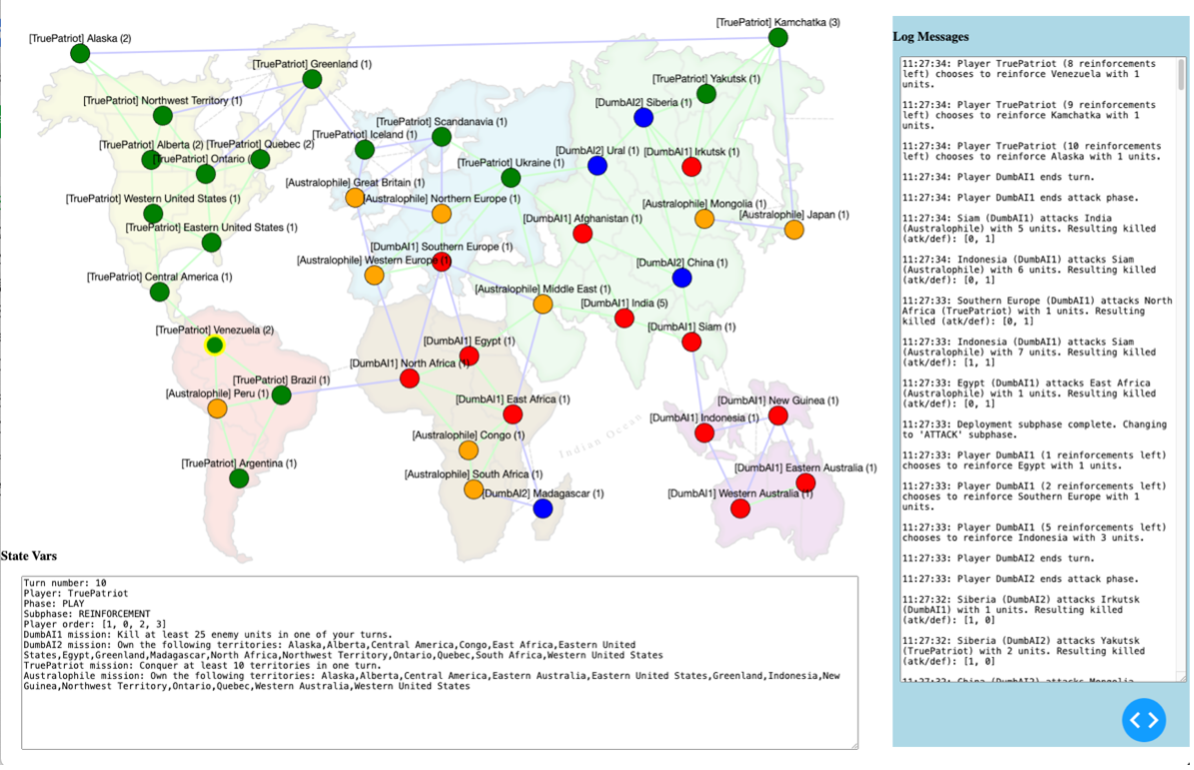
Isolating strategic reasoning ability is difficult, especially when that strategy must apply to an environment that has a large search space, nondeterministic outcomes, and high-pressure conditions that require rapid decision-making under time and computation constraints. In such environments, strategic actors may benefit from precommitment, or the fixing of rules and heuristics that will constrain one’s behavior ahead of time, so that cog-arXiv:2512.06867v1 [cs.AI] 7 Dec 2025 nitive overhead, behavioral inconsistencies, and the effect of time pressure on decisions will be minimized later. In this paper, we will focus on this aspect of strategic thinking by studying the performance of LLMs in a variant of a popular strategy board game. More specifically, we will study the effect of persona prompting, a prompting strategy in which a pre-trained LLM is prompted with a description of a personality and asked to act in accordance with it. We do this through a fixed set of heuristics tailored to the PERIL environment, which should be understood as design choices rather than a comprehensive taxonomy of player attributes. Despite its promise, the effect of persona prompting on tasks requiring strategic reasoning, particularly in dynamic and uncertain environments, remains underexplored.
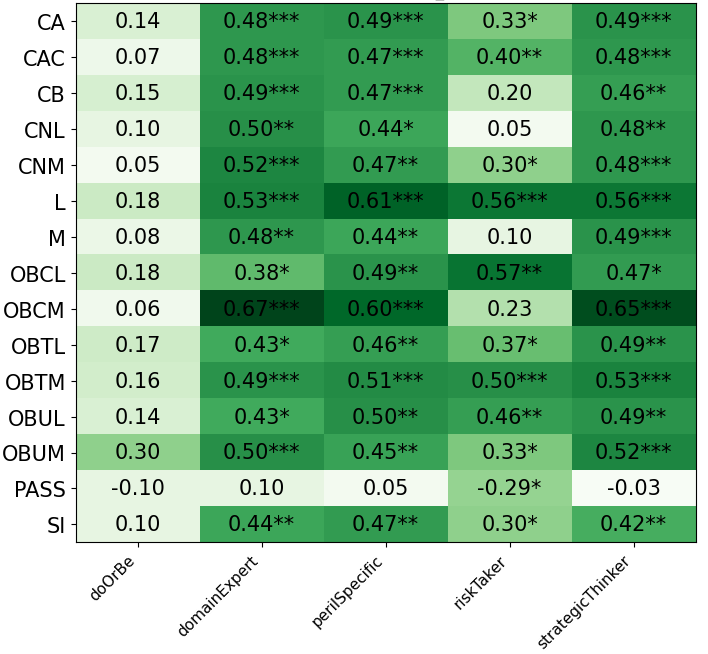
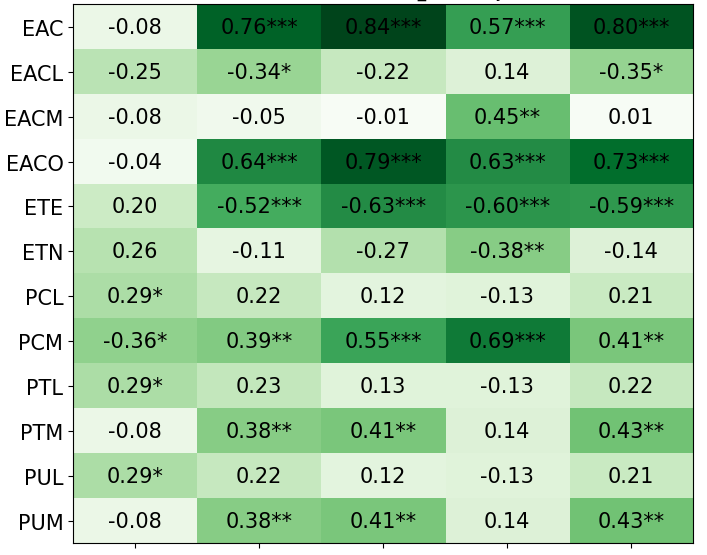
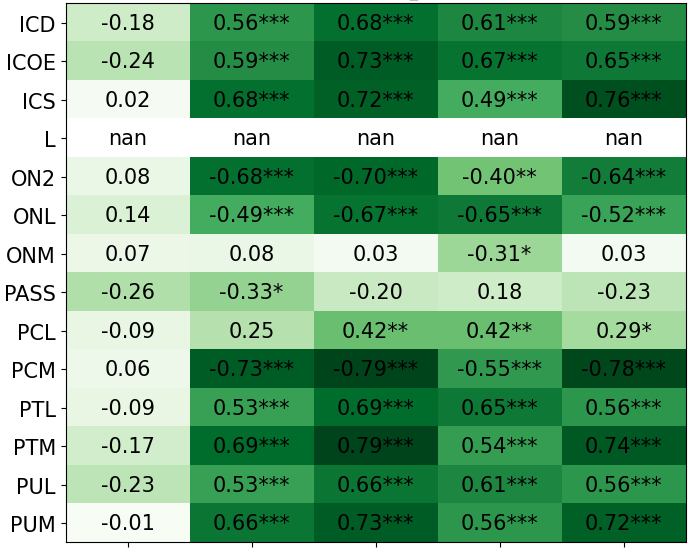
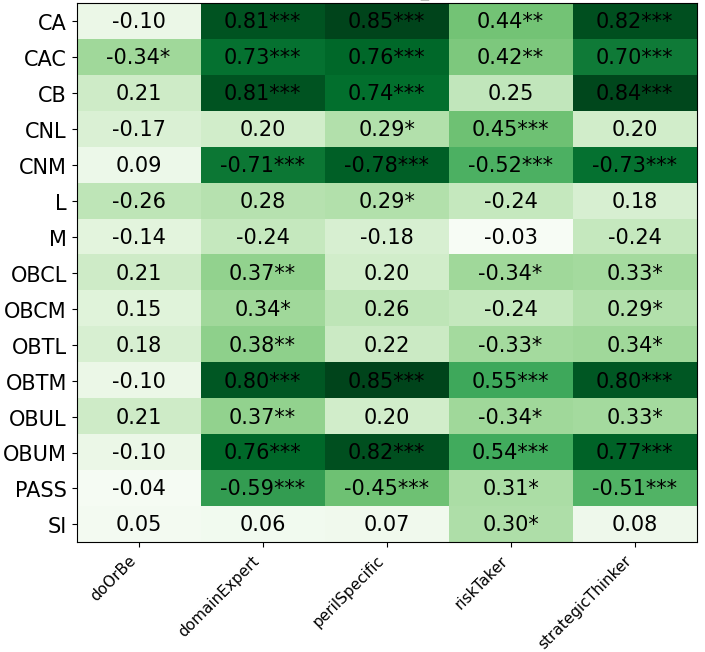
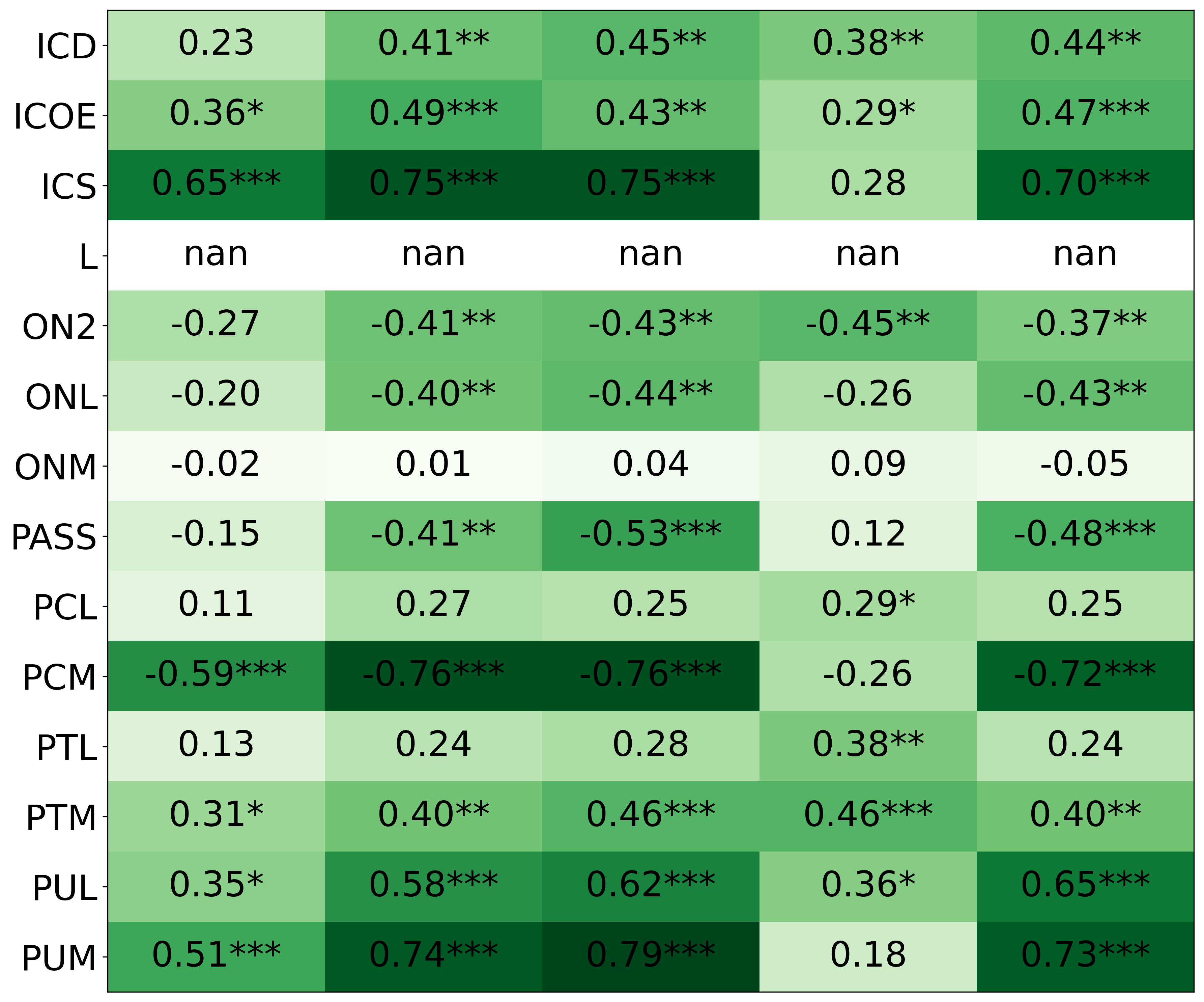
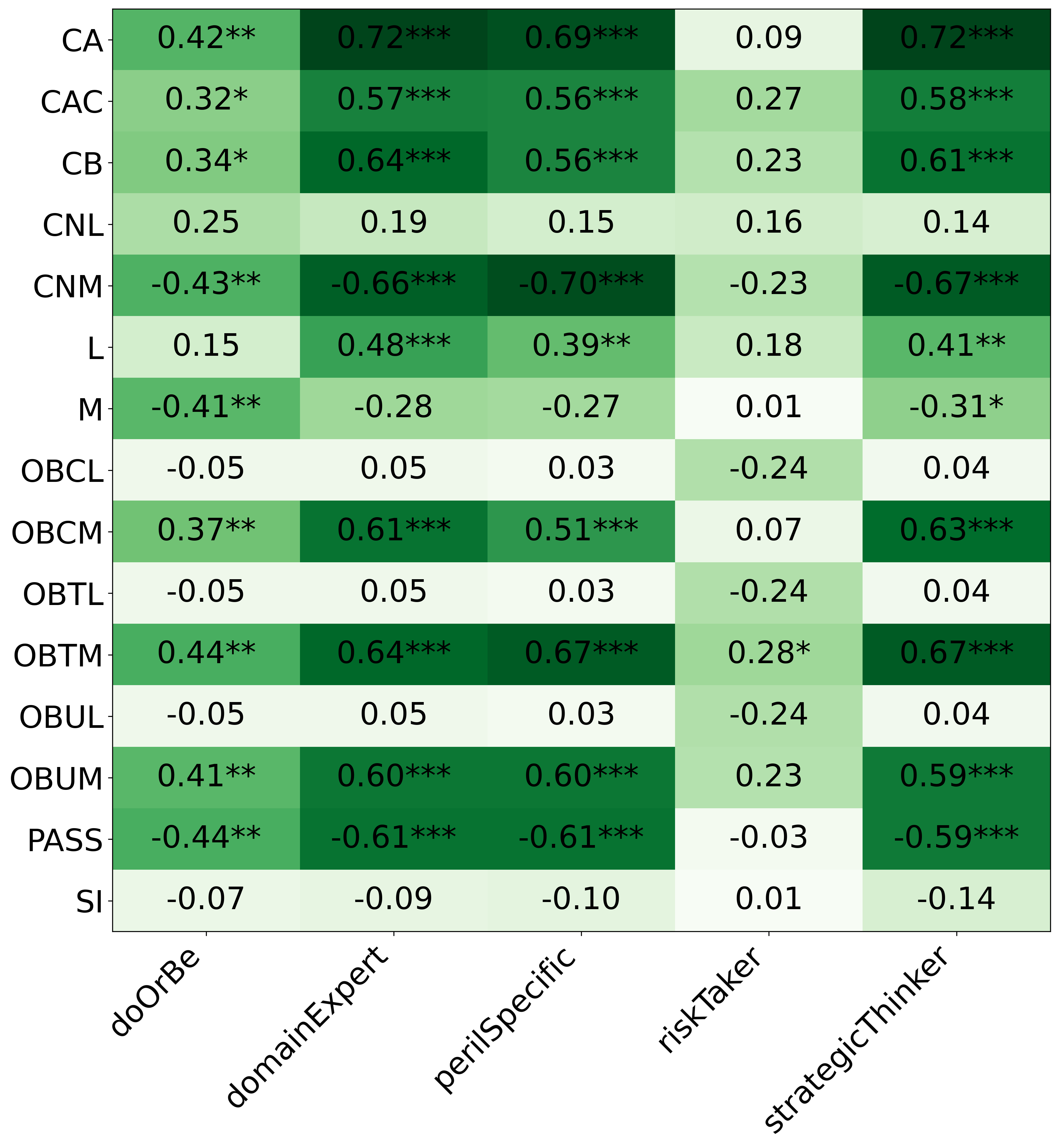
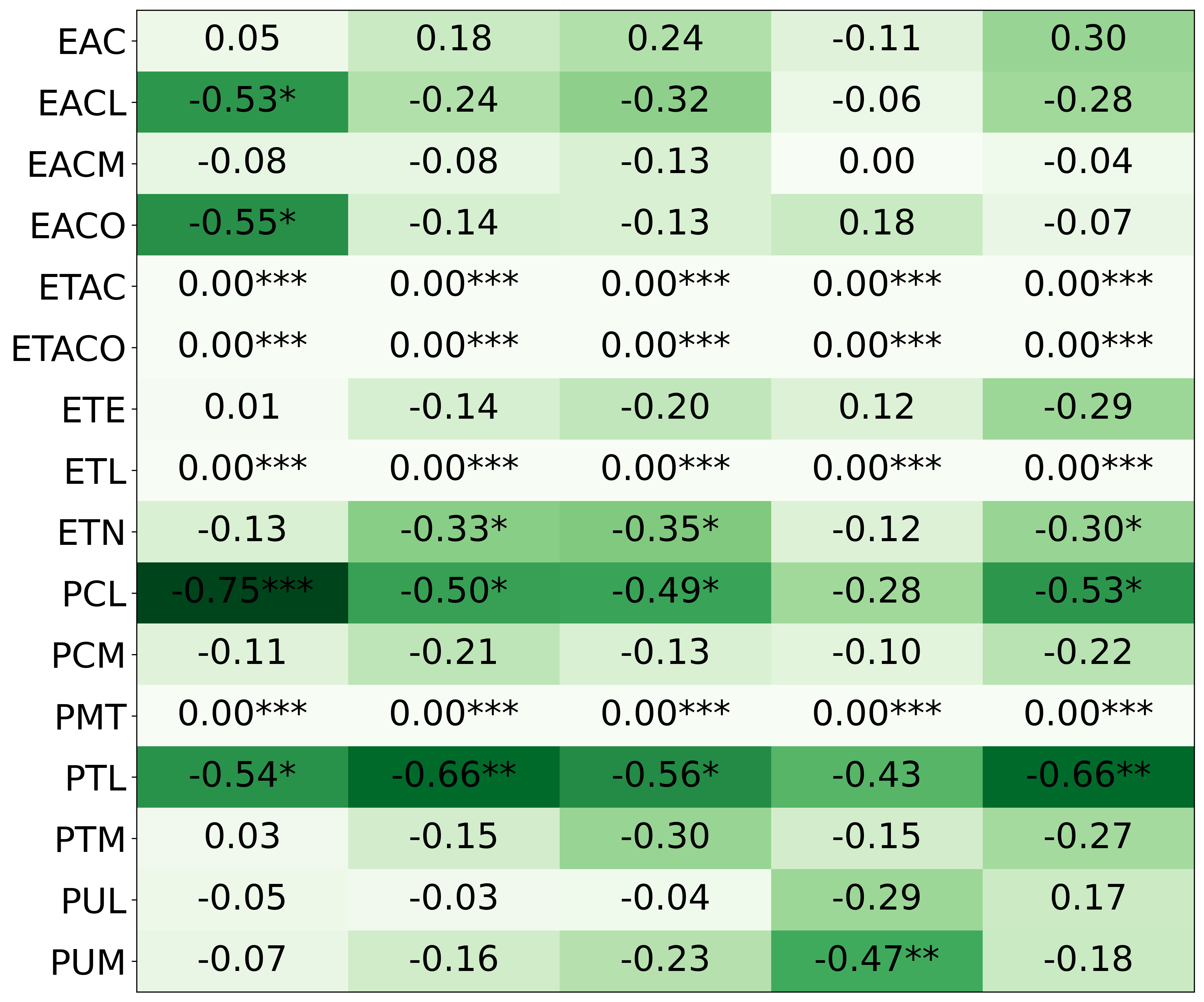
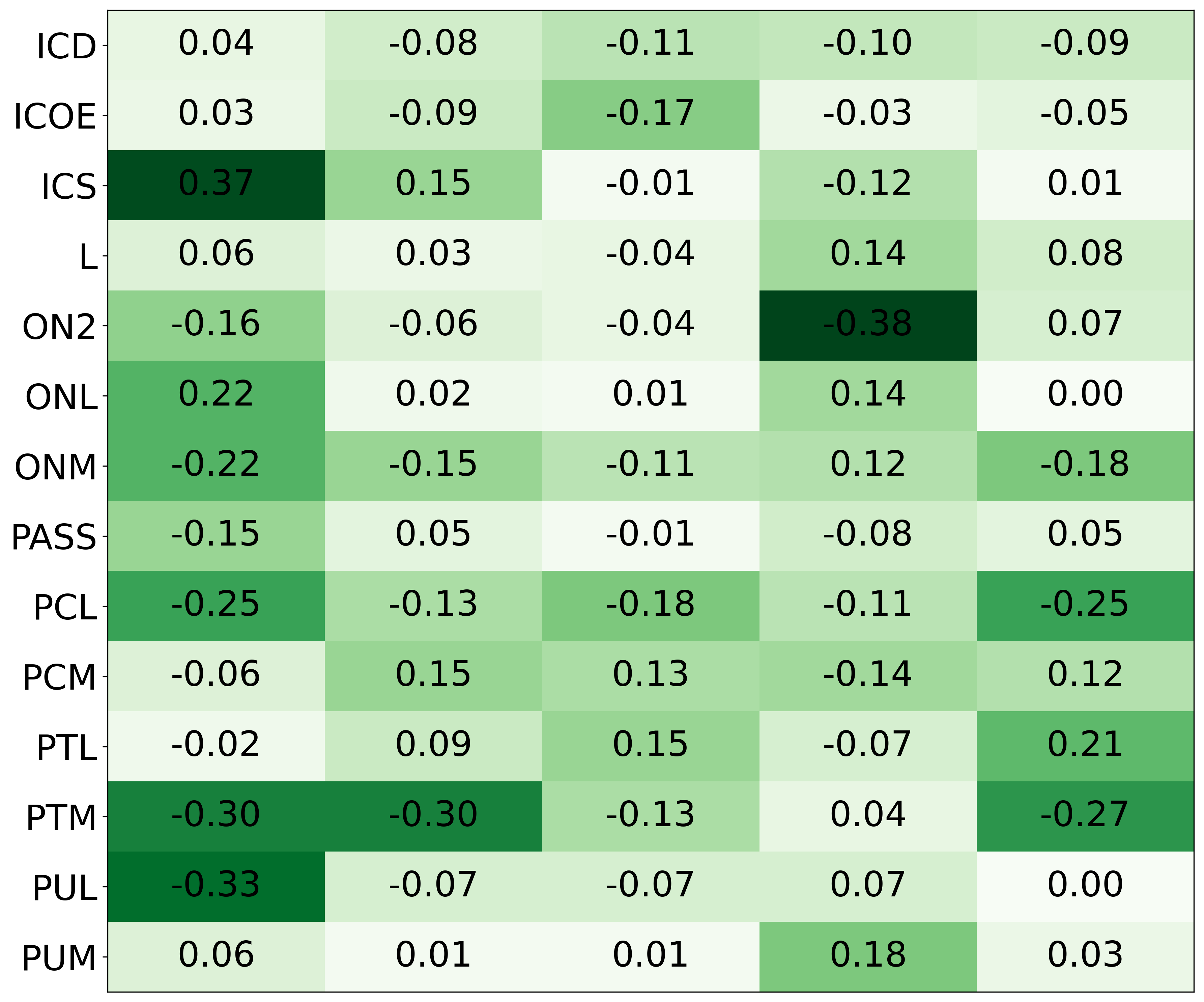
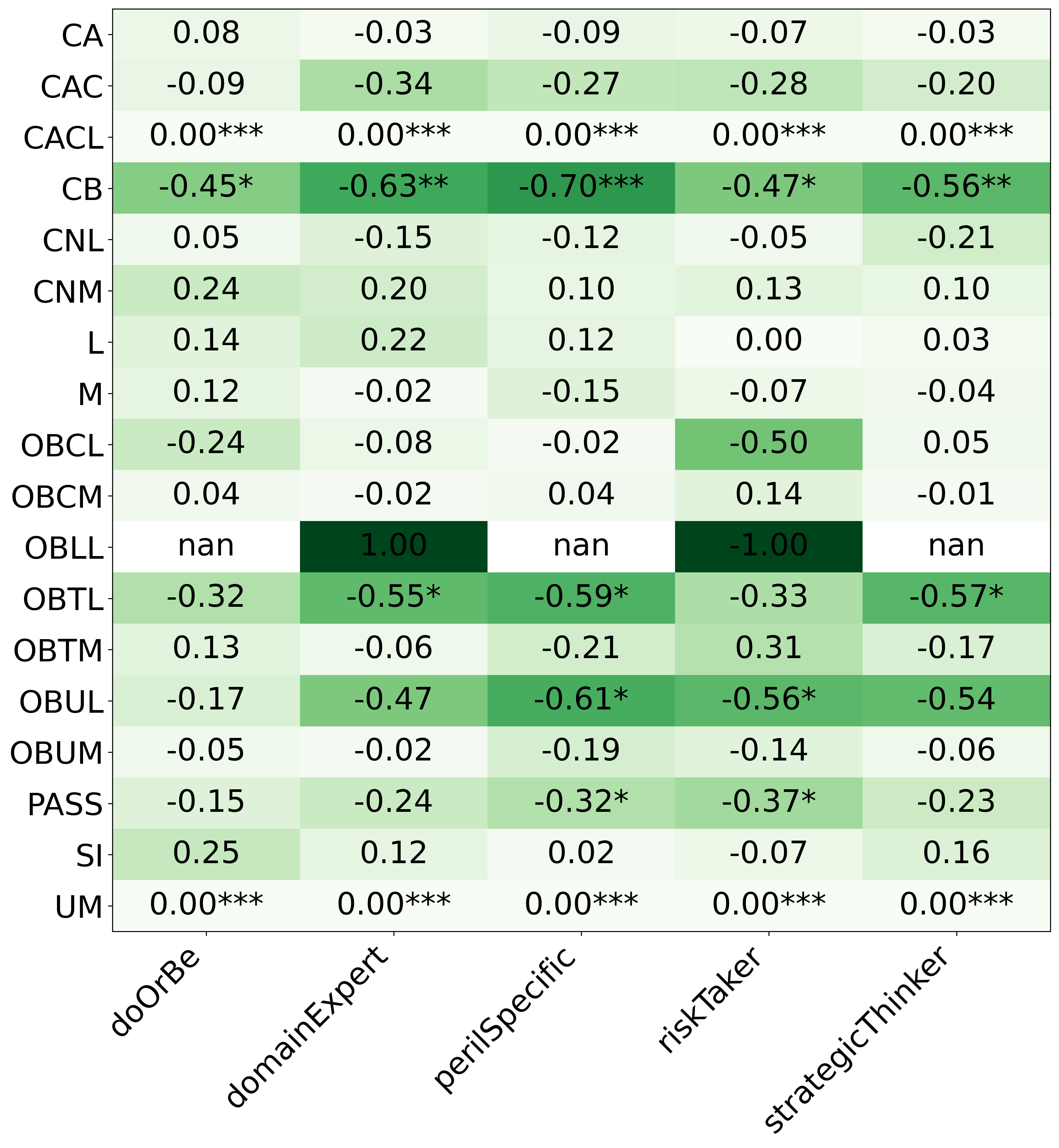
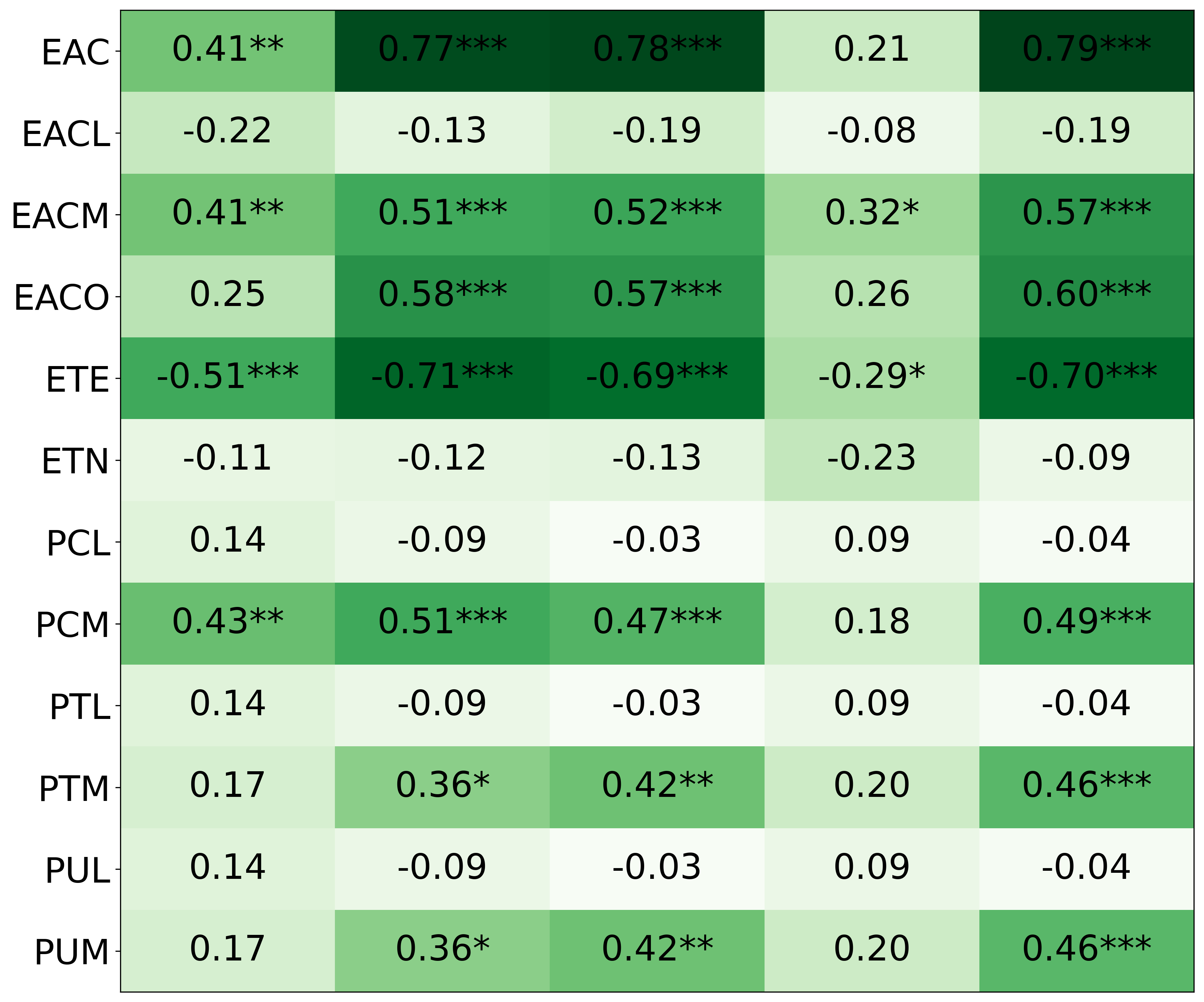
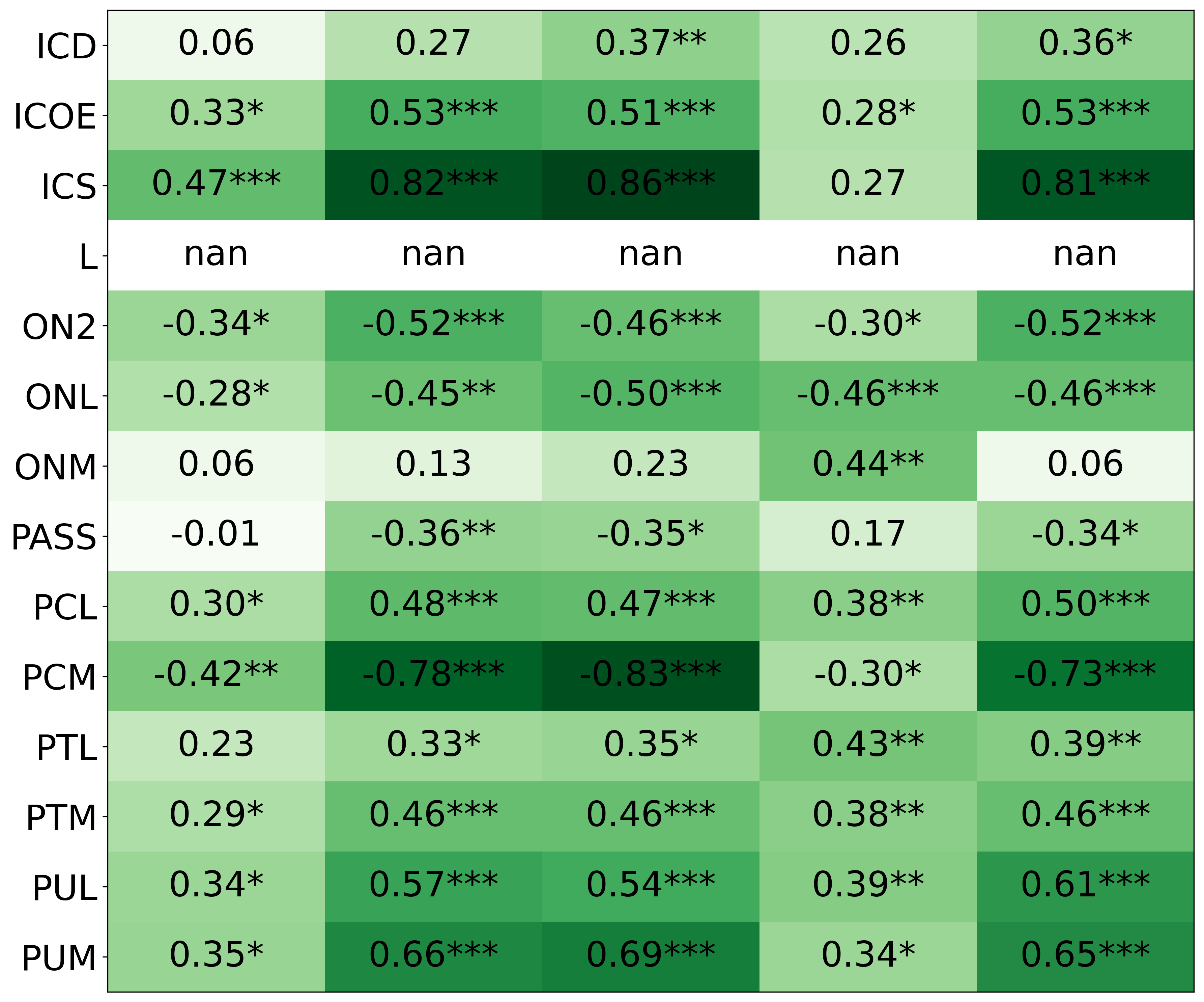
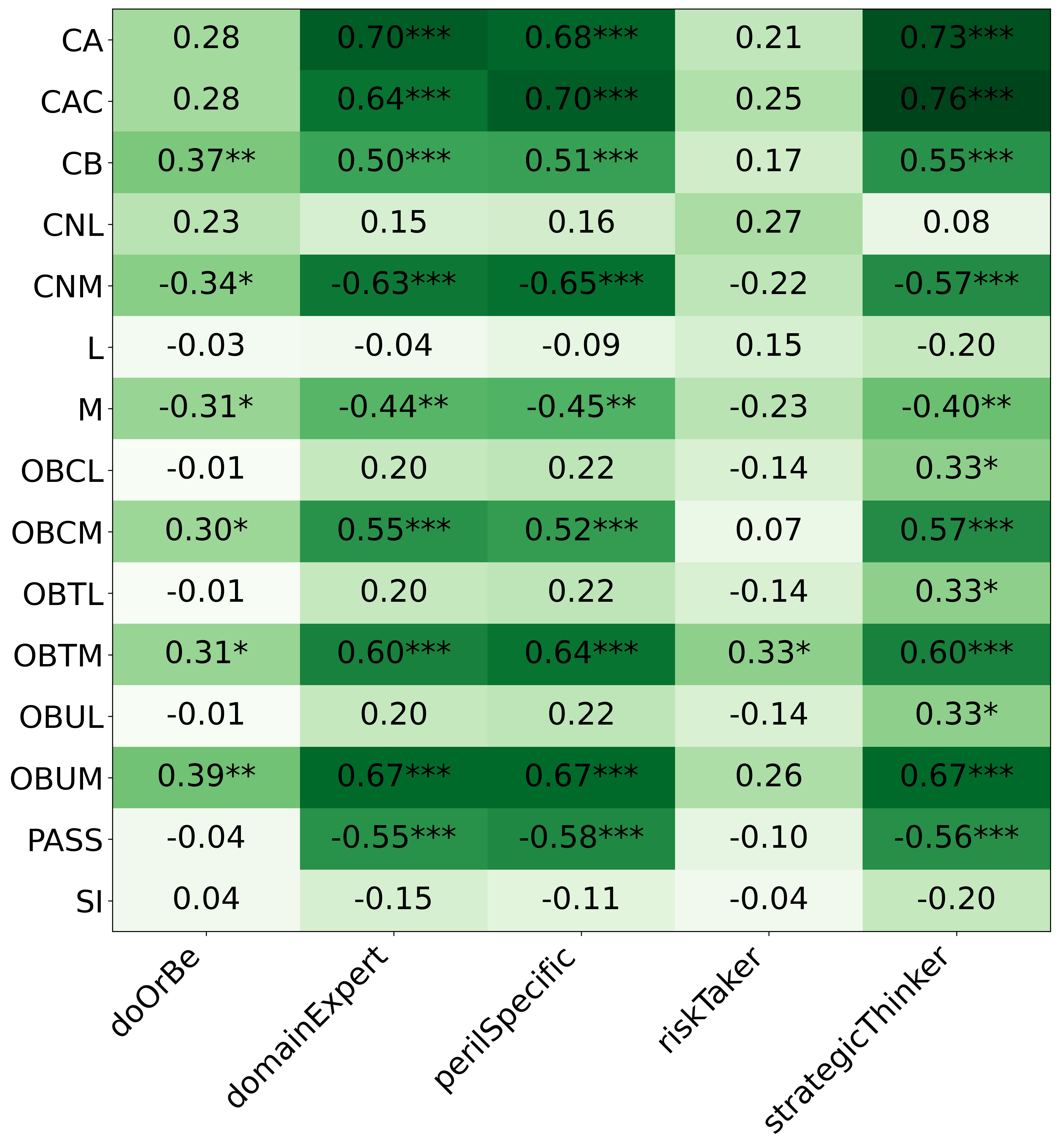
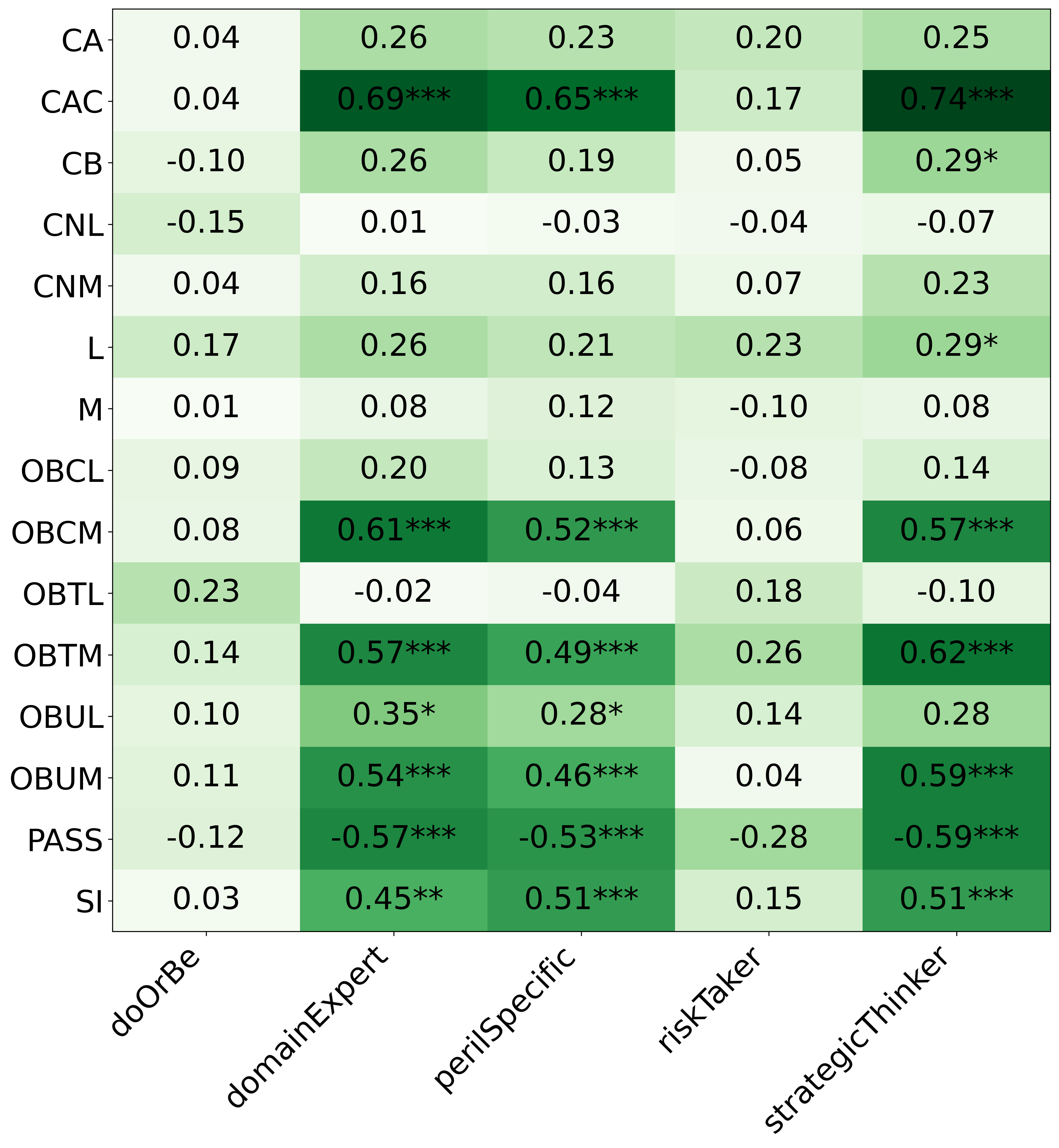
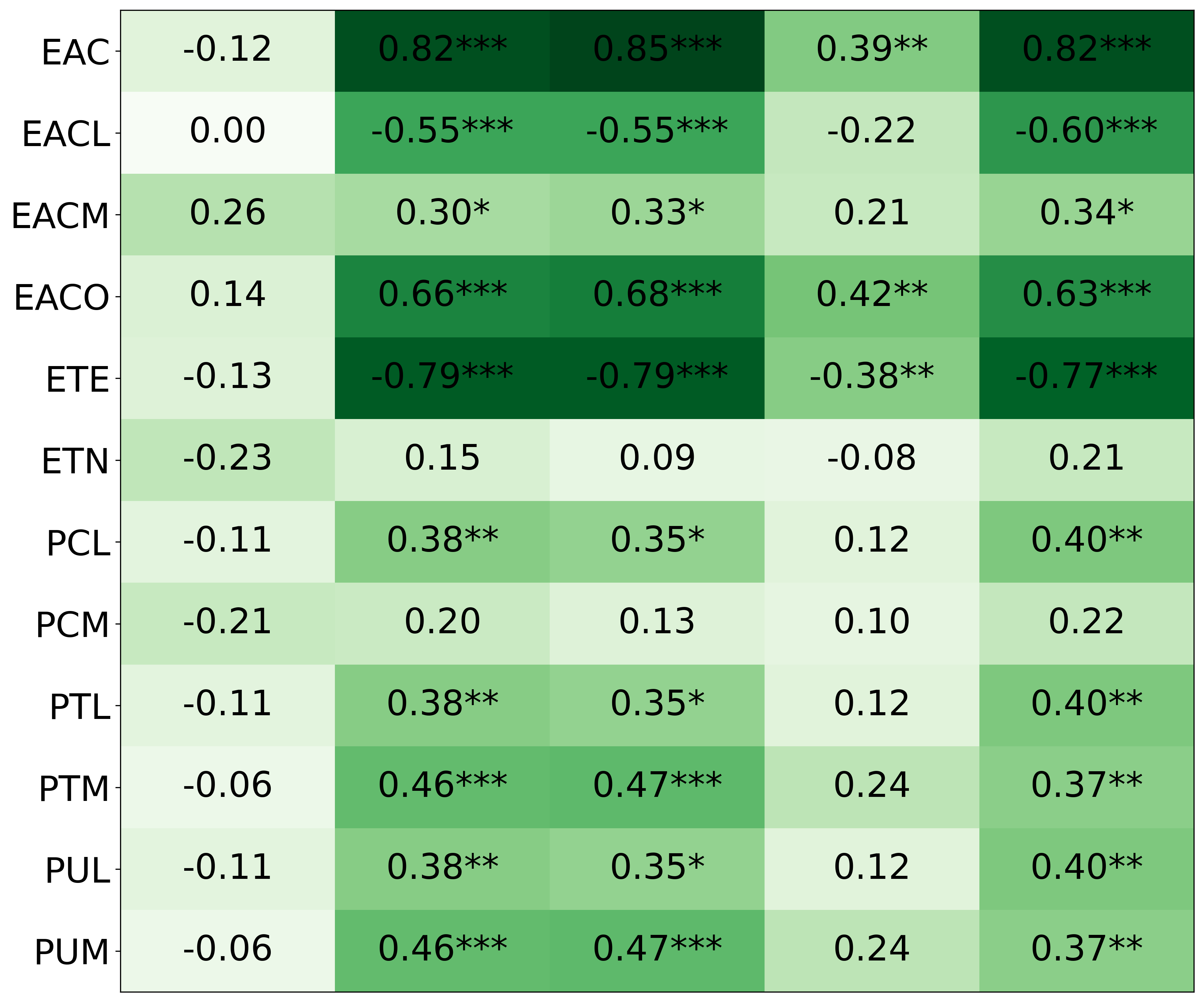
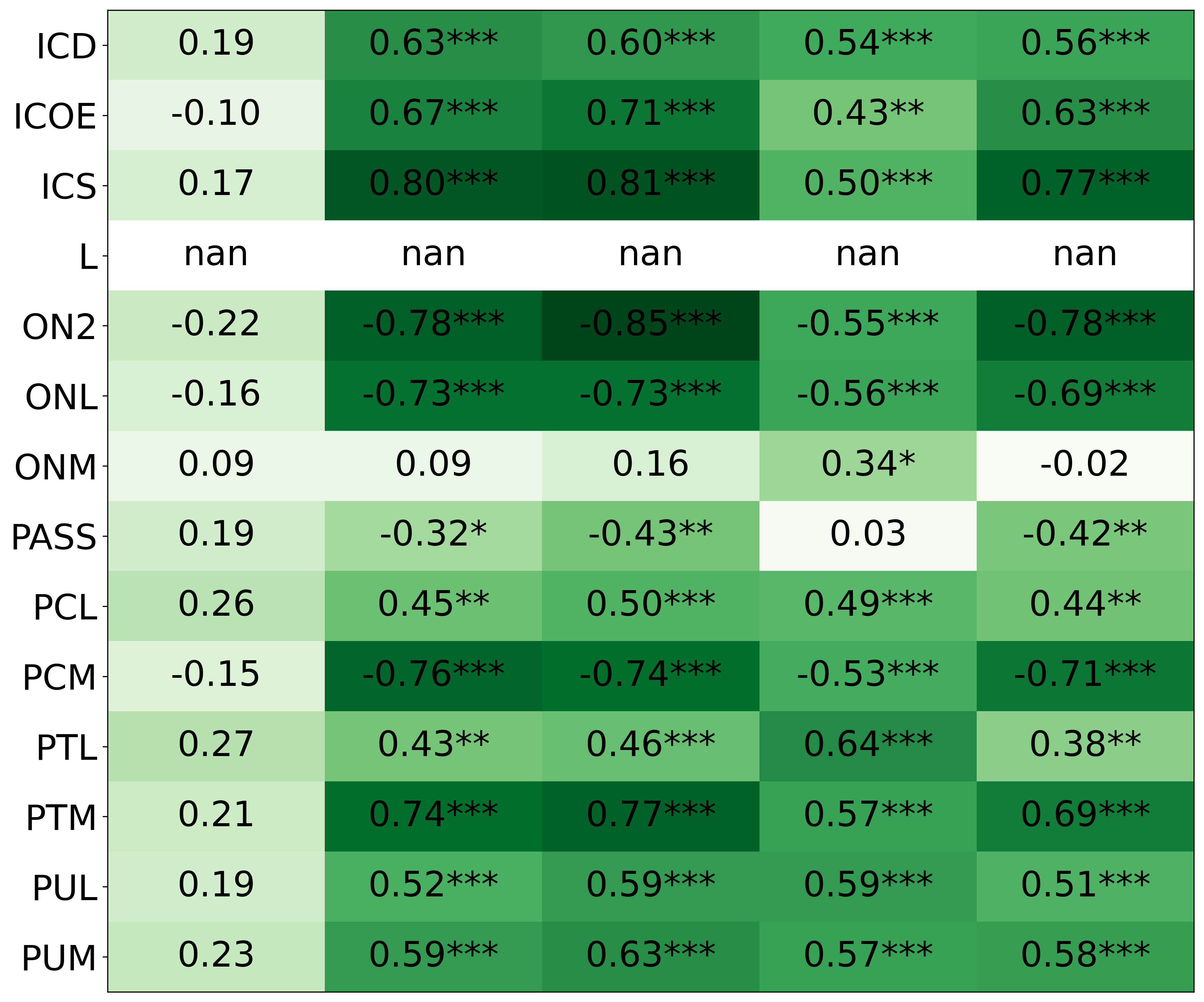
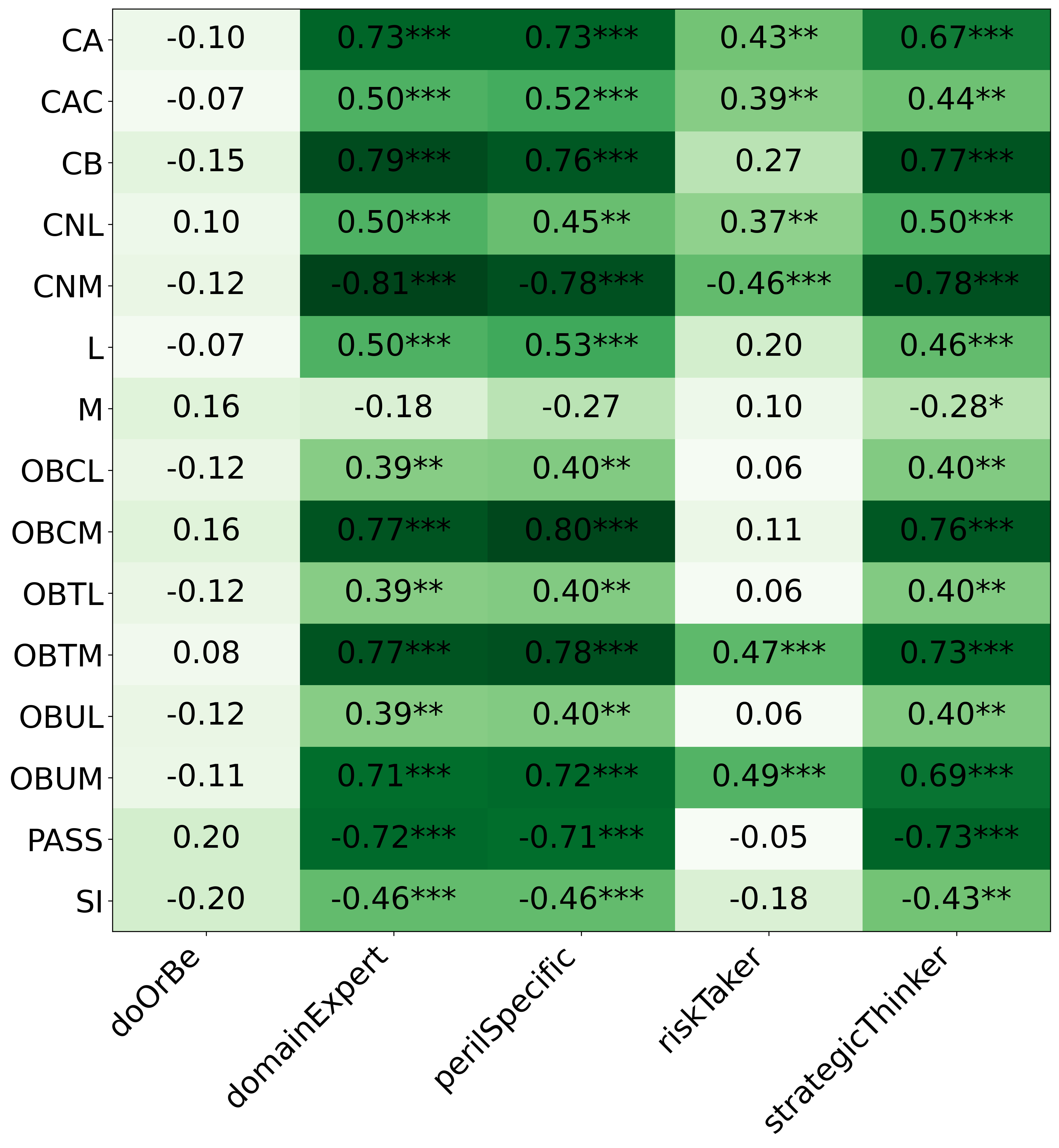
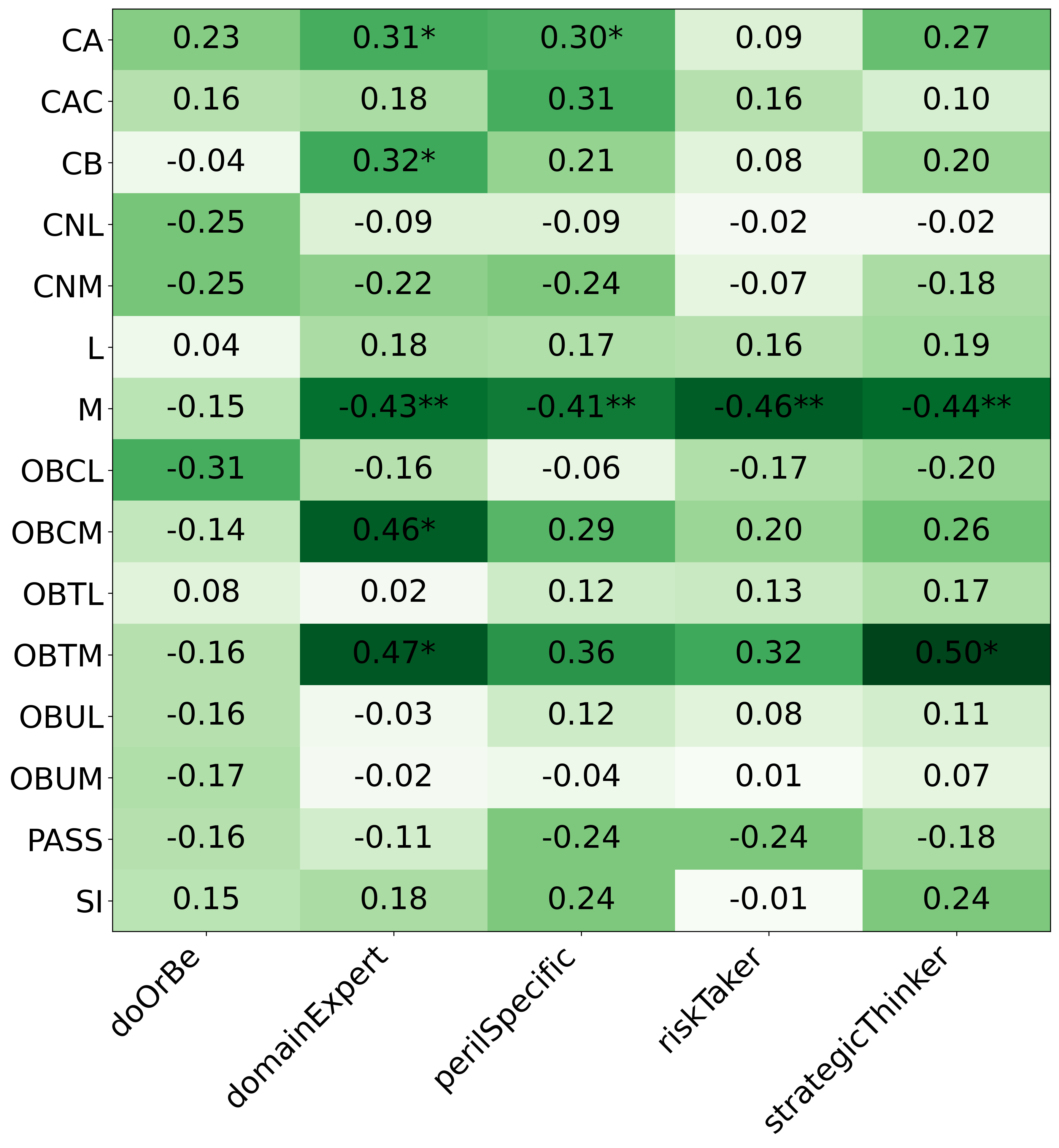
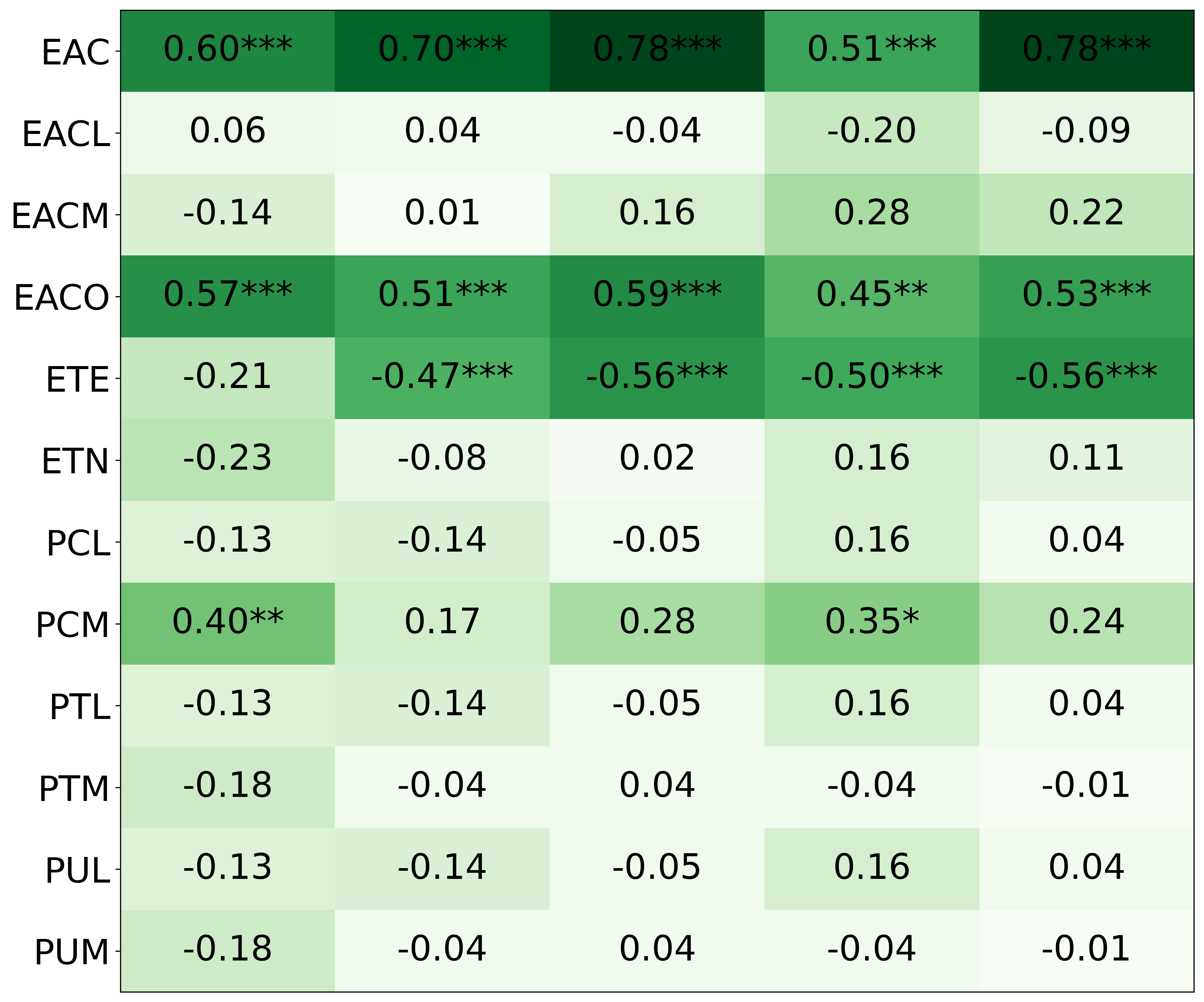
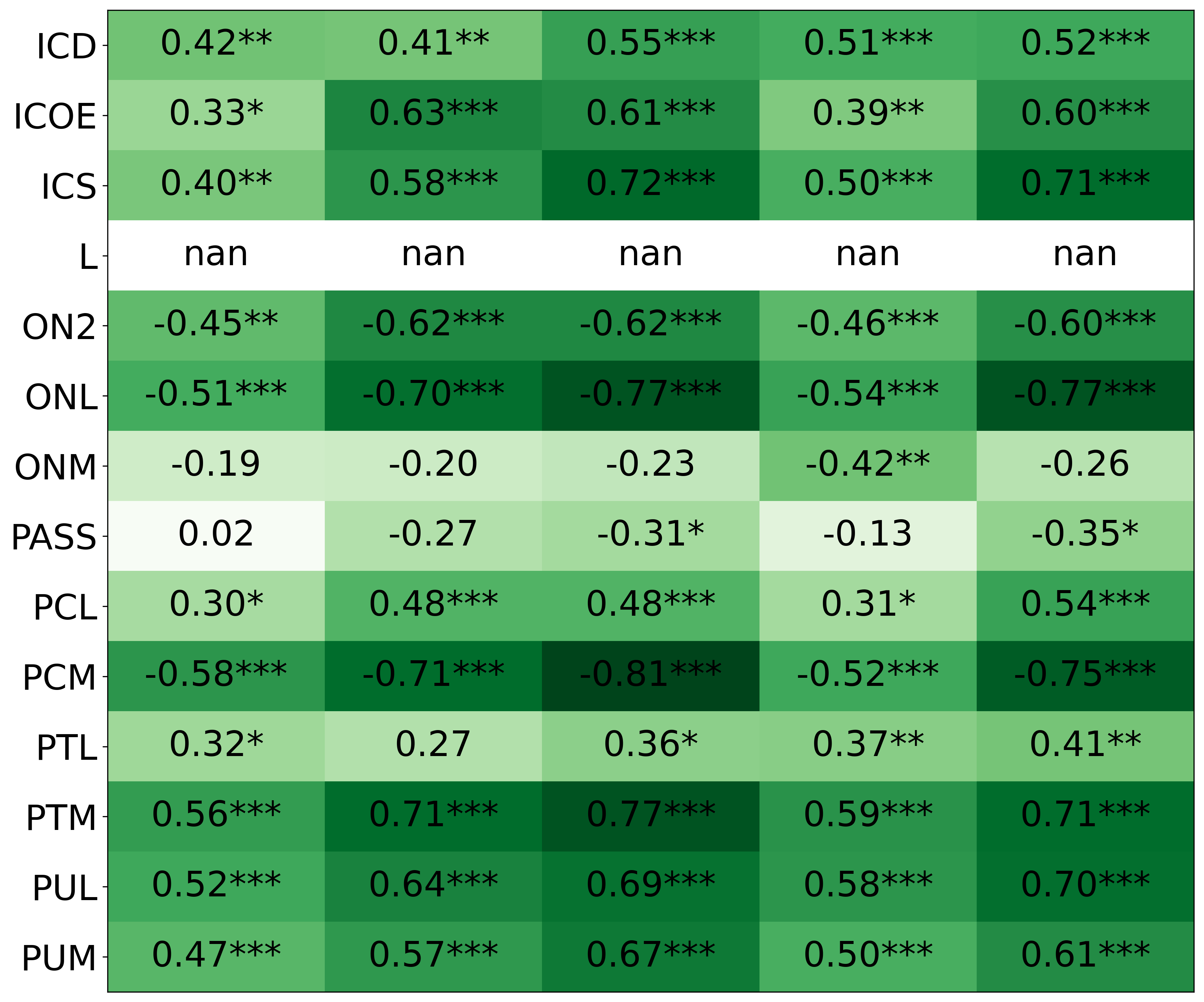
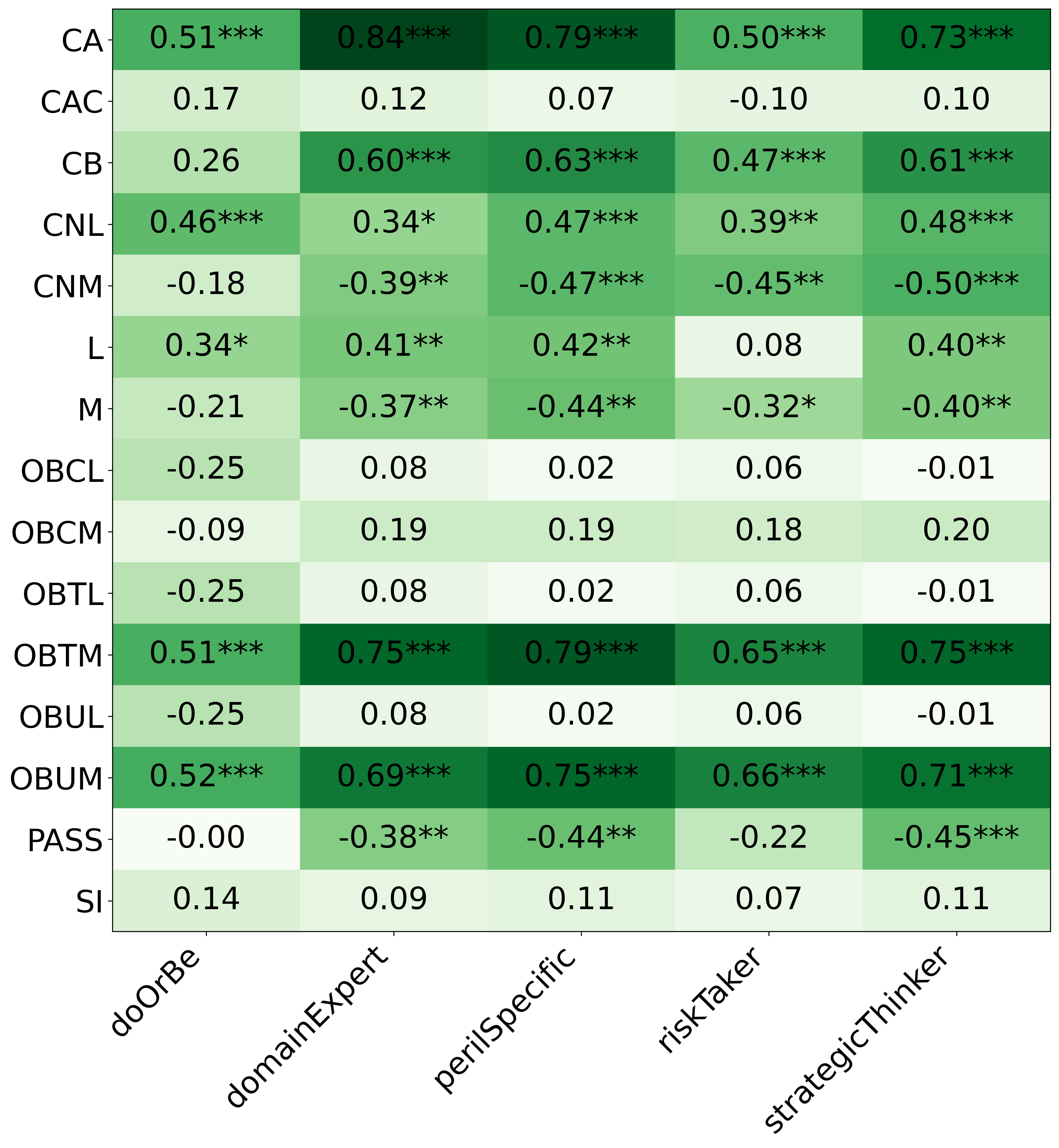
We primarily address two research questions: (1) Does persona prompting using personalities with traits associated with strategic reasoning improve performance on strategic games? (2) Does using a personality inventory to translate persona descriptions into heuristics lead to decision-making heuristics with more face validity?
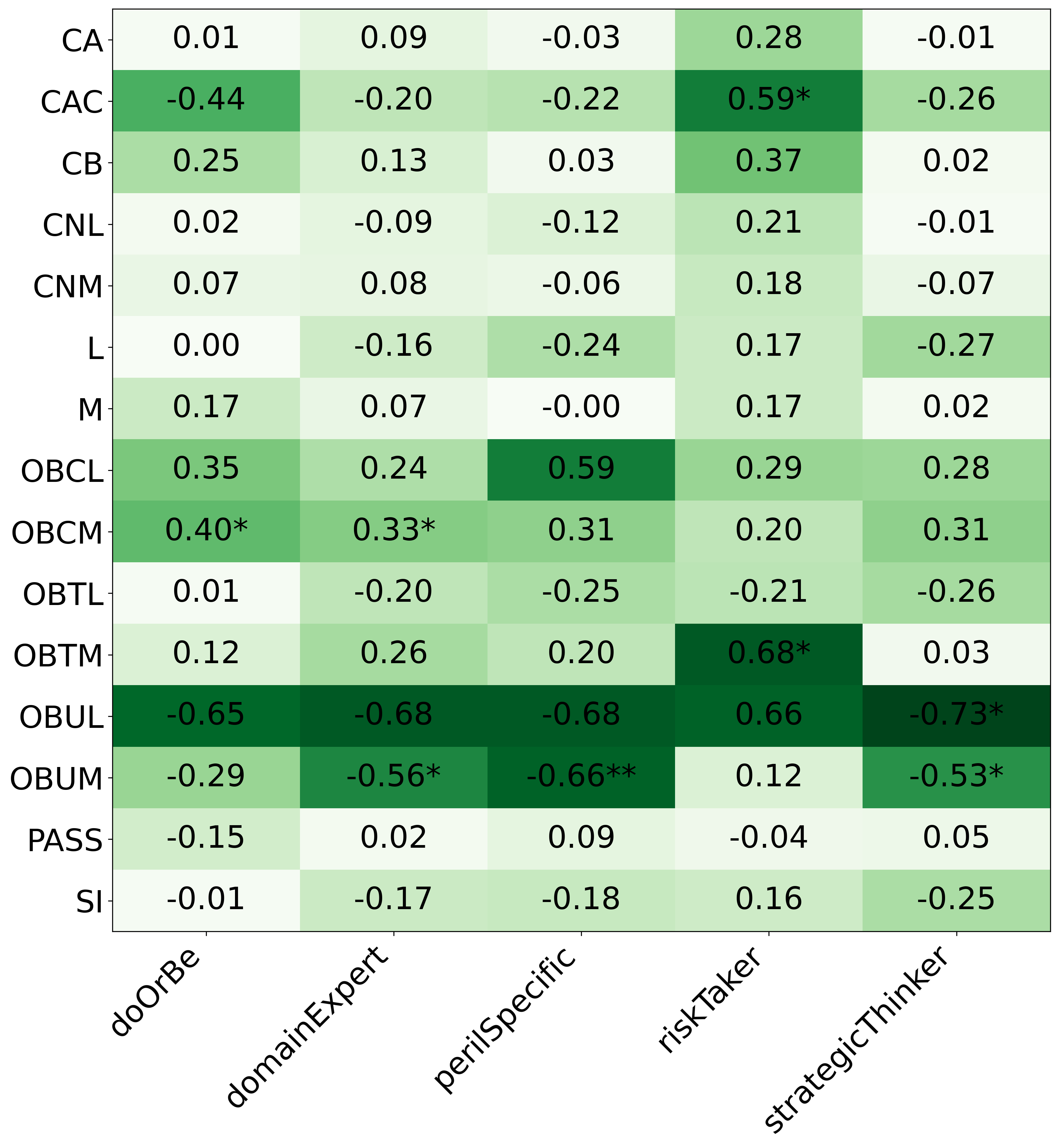
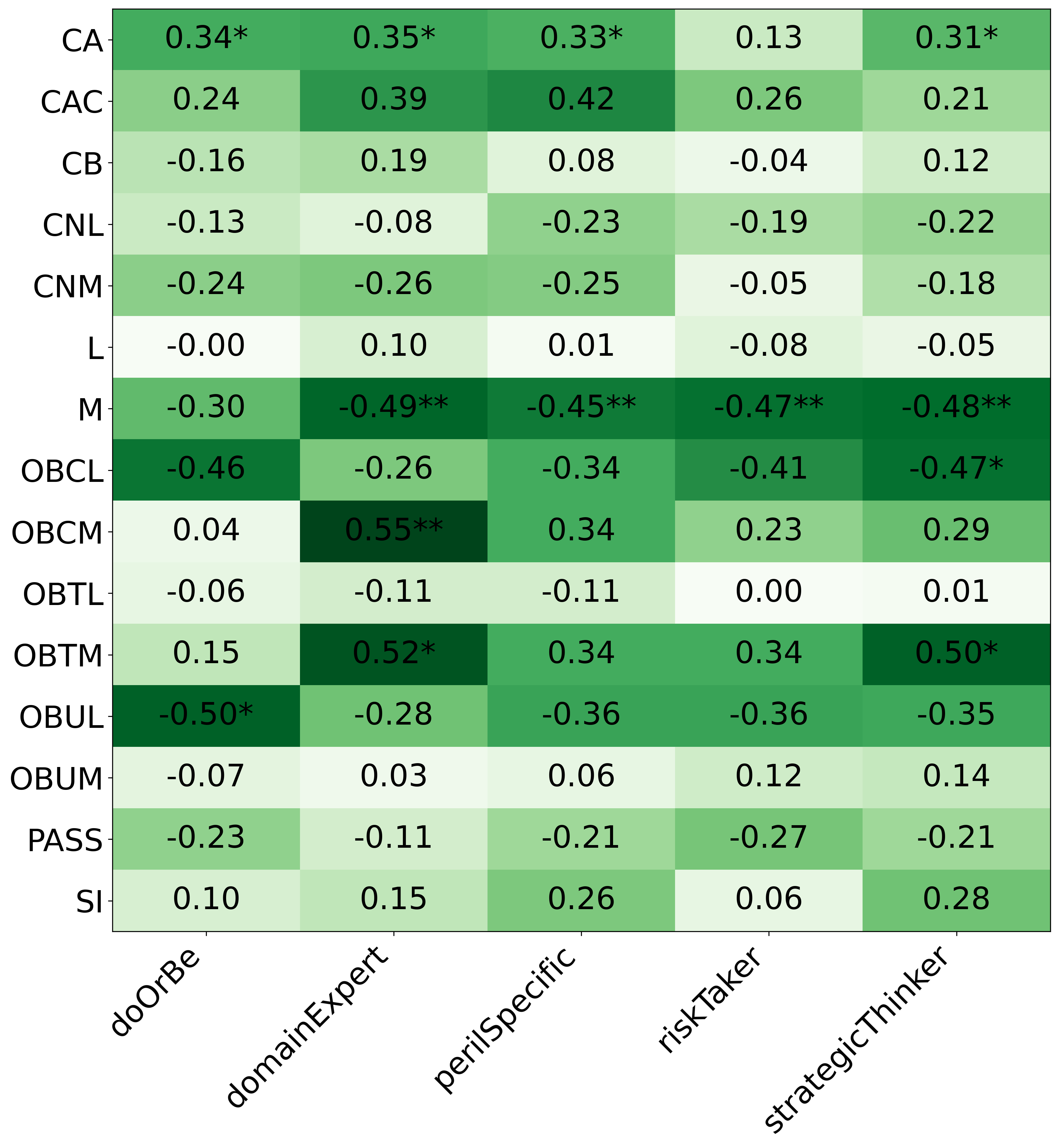
• This is the first work to specifically study the effect of persona prompting on decisionmaking in a strategic reasoning game. We found a positive relationship between personality traits that intuitively would lead to better performance in the game and actual game performance, thus contributing to the ongoing research on how and when to use persona prompting.
• We introduce PERIL, a new platform for evaluating strategic decision-making capabilities of AI players. In this paper, we compare the effects of persona prompting on players with the same mission, but the platform we implemented allows for multiple missions (which can in the future be used for studying strategic deception). We will make our full source code and platform available.
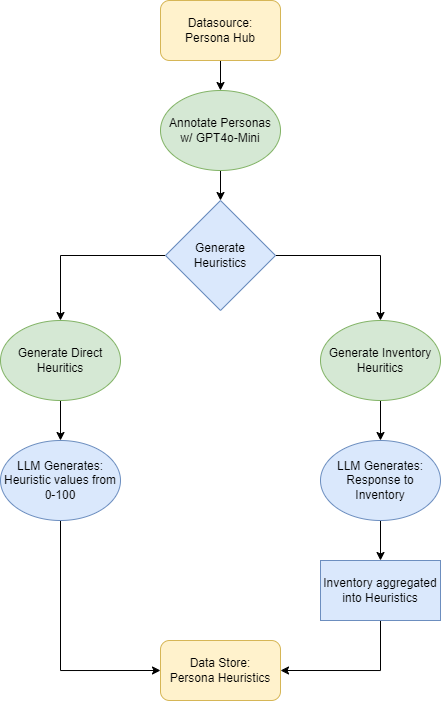
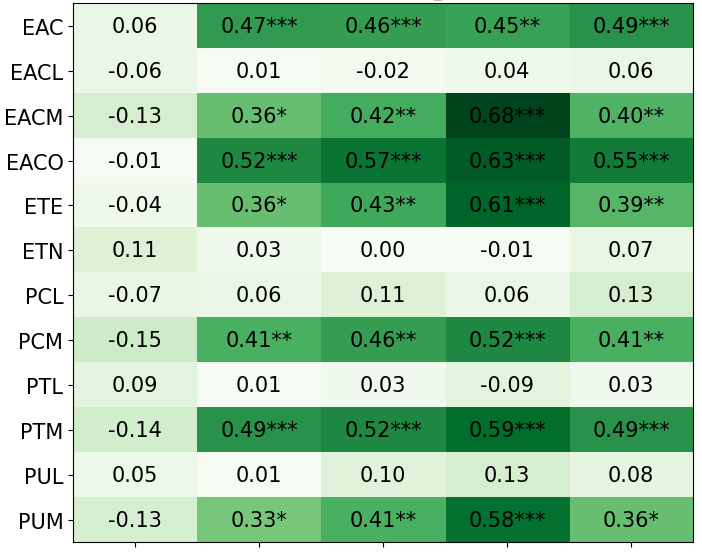
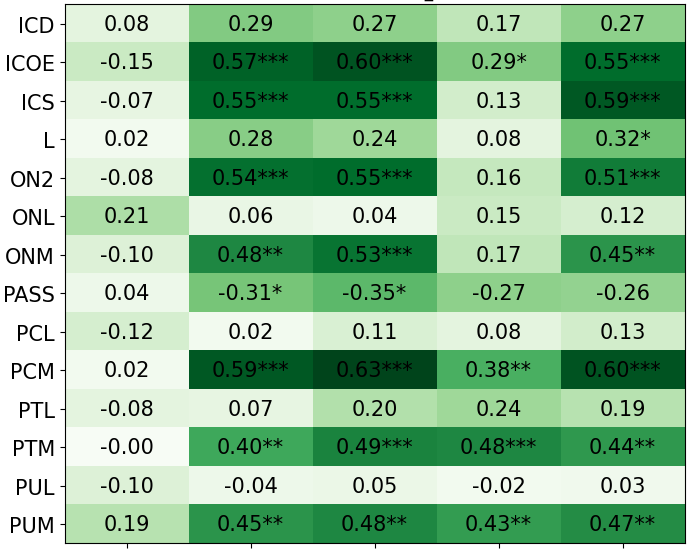
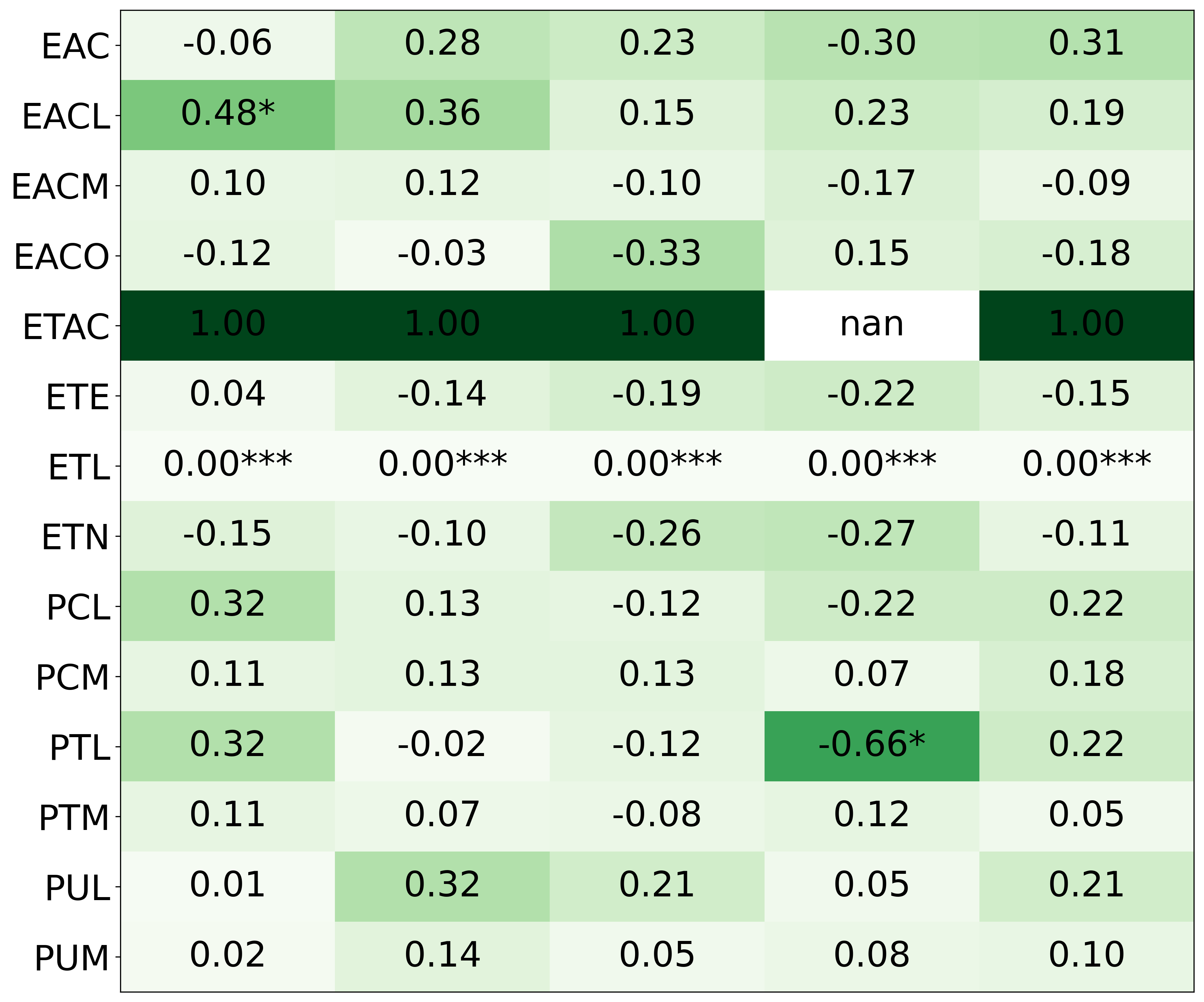
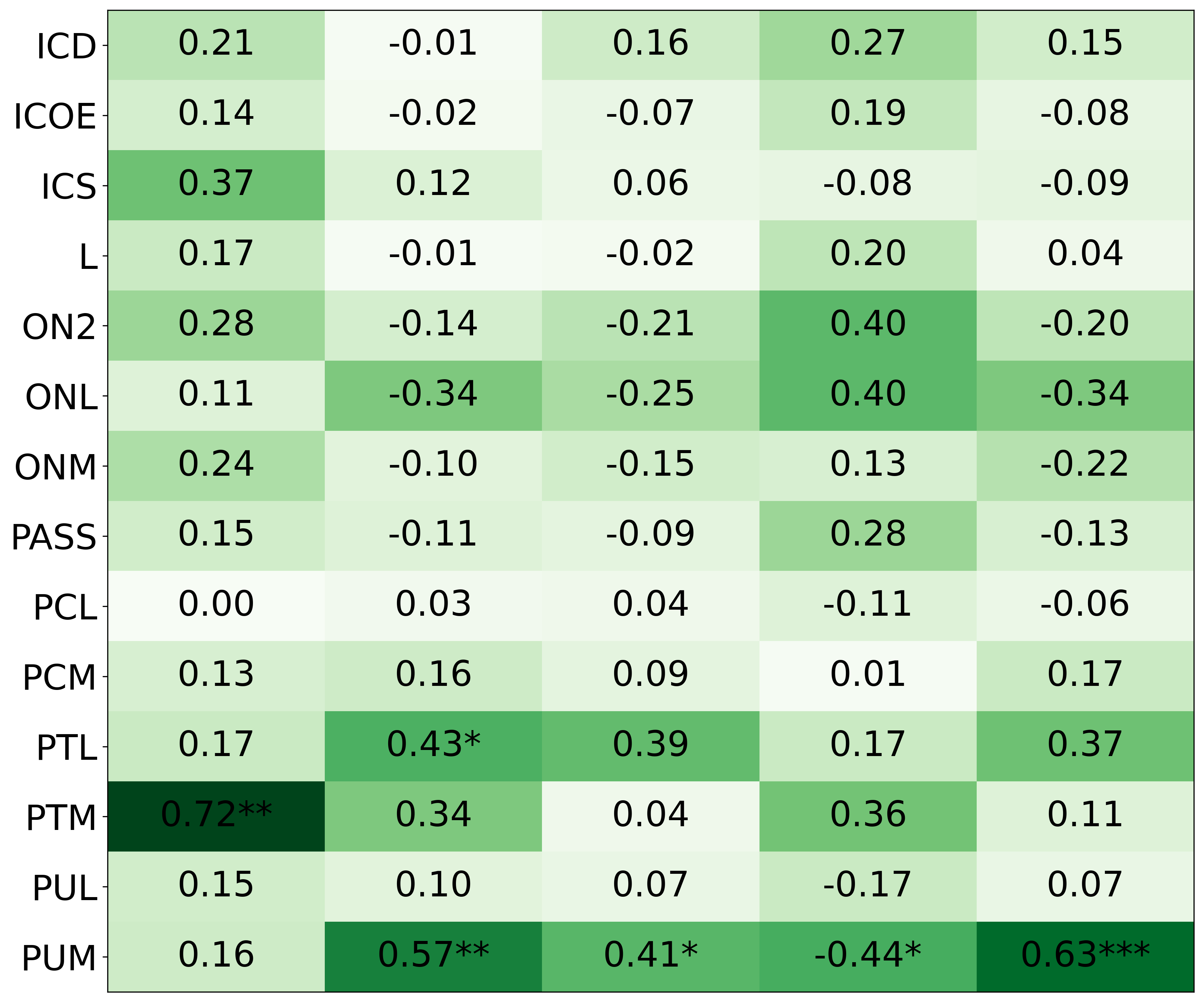
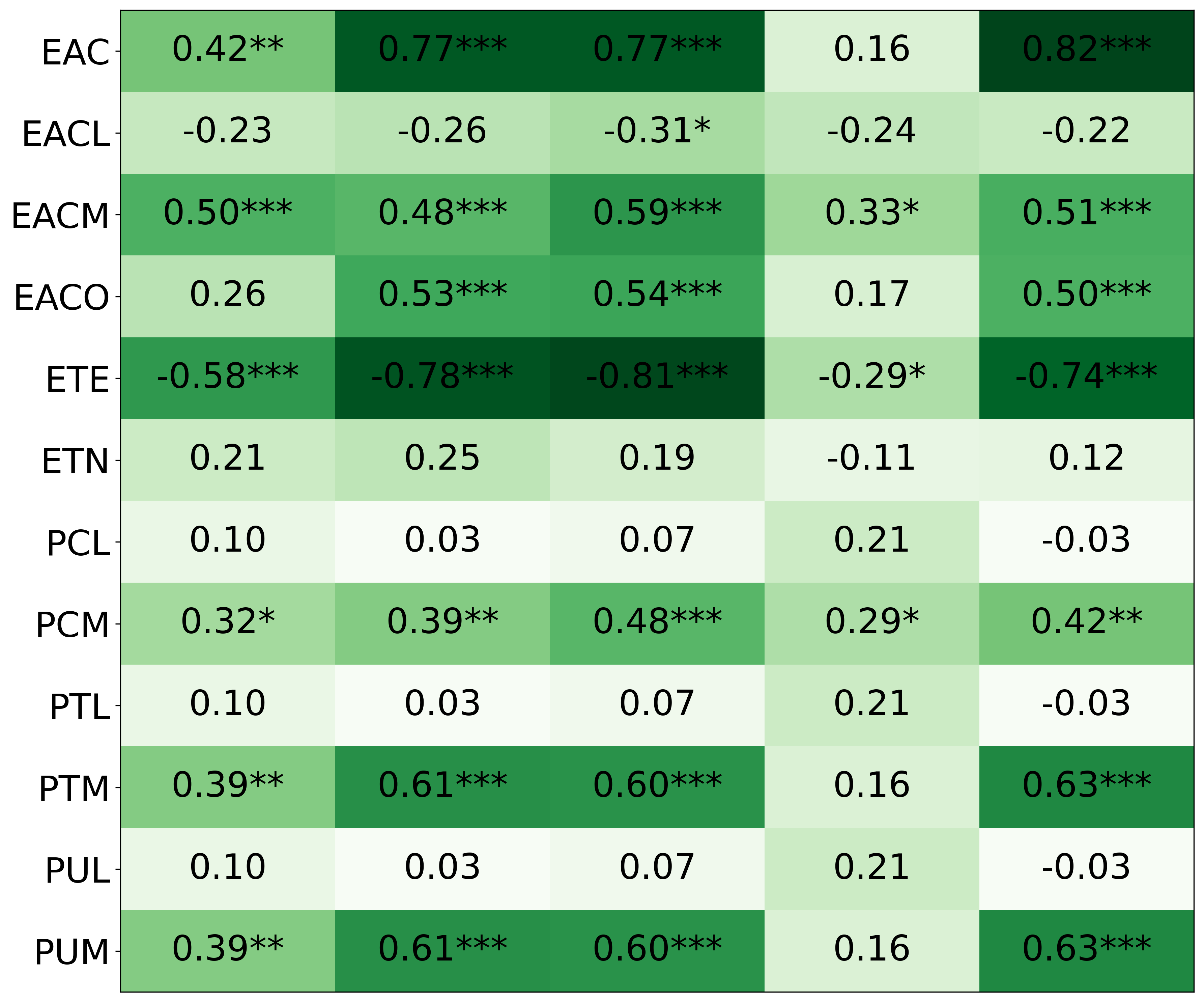
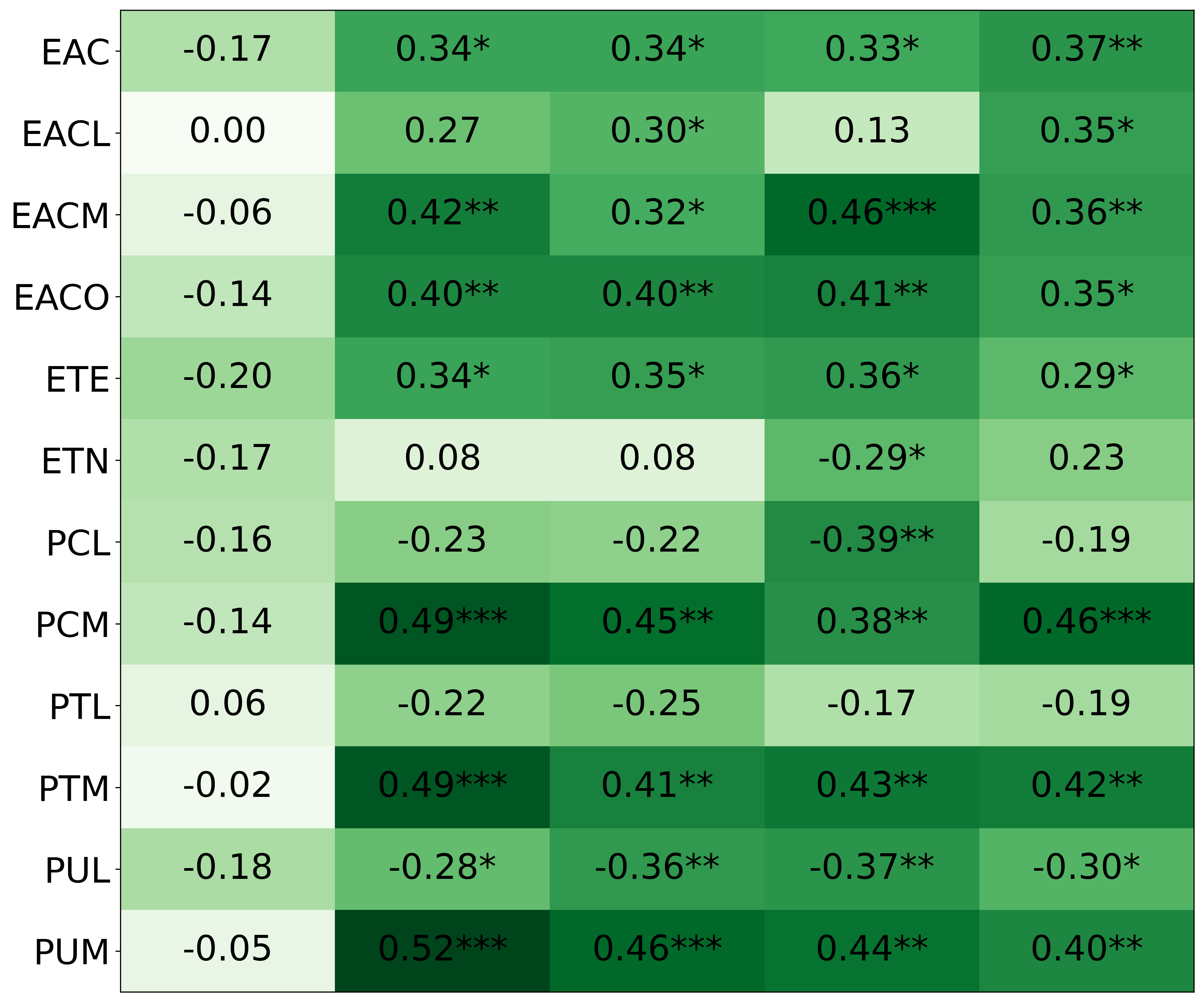
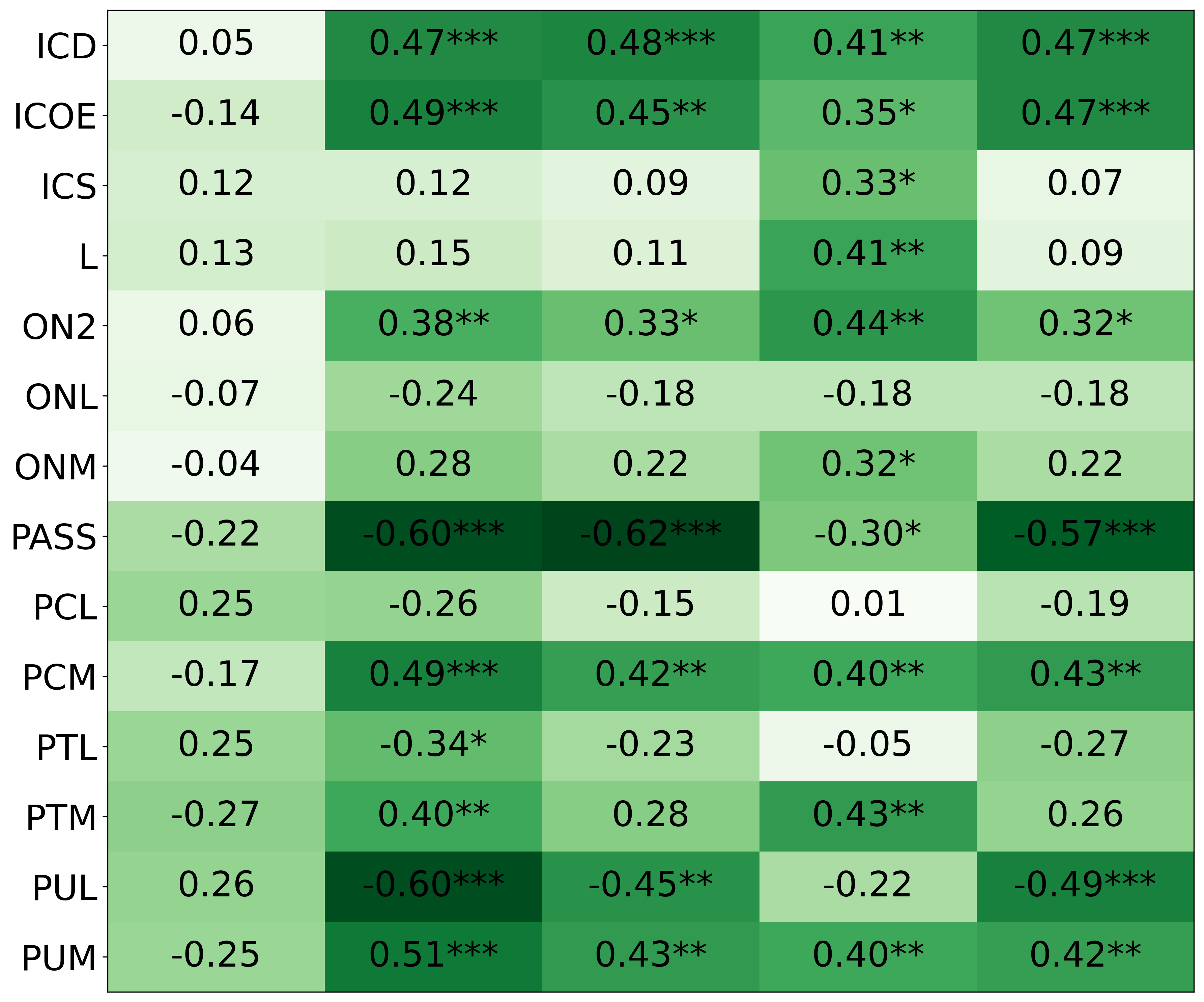
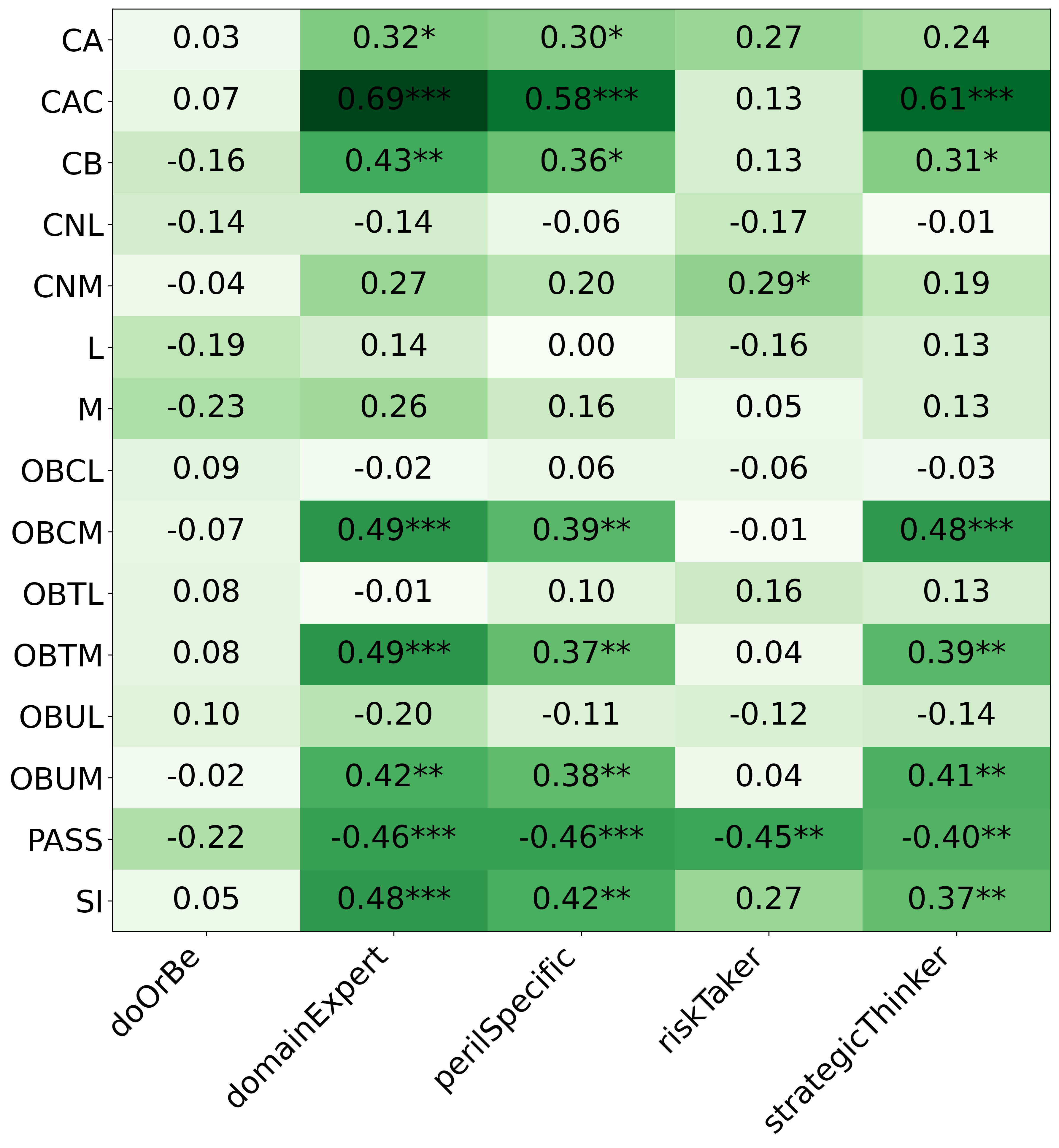
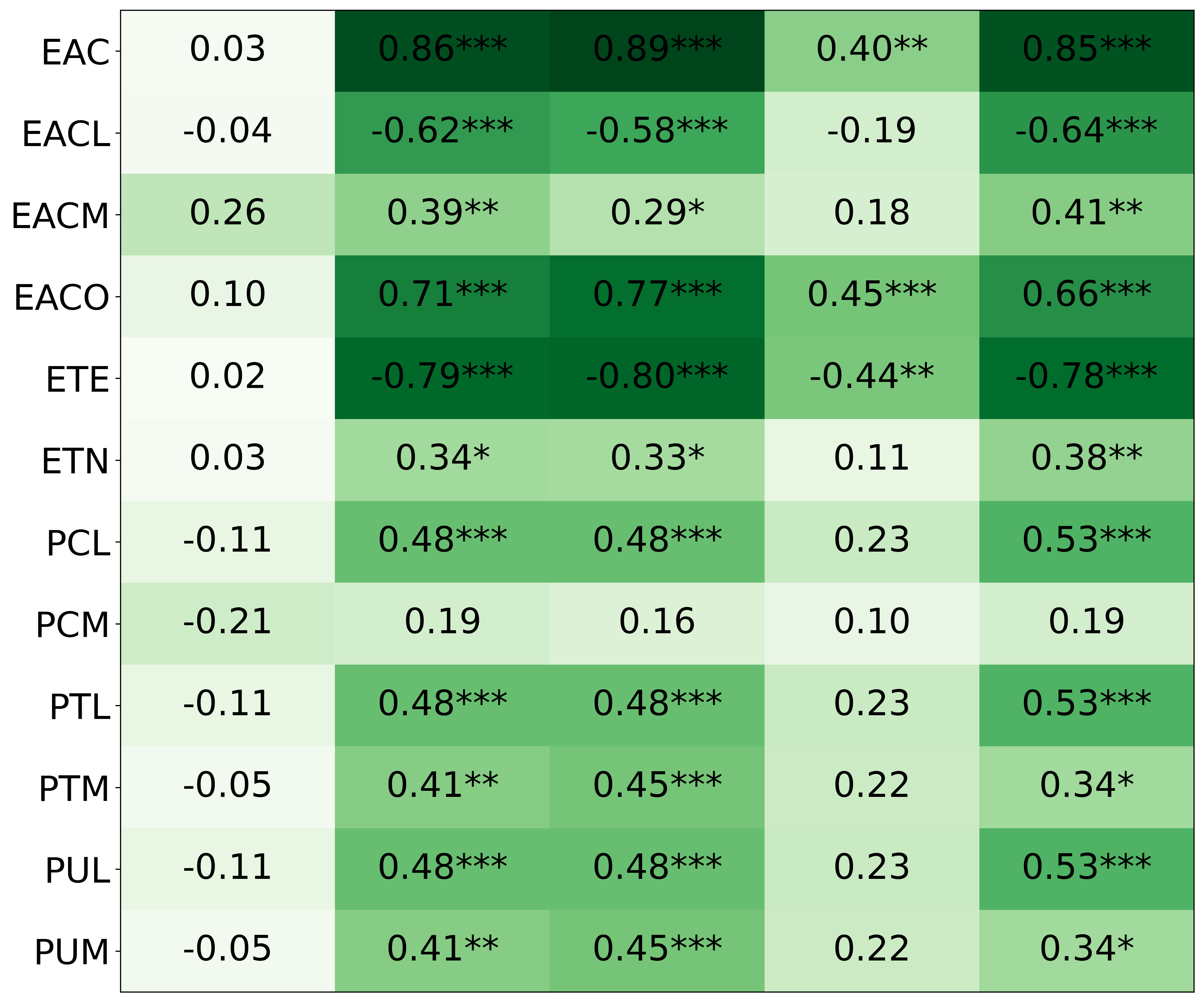
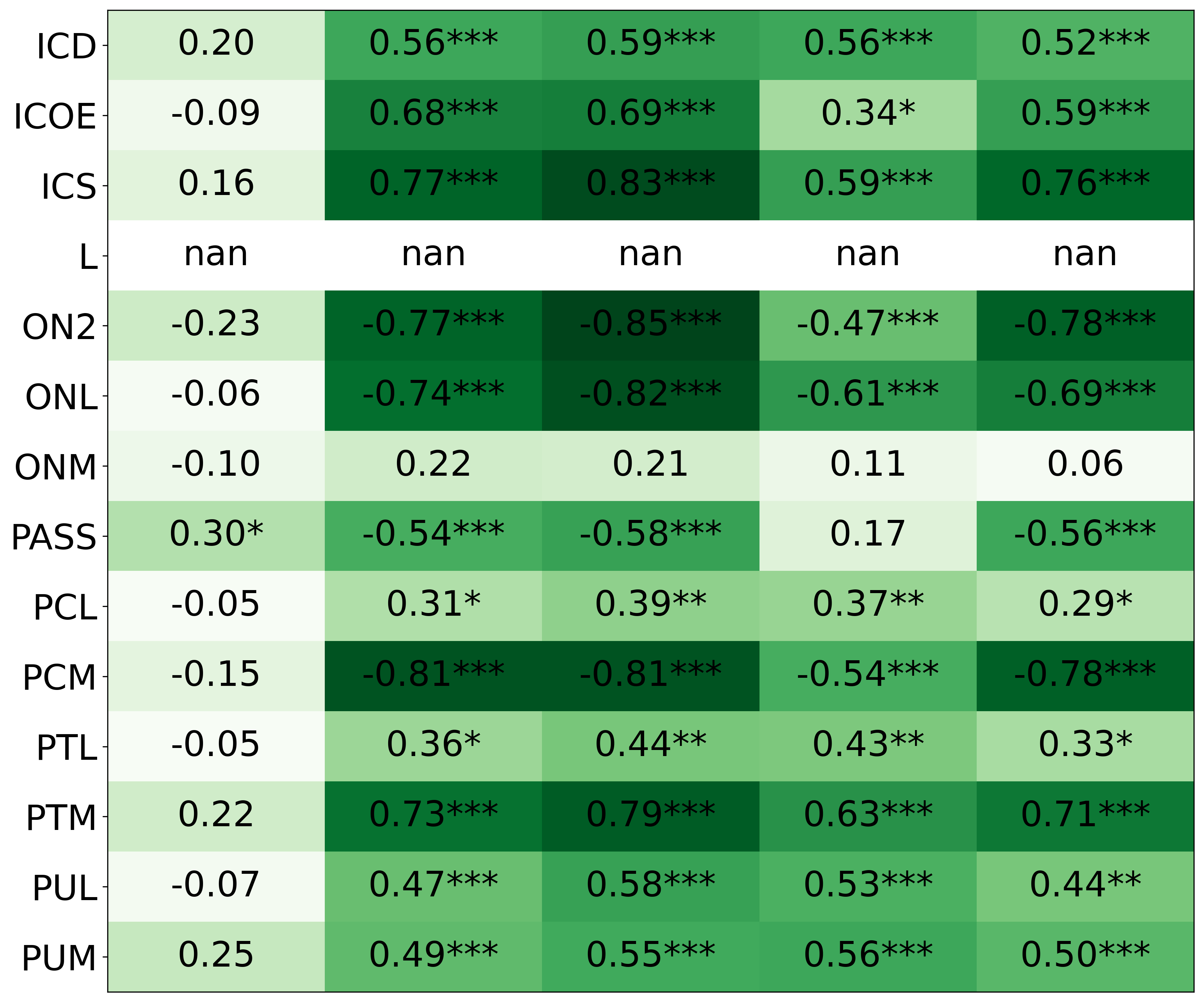
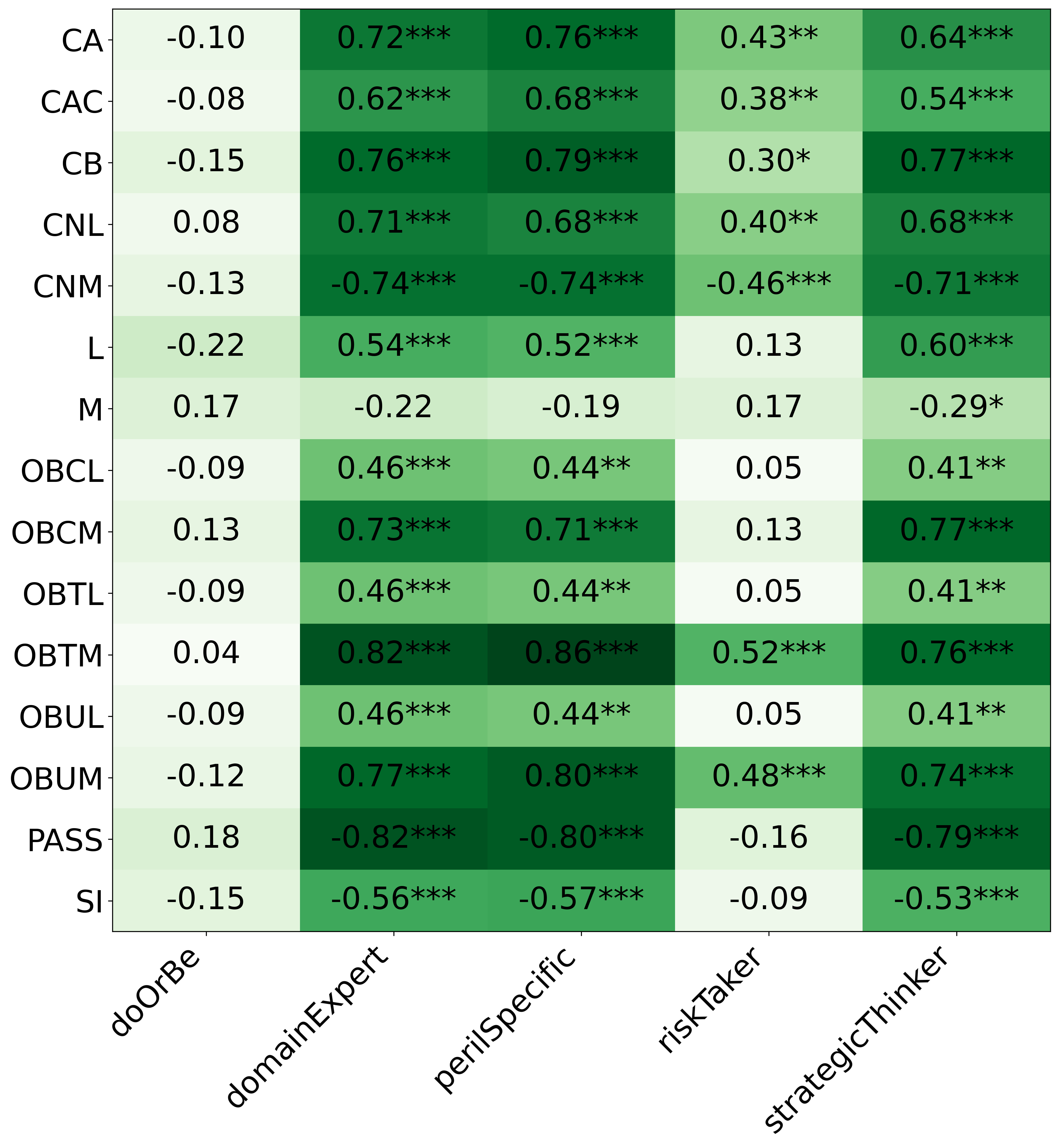
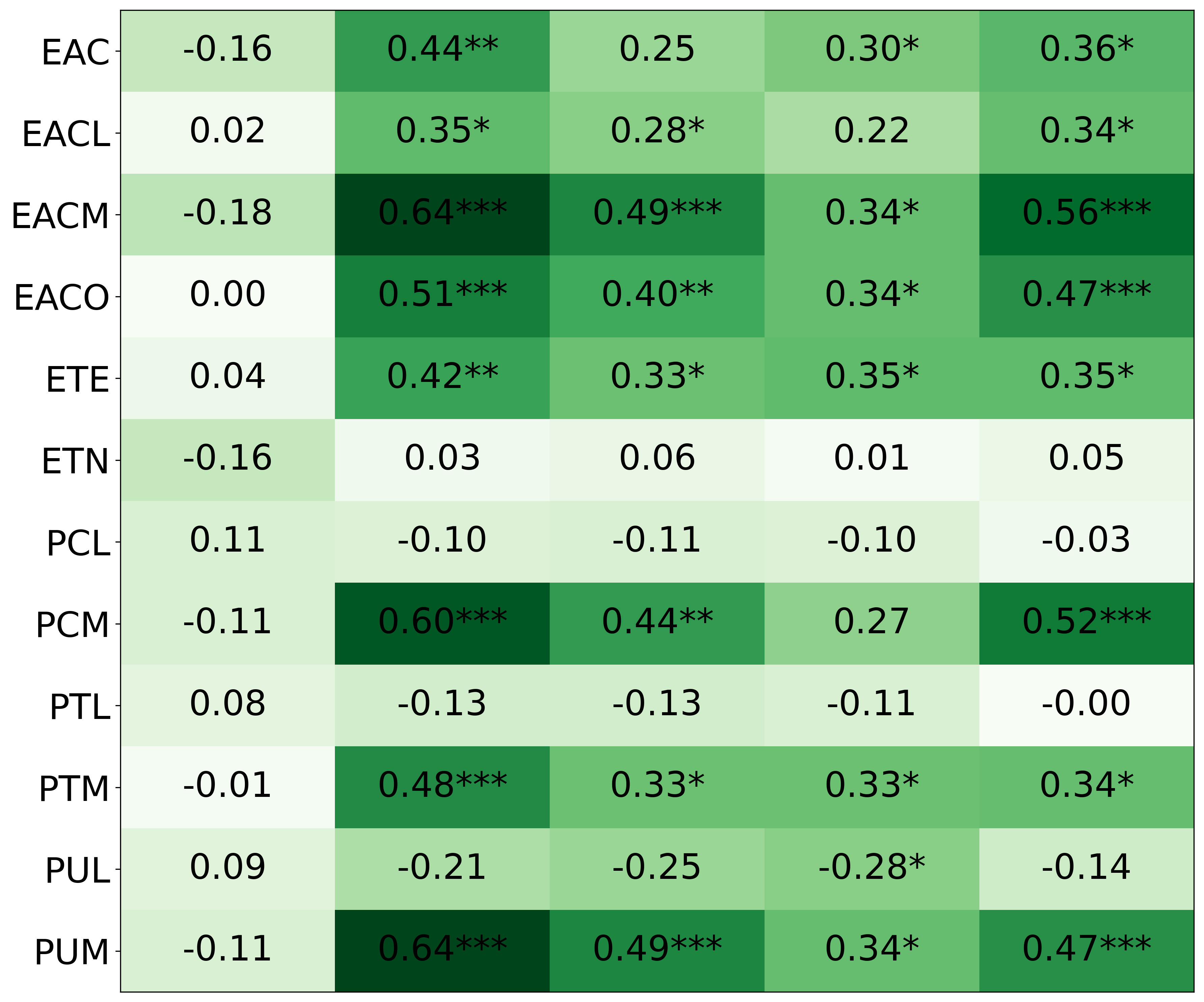
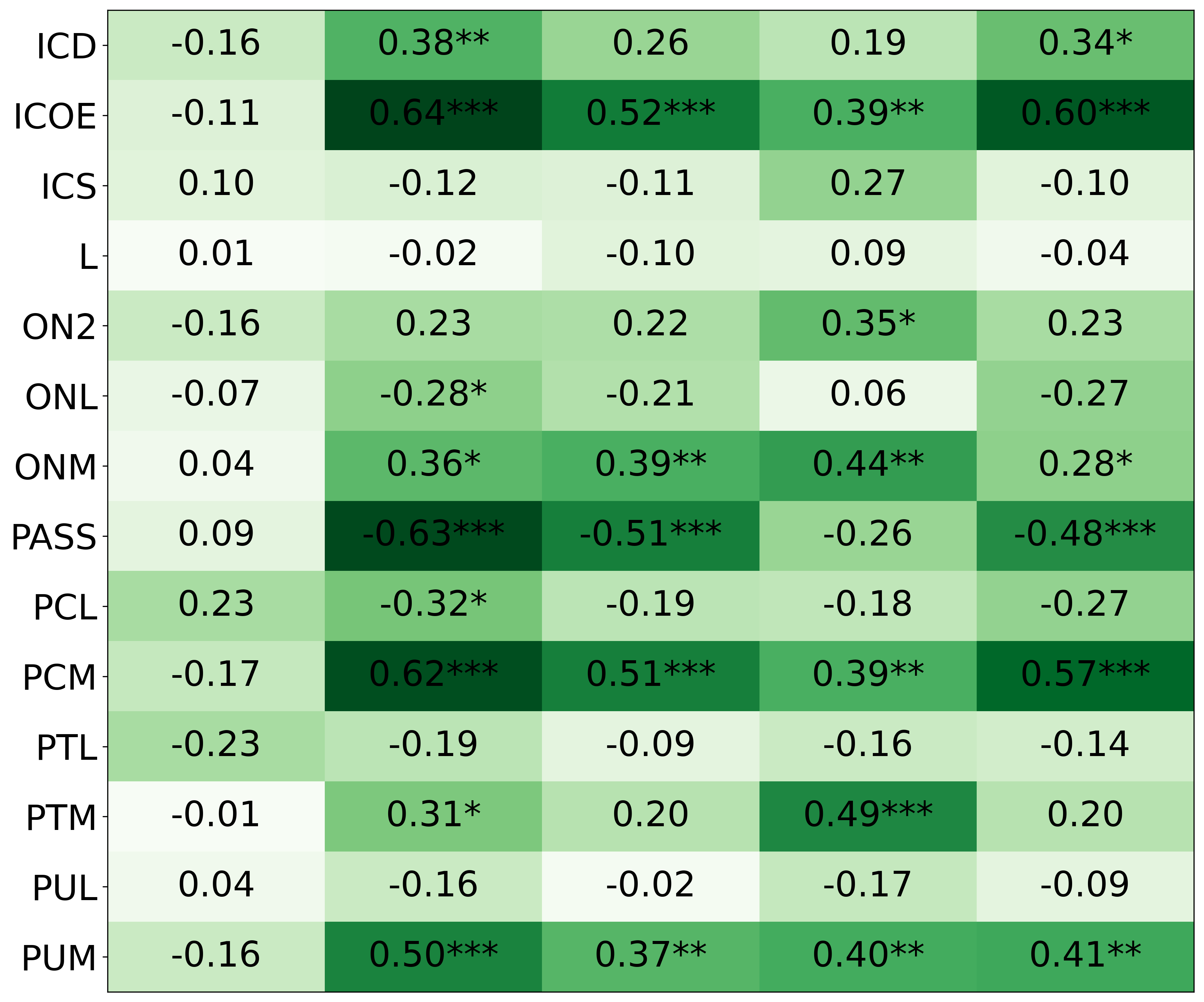
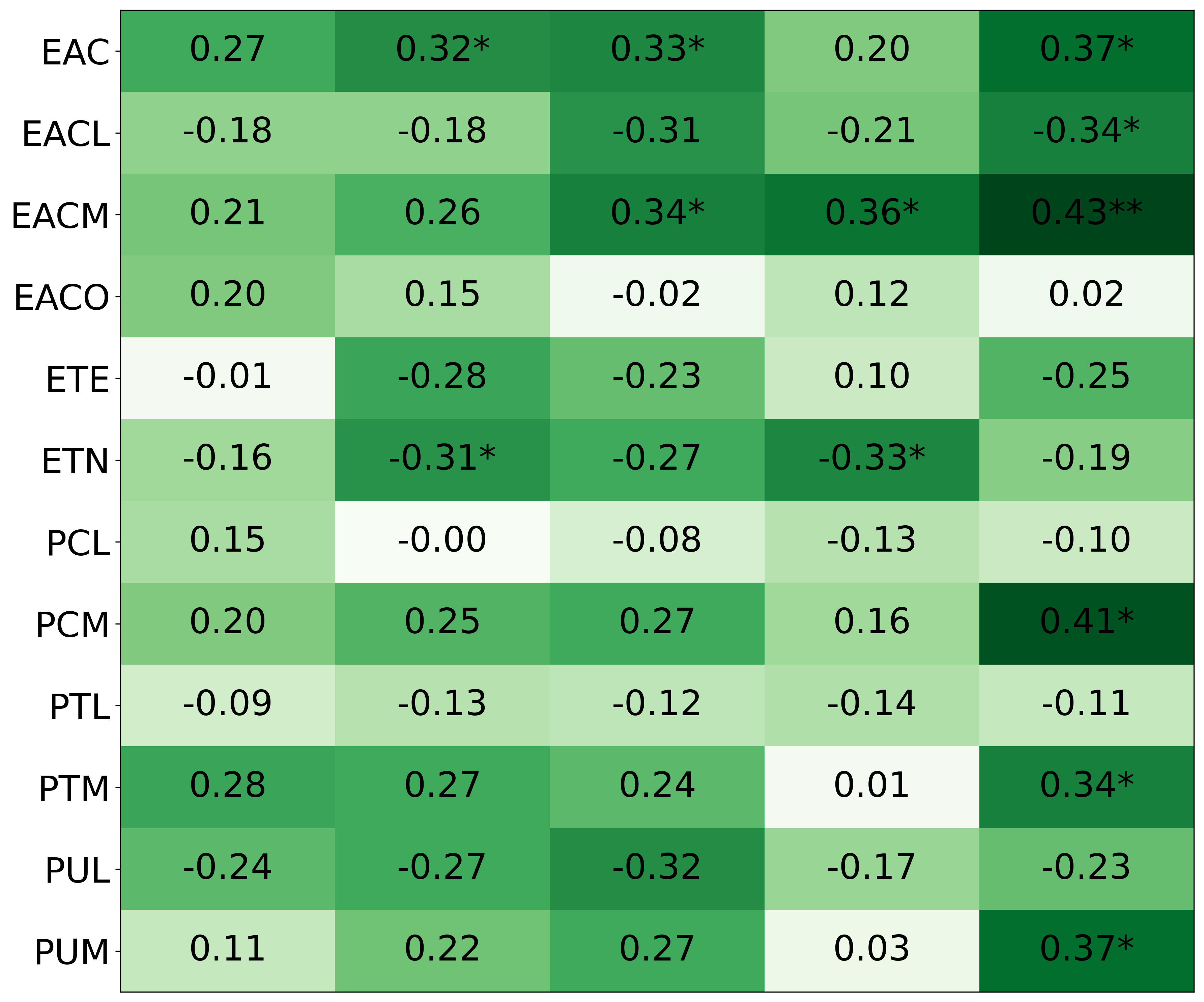
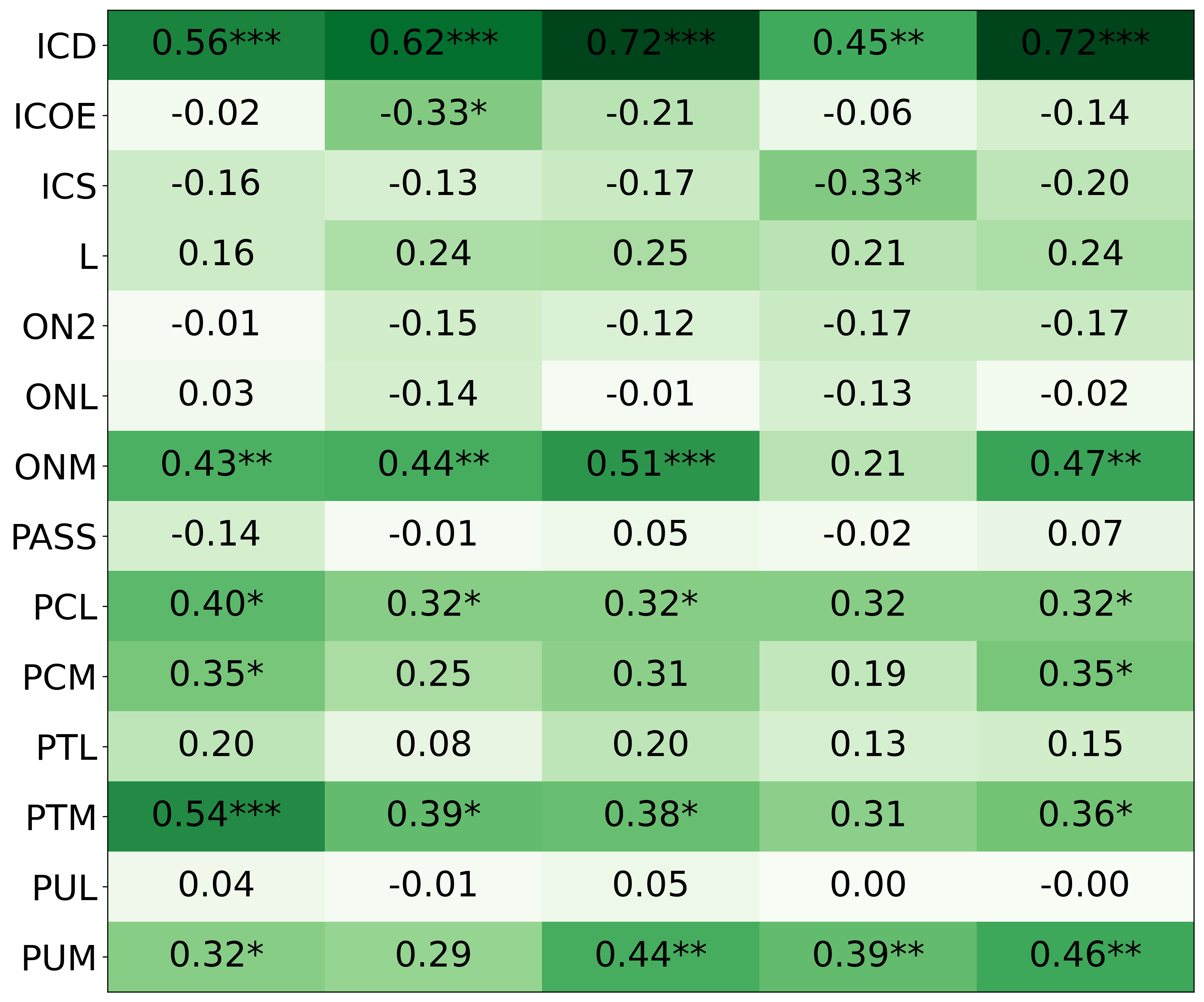
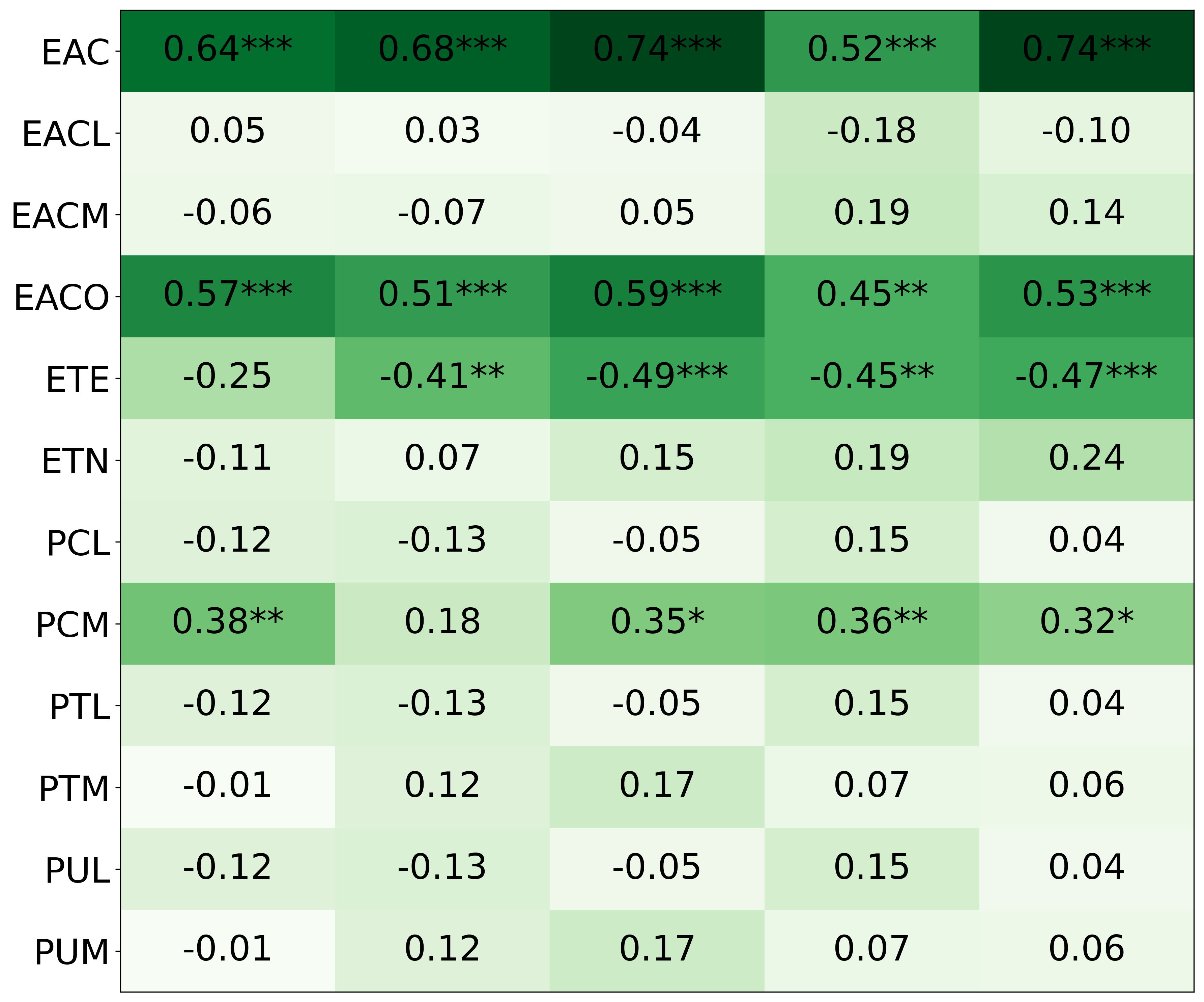
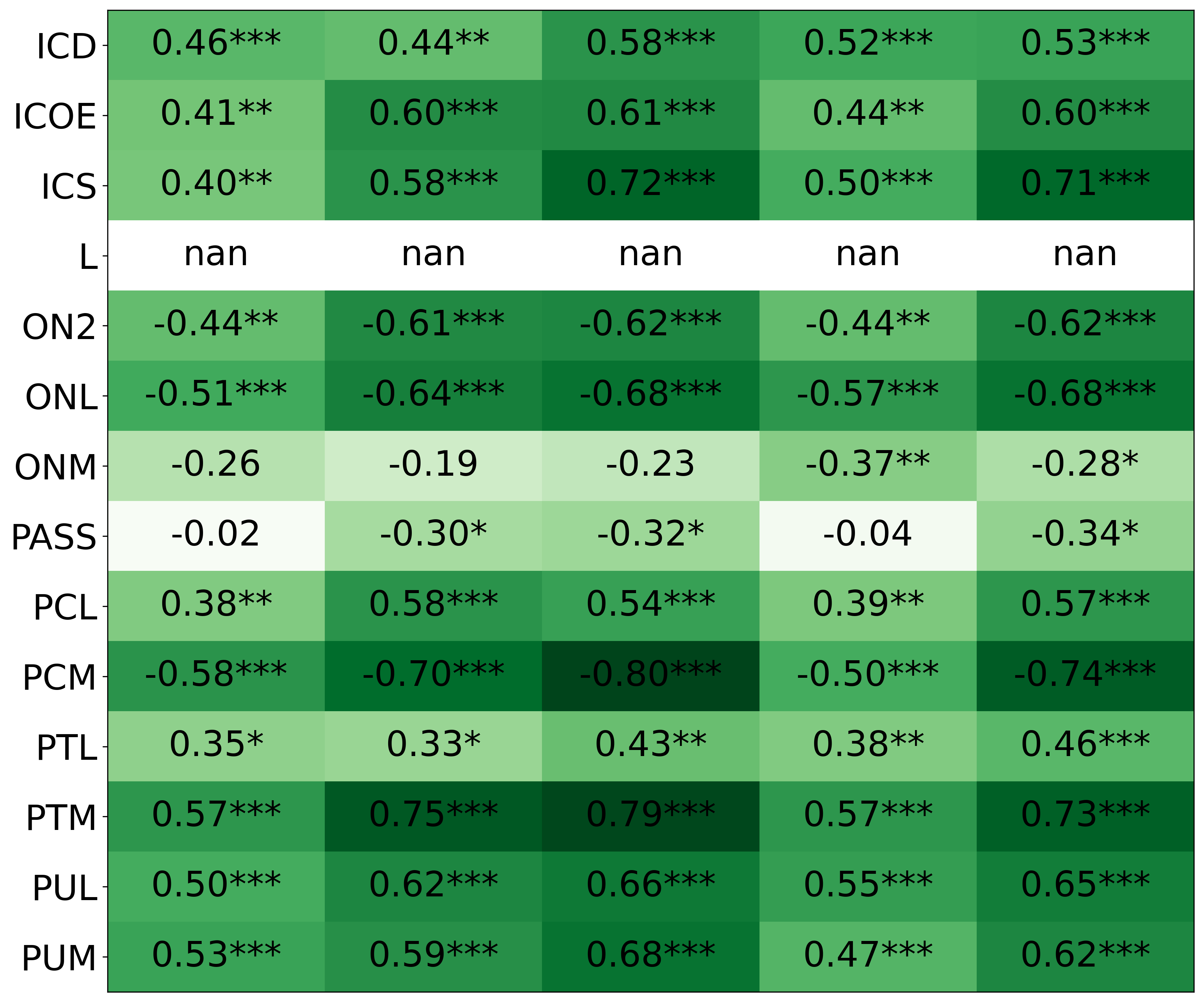
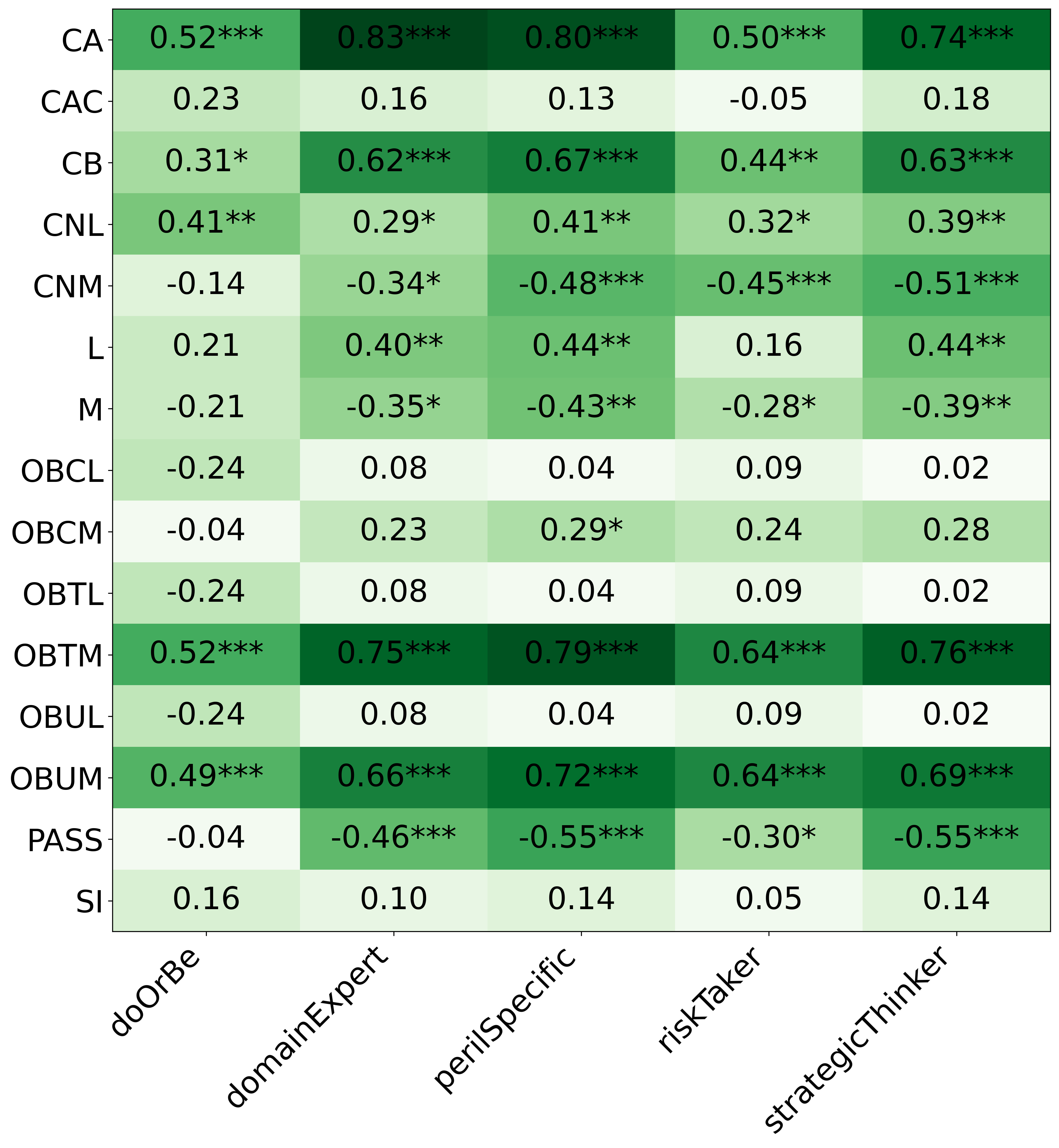
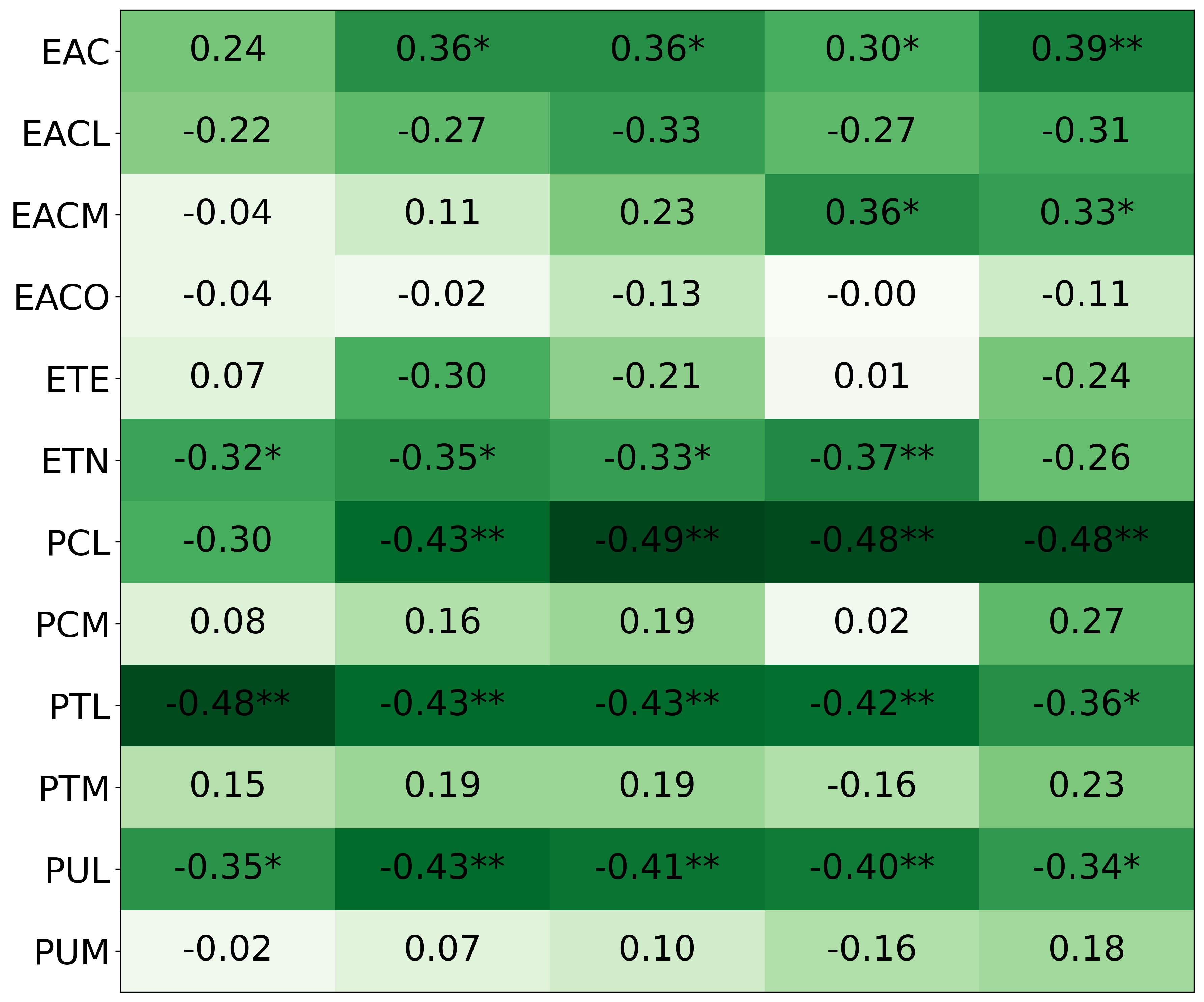
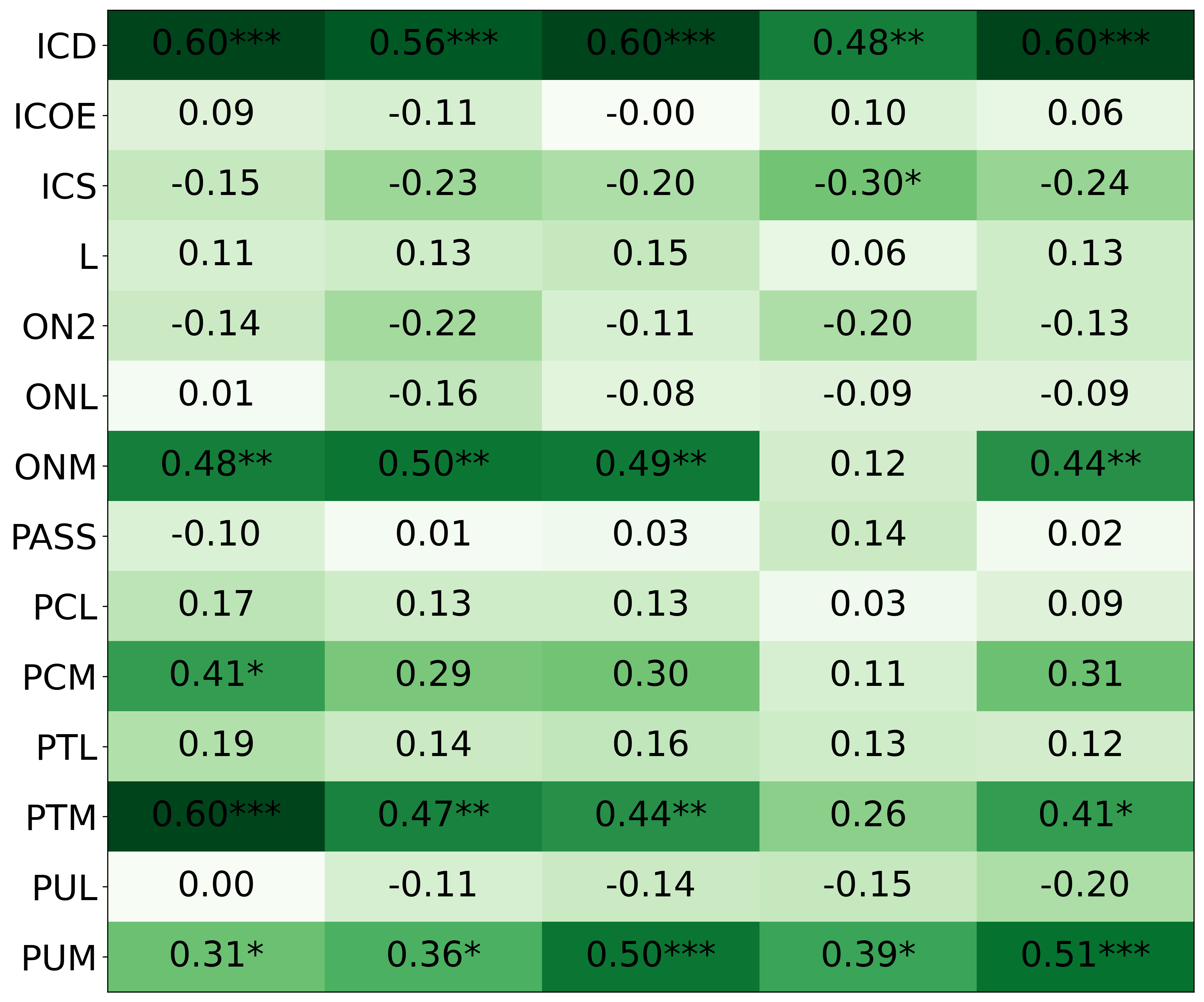
• We introduce the use of personality inventory questionnaires to translate personas into heuristic choices in an end-to-end fashion. We observe that this method results in heuristics that align with features of those personalities (much more so than when the questionnaire is not used). Without it the variation in how each persona translates into heuristics is small, suggesting that persona prompting alone does not lead to significant behavior differences.
In recent years, pre-trained LLMs have become increasingly difficult to fine-tune, due to a combination of model size, computation requirements, and reduced access to pre-trained models’ weights.
As a result, many researchers have turned to strategies exploring the extent to which prompts can be adjusted to improve performance. An approach rapidly gaining popularity is based on the concept of the persona, where a personality description is provided to the LLM, and it is asked to act in accordance with that personality (Tseng et al., 2024;Zhang et al., 2024;Bhandari et al., 2025a). New frameworks are rapidly emerging to compare different persona prompts on a variety of tasks (Pan et al., 2024;Lin et al., 2024;Samuel et al., 2024;Liu et al., 2024;Potertì et al., 2025), and datasets of high-quality LLM-generated personas are now ava
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.