📝 Original Info Title: Towards Efficient Hypergraph and Multi-LLM Agent Recommender SystemsArXiv ID: 2512.06590Date: 2025-12-06Authors: - Tendai Mukande (Research Ireland ML‑LABS, Dublin City University) – tendai.mukande2@mail.dcu.ie - Esraa Ali (ADAPT Centre, Dublin City University) – abdelmoe@tcd.ie - Annalina Caputo (School of Computing, Dublin City University) – annalina.caputo@dcu.ie - Ruihai Dong (Insight Research Ireland Centre for Data Analytics, University College Dublin) – ruihai.dong@ucd.ie - Noel O’Connor (Insight Research Ireland Centre for Data Analytics, Dublin City University) – Noel.OConnor@dcu.ie 📝 Abstract Recommender Systems (RSs) have become the cornerstone of various applications such as e-commerce and social media platforms. The evolution of RSs is paramount in the digital era, in which personalised user experience is tailored to the user's preferences. Large Language Models (LLMs) have sparked a new paradigm - generative retrieval and recommendation. Despite their potential, generative RS methods face issues such as hallucination, which degrades the recommendation performance, and high computational cost in practical scenarios. To address these issues, we introduce HGLMRec, a novel Multi-LLM agent-based RS that incorporates a hypergraph encoder designed to capture complex, multi-behaviour relationships between users and items. The HGLMRec model retrieves only the relevant tokens during inference, reducing computational overhead while enriching the retrieval context. Experimental results show performance improvement by HGLMRec against state-of-the-art baselines at lower computational cost.
💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content Towards Efficient Hypergraph and Multi-LLM Agent
Recommender Systems
Tendai Mukande
Research Ireland ML-LABS
Dublin City University
Dublin, Ireland
tendai.mukande2@mail.dcu.ie
Esraa Ali
ADAPT Centre
Dublin City University
Dublin, Ireland
abdelmoe@tcd.ie
Annalina Caputo
School of Computing
Dublin City University
Dublin, Ireland
annalina.caputo@dcu.ie
Ruihai Dong
Insight Research Ireland Centre for
Data Analytics
University College Dublin
Dublin, Ireland
ruihai.dong@ucd.ie
Noel O’Connor
Insight Research Ireland Centre for
Data Analytics
Dublin City University
Dublin, Ireland
Noel.OConnor@dcu.ie
Abstract
Recommender Systems (RSs) have become the cornerstone of vari-
ous applications such as e-commerce and social media platforms.
The evolution of RSs is paramount in the digital era, in which per-
sonalised user experience is tailored to the user’s preferences. Large
Language Models (LLMs) have sparked a new paradigm - generative
retrieval and recommendation. Despite their potential, generative
RS methods face issues such as hallucination, which degrades the
recommendation performance, and high computational cost in
practical scenarios. To address these issues, we introduce HGLM-
Rec, a novel multi-LLM agent-based RS model that incorporates
a hypergraph encoder designed to capture complex relationships
between users and items. The HGLMRec model retrieves only the
relevant tokens during inference, reducing computational overhead
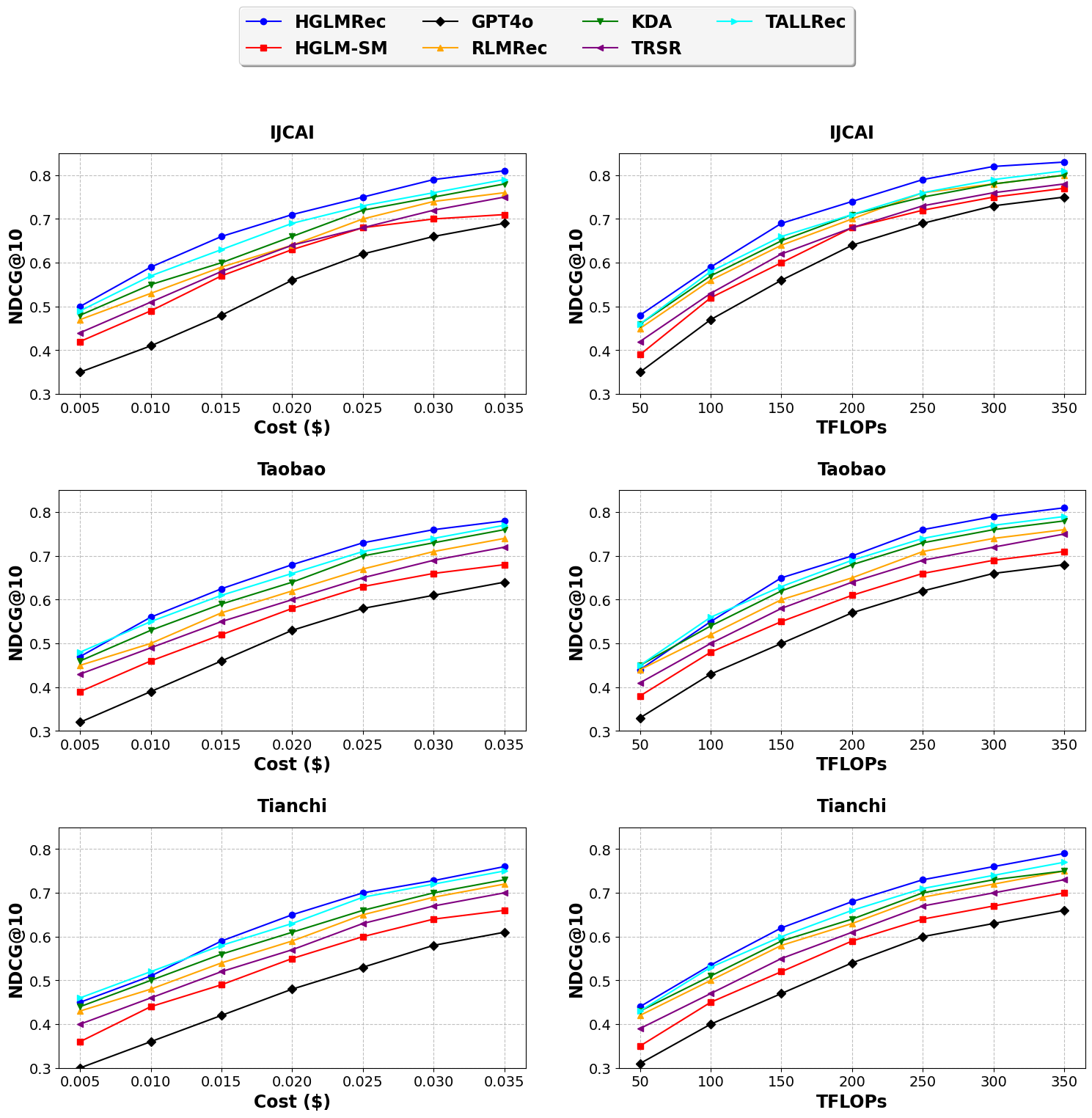
while enriching the retrieval context. Experimental results show
performance improvement by HGLMRec against state-of-the-art
baselines at lower computational cost.
CCS Concepts
• Information systems →Recommender systems.
Keywords
LLM, Mixture of Agents, Hypergraph Neural Networks, Computa-
tional Efficiency.
ACM Reference Format:
Tendai Mukande, Esraa Ali, Annalina Caputo, Ruihai Dong, and Noel
O’Connor. 2025. Towards Efficient Hypergraph and Multi-LLM Agent Rec-
ommender Systems. In Proceedings of (Preprint). ACM, New York, NY, USA,
8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/nnnnnnn.nnnnnnn
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Preprint,
© 2025 Copyright held by the owner/author(s).
ACM ISBN 978-x-xxxx-xxxx-x/YYYY/MM
https://doi.org/10.1145/nnnnnnn.nnnnnnn
1
Introduction
In real-world recommendation scenarios, user preferences evolve
continuously over time, leading to complex and dynamic interaction
patterns [23]. Static representation learning models [9, 16, 31] often
struggle to capture these dynamics as they assume a static structure
and ignore the time-dependent nature of user-item interactions
[44]. With the recent surge in LLMs, a new paradigm in RSs has
emerged that combines information retrieval with LLMs to produce
contextually relevant recommendations [5, 20, 26, 29]. Generative
recommendation models have shown benefits, such as semantic
understanding and interactive reasoning, which can improve the
relevance and quality of recommendations by generating output
that aligns with user preferences [21, 33].
Despite these advances, most of the existing LLM-based RS ap-
proaches face two major limitations. Firstly, hallucination, where
the model generates inaccurate or misleading recommendations,
can compromise the reliability of the system [13–15]. Secondly,
the high computational cost, resulting from the need to search
through large vocabularies or fine-tune LLMs on domain-specific
data, makes these methods impractical for real-time or large-scale
deployment [6, 34, 41]. Although pretraining or fine-tuning LLMs in
recommendation-specific datasets can improve performance, these
strategies require substantial computational resources [11, 22, 42],
domain expertise, and large volumes of high-quality data, further
complicating real-world implementation [46]. Consequently, effi-
cient recommendation models are needed that can adapt to evolving
user preferences and dynamic interaction patterns while maintain-
ing high accuracy [12, 36].
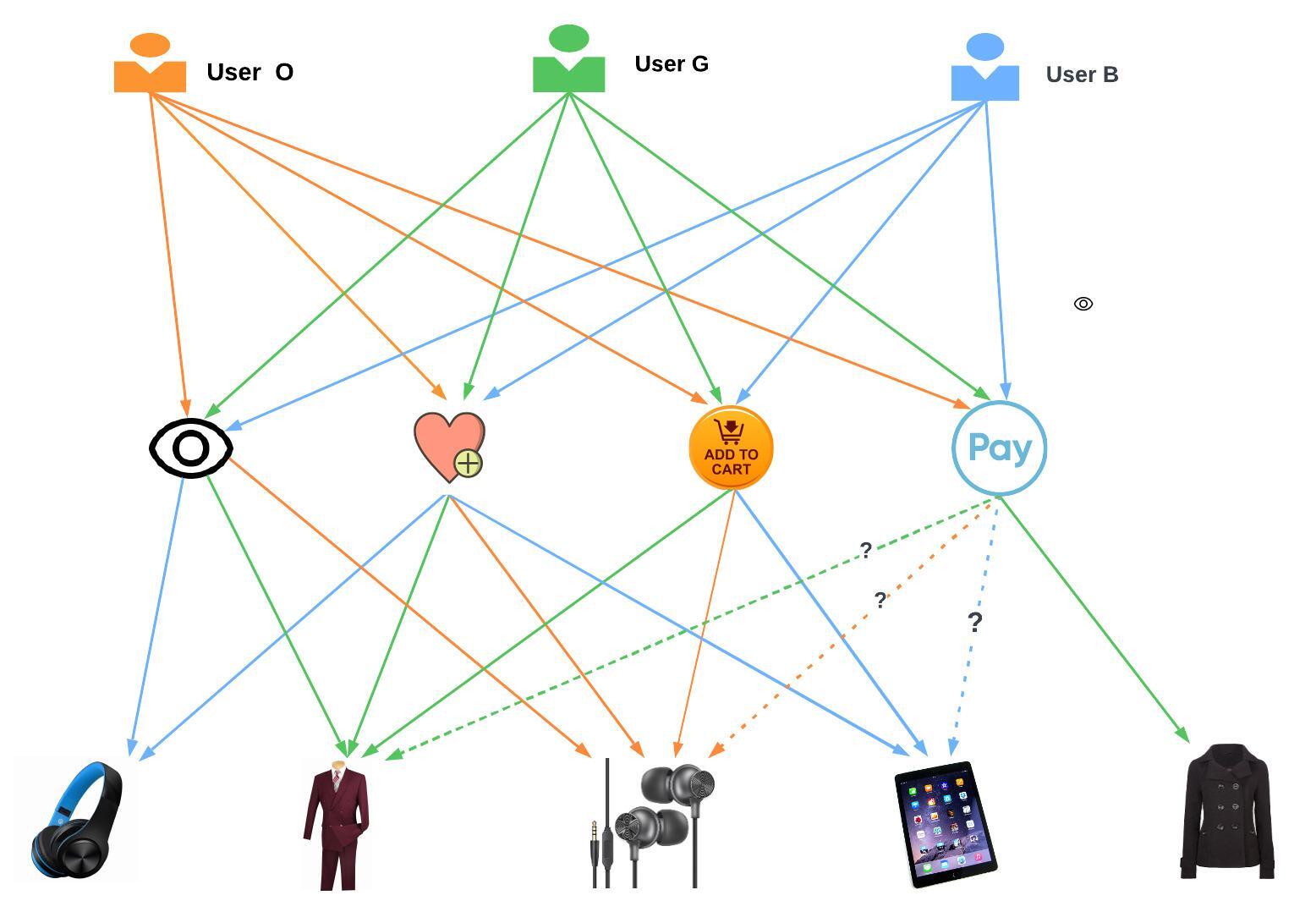
Motivated by these challenges, we explore whether hypergraph
representation learning can be harnessed to improve recommen-
dation performance in dynamic, multi-behaviour scenarios. As il-
lustrated in Figure 1, hypergraphs allow modelling of higher-order
user-item interactions, unlike bipartite graphs that are limited to
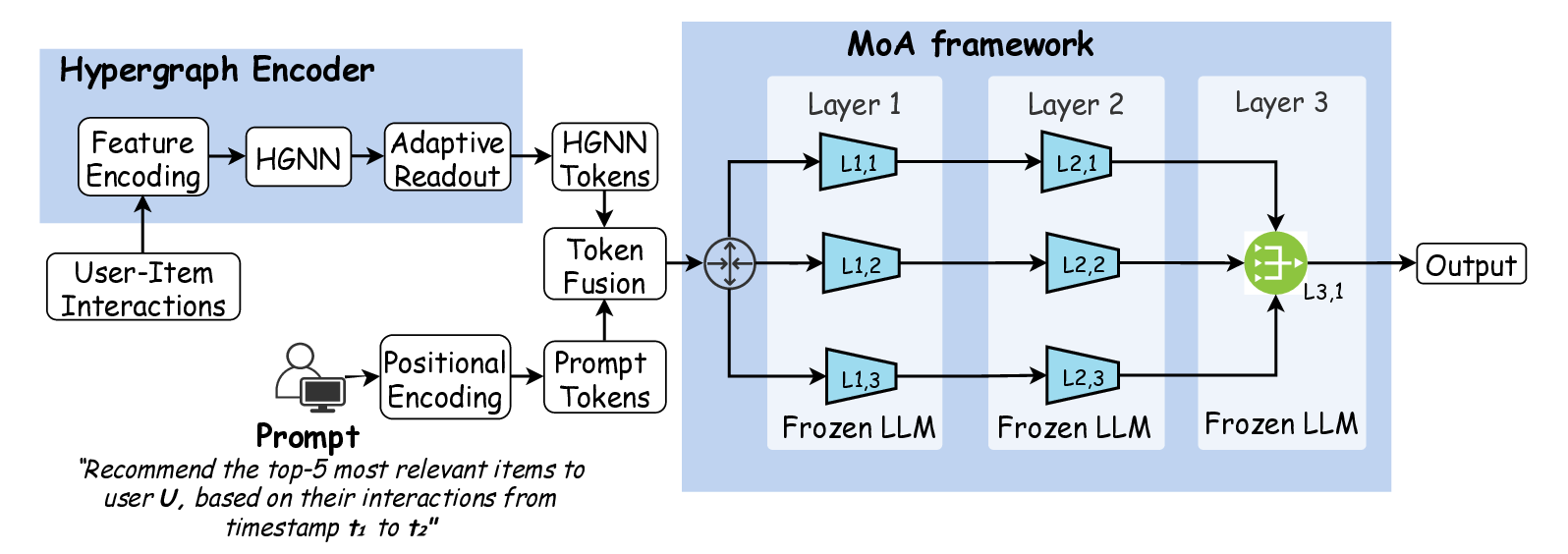
pairwise interactions [19]. We propose HGLMRec, a novel frame-
work that integrates an HGNN encoder with an MoA architecture.
The central idea of HGLMRec is to enhance modelling of user-item
arXiv:2512.06590v1 [cs.IR] 6 Dec 2025
Preprint,
Tendai Mukande, Esraa Ali, Annalina Caputo, Ruihai Dong, and Noel O’Connor
interactions, allowing the model to capture higher-order depen-
dencies across multiple behaviours. Hyperedges in this represen-
tation connect a user with multiple items and behavioural types,
generating dense token embeddings that encode local and global
preference patterns [2]. These embeddings are then processed by
the MoA framework, which employs multiple specialised agents to
refine rec
📸 Image Gallery
Reference This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.