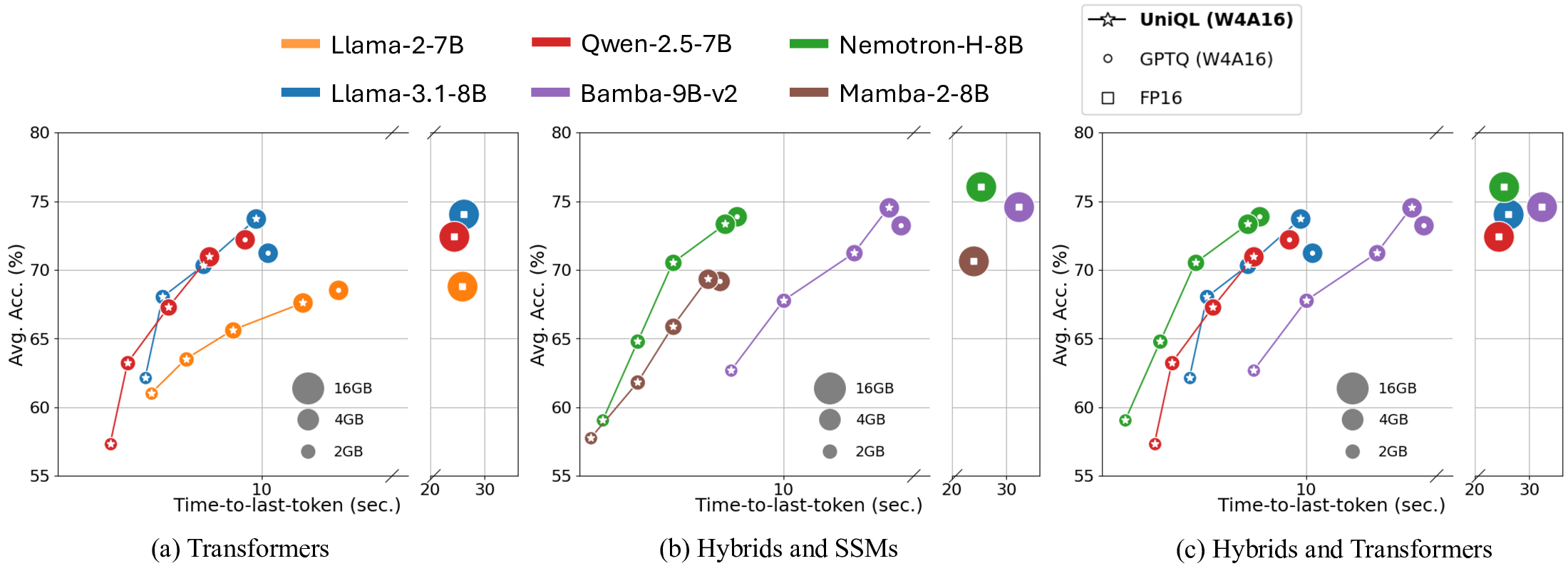
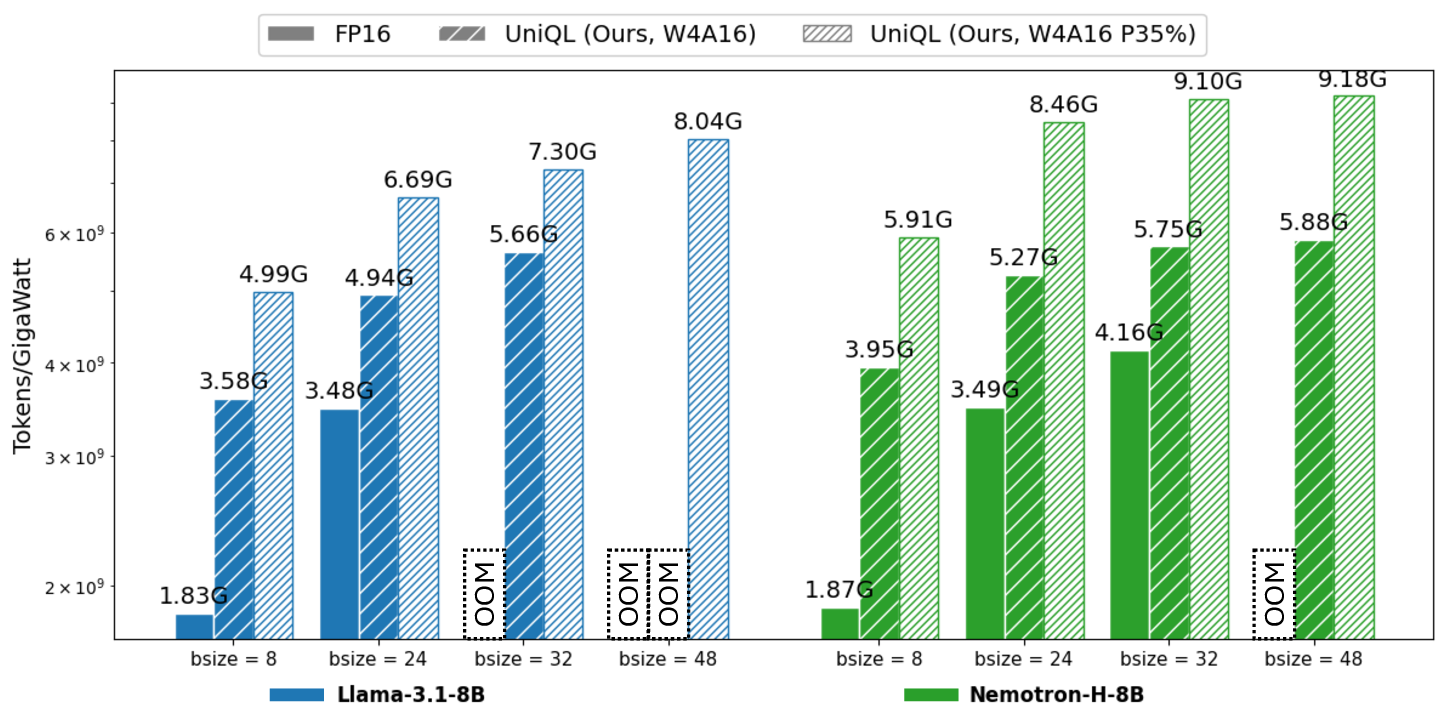
Deploying large language models (LLMs) on mobile platforms faces significant challenges due to the limited memory and shared computational resources of the device. Resource availability may be an issue as it is directly impacted by the current device workload, adding to the uncertainty of model deployment. We introduce UniQL, a unified post-training quantization and low-rank compression framework with on-device configurable pruning rates for edge LLMs. UniQL is a general framework that integrates quantization and low-rank compression for Transformers, State Space Models (SSMs), and hybrid models to support diverse edge applications. In our proposed joint framework, we introduce an efficient structured weight-sorting method that speeds up computation by 20x, quantization-aware singular value decomposition (SVD) to minimize quantization errors, state-aware weight sorting for SSMs, and a fused rotary positional embedding (RoPE) kernel for pruned models. Our framework performs weight-sorting, fine-tuning, and quantization in the cloud in a single-pass workflow, while enabling on-device configurable pruning rates up to 35%. Our experiments show that quantized and pruned models achieve a memory reduction of 4x-5.7x and a token-throughput improvement of 2.7x-3.4x, maintaining accuracy within 5% of the original models at 15% pruning across Transformers (Llama3 and Qwen2.5), SSMs (Mamba2), and hybrid models (Nemotron-H and Bamba-v2). The code and quantized models are available at: https://github.com/enyac-group/UniQL.
Numerous emerging applications, such as question answering on VR/AR glasses, are powered by large language models (LLMs). Yet, models with parameters on the order of billions (e.g., 10B) restrict the platforms and applications that can utilize them. Extensive research investigates quantization [Xiao et al., 2023, Lin et al., 2024a,b] and compression [Qinsi et al., 2025, Wang et al., 2025b, Lin et al., 2025, Wang et al., 2025c] for LLMs to lower memory and computing needs for deployment. However, the limited and shared resources (e.g., the unified memory architecture) on edge devices still pose huge challenges for model deployment. Since resources (e.g., memory) are dynamically managed by the operating system, the availability of the resources highly depends on the system workload. As a result, the pre-compressed or pre-quantized language models with fixed model sizes may not run on a device under high workload scenarios.
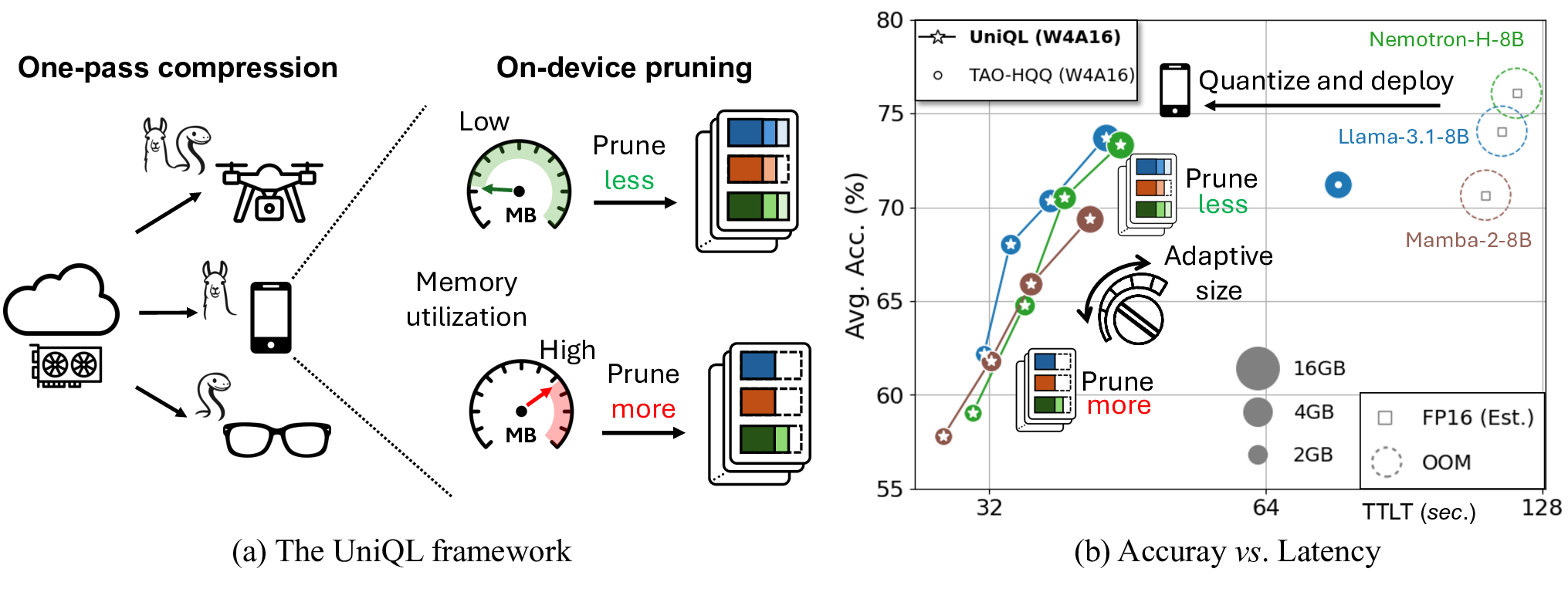
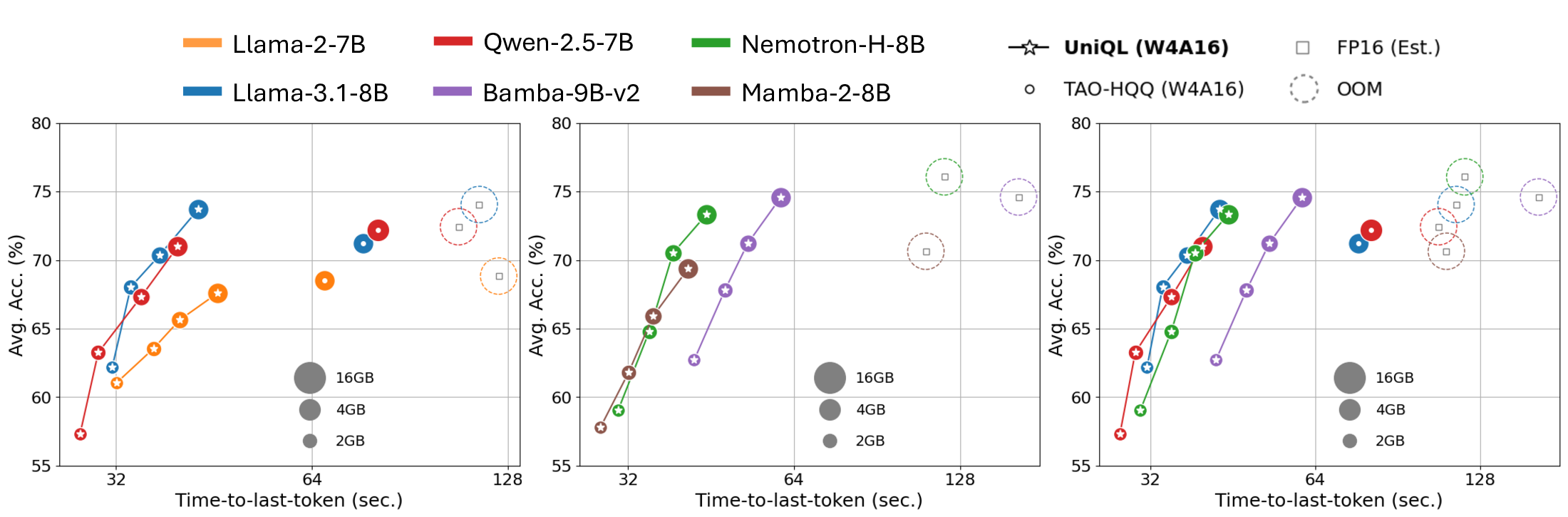
Figure 1: (Proposed framework overview.) UniQL supports Transformers, SSMs, and hybrid models, enabling one-shot compression using a single server-class GPU. The on-device pruning of the quantized model is feasible and configurable based on the current device workload. We present actual latency on Nano 8G in relation to accuracy for different pruning rates across three distinct models on the right. Circle sizes correspond to model sizes. Latency is measured using 512 prefilling tokens and 512 generated tokens on Nano.
Re-compressing or re-quantizing the model to fit it into available memory is not practical due to the high computational costs, i.e., several hours on cloud GPUs [Lin et al., 2025, Frantar et al., 2023]. A solution to address this issue is storing several model replicas at different compression rates. Nonetheless, producing pre-compressed replicas of different sizes is both time-and storage-consuming. Alternatively, employing elastic training [Cai et al., 2024[Cai et al., , 2025] ] to a pre-trained model enables the derivation of various sizes from the model. Yet, this approach requires availability of GPU resources and training on curated datasets to support flexible deployment for one specific type of model, e.g., Llama-3.1-8B, limiting the applicability.
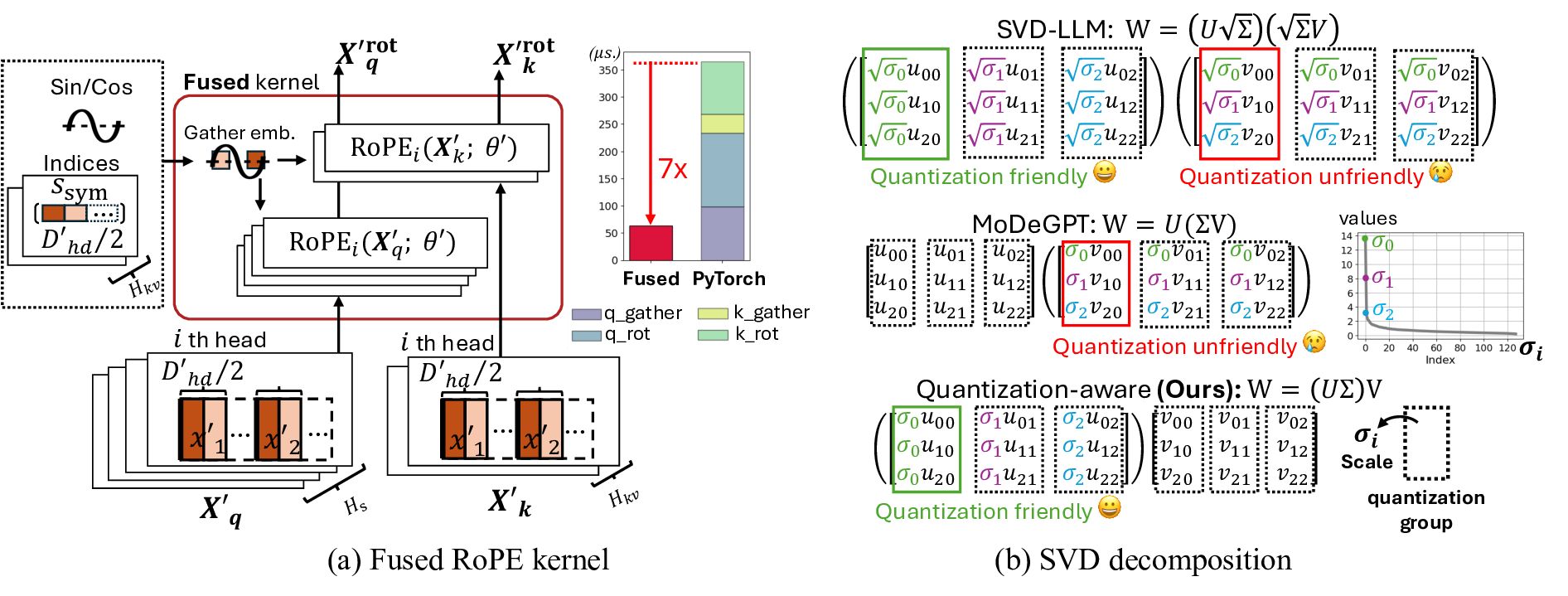
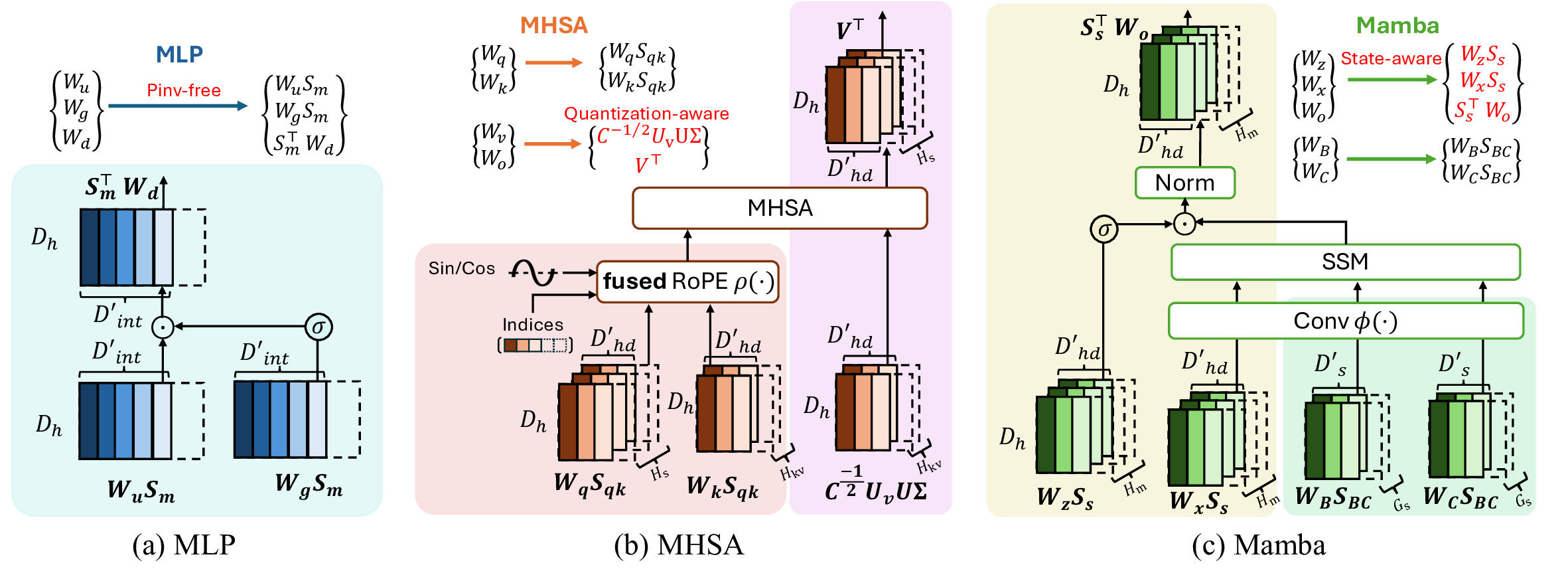
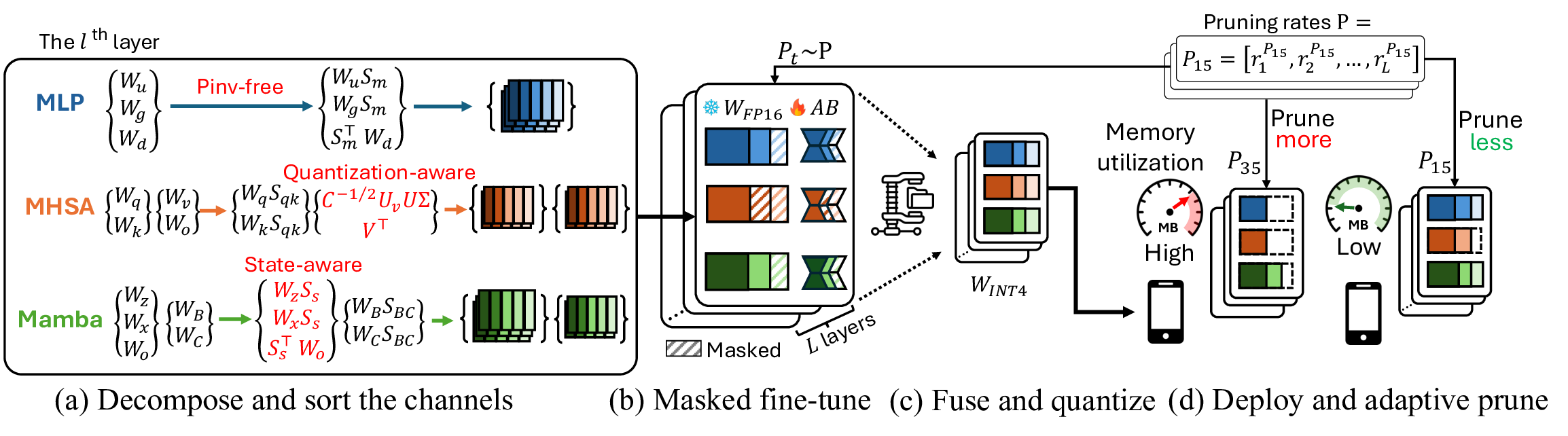
Our proposed work addresses this issue under the post-training setting when access to server-class GPUs and curated datasets is limited. As illustrated in Figure 1, our framework supports quantization and structured pruning, performing efficiently on one server GPU. Our objective is to support and design compression algorithms for various model architectures, including Transformers, State Space Models (SSMs), and hybrid models. Our pipeline is shown in Figure 2. We group the weights within the block, gather channel corrections from a calibration dataset, and apply weight-sorting algorithms. Our multi-layer perceptron (MLP) weights are decomposed without any gradient information or expensive full matrix pseudo-inverse, yielding a speedup of 20× compared to prior art [Lin et al., 2025]. For 𝑊 𝑣 and 𝑊 𝑜 in self-attention layers, we develop a quantization-aware singular value decomposition (SVD) of weights to minimize quantization errors. For SSMs and hybrids models, we find that SSM blocks are particularly sensitive to state matrices, and propose a state-aware weight-sorting strategy to mitigate this. We then apply a masked fine-tuning to the sorted model. In each fine-tuning step, a global pruning rate 𝑃 𝑡 is chosen randomly, masking the least ranked channels in the layers. The refined model is then quantized in low bit-width and deployed on the edge platform. The entire process is performed once in the cloud. For the deployed model, we prune the models according to a specified global pruning rate, e.g., 𝑃 35 = 35%, on the edge device. Our contributions are summarized as follows:
• Our study explores a broad spectrum of models, such as Transformers, SSMs, and hybrid, and introduces efficient pruning and quantization-friendly algorithms for these blocks.
• To the best of our knowledge, UniQL is the first post-training framework that systematically combines quantization and structured pruning for LLMs in a one-shot fashion.
• We develop an integrated kernel to support the pruned RoPE, conducting comprehensive profiling to demonstrate 2.7×-3.4× latency speedups for adaptive pruning on edge devices.
Transformer compression. Prior work has aimed to reduce the size of Transformer-based LLMs for efficient deployment by utilizing low bit-width data types [Xiao et al., 2023, Lin et al., 2024b,a, Zhao et al., 2024, Ashkboos et al., 2024b, Liu et al., 2025], minimizing storage needs and optimizing hardware for low-bit computations. Unstructured [Frantar andAlistarh, 2023, Sun et al., 2024] and semi-structured pruning (e.g., N:M sparsity) [Li et al., 2023] for reducing model size by removing specific parameters while minimizing accuracy loss. Nonetheless, deploying such methods requires specialized hardware [Taka et al., 2025, Xia
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.