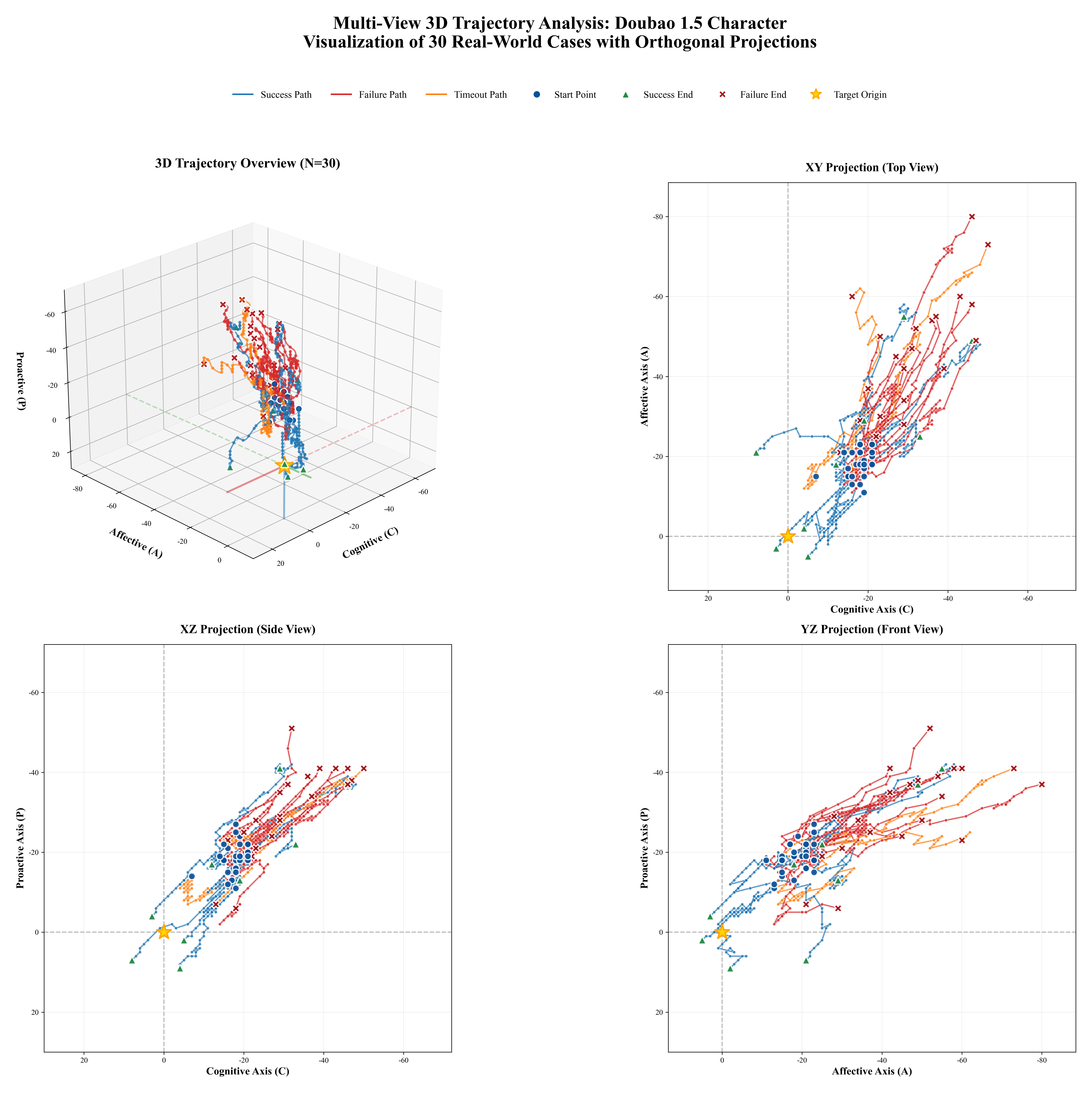
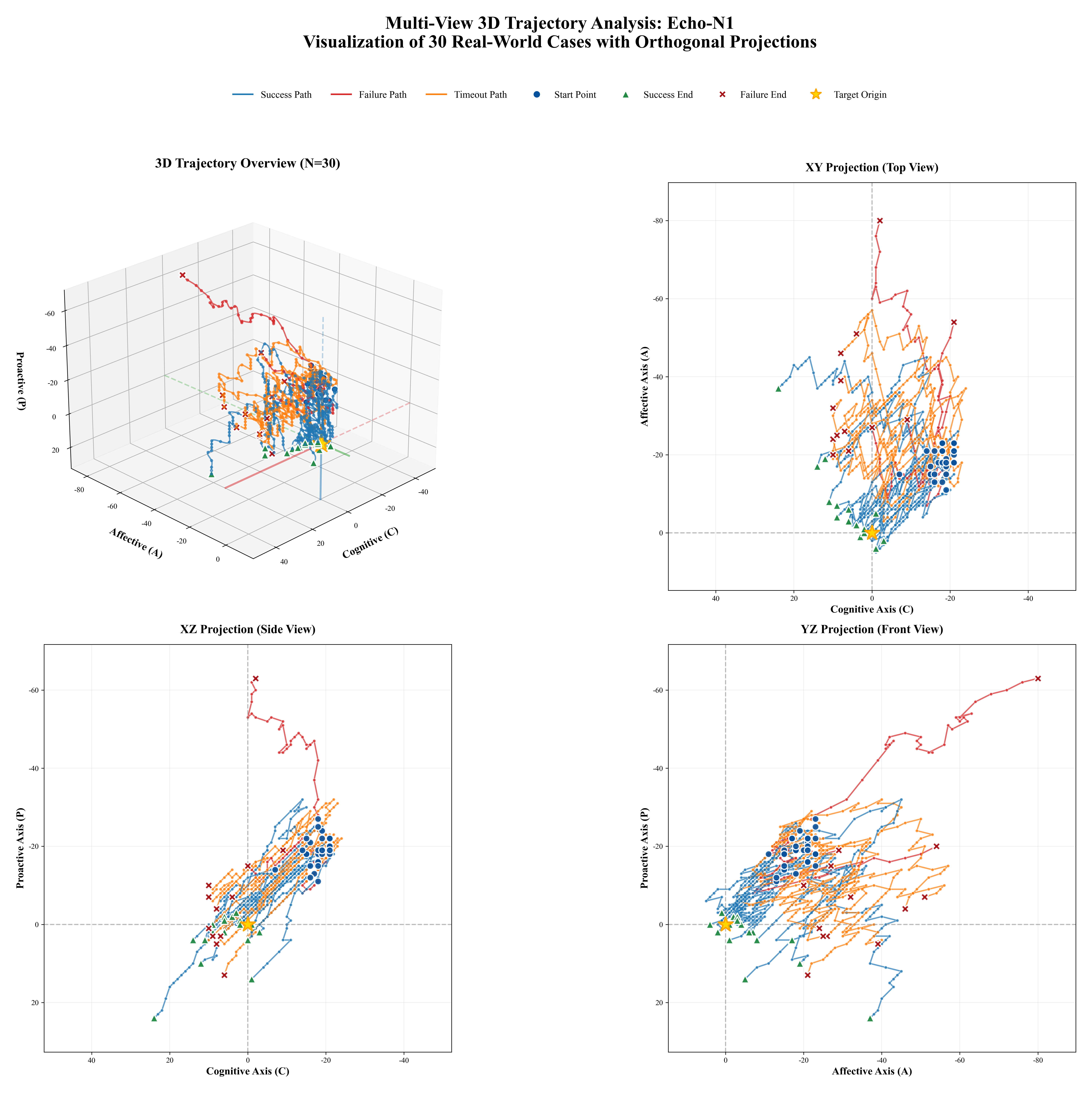
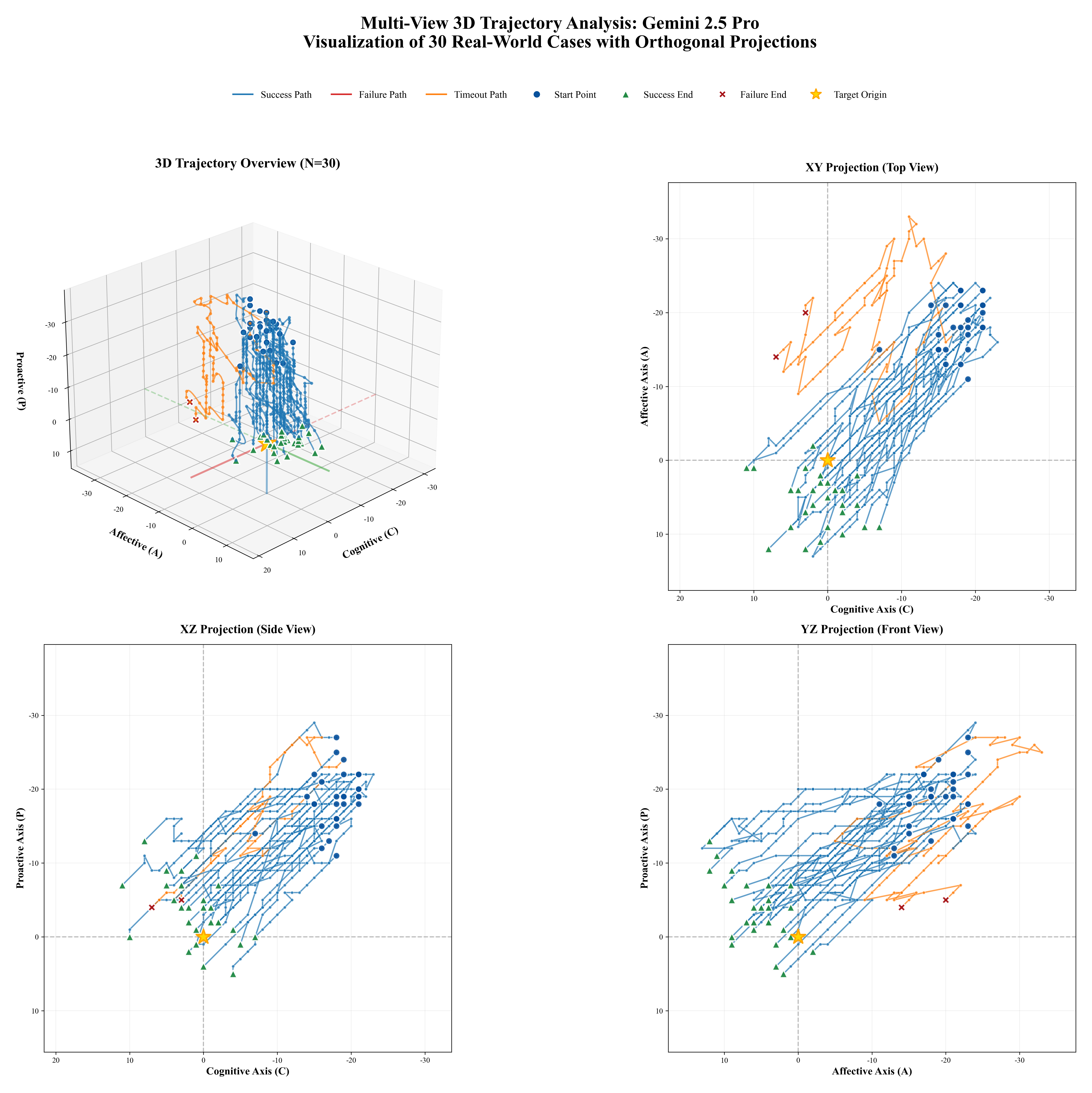
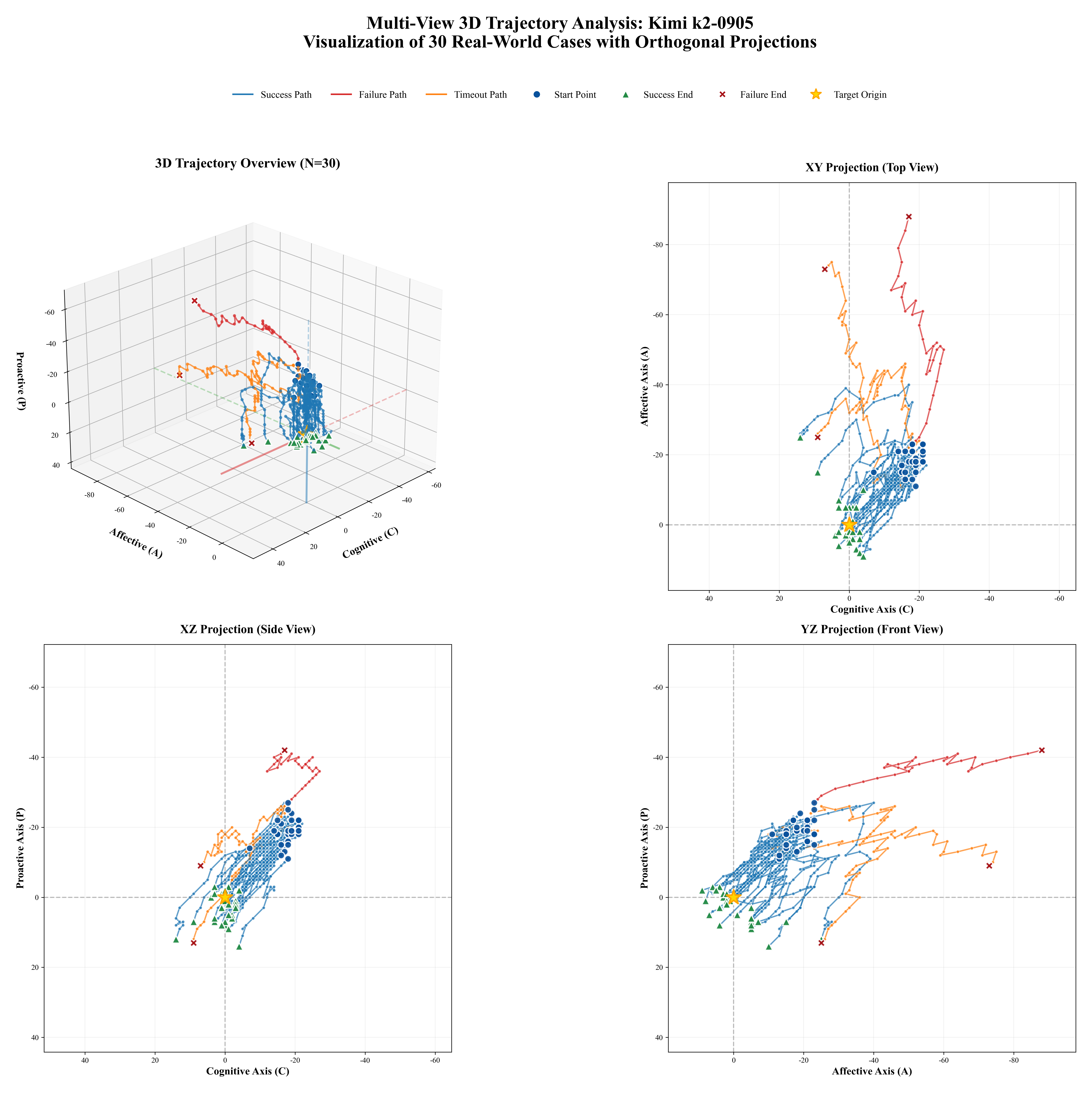
📝 Original Info Title: 대화형 인격 맞춤 강화학습 감성 지능의 새로운 프레임워크ArXiv ID: 2512.00344Date: 2025-12-02Authors: Naifan Zhang, Ruihan Sun, Ruixi Su, Shiqi Ma, Shiya Zhang, Xianna Weng, Xiaofan Zhang, Yuhan Zhan, Yuyang Xu, Zhaohan Chen, Zhengyuan Pan, Ziyi Song📝 Abstract The LLM field has spent a year perfecting RL for tasks machines already excel at, math, code, and deterministic reasoning, while completely sidestepping the domain that actually defines human intelligence: subjective, emotionally grounded, personality sensitive conversation. This space has often been regarded as inherently subjective and challenging to formalize, making it appear unsuitable for conventional RL pipelines. We show that it is not only possible and it is a solvable and transformative RL problem. We propose the first framework that infers user personality on the fly and optimizes model behavior toward personalized conversational preferences. Contrary to the widespread belief that RL collapses in non-verifiable settings, our method produces consistent, robust, and dramatic improvements in humanlike interaction quality. We also introduce the first dynamic emotional intelligence evaluation suite to quantify these gains. Our model, which is introduced as Echo-N1, behaves far above its base version and outperforming the proprietary Doubao 1.5 Character. This work establishes a new frontier for RL: optimizing models for the deeply subjective, deeply human dimensions of conversation.
💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content Echo-N1: Affective RL Frontier
Team Echo∗,†, NatureSelect
Abstract
The LLM field has spent a year perfecting RL for tasks machines already excel at—math,
code, and deterministic reasoning—while completely sidestepping the domain that
actually defines human intelligence: subjective, emotionally grounded, personality-
sensitive conversation. This space has often been regarded as inherently subjective and
challenging to formalize, making it appear unsuitable for conventional RL pipelines. We
show that it is not only possible—it is a solvable and transformative RL problem. We
propose the first framework that infers a user’s personality on the fly and optimizes model
behavior toward personalized conversational preferences. Contrary to the widespread
belief that RL collapses in non-verifiable settings, our method produces consistent,
robust, and dramatic improvements in humanlike interaction quality. We also introduce
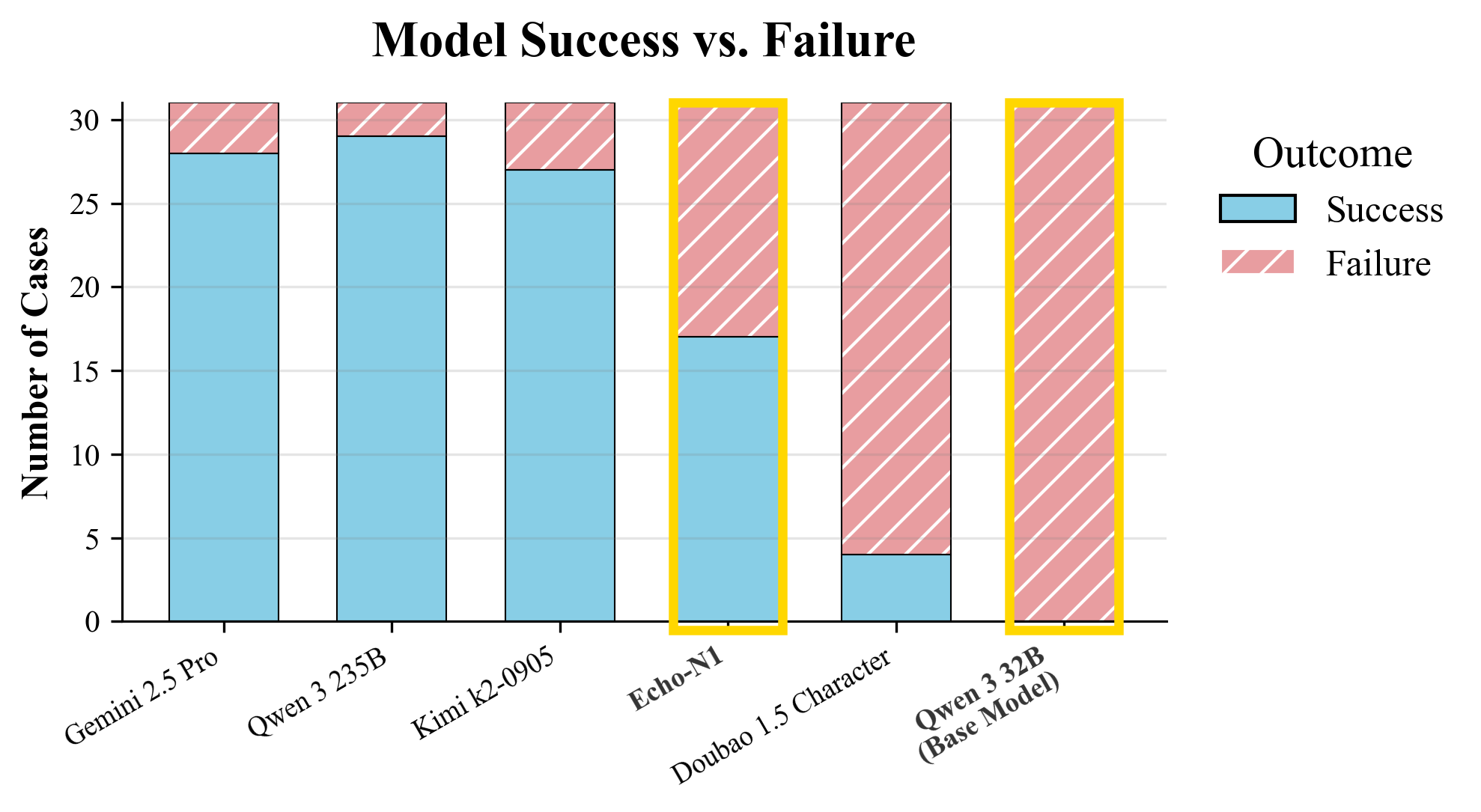
the first dynamic emotional-intelligence evaluation suite to quantify these gains. Our
32B model, which is introduced as Echo-N1, behaves far above its base version and
outperforming the proprietary Doubao 1.5 Character. This work establishes a new
frontier for RL: optimizing models for the deeply subjective, deeply human dimensions
of conversation.
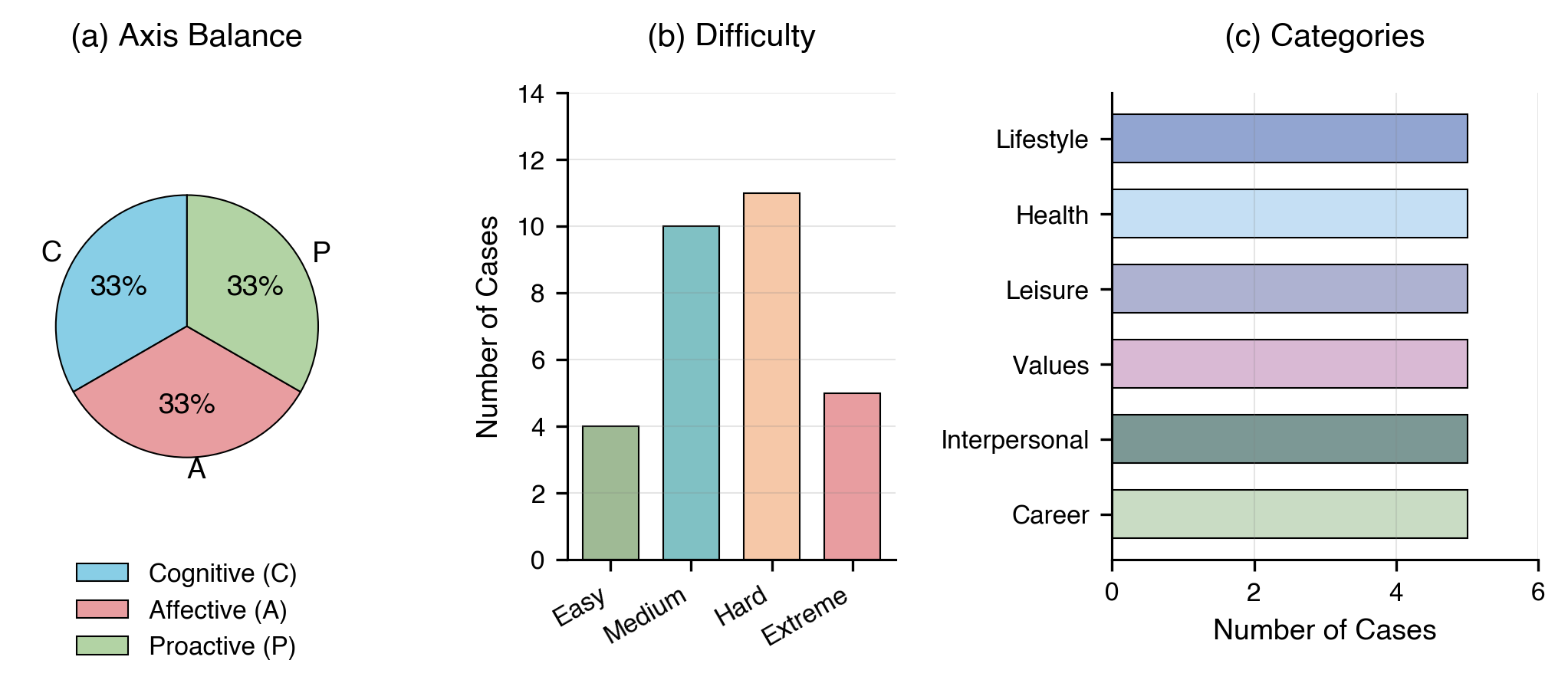
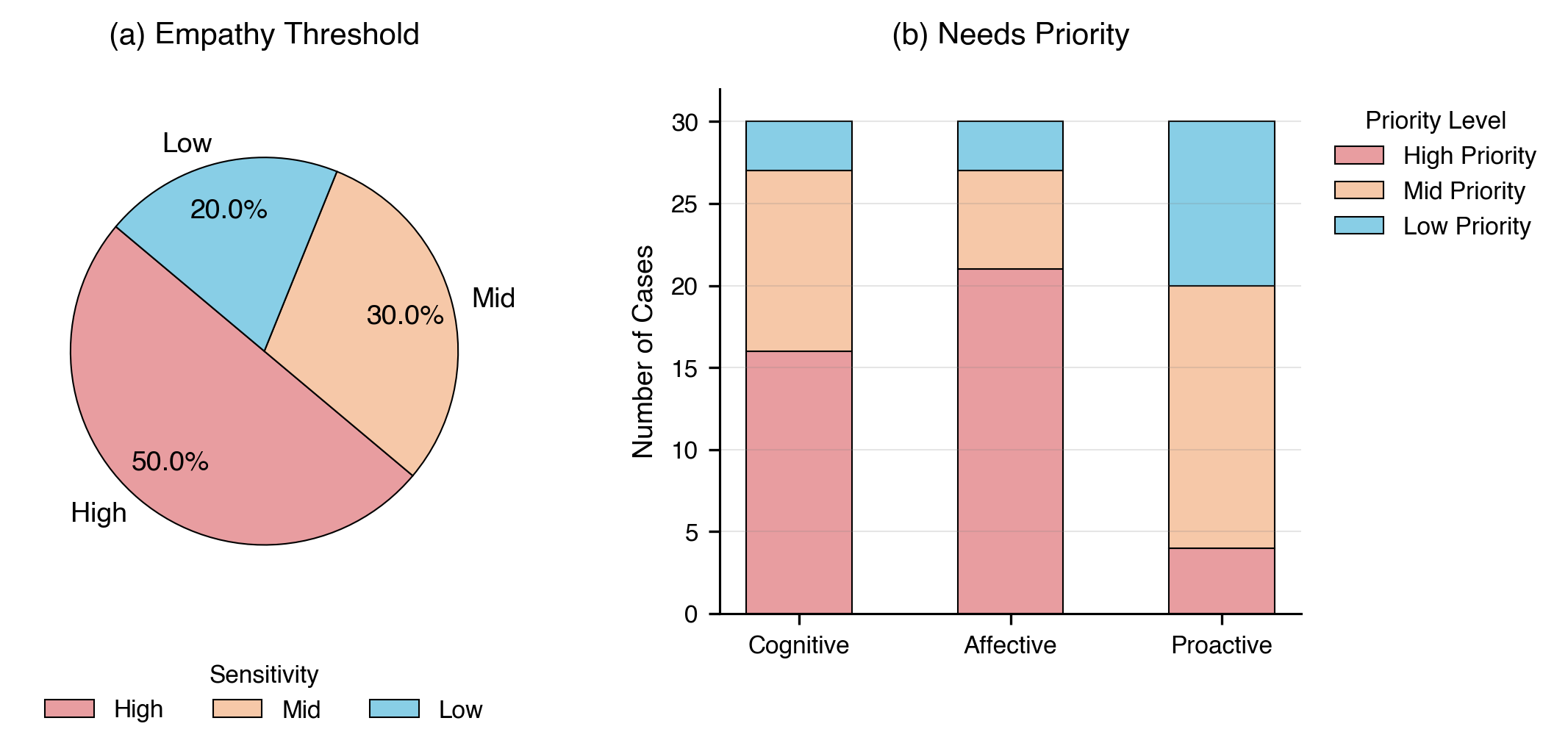
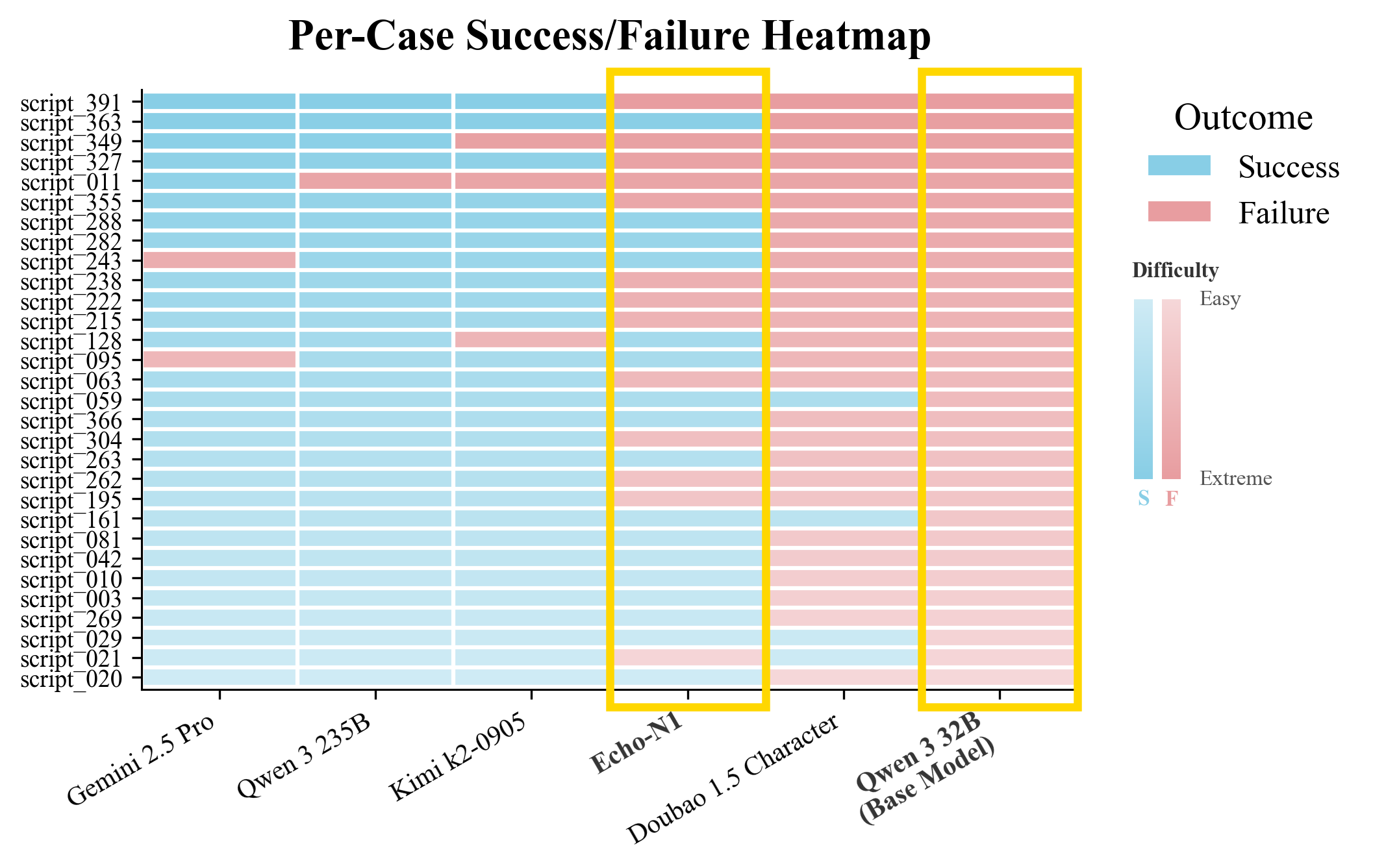
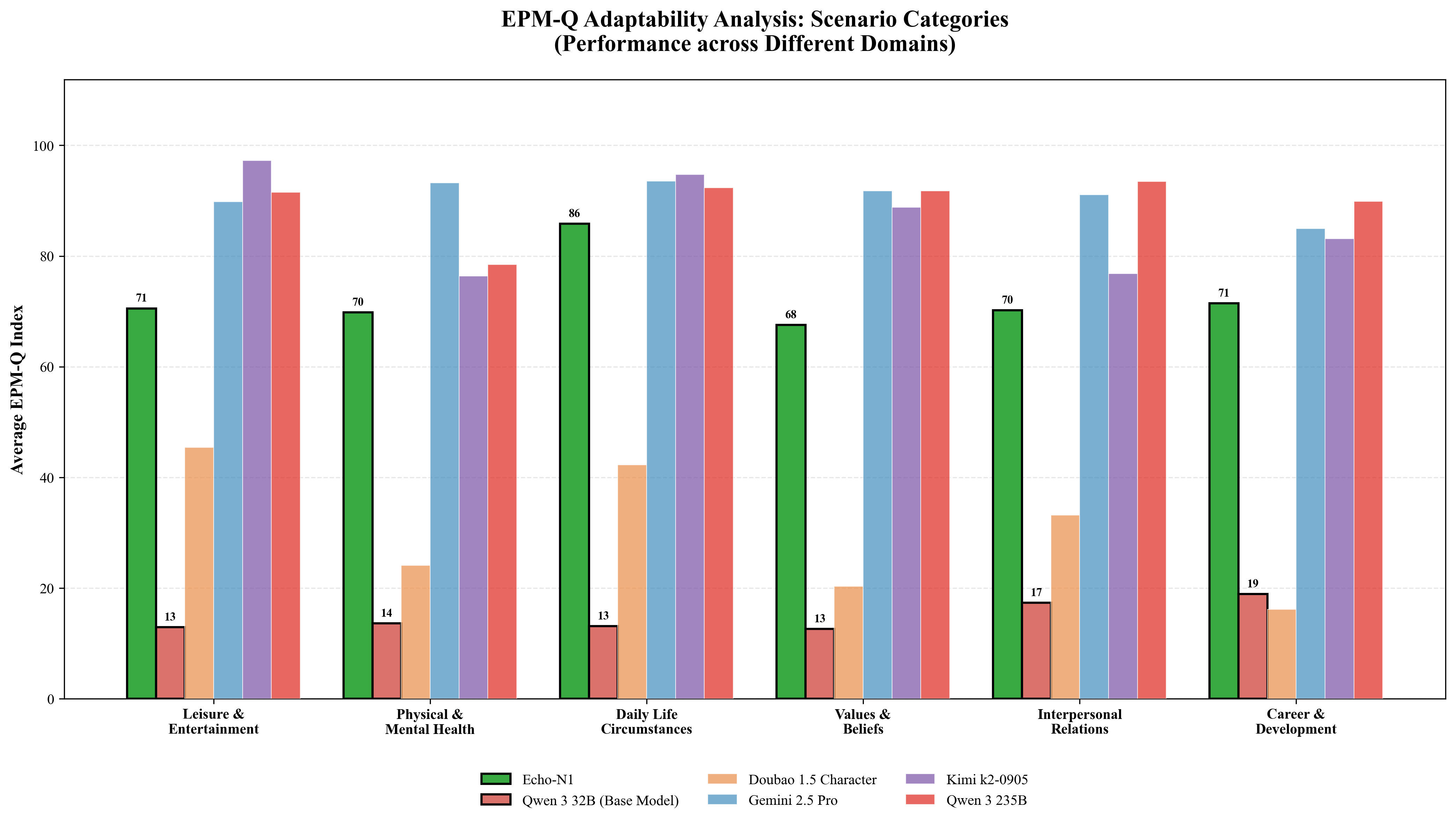
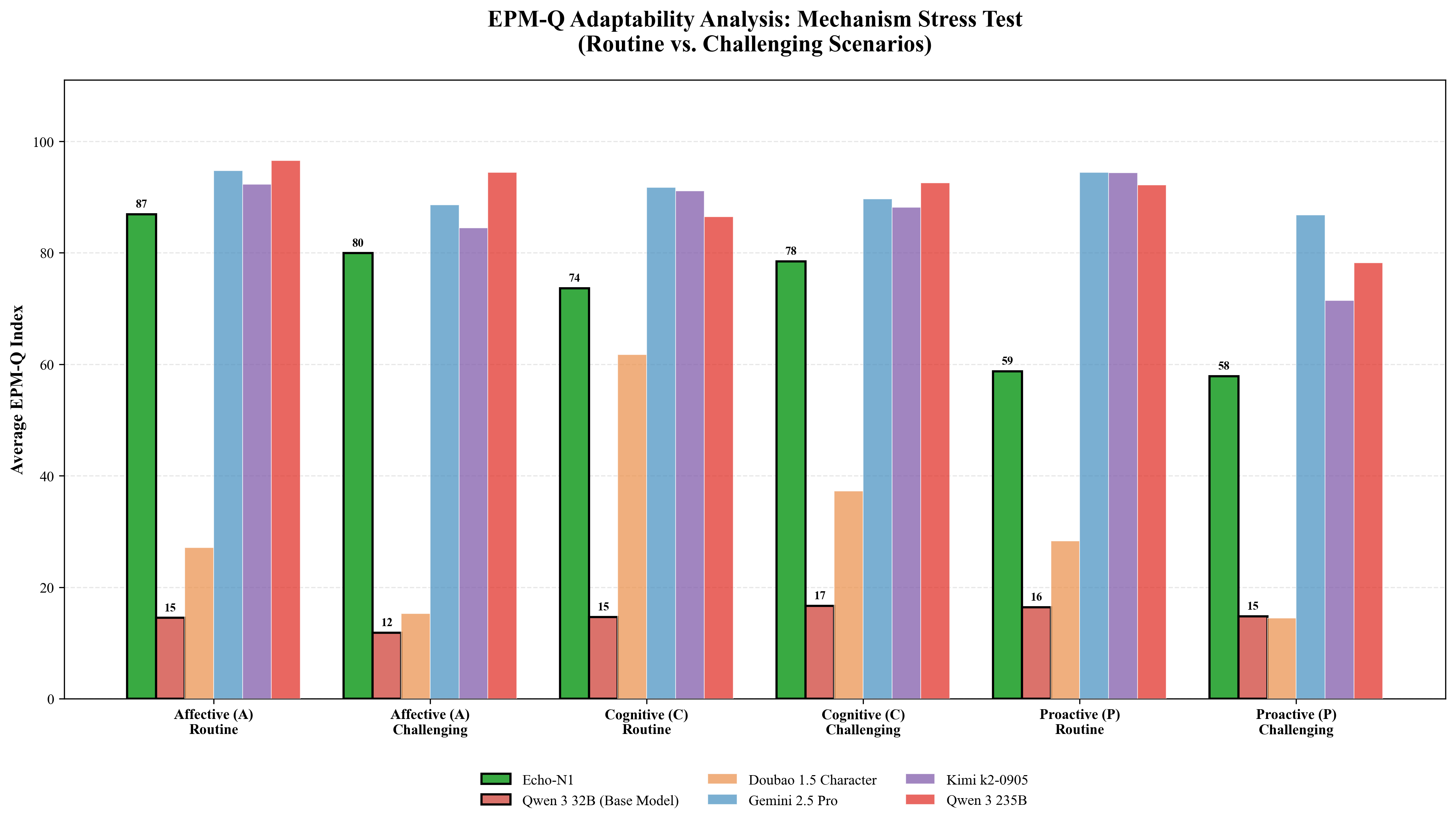
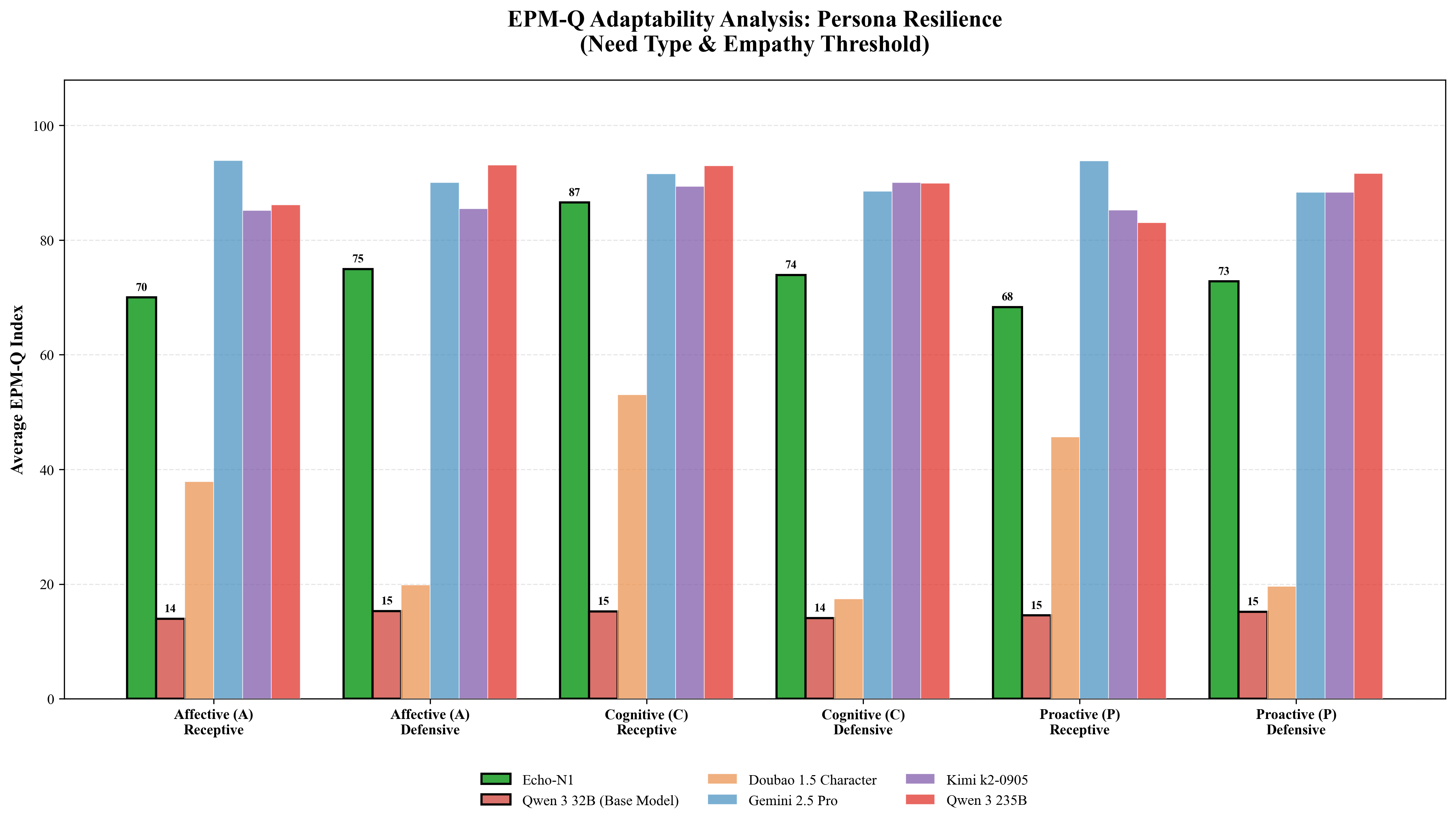
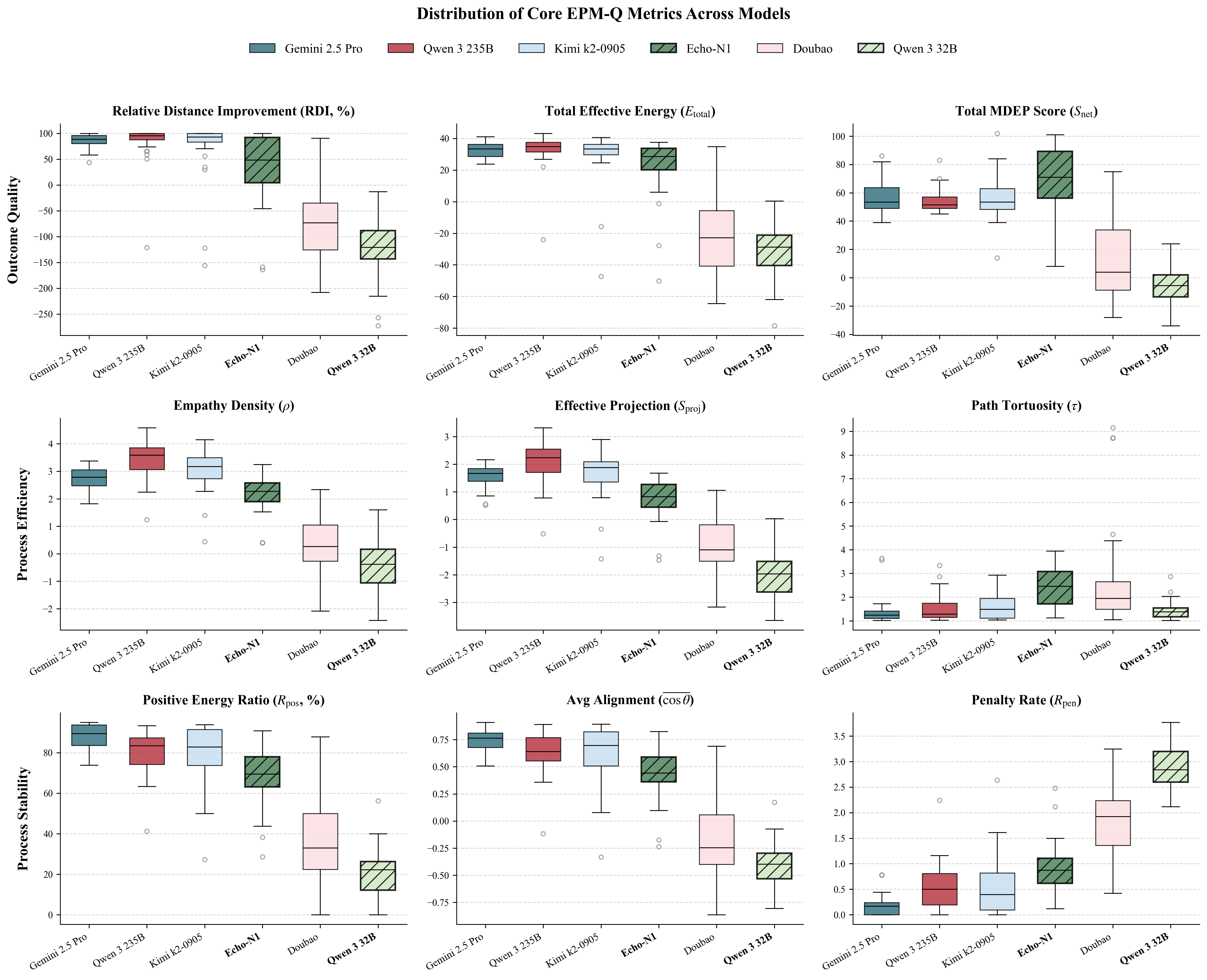
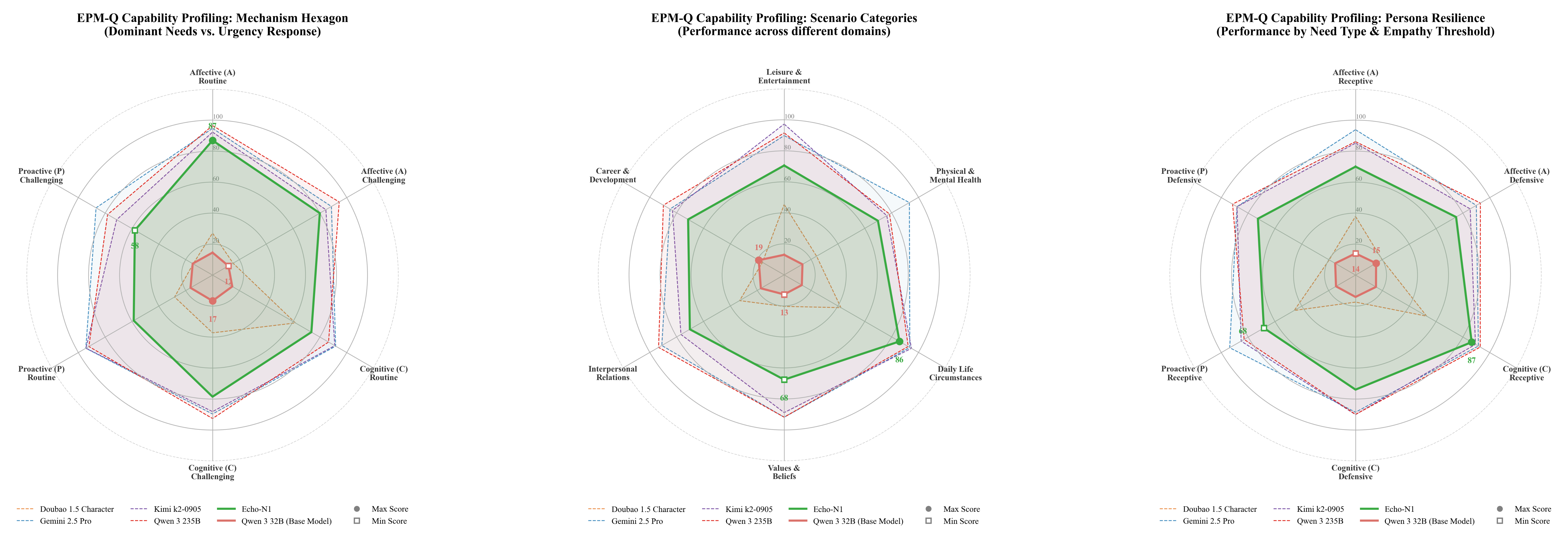
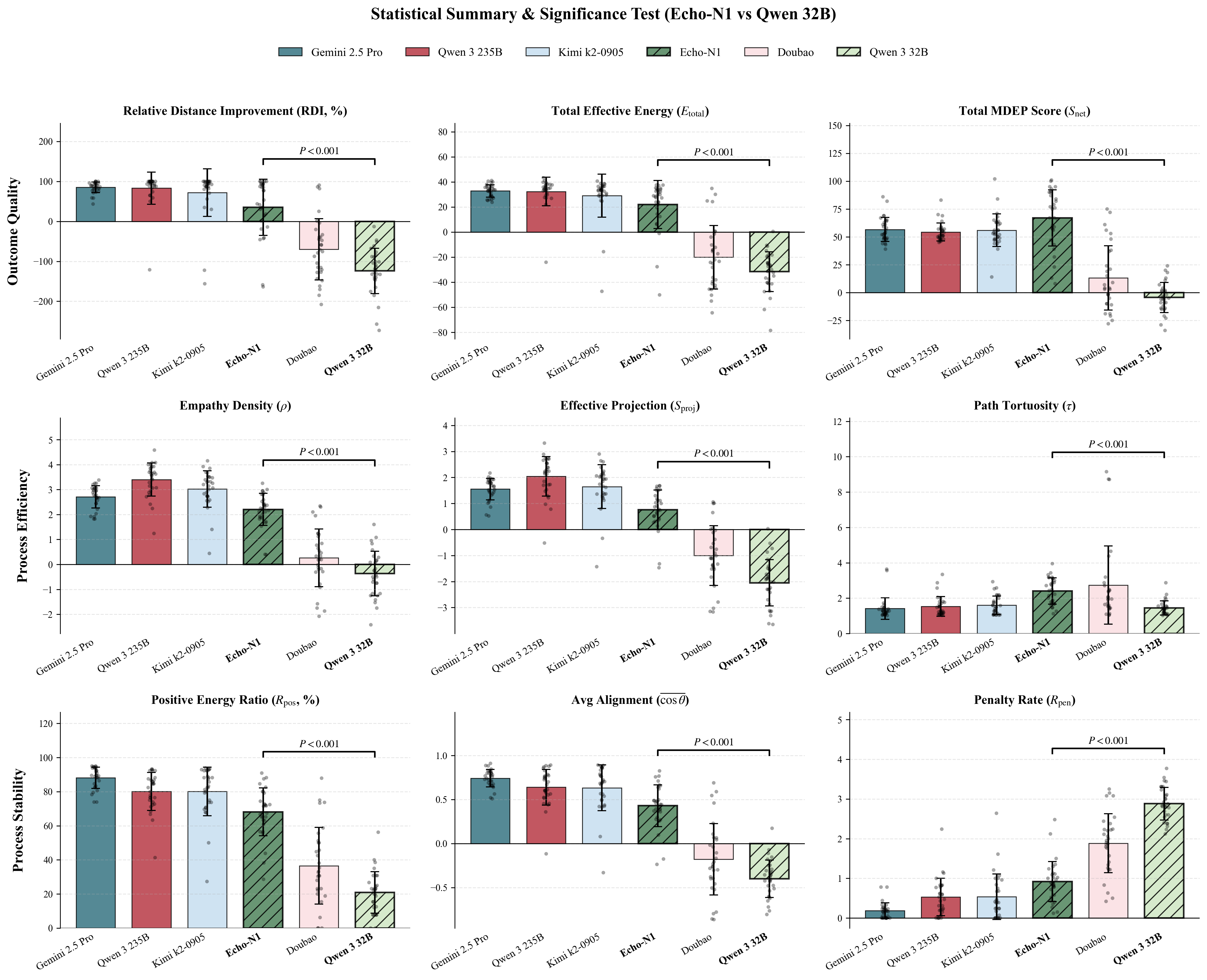
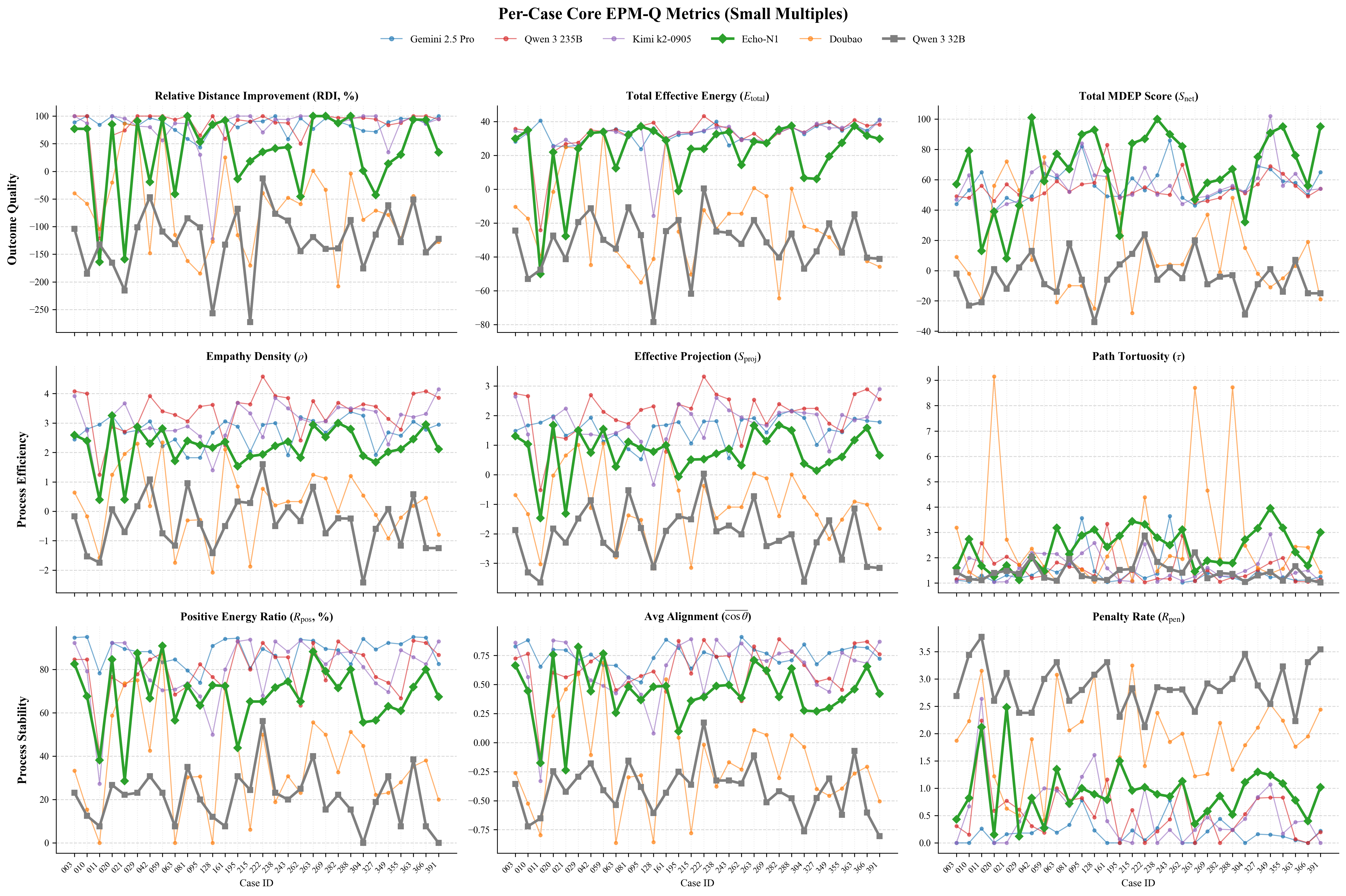
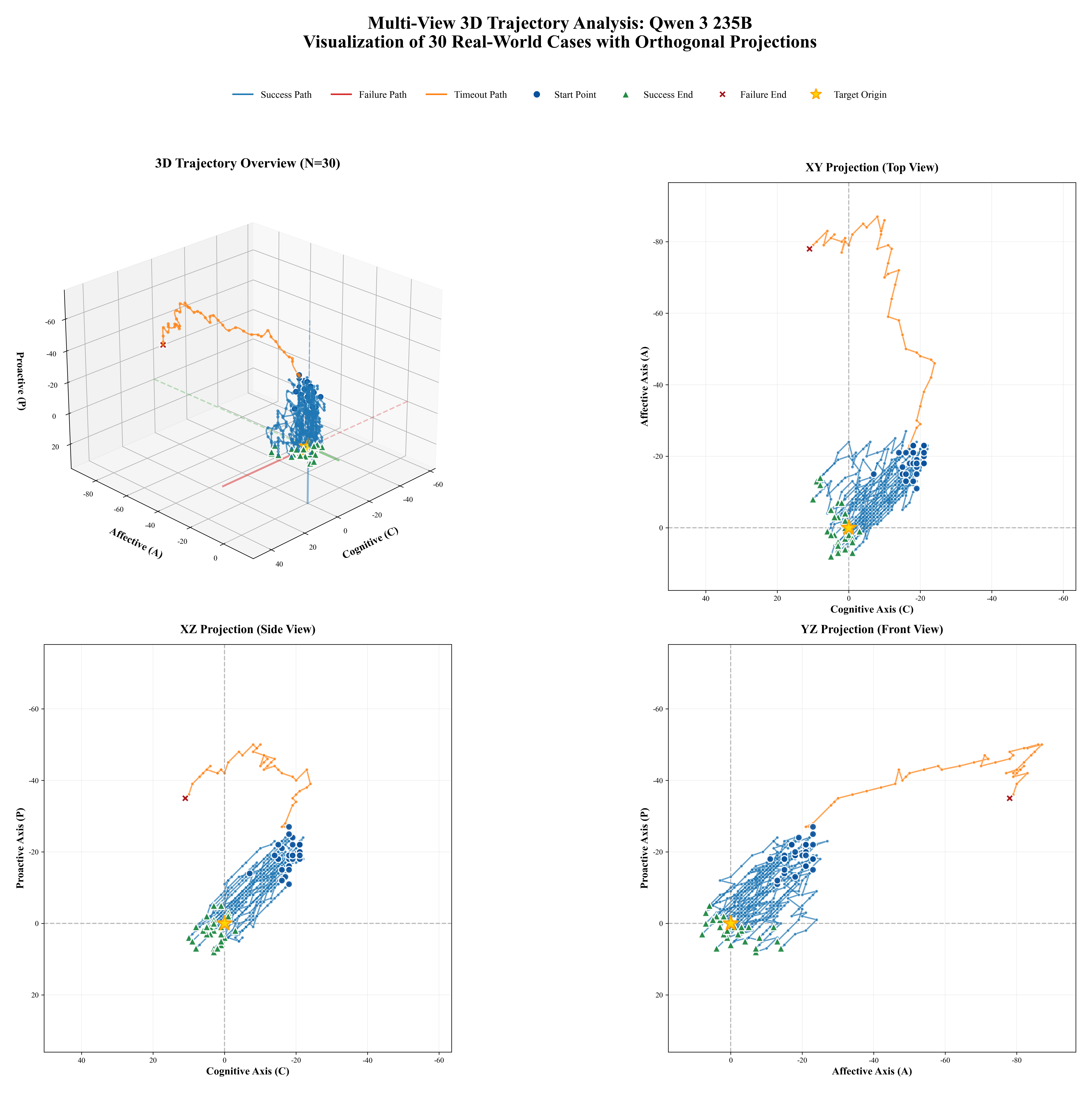
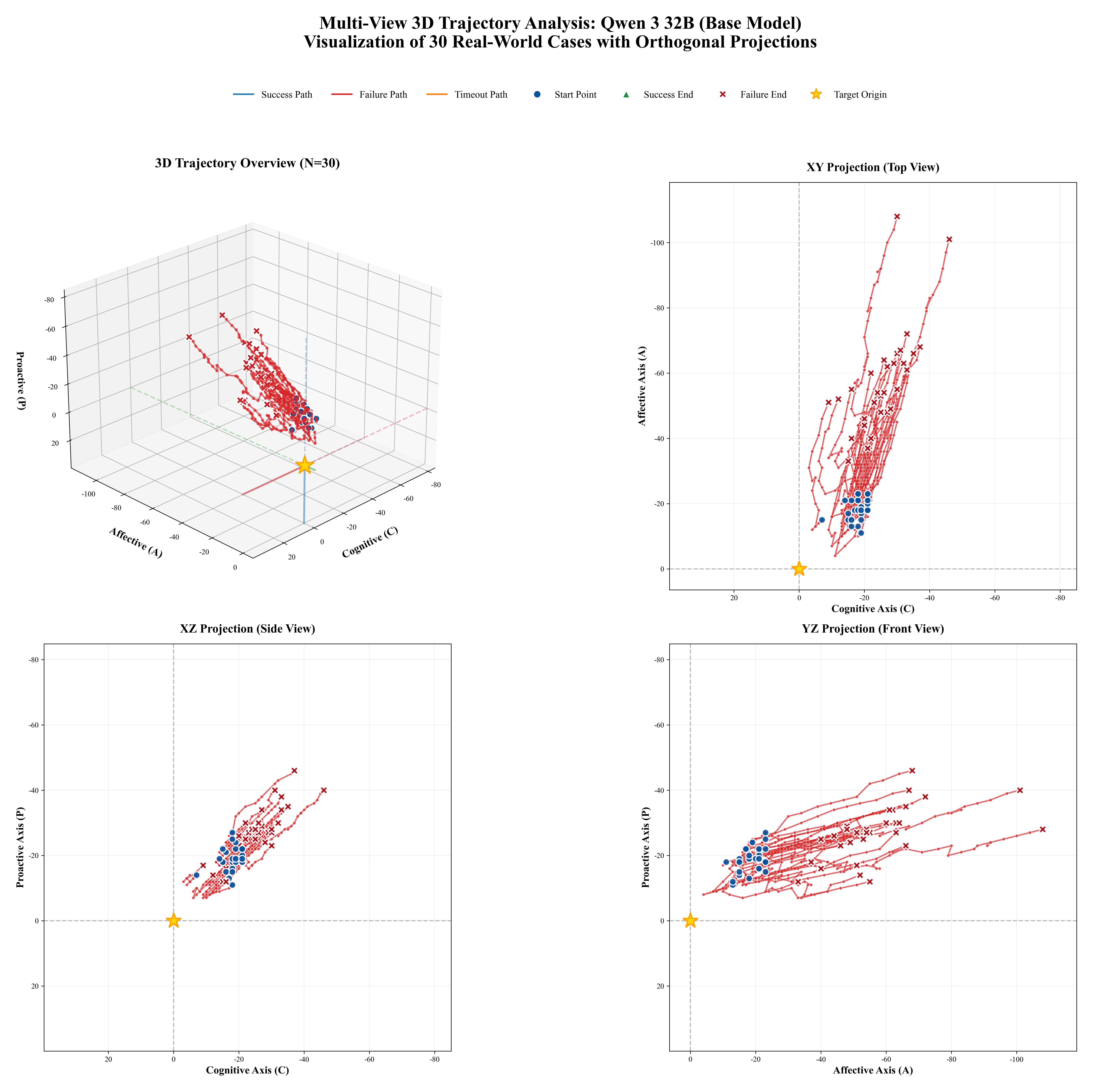
Figure 1: Comprehensive Adaptability Analysis of EPM-Q: (a)EPM-Q Adaptability Analysis: Mech-
anism Stress Test (Routine vs. Challenging Scenarios); (b)EPM-Q Adaptability Analysis: Persona
Resilience (Need Type & Empathy Threshold); (c)EPM-Q Adaptability Analysis: Scenario Cate-
gories (Performance across Different Domains)
*Team Echo: Naifan Zhang, Ruihan Sun, Ruixi Su, Shiqi Ma, Shiya Zhang, Xianna Weng, Xiaofan Zhang,
Yuhan Zhan, Yuyang Xu, Zhaohan Chen, Zhengyuan Pan, Ziyi Song
†Team members are listed alphabetically by first name.
1
arXiv:2512.00344v1 [cs.AI] 29 Nov 2025
Contents
1
Introduction
3
2
Data
3
2.1
SFT Training Data
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3
2.2
Humanlike Reward Model Training Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
2.3
Empathetic Reward Model Training Data
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5
2.4
RL Training Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6
3
Method
7
3.1
Supervised Fine-tuning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
3.2
Reward Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
3.2.1
Humanlike Reward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8
3.2.2
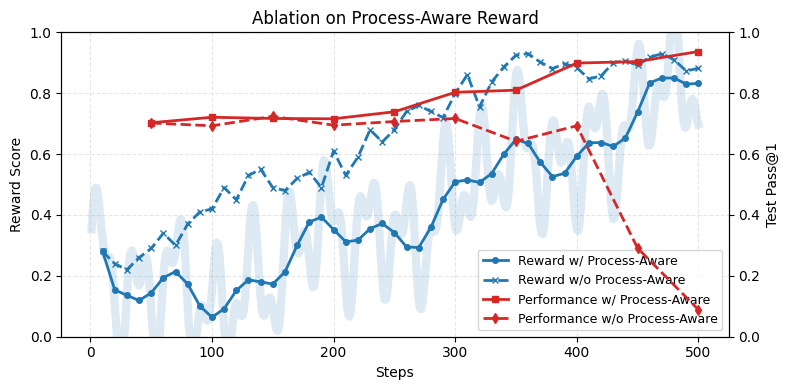
Empathy Reward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
9
3.3
RL Training . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11
4
Evaluation Framework
11
4.1
General Evaluation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
11
4.2
Static IQ and EQ Evaluation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13
4.2.1
Static Intelligence (IQ) Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13
4.2.2
Static Empathy (EQ) Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13
4.3
Dynamic Empathy Evaluation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13
4.3.1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13
4.3.2
Core Mechanism Design . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14
4.3.3
Evaluation Dimensions and Metric System
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15
5
Results and Analysis
18
5.1
SFT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18
5.2
Reward Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18
5.2.1
Humanlike Reward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18
5.2.2
Empathy Reward . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19
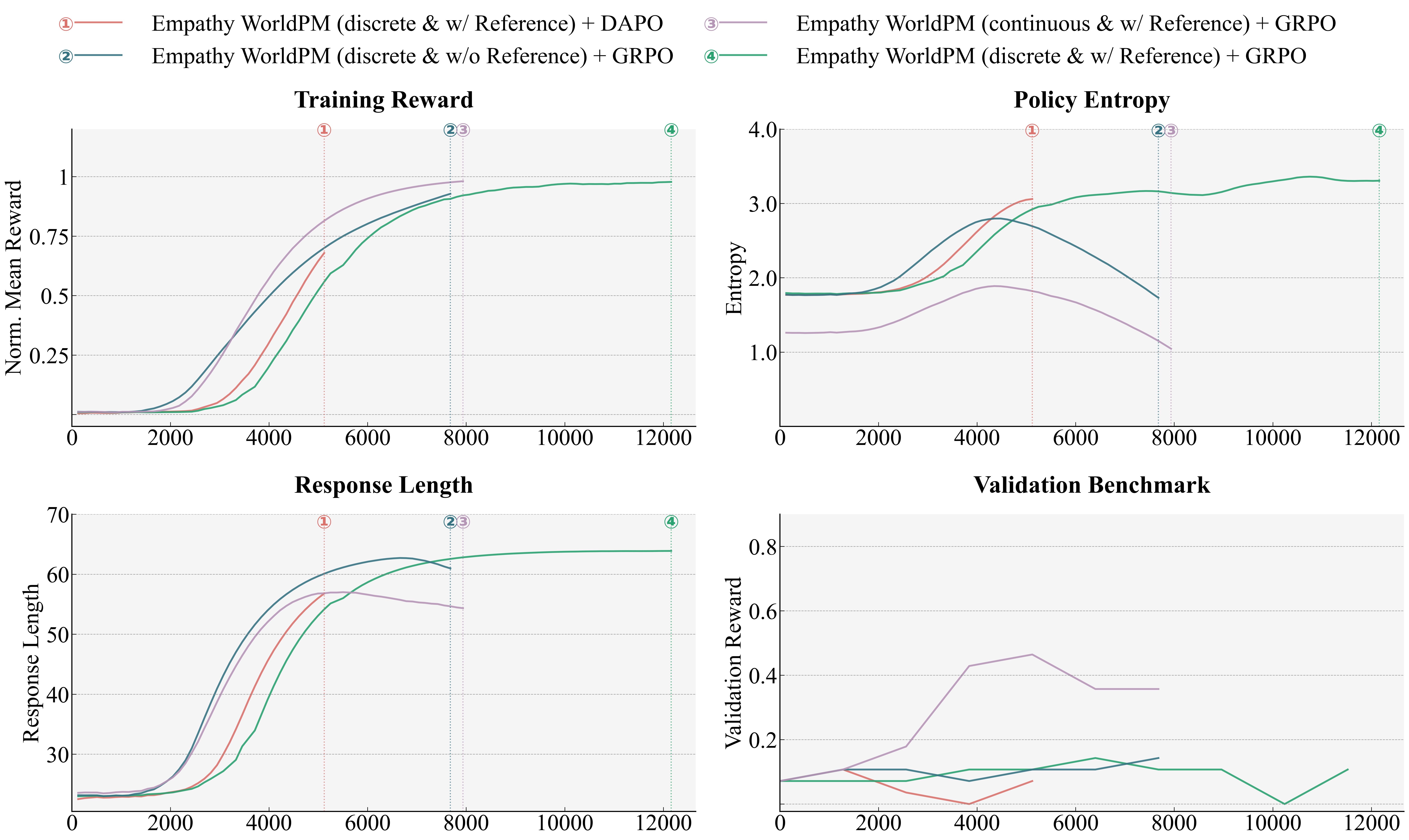
5.3
Echo-N1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20
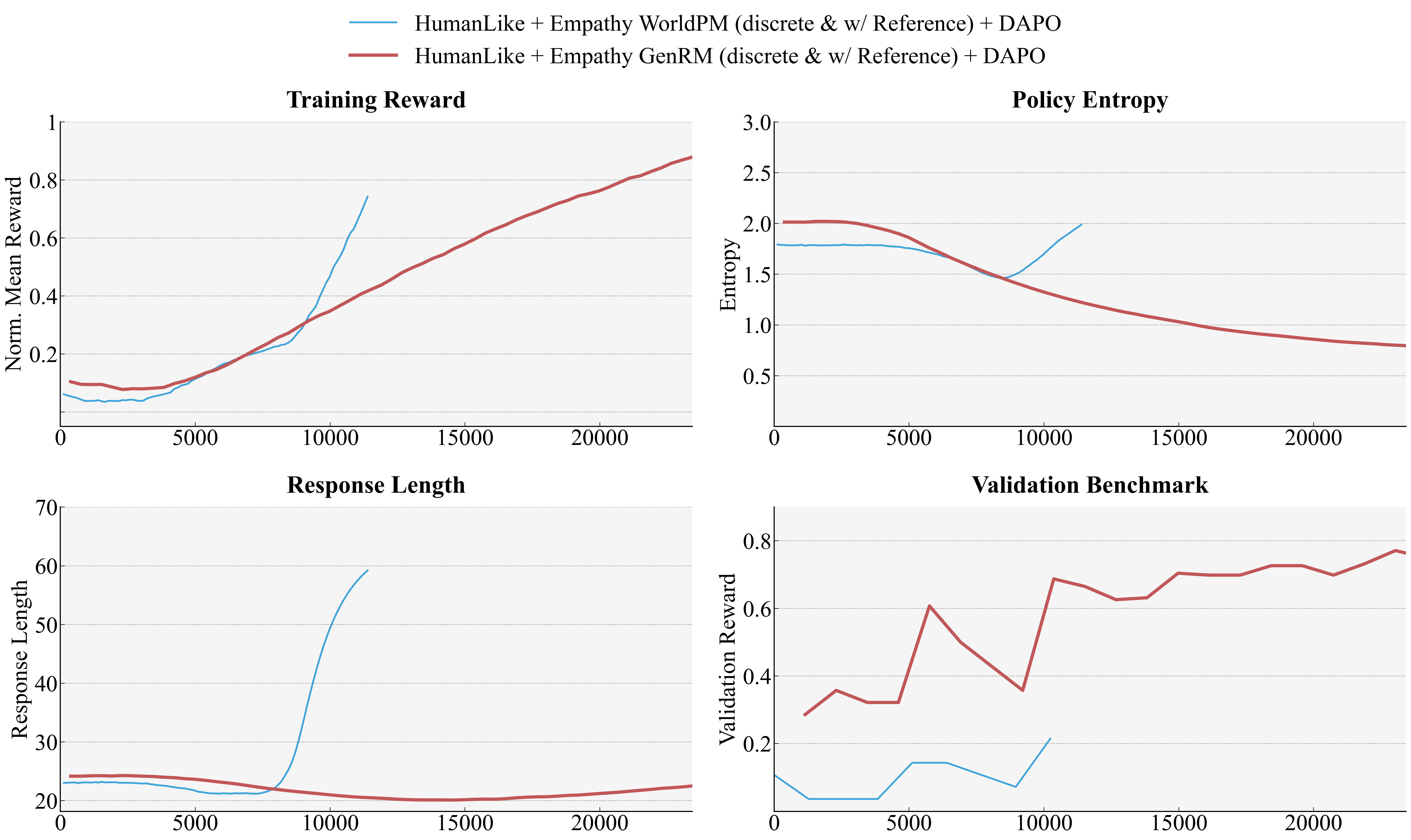
5.3.1
GenRM vs Scalar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21
5.3.2
Performance on Private IQ and EQ Benchmarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23
5.3.3
Dynamic EQ Evaluation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23
5.3.4
NEE Qualitative Evaluation: Context-Diagnosed Holistic Experiential Review 38
5.3.5
Final Result . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
39
6
Conclusion
39
7
Discussion
40
A Prompts
42
A.1
HumanLike Judger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
42
A.2
Empathetic Judger
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
42
A.3
NEE Qualitative Evaluation Judger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
43
B
Cases
46
B.1
Humanlike Failure Cases of Prompted SOTA Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
46
B.2
Cases of Trained Empethetic Judger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
46
2
1
Introduction
Large language models (LLMs) have rapidly advanced in instruction following, reasoning, and
generalizat
📸 Image Gallery
Reference This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.