UltraGS: Real-Time Physically-Decoupled Gaussian Splatting for Ultrasound Novel View Synthesis
Reading time: 1 minute
...
📝 Original Info
- Title: UltraGS: Real-Time Physically-Decoupled Gaussian Splatting for Ultrasound Novel View Synthesis
- ArXiv ID: 2511.07743
- Date: 2025-11-11
- Authors: ** 논문에 명시된 저자 정보가 제공되지 않았습니다. (원문 혹은 GitHub 저장소에서 확인 필요) **
📝 Abstract
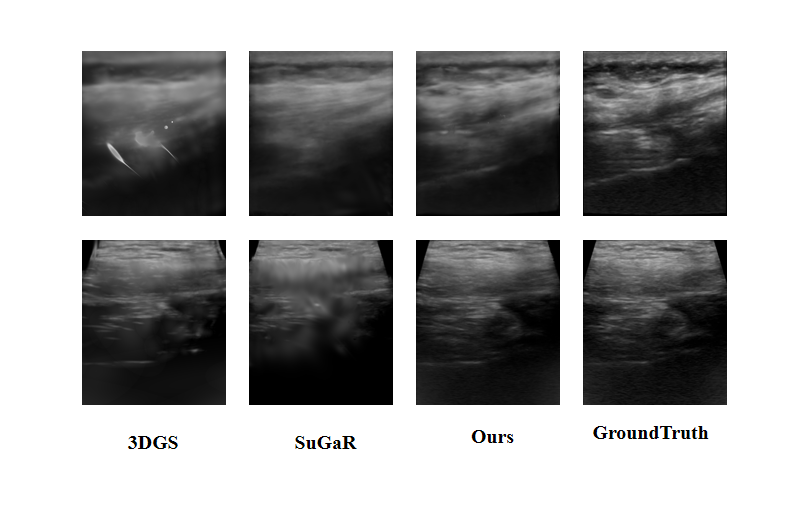
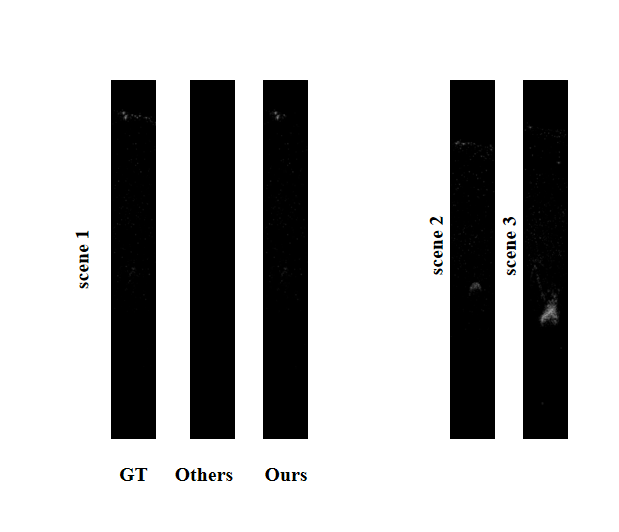
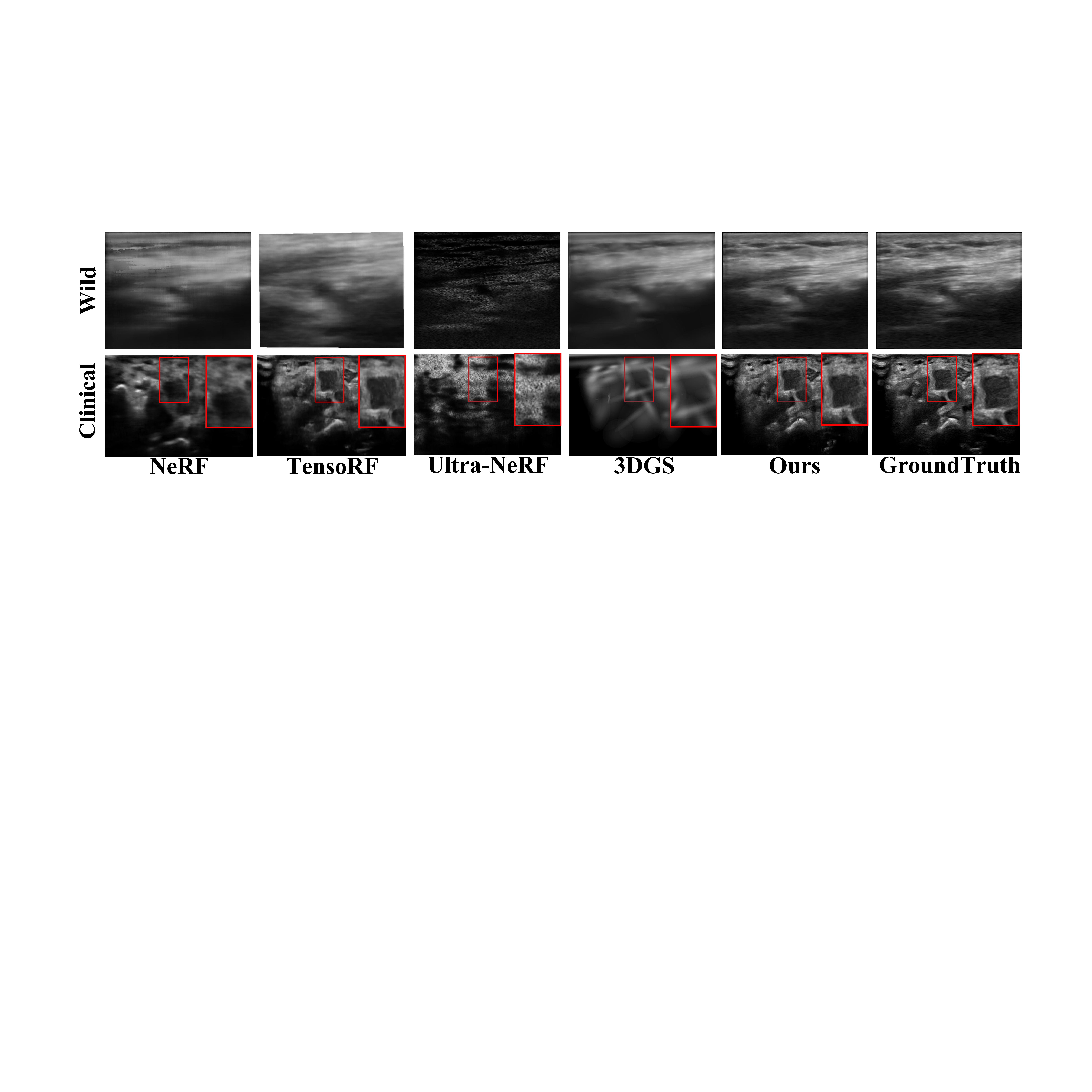
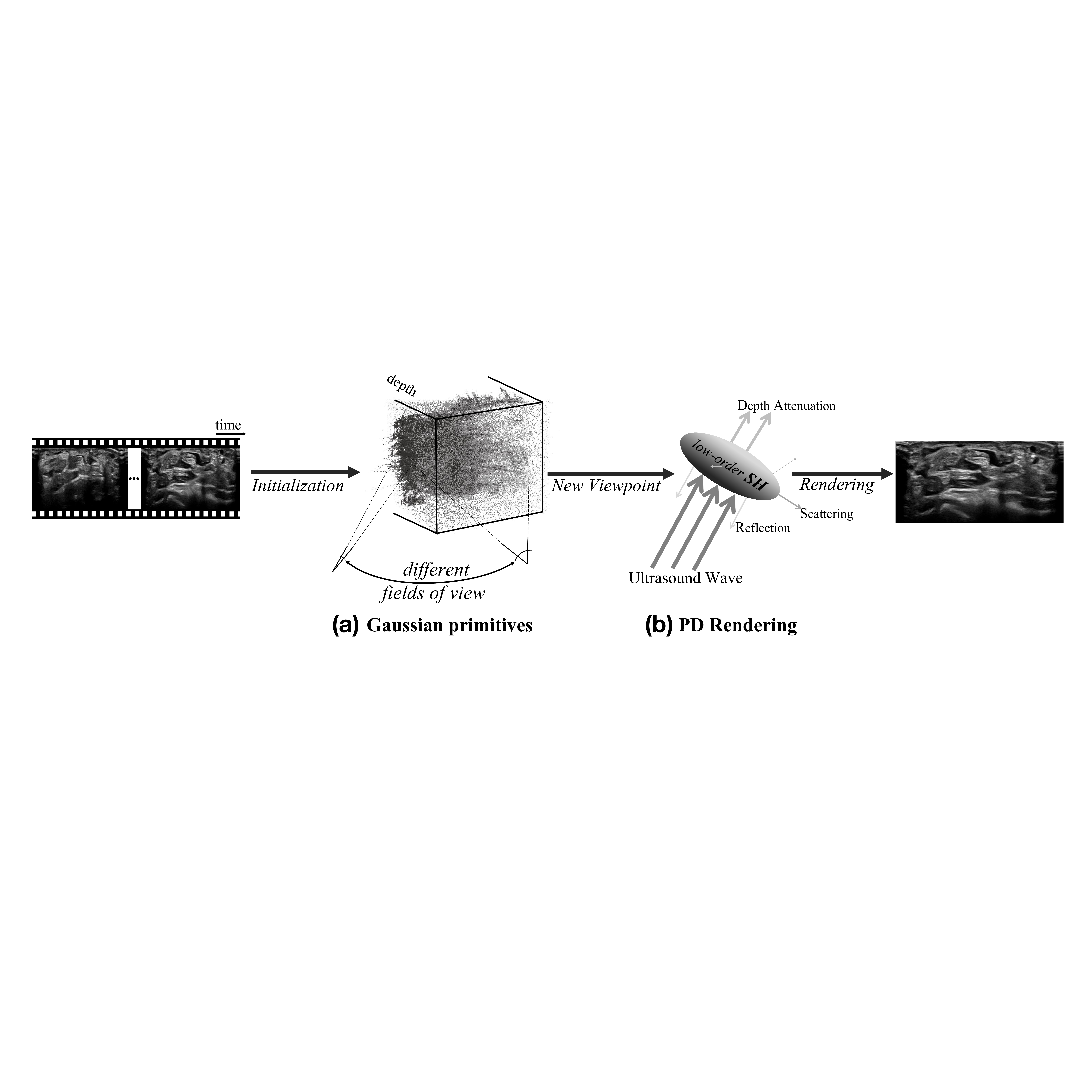
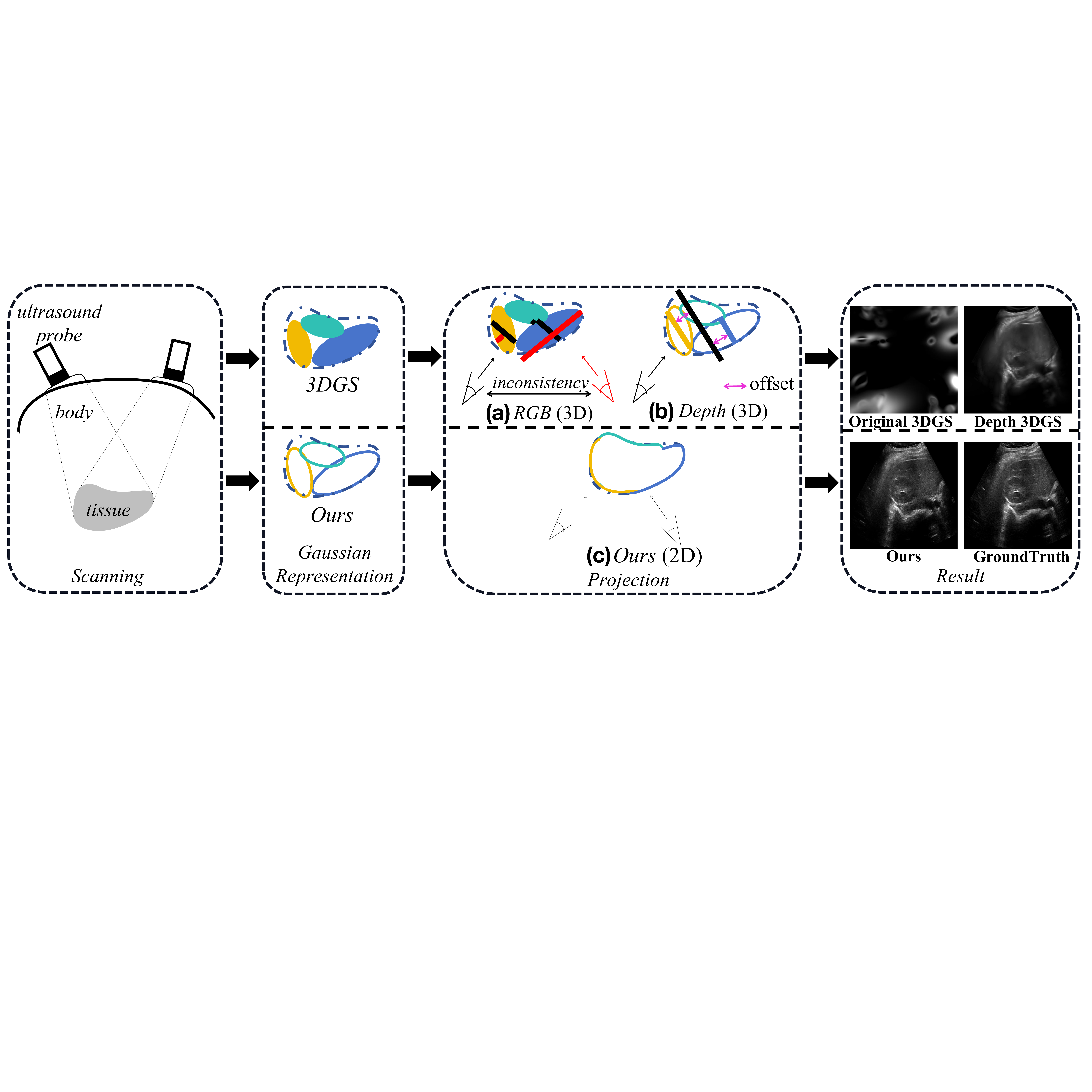
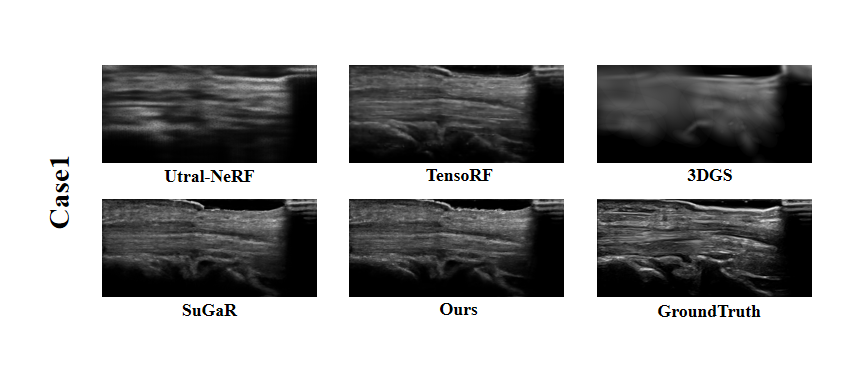
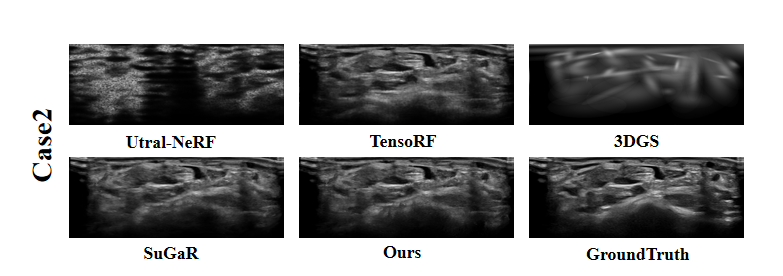
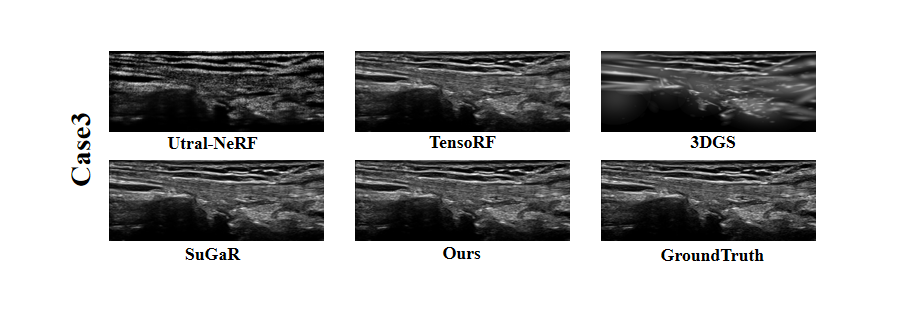
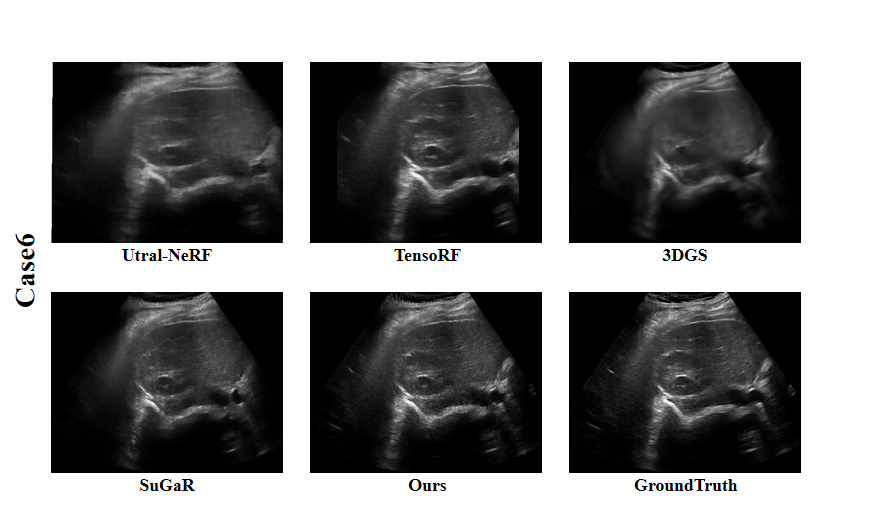
Ultrasound imaging is a cornerstone of non-invasive clinical diagnostics, yet its limited field of view poses challenges for novel view synthesis. We present UltraGS, a real-time framework that adapts Gaussian Splatting to sensorless ultrasound imaging by integrating explicit radiance fields with lightweight, physics-inspired acoustic modeling. UltraGS employs depth-aware Gaussian primitives with learnable fields of view to improve geometric consistency under unconstrained probe motion, and introduces PD Rendering, a differentiable acoustic operator that combines low-order spherical harmonics with first-order wave effects for efficient intensity synthesis. We further present a clinical ultrasound dataset acquired under real-world scanning protocols. Extensive evaluations across three datasets demonstrate that UltraGS establishes a new performance-efficiency frontier, achieving state-of-the-art results in PSNR (up to 29.55) and SSIM (up to 0.89) while achieving real-time synthesis at 64.69 fps on a single GPU. The code and dataset are open-sourced at: https://github.com/Bean-Young/UltraGS.💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery

Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.