Biologically-Informed Hybrid Membership Inference Attacks on Generative Genomic Models
📝 Original Info
- Title: Biologically-Informed Hybrid Membership Inference Attacks on Generative Genomic Models
- ArXiv ID: 2511.07503
- Date: 2025-11-10
- Authors: ** 제공된 정보에 저자 명단이 포함되지 않았습니다. **
📝 Abstract
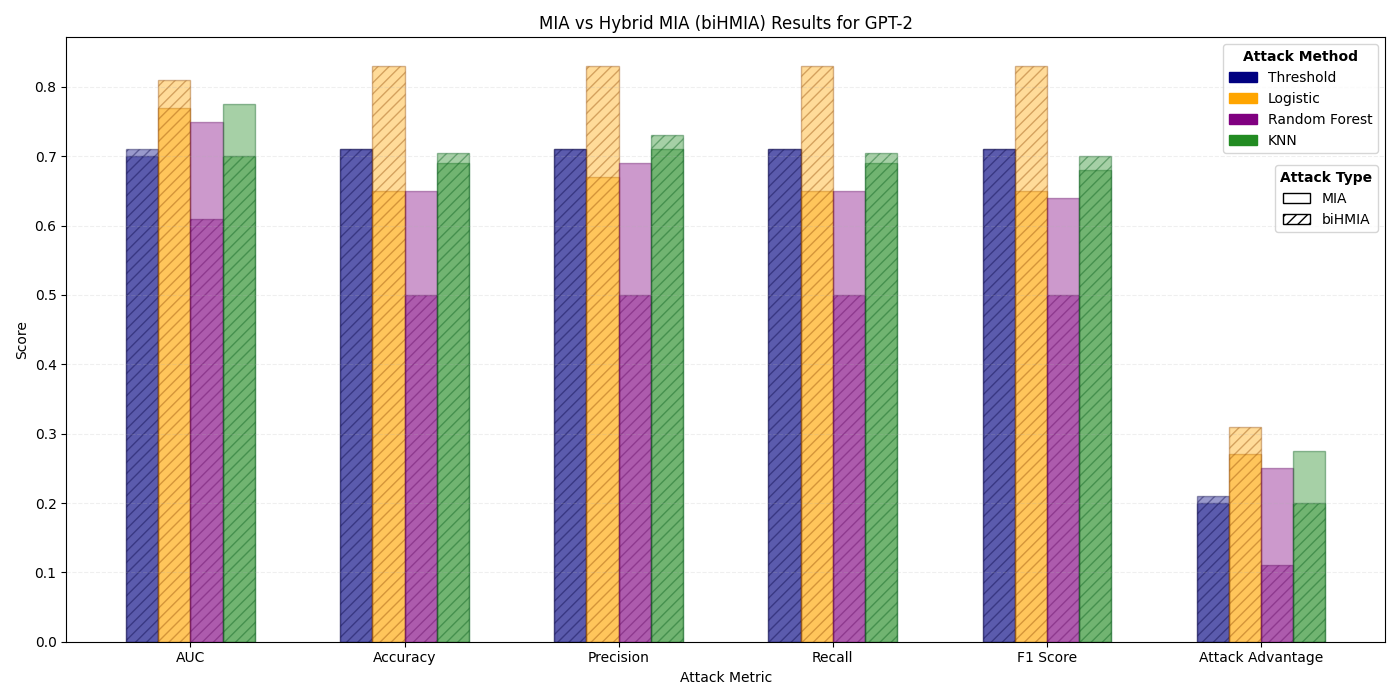
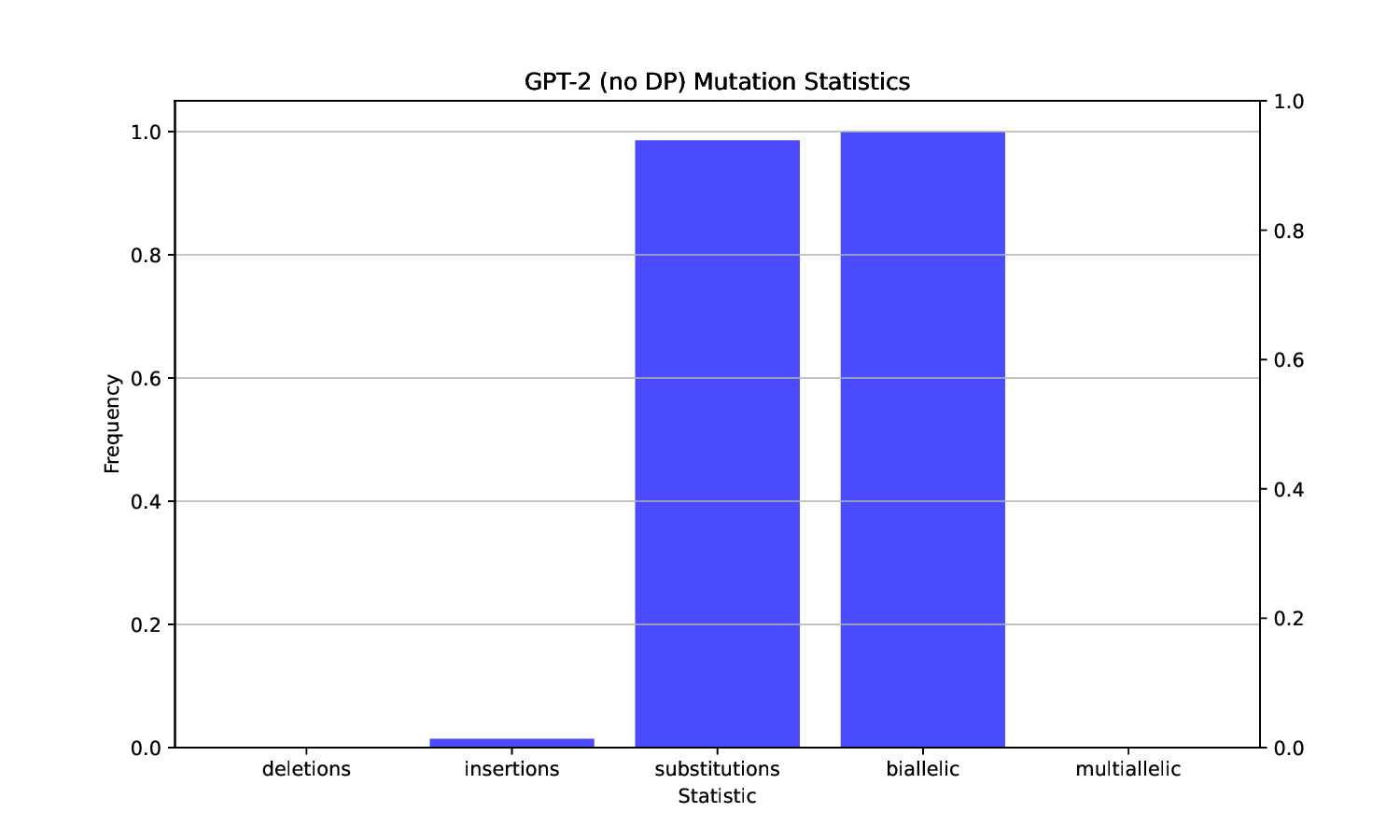
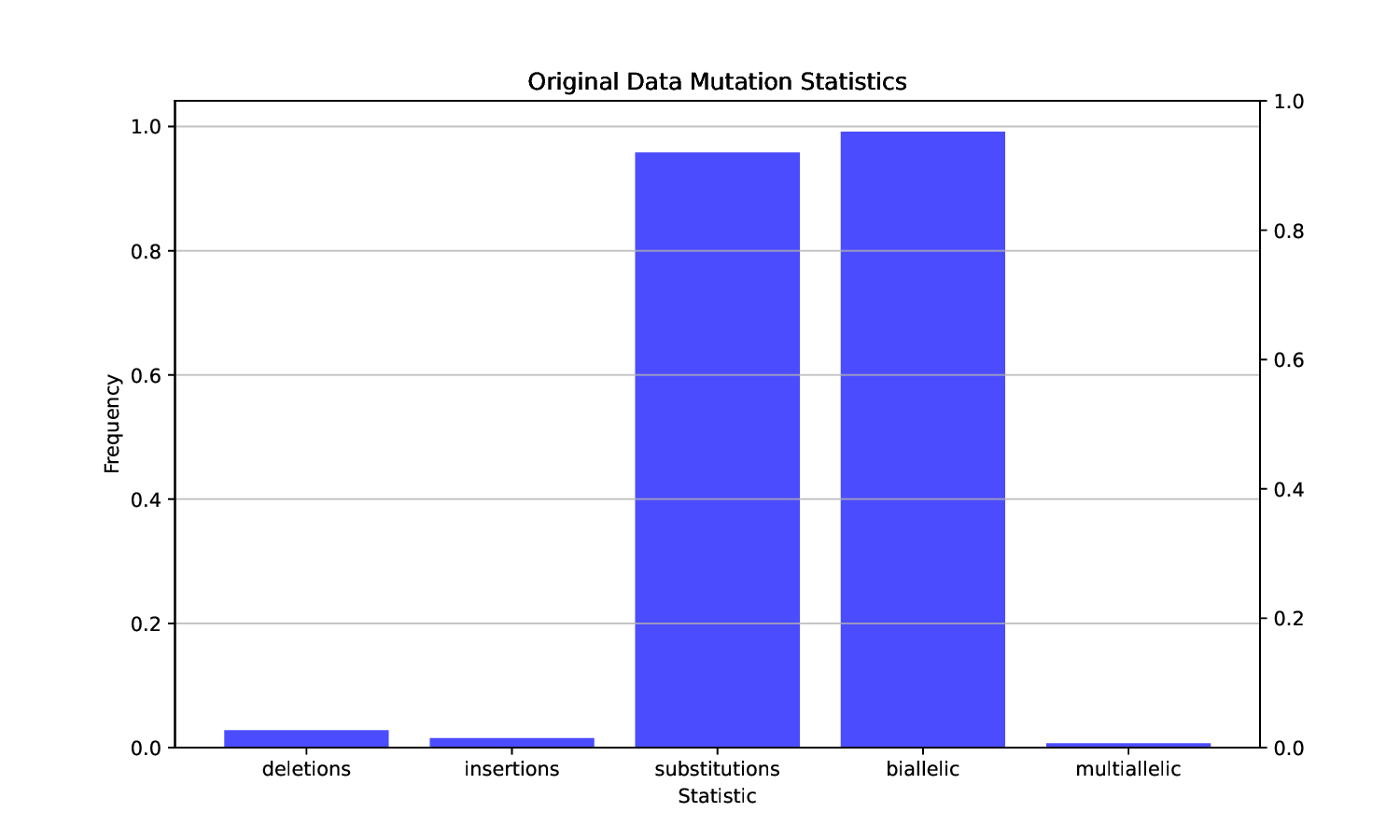
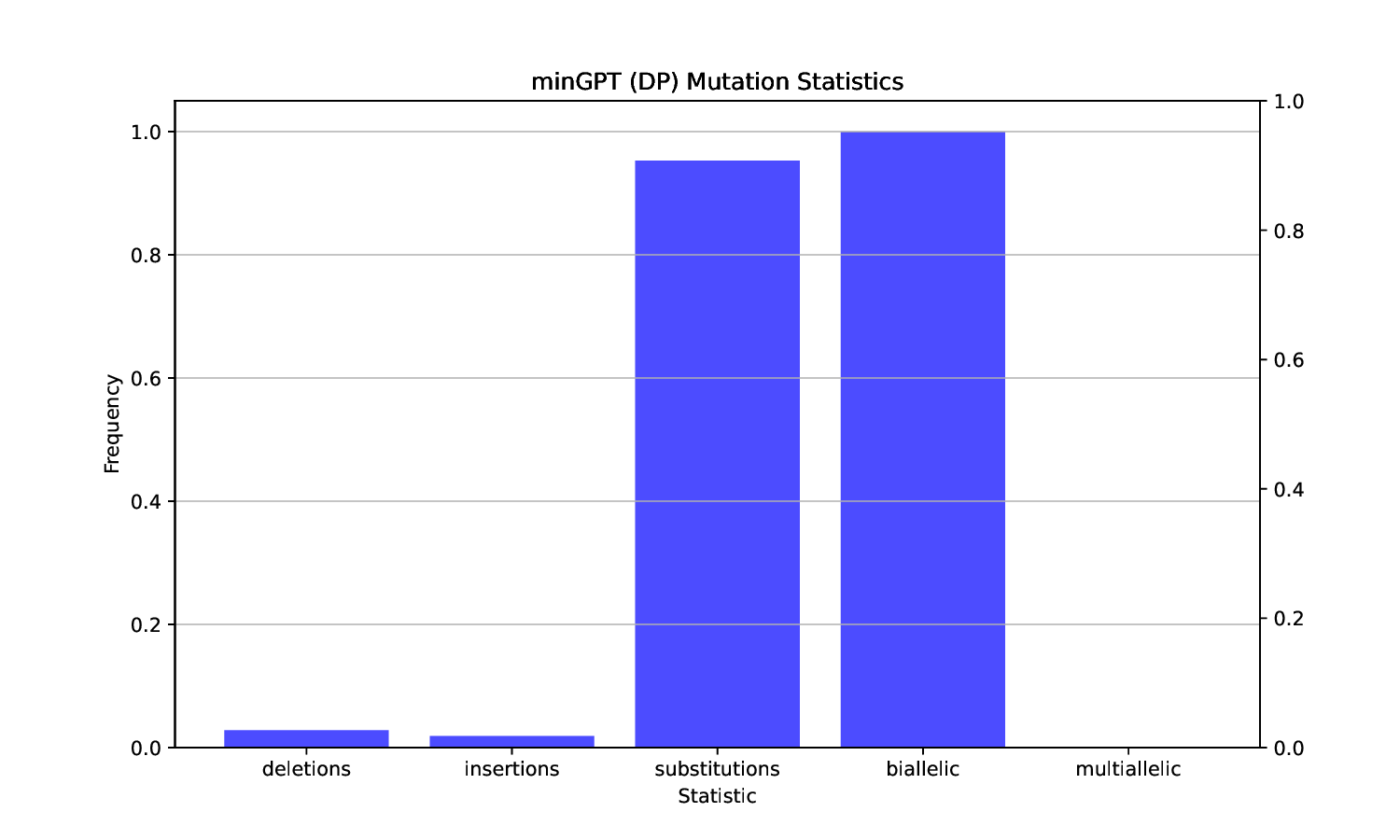
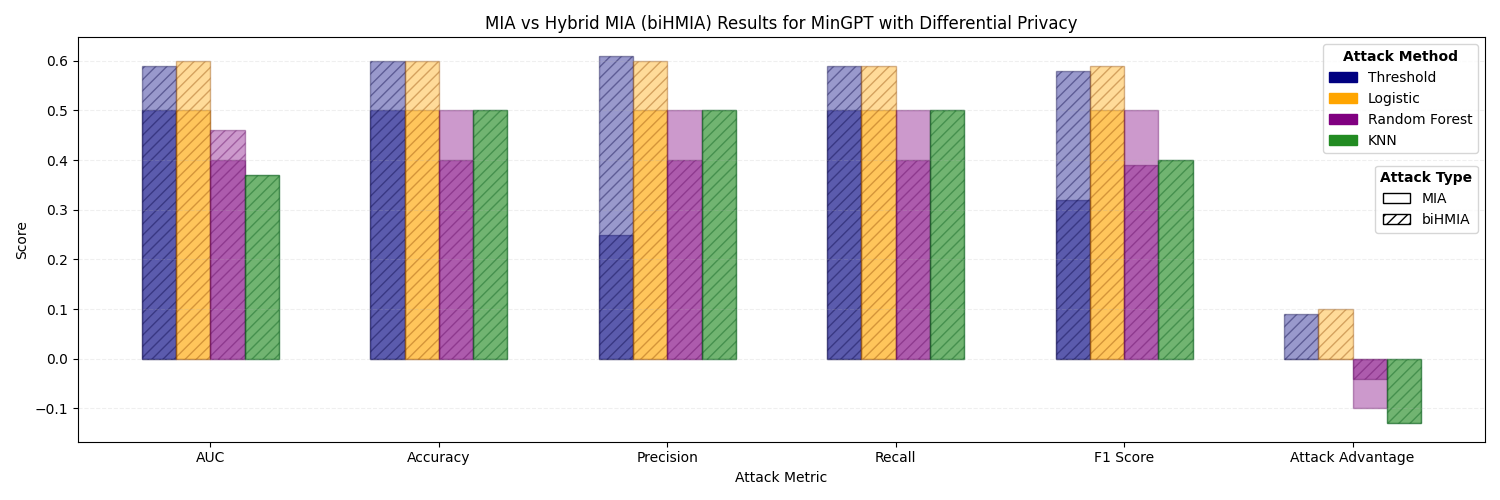
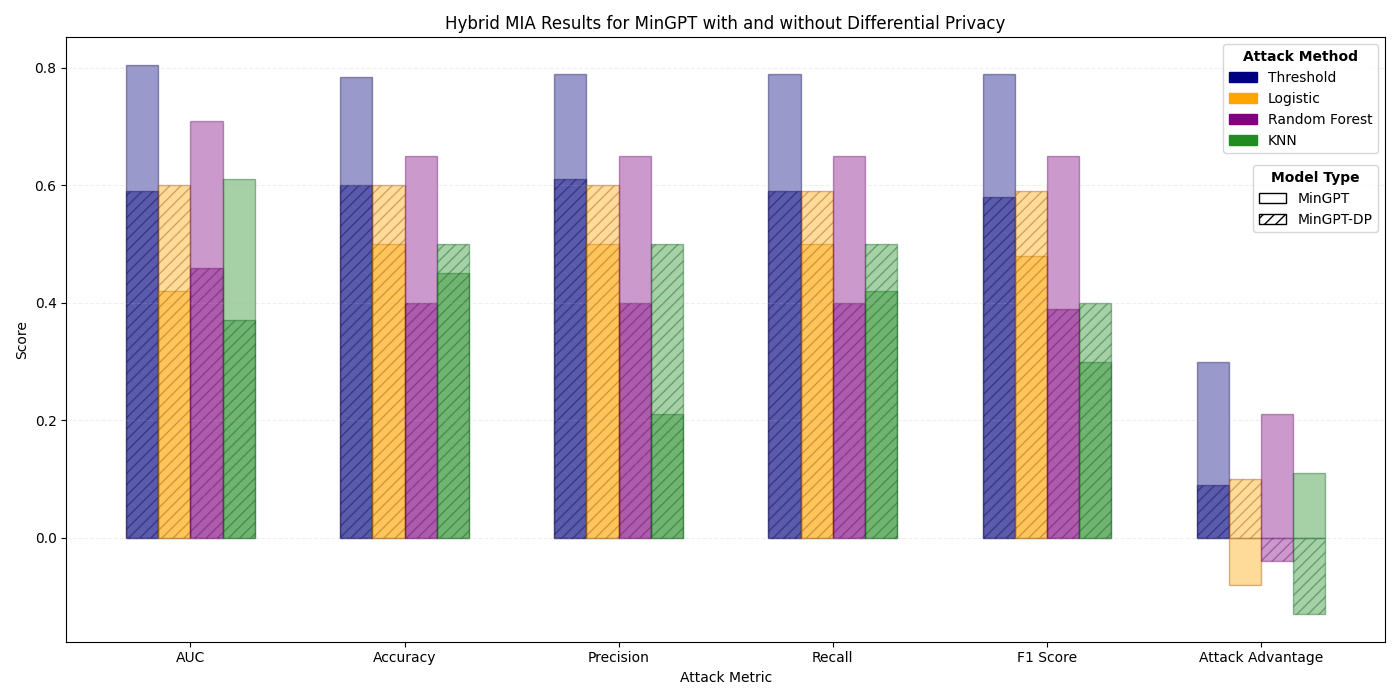
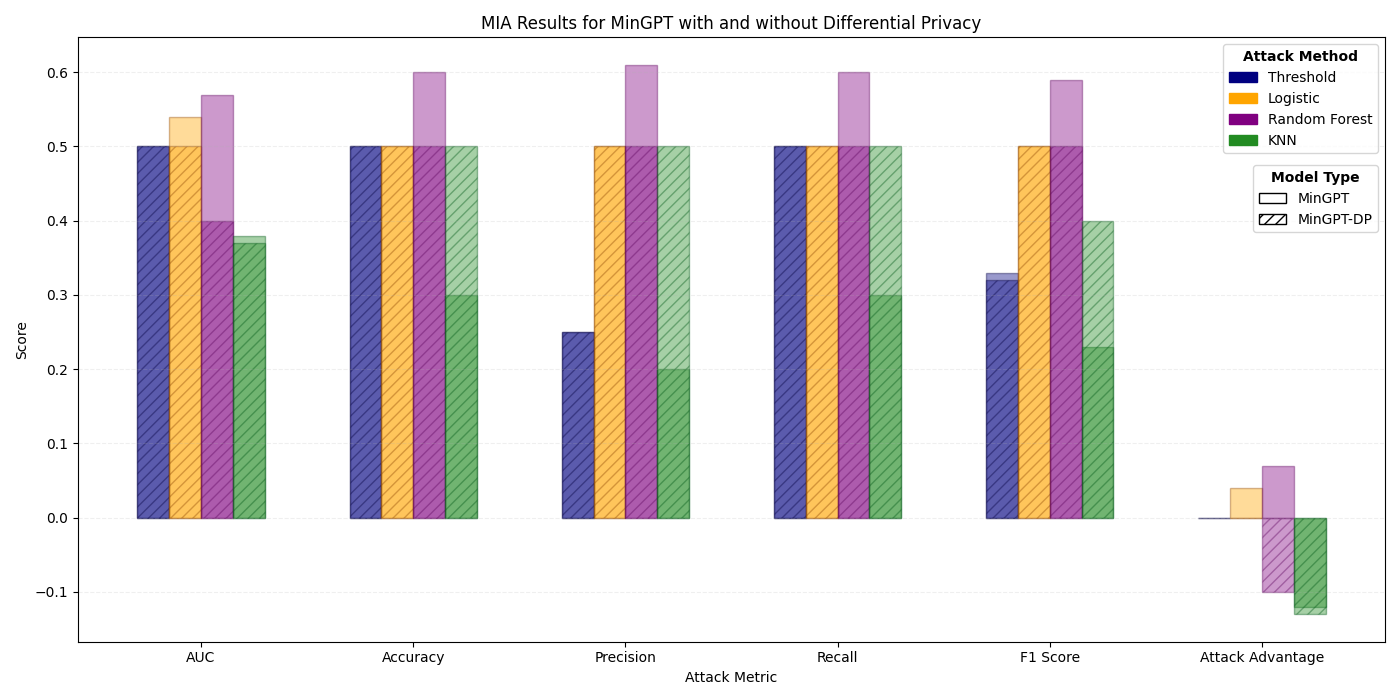
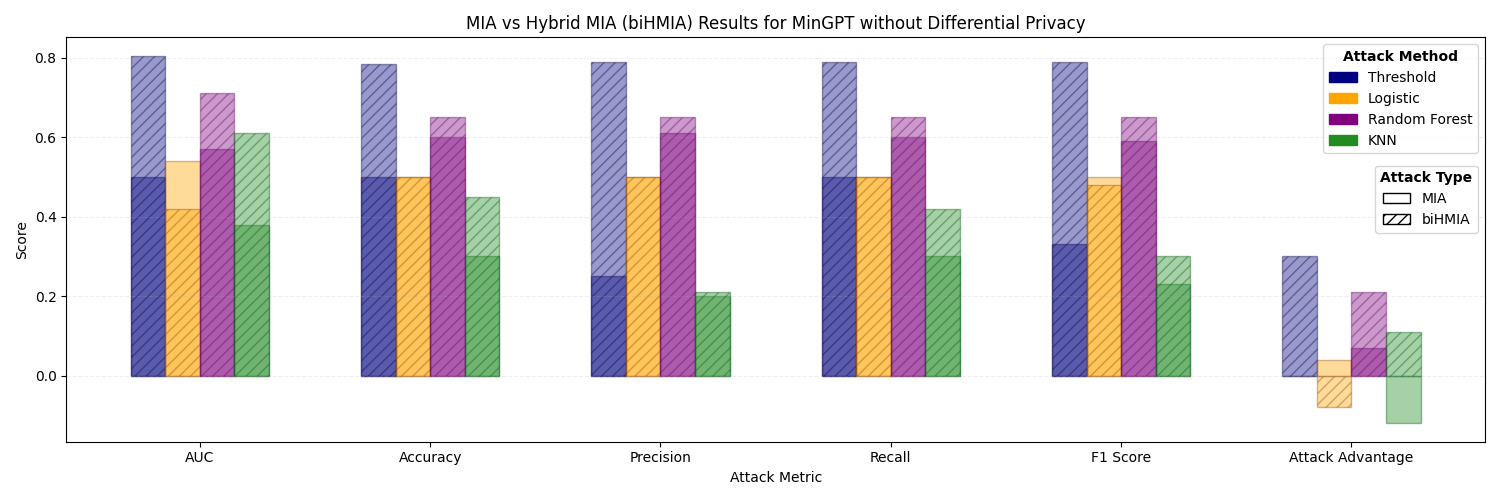
The increased availability of genetic data has transformed genomics research, but raised many privacy concerns regarding its handling due to its sensitive nature. This work explores the use of language models (LMs) for the generation of synthetic genetic mutation profiles, leveraging differential privacy (DP) for the protection of sensitive genetic data. We empirically evaluate the privacy guarantees of our DP modes by introducing a novel Biologically-Informed Hybrid Membership Inference Attack (biHMIA), which combines traditional black box MIA with contextual genomics metrics for enhanced attack power. Our experiments show that both small and large transformer GPT-like models are viable synthetic variant generators for small-scale genomics, and that our hybrid attack leads, on average, to higher adversarial success compared to traditional metric-based MIAs.💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery

Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.