Purrturbed but Stable: Human-Cat Invariant Representations Across CNNs, ViTs and Self-Supervised ViTs
Reading time: 2 minute
...
📝 Original Info
- Title: Purrturbed but Stable: Human-Cat Invariant Representations Across CNNs, ViTs and Self-Supervised ViTs
- ArXiv ID: 2511.02404
- Date: 2025-11-04
- Authors: 논문에 명시된 저자 정보가 제공되지 않았습니다. 저자 명단이 확인되면 해당 섹션을 업데이트해 주세요.
📝 Abstract
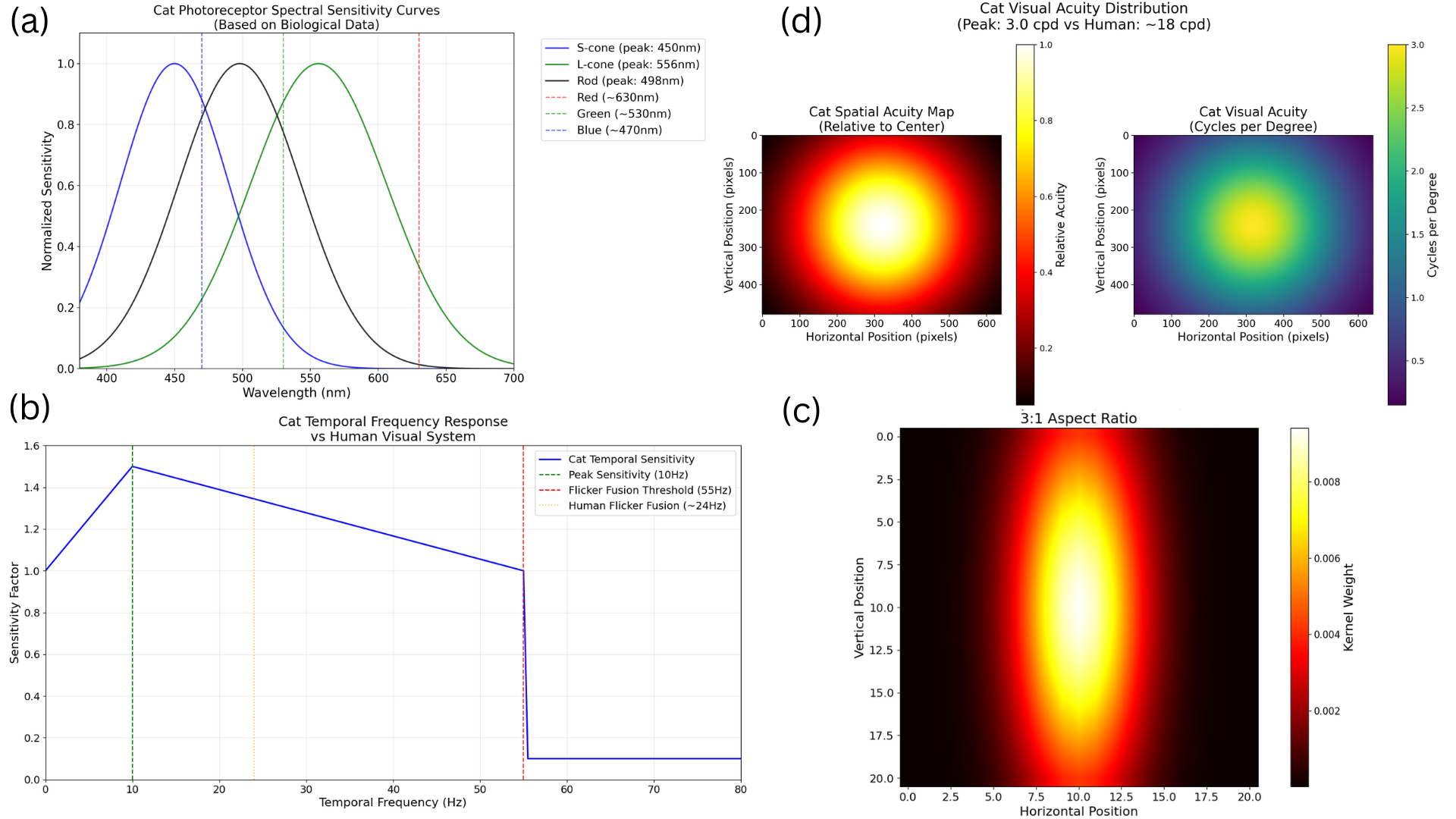
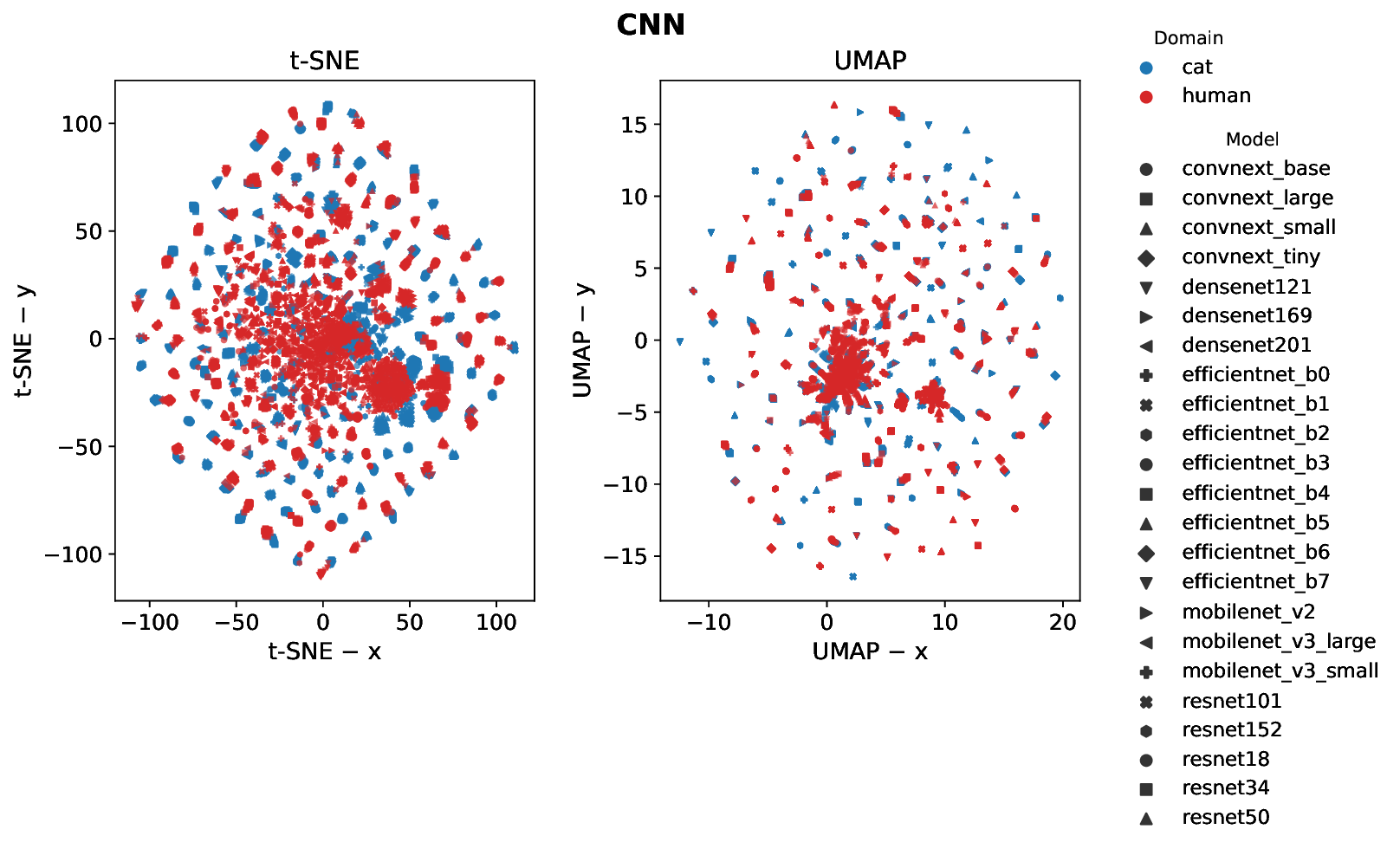
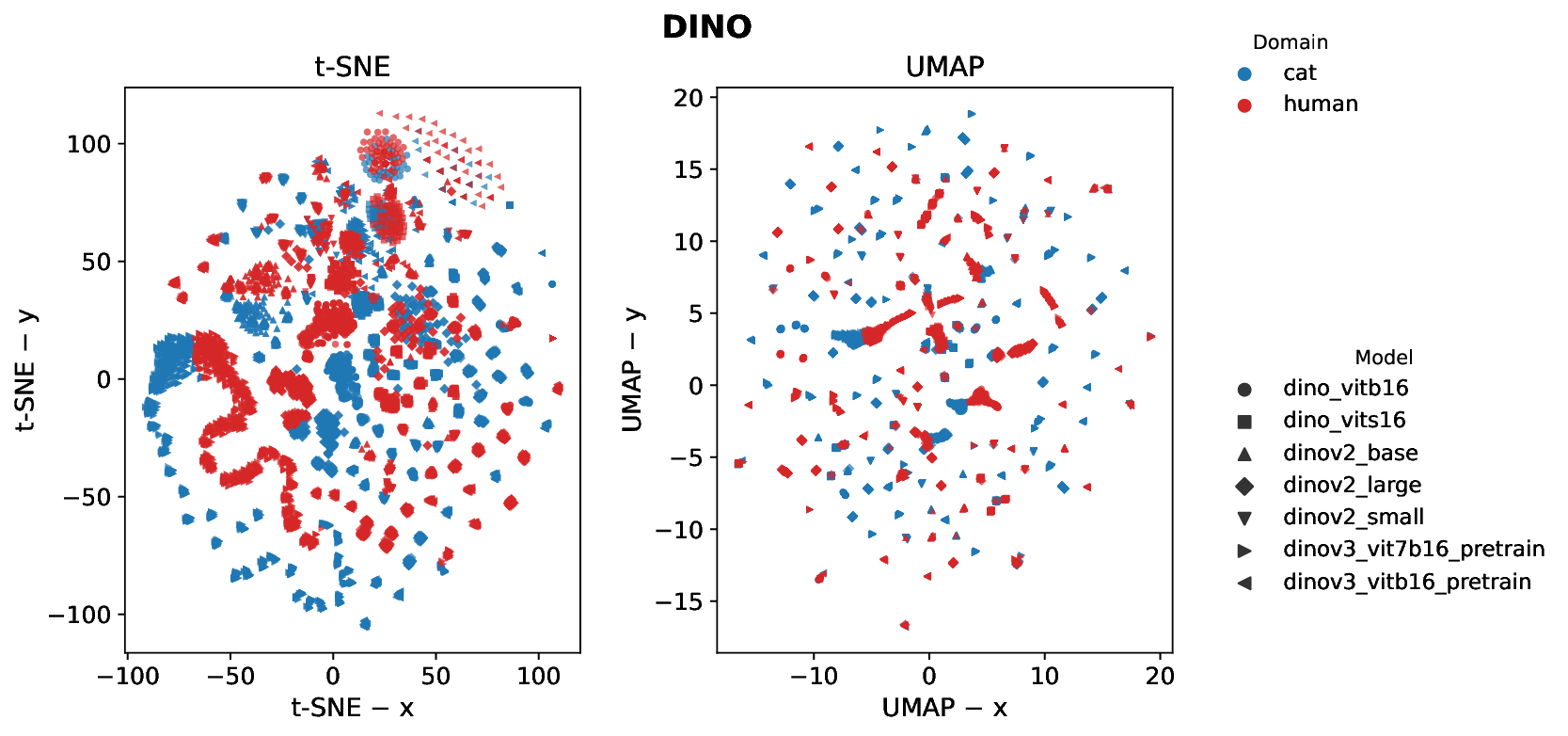
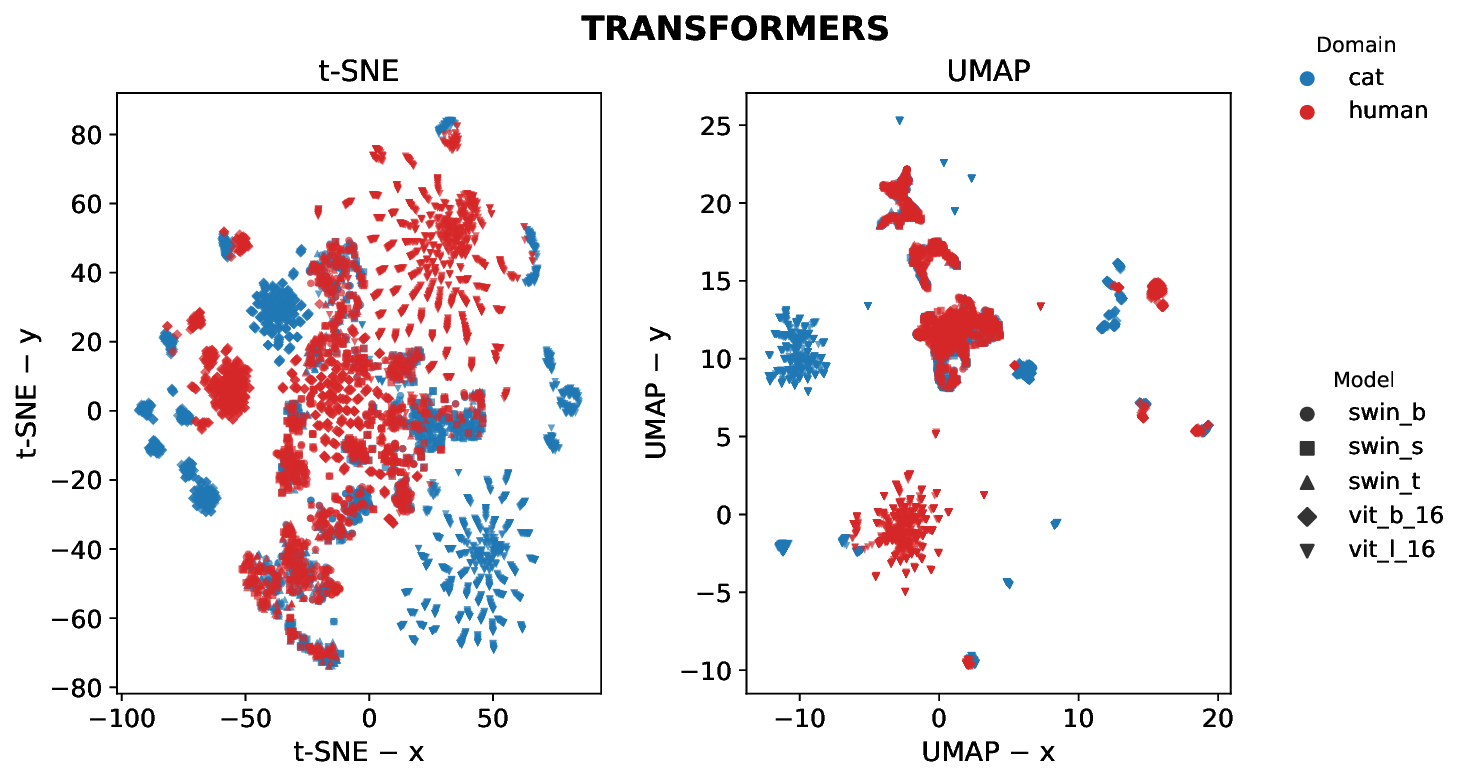
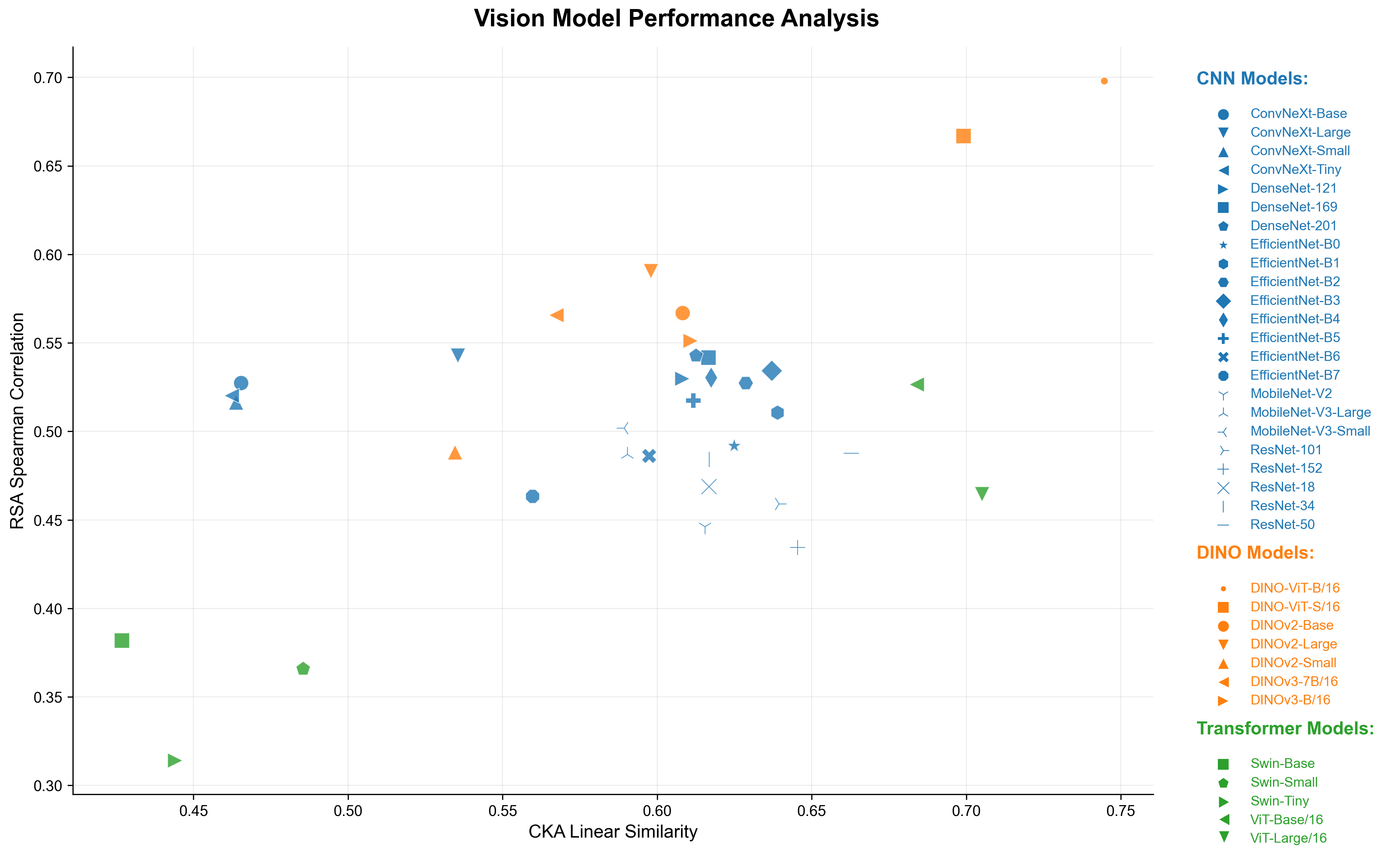
Cats and humans differ in ocular anatomy. Most notably, Felis Catus (domestic cats) have vertically elongated pupils linked to ambush predation; yet, how such specializations manifest in downstream visual representations remains incompletely understood. We present a unified, frozen-encoder benchmark that quantifies feline-human cross-species representational alignment in the wild, across convolutional networks, supervised Vision Transformers, windowed transformers, and self-supervised ViTs (DINO), using layer-wise Centered Kernel Alignment (linear and RBF) and Representational Similarity Analysis, with additional distributional and stability tests reported in the paper. Across models, DINO ViT-B/16 attains the most substantial alignment (mean CKA-RBF $\approx0.814$, mean CKA-linear $\approx0.745$, mean RSA $\approx0.698$), peaking at early blocks, indicating that token-level self-supervision induces early-stage features that bridge species-specific statistics. Supervised ViTs are competitive on CKA yet show weaker geometric correspondence than DINO (e.g., ViT-B/16 RSA $\approx0.53$ at block8; ViT-L/16 $\approx0.47$ at block14), revealing depth-dependent divergences between similarity and representational geometry. CNNs remain strong baselines but below plain ViTs on alignment, and windowed transformers underperform plain ViTs, implicating architectural inductive biases in cross-species alignment. Results indicate that self-supervision coupled with ViT inductive biases yields representational geometries that more closely align feline and human visual systems than widely used CNNs and windowed Transformers, providing testable neuroscientific hypotheses about where and how cross-species visual computations converge. We release our code and dataset for reference and reproducibility.💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery

Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.