Self-supervised Synthetic Pretraining for Inference of Stellar Mass Embedded in Dense Gas
Reading time: 2 minute
...
📝 Original Info
- Title: Self-supervised Synthetic Pretraining for Inference of Stellar Mass Embedded in Dense Gas
- ArXiv ID: 2510.24159
- Date: 2025-10-28
- Authors: ** 논문에 명시된 저자 정보가 제공되지 않았으므로, 실제 저자 목록은 원문을 확인하시기 바랍니다. — **
📝 Abstract
Stellar mass is a fundamental quantity that determines the properties and evolution of stars. However, estimating stellar masses in star-forming regions is challenging because young stars are obscured by dense gas and the regions are highly inhomogeneous, making spherical dynamical estimates unreliable. Supervised machine learning could link such complex structures to stellar mass, but it requires large, high-quality labeled datasets from high-resolution magneto-hydrodynamical (MHD) simulations, which are computationally expensive. We address this by pretraining a vision transformer on one million synthetic fractal images using the self-supervised framework DINOv2, and then applying the frozen model to limited high-resolution MHD simulations. Our results demonstrate that synthetic pretraining improves frozen-feature regression stellar mass predictions, with the pretrained model performing slightly better than a supervised model trained on the same limited simulations. Principal component analysis of the extracted features further reveals semantically meaningful structures, suggesting that the model enables unsupervised segmentation of star-forming regions without the need for labeled data or fine-tuning.💡 Deep Analysis
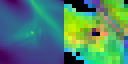
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery

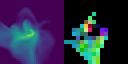
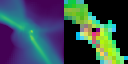
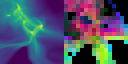
Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.