Multitask Multimodal Self-Supervised Learning for Medical Images
📝 Original Info
- Title: Multitask Multimodal Self-Supervised Learning for Medical Images
- ArXiv ID: 2510.23325
- Date: 2025-10-27
- Authors: ** 정보 없음 (논문에 명시된 저자 정보가 제공되지 않음) **
📝 Abstract
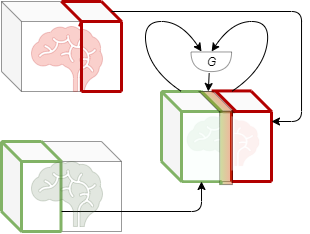
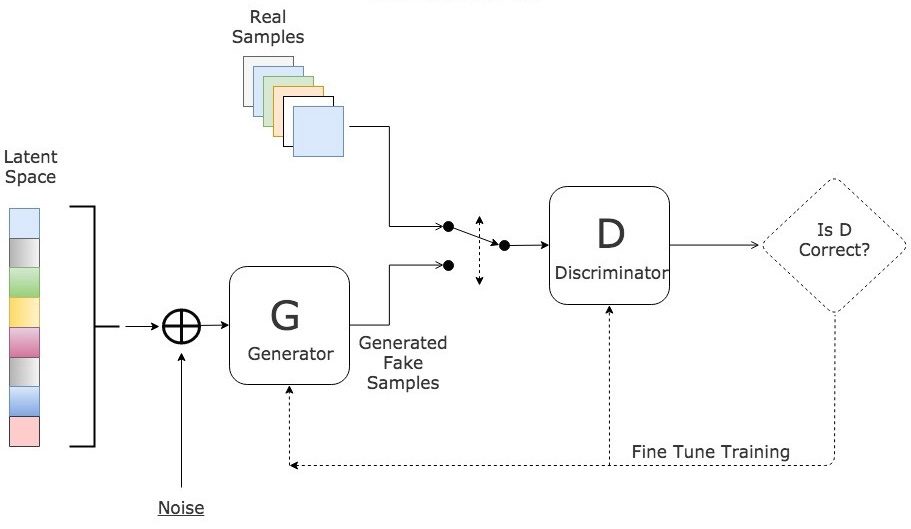
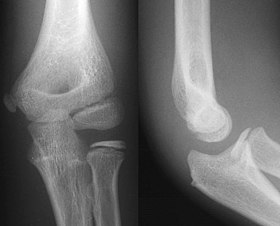
This thesis works to address a pivotal challenge in medical image analysis: the reliance on extensive labeled datasets, which are often limited due to the need for expert annotation and constrained by privacy and legal issues. By focusing on the development of self-supervised learning techniques and domain adaptation methods, this research aims to circumvent these limitations, presenting a novel approach to enhance the utility and efficacy of deep learning in medical imaging. Central to this thesis is the development of the Medformer, an innovative neural network architecture designed for multitask learning and deep domain adaptation. This model is adept at pre-training on diverse medical image datasets, handling varying sizes and modalities, and is equipped with a dynamic input-output adaptation mechanism. This enables efficient processing and integration of a wide range of medical image types, from 2D X-rays to complex 3D MRIs, thus mitigating the dependency on large labeled datasets. Further, the thesis explores the current state of self-supervised learning in medical imaging. It introduces novel pretext tasks that are capable of extracting meaningful information from unlabeled data, significantly advancing the model's interpretative abilities. This approach is validated through rigorous experimentation, including the use of the MedMNIST dataset, demonstrating the model's proficiency in learning generalized features applicable to various downstream tasks. In summary, this thesis contributes to the advancement of medical image analysis by offering a scalable, adaptable framework that reduces reliance on labeled data. It paves the way for more accurate, efficient diagnostic tools in healthcare, signifying a major step forward in the application of deep learning in medical imaging.💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery



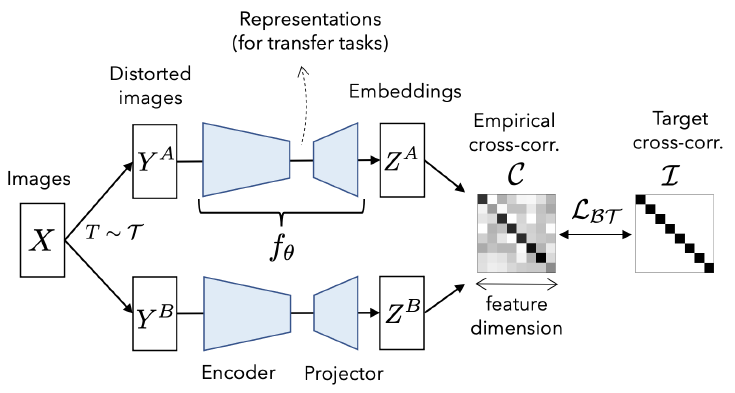
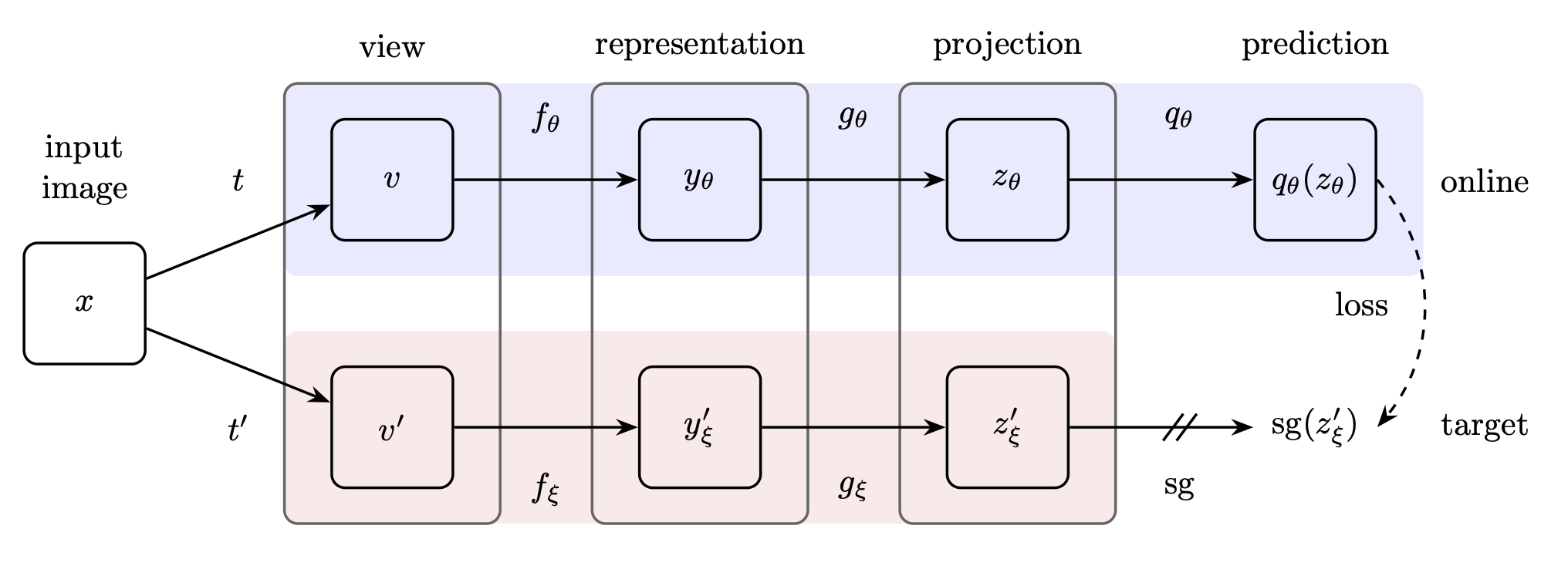
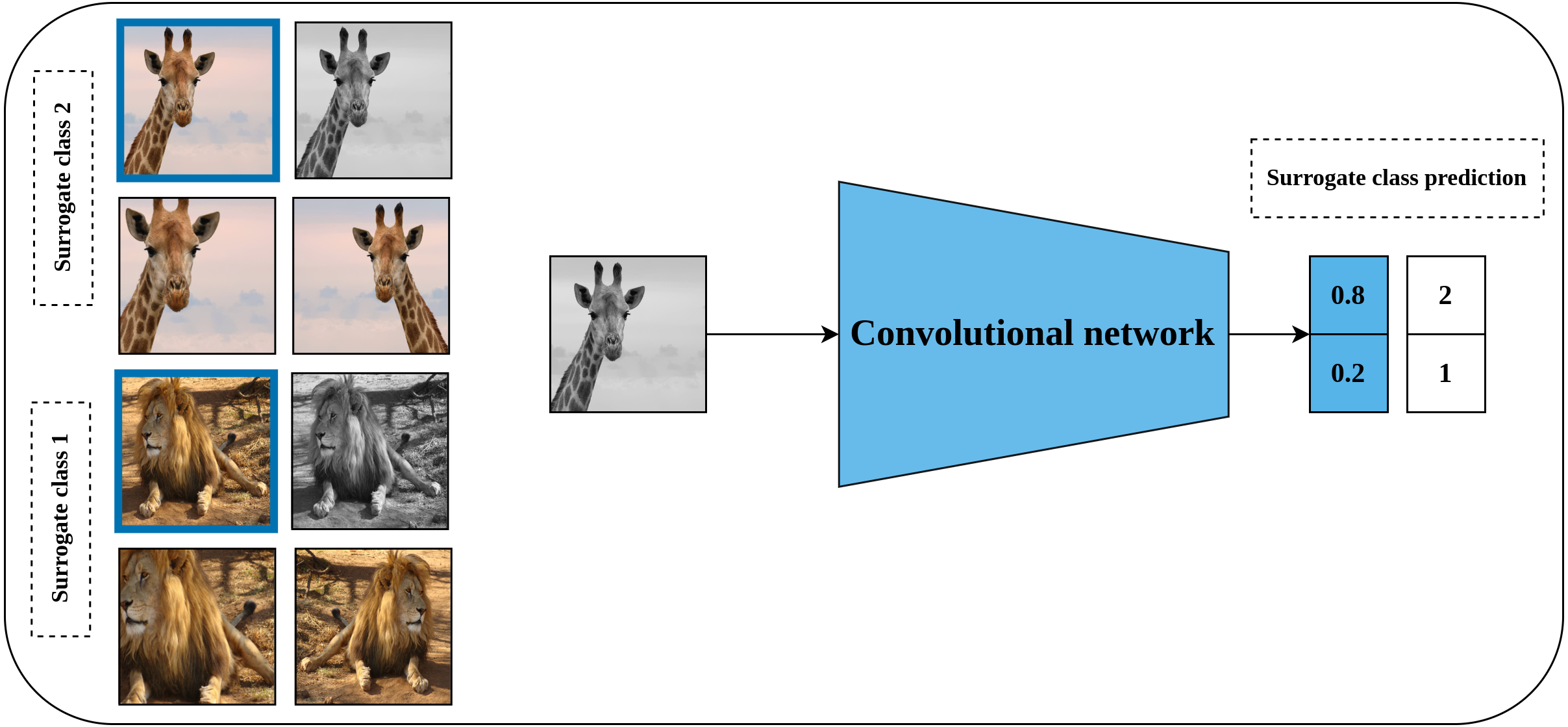

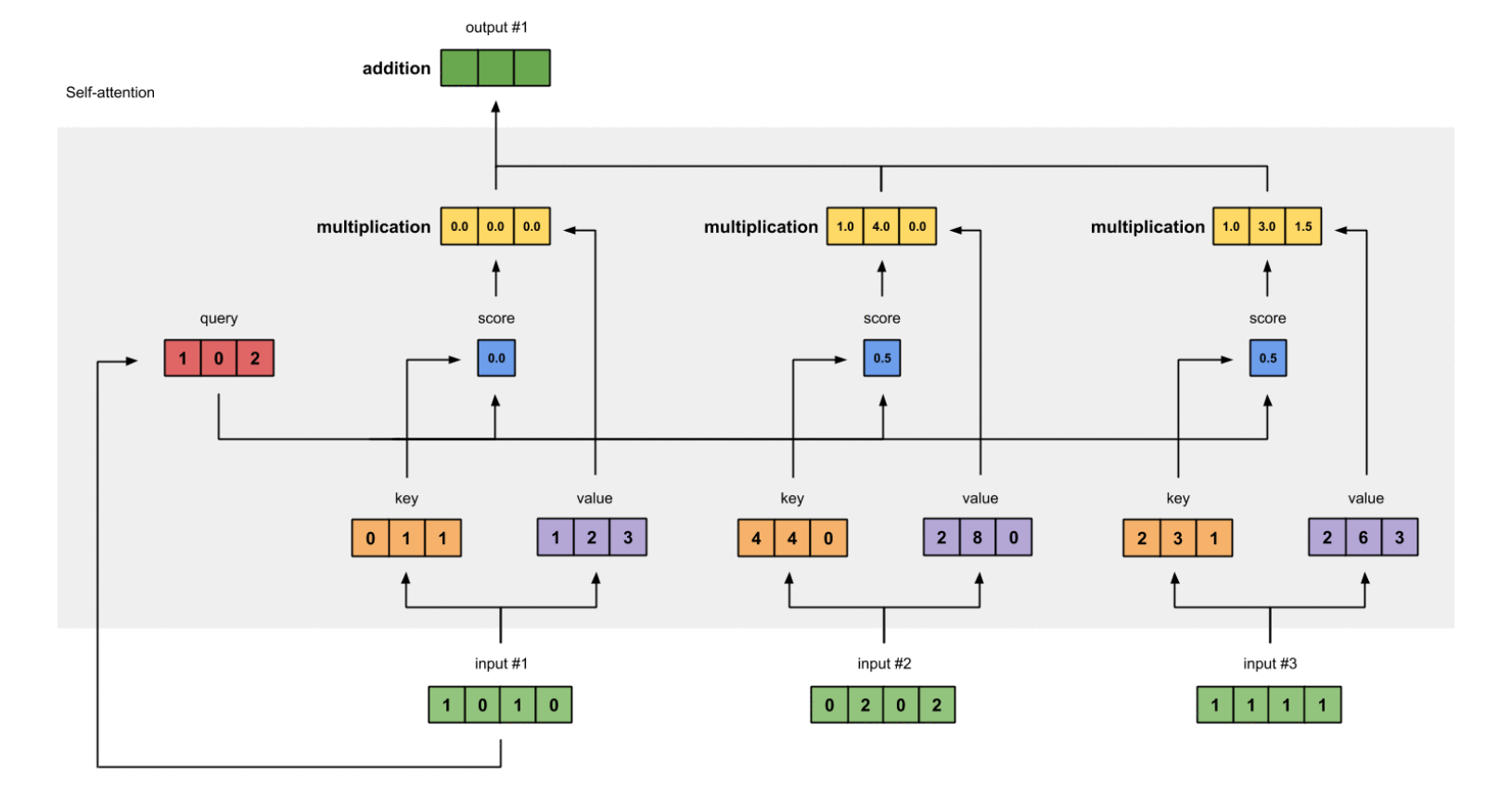



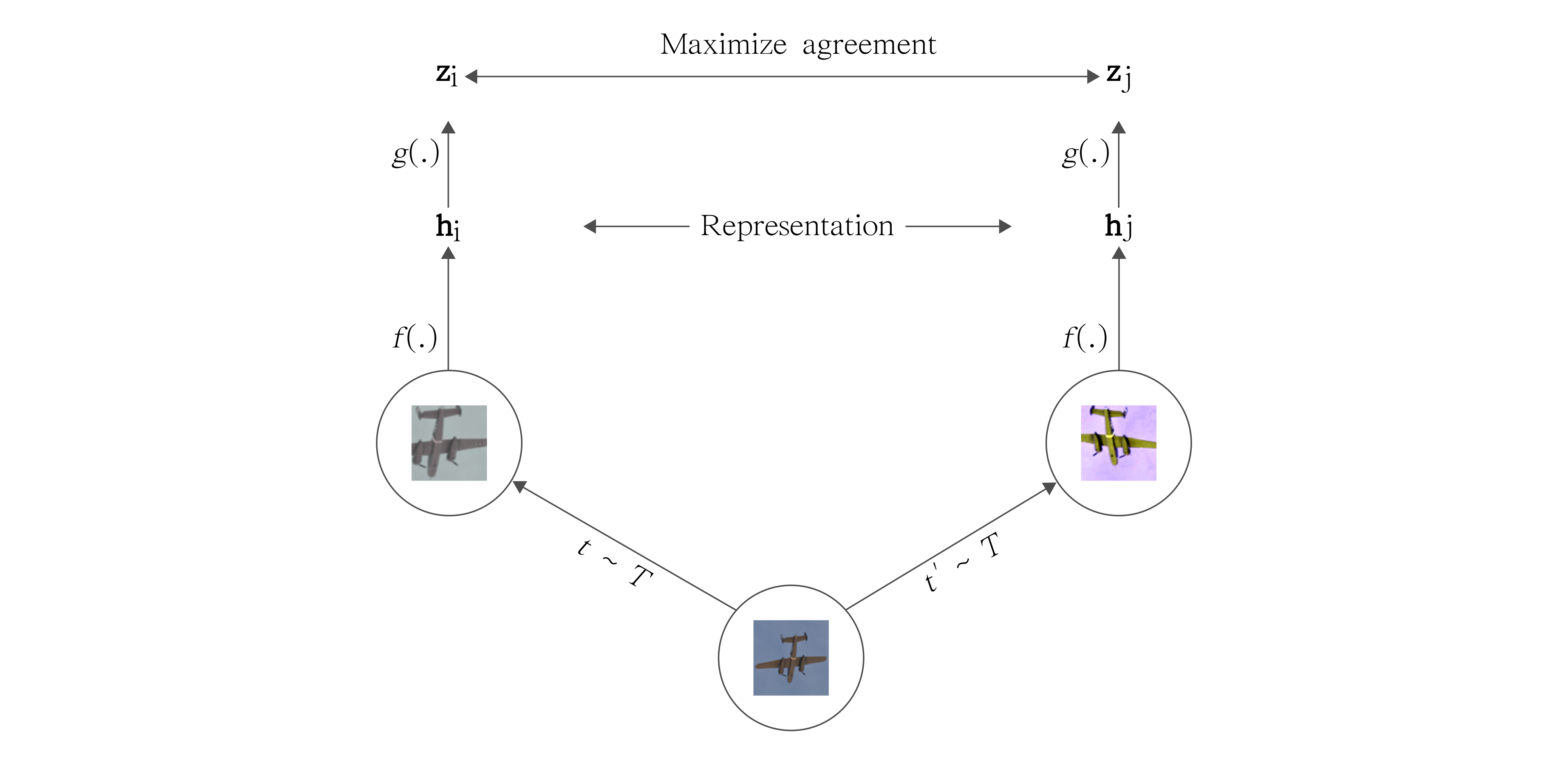

Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.