NOSA: Native and Offloadable Sparse Attention
Reading time: 2 minute
...
📝 Original Info
- Title: NOSA: Native and Offloadable Sparse Attention
- ArXiv ID: 2510.13602
- Date: 2025-10-15
- Authors: ** 논문에 명시된 저자 정보가 제공되지 않았습니다. (추후 논문 본문 혹은 arXiv 페이지에서 확인 필요) **
📝 Abstract
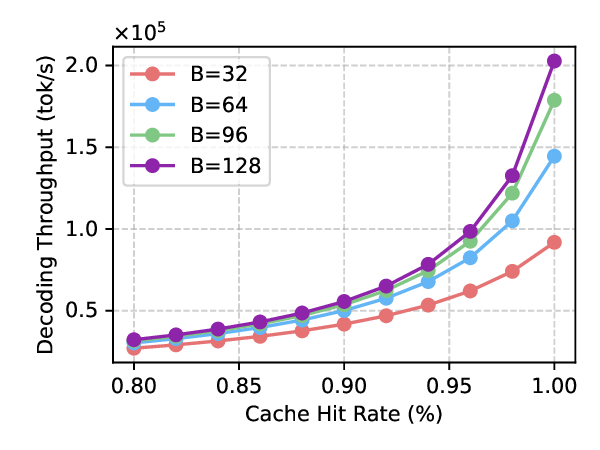
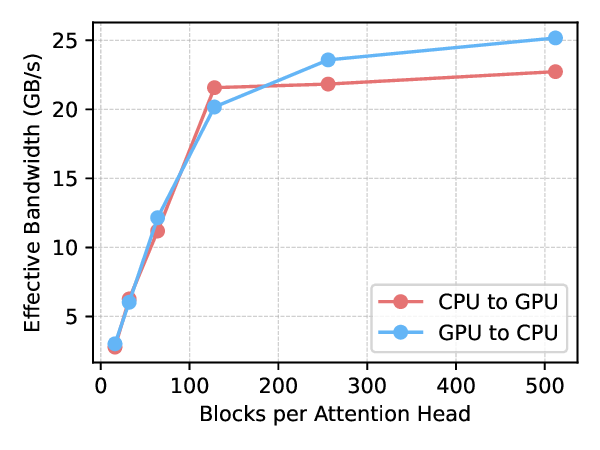
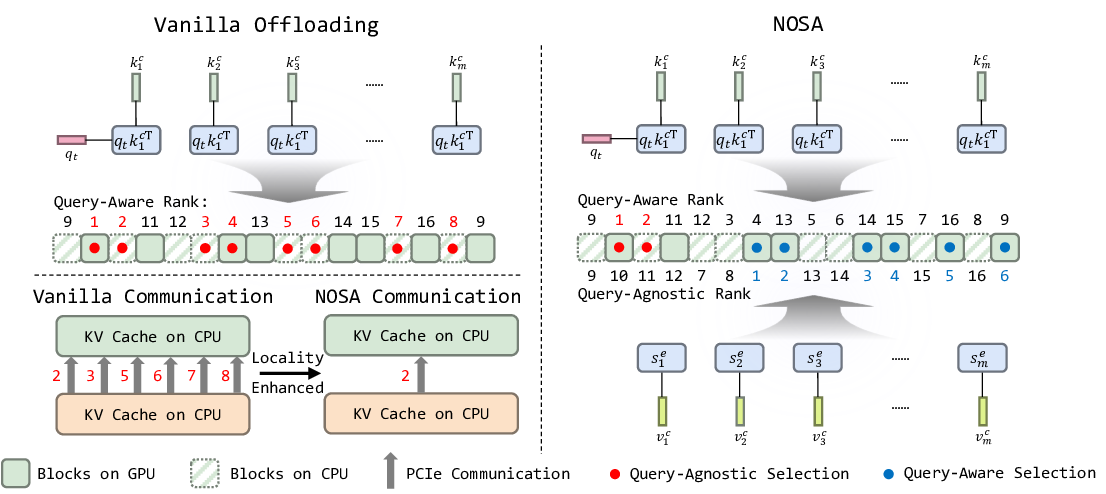
Decoding throughput improvements from larger inference batches are limited by GPU memory, which is largely consumed by the key-value (KV) cache. Prior training-free KV cache offloading alleviates this by keeping redundant context on the CPU and fetching only a sparse subset for attention, but it often degrades long-generation quality due to training-inference mismatch on sparse patterns. Meanwhile, trainable sparse attention is incompatible with efficient offloading, as unconstrained KV accesses may force large CPU-to-GPU transfers and erase throughput gains. To this end, we propose NOSA, a trainable sparse attention mechanism natively designed for KV cache offloading. NOSA explicitly constrains the volume of CPU-GPU KV transfers, thereby achieving low communication overhead and high decoding throughput. We further build NOSI, a KV cache offloading inference system that fully unlocks NOSA's efficiency. Empirical results on 1,3,8B LLMs demonstrate that NOSA outperforms KV cache offloading baselines on general, long-input, and long-generation tasks, while boosting decoding throughput by up to 5.04x, 1.92x, and 1.83x over FullAttn, InfLLMv2, and ShadowKV, respectively. We release our code at https://github.com/thunlp/NOSA.💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery

Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.