A Multimodal XAI Framework for Trustworthy CNNs and Bias Detection in Deep Representation Learning
📝 Original Info
- Title: A Multimodal XAI Framework for Trustworthy CNNs and Bias Detection in Deep Representation Learning
- ArXiv ID: 2510.12957
- Date: 2025-10-14
- Authors: Researchers mentioned in the ArXiv original paper
📝 Abstract
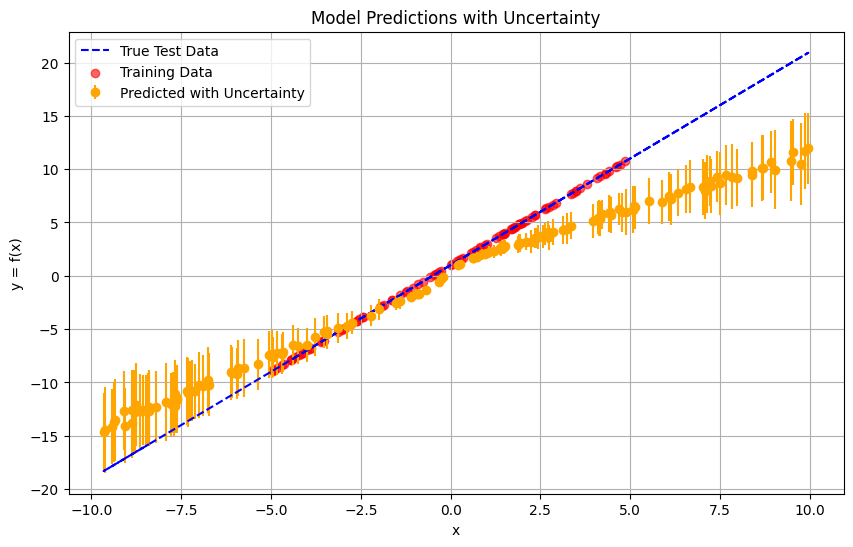
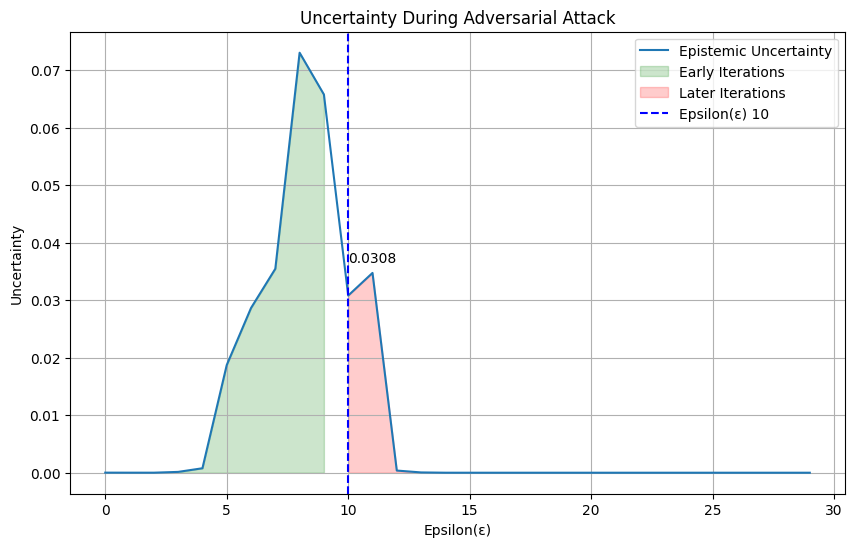
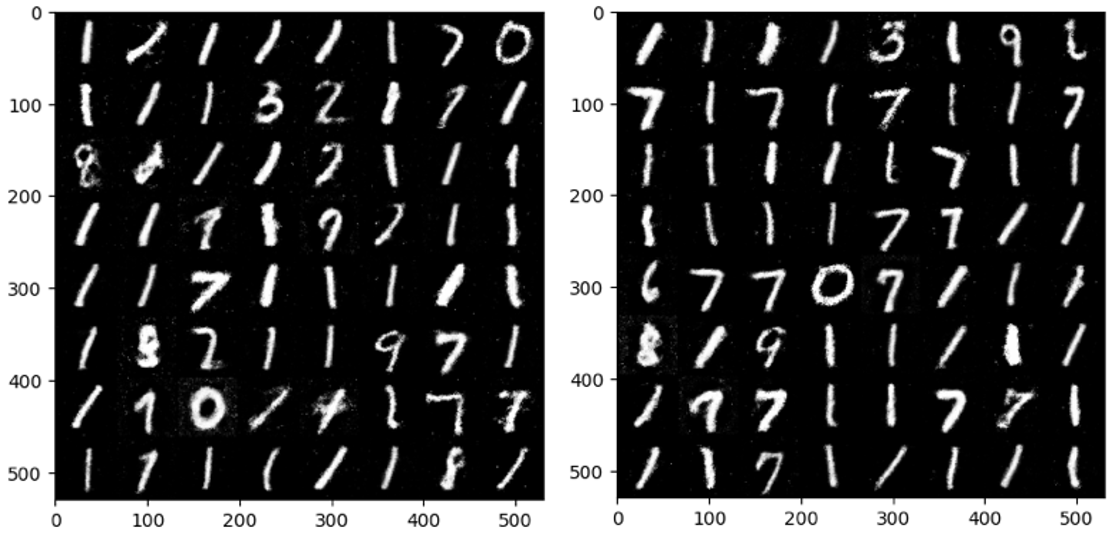
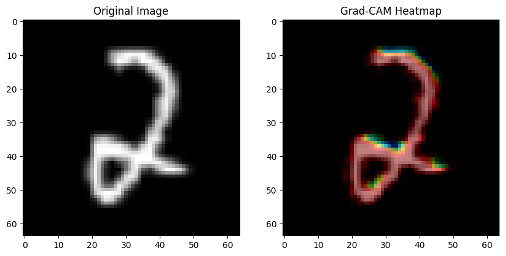
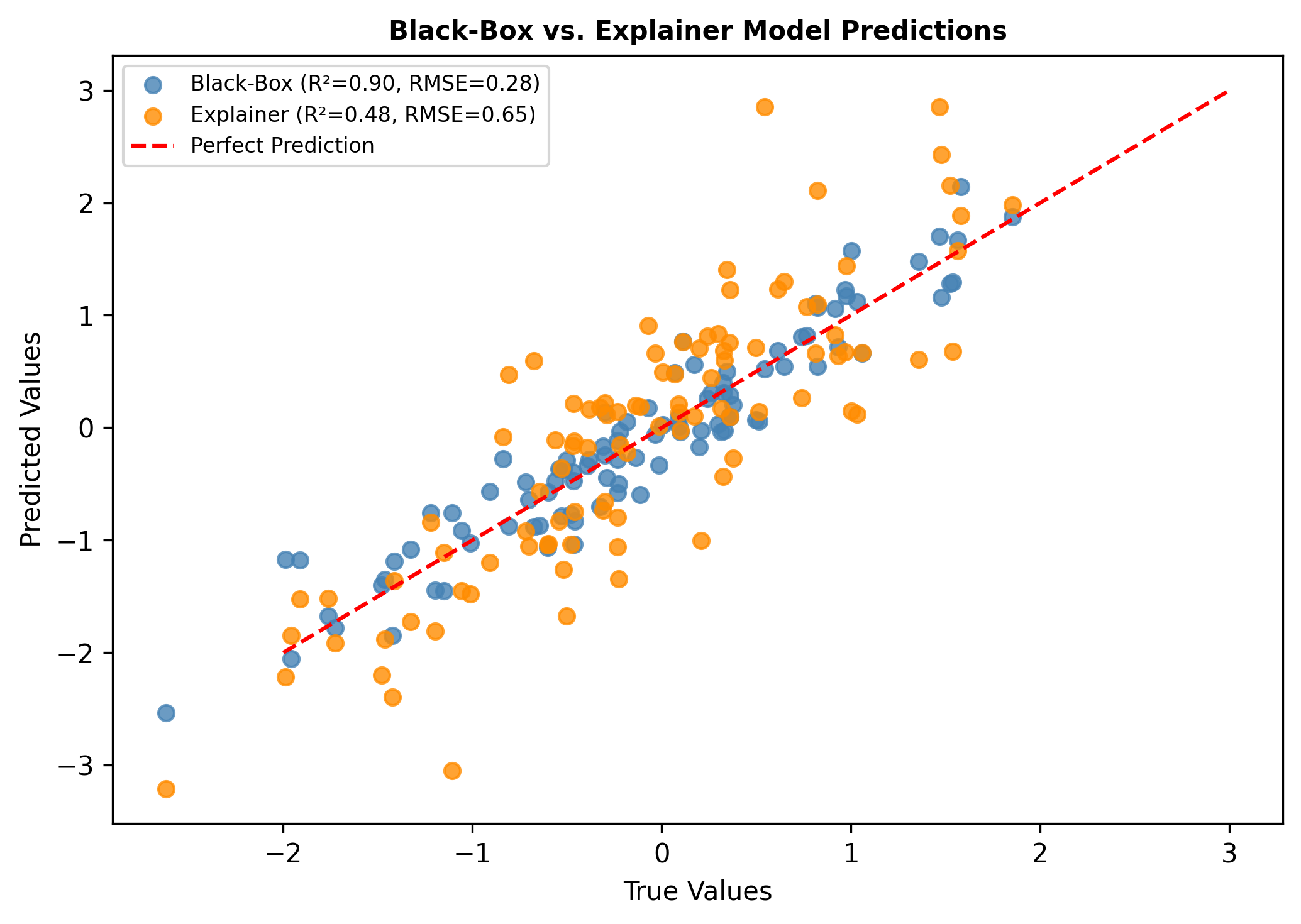
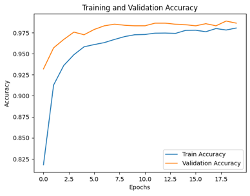
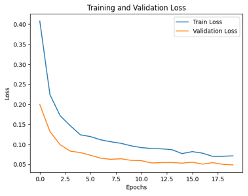
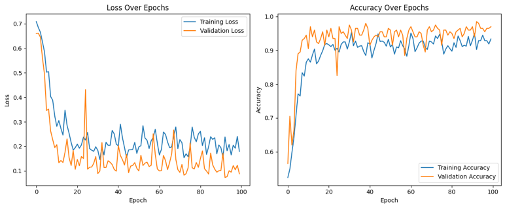
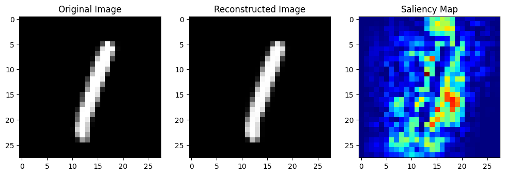
Standard benchmark datasets, such as MNIST, often fail to expose latent biases and multimodal feature complexities, limiting the trustworthiness of deep neural networks in high-stakes applications. We propose a novel multimodal Explainable AI (XAI) framework that unifies attention-augmented feature fusion, Grad-CAM++-based local explanations, and a Reveal-to-Revise feedback loop for bias detection and mitigation. Evaluated on multimodal extensions of MNIST, our approach achieves 93.2% classification accuracy, 91.6% F1-score, and 78.1% explanation fidelity (IoU-XAI), outperforming unimodal and non-explainable baselines. Ablation studies demonstrate that integrating interpretability with bias-aware learning enhances robustness and human alignment. Our work bridges the gap between performance, transparency, and fairness, highlighting a practical pathway for trustworthy AI in sensitive domains.💡 Deep Analysis
This research explores the key findings and methodology presented in the paper: A Multimodal XAI Framework for Trustworthy CNNs and Bias Detection in Deep Representation Learning.Standard benchmark datasets, such as MNIST, often fail to expose latent biases and multimodal feature complexities, limiting the trustworthiness of deep neural networks in high-stakes applications. We propose a novel multimodal Explainable AI (XAI) framework that unifies attention-augmented feature fusion, Grad-CAM++-based local explanations, and a Reveal-to-Revise feedback loop for bias detection and mitigation. Evaluated on multimodal extensions of MNIST, our approach achieves 93.2% classification accuracy, 91.6% F1-score, and 78.1% explanation fidelity (IoU-XAI), outperforming unimodal and non-explainable baselines. Ablation studies demonstrate that integrating interpretability with bias-aware learning enhances robustness and human alignment. Our work bridges the gap between performance, transparency, and fairness, highlighting a practical pathway for trustworthy AI in sensitive domains.
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery