Blockchain Meets Adaptive Honeypots: A Trust-Aware Approach to Next-Gen IoT Security
Reading time: 2 minute
...
📝 Original Info
- Title: Blockchain Meets Adaptive Honeypots: A Trust-Aware Approach to Next-Gen IoT Security
- ArXiv ID: 2504.16226
- Date: 2025-04-22
- Authors: 논문에 명시된 저자 정보가 제공되지 않았습니다.
📝 Abstract
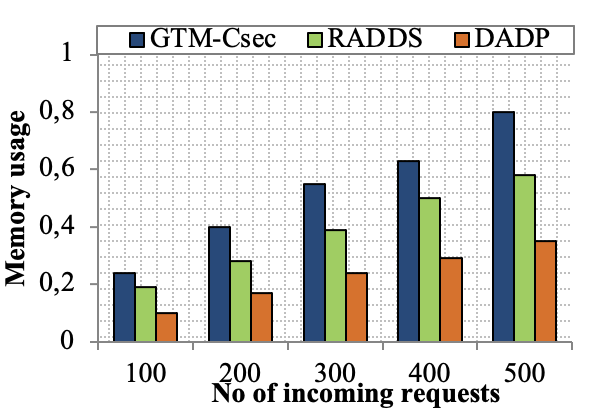
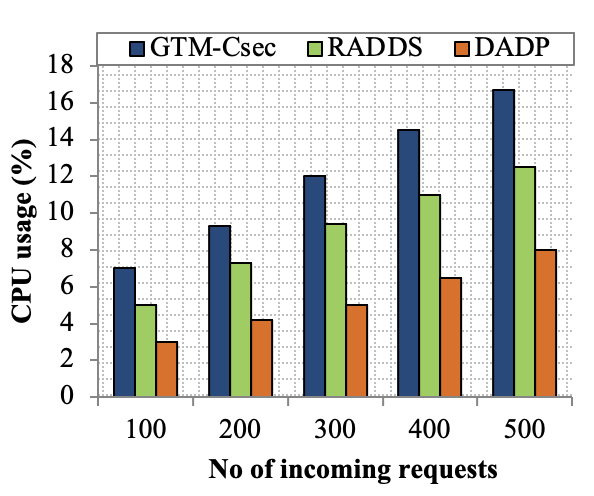
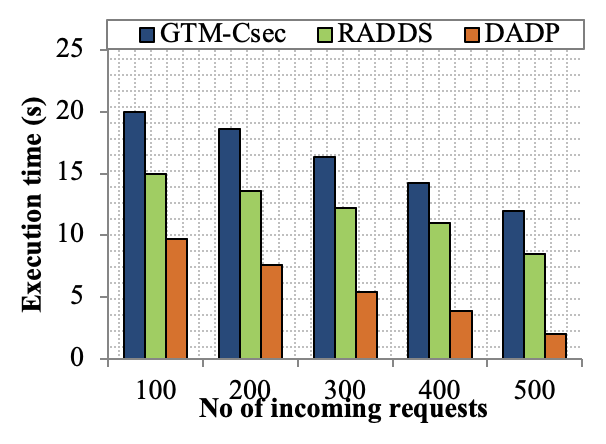
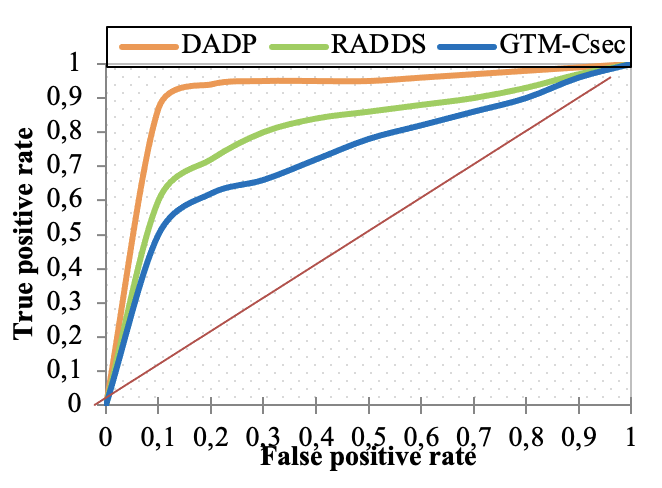
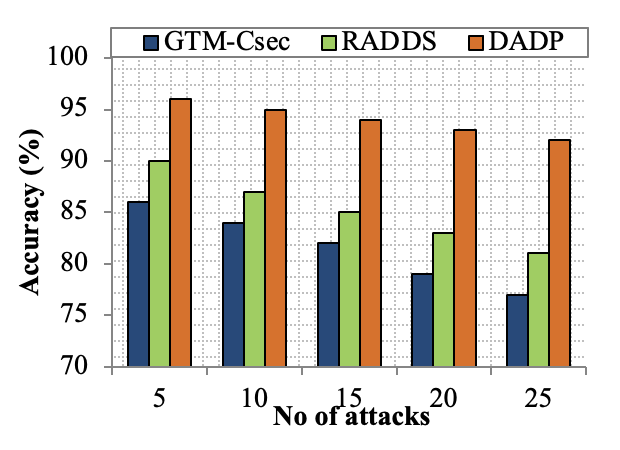
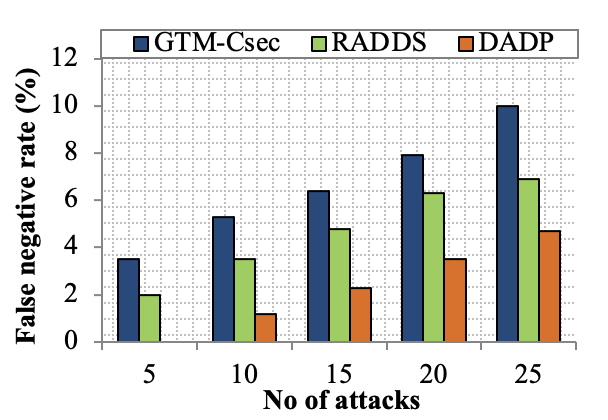
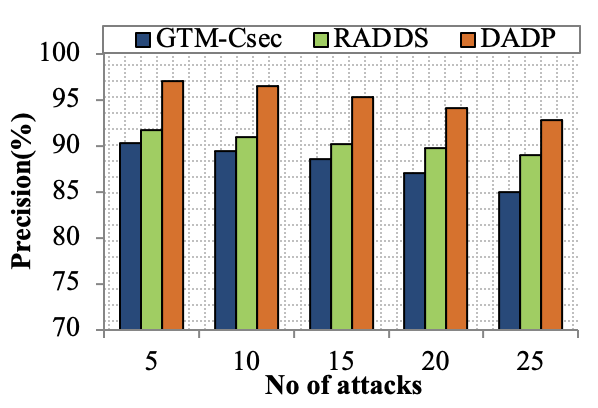
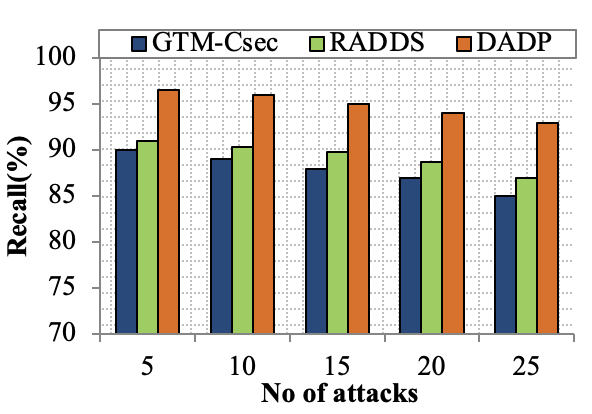
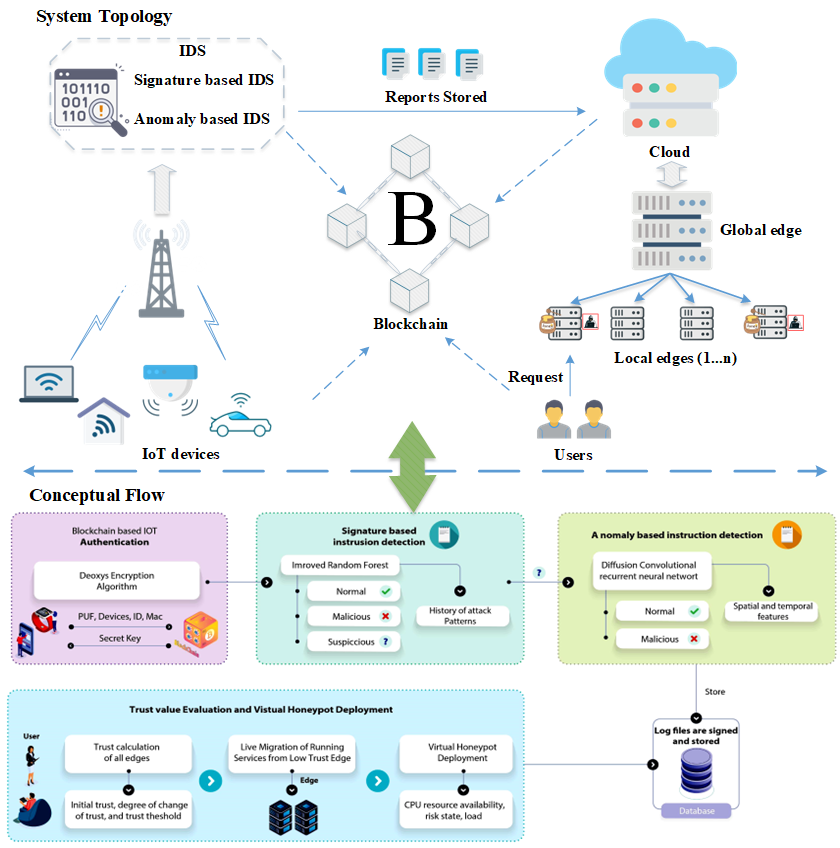
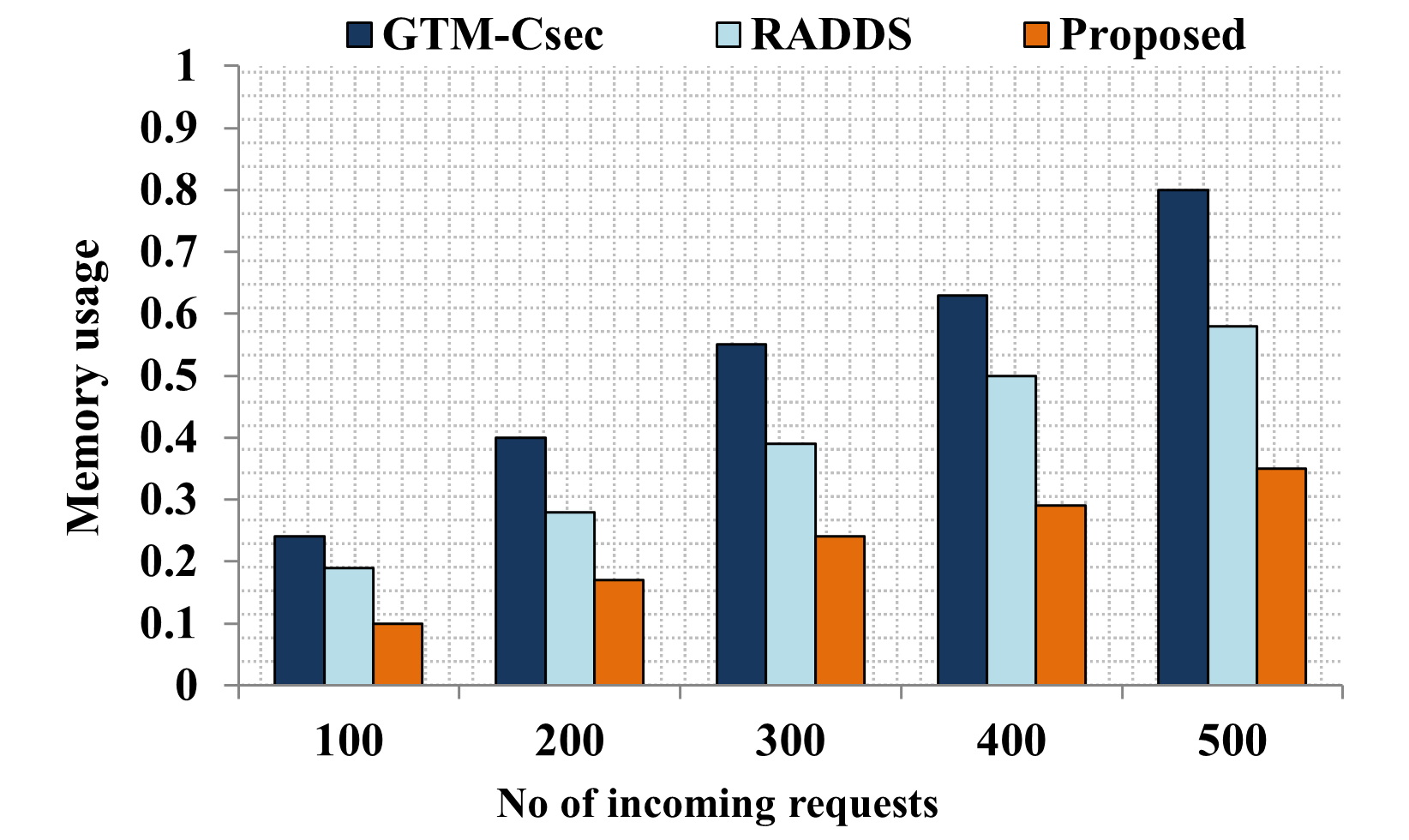
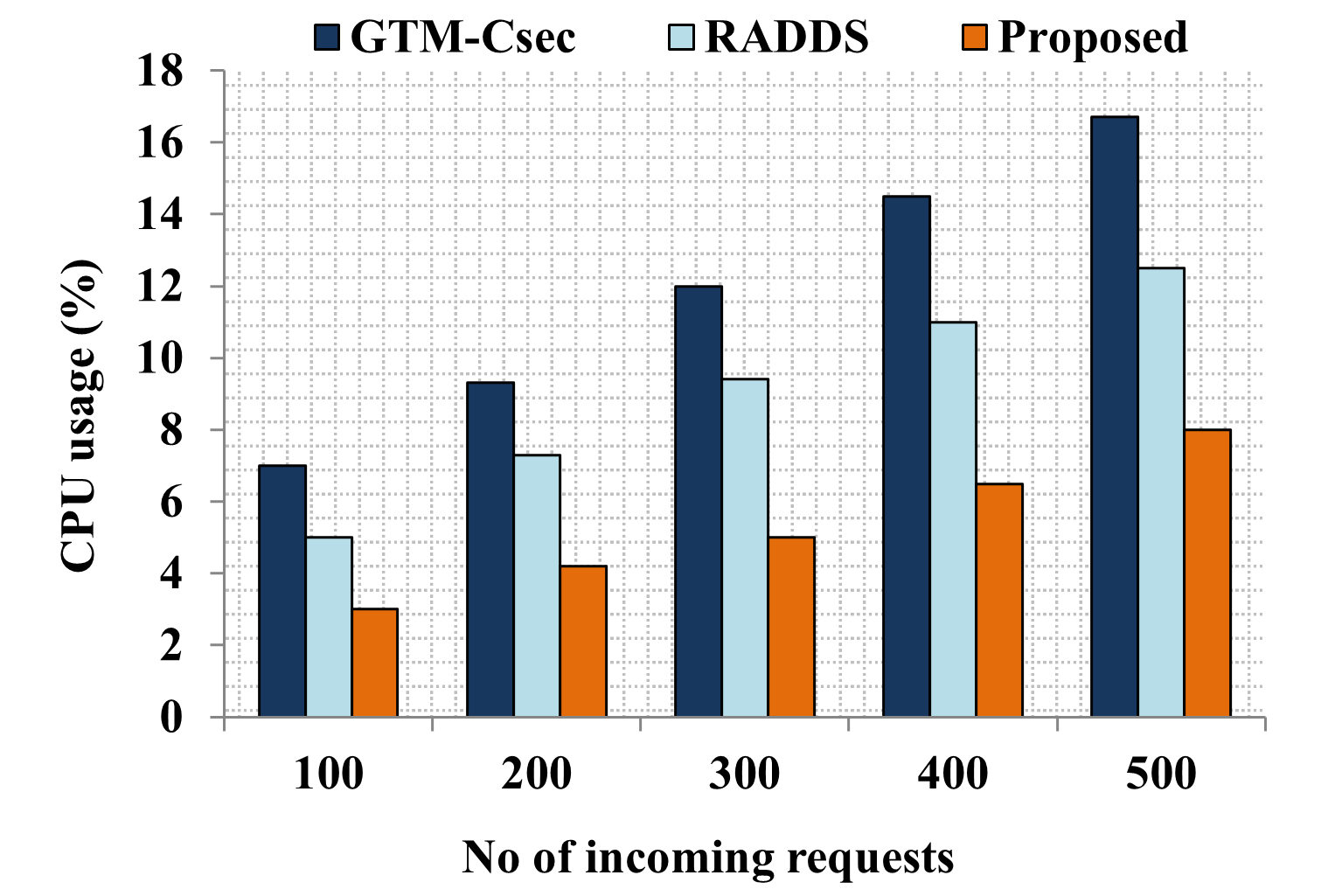
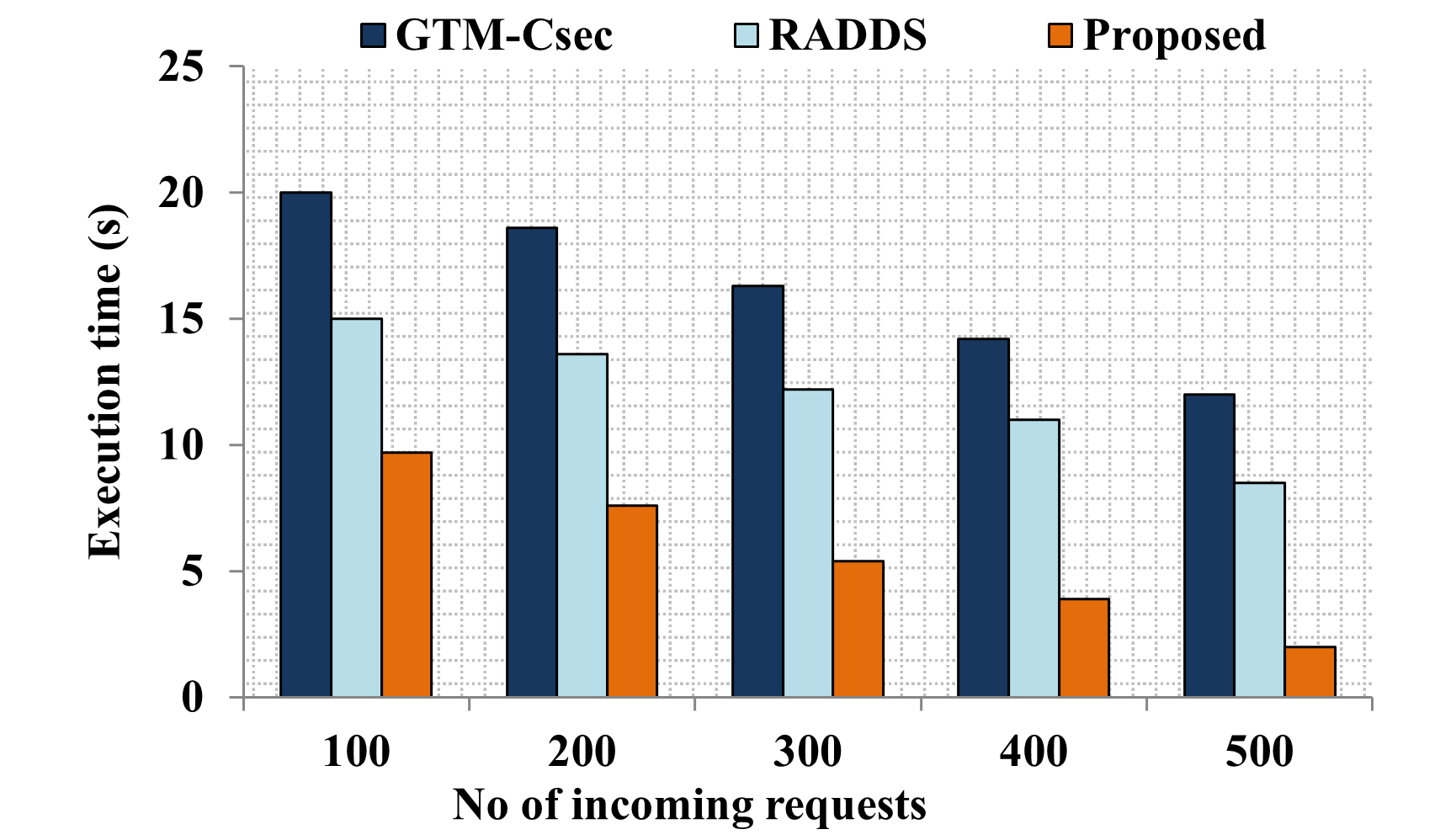
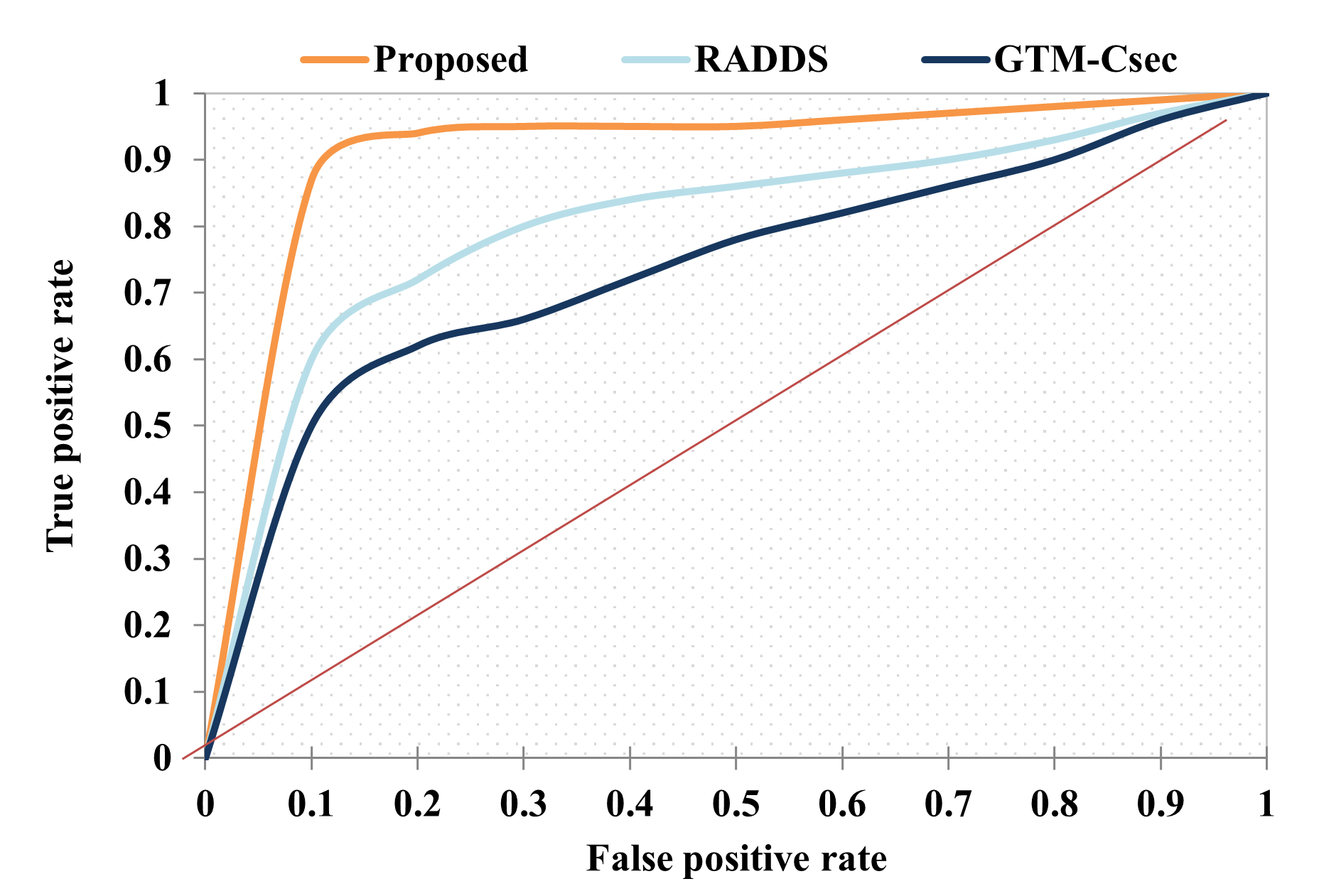
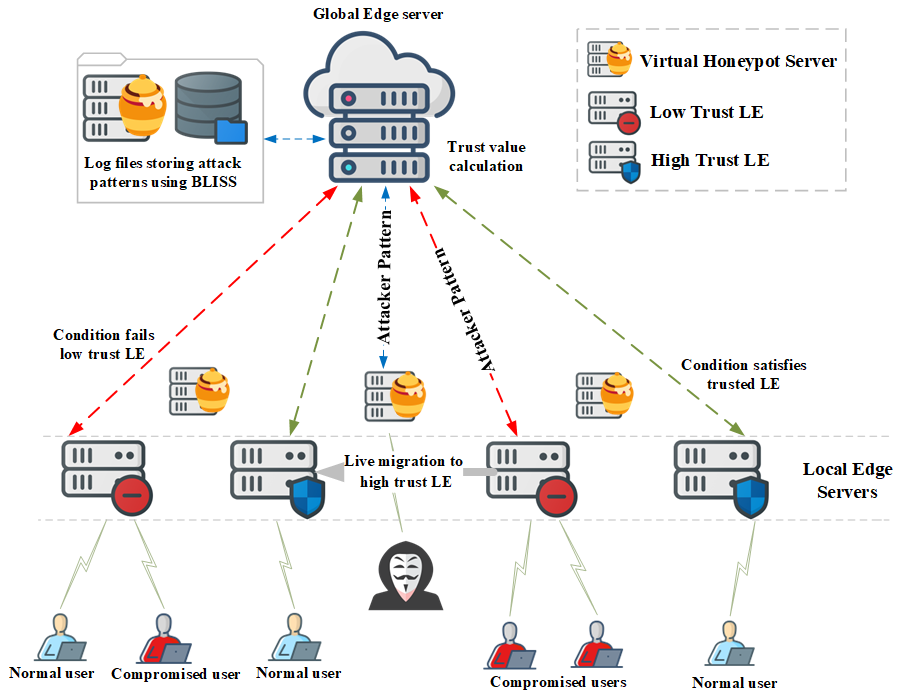
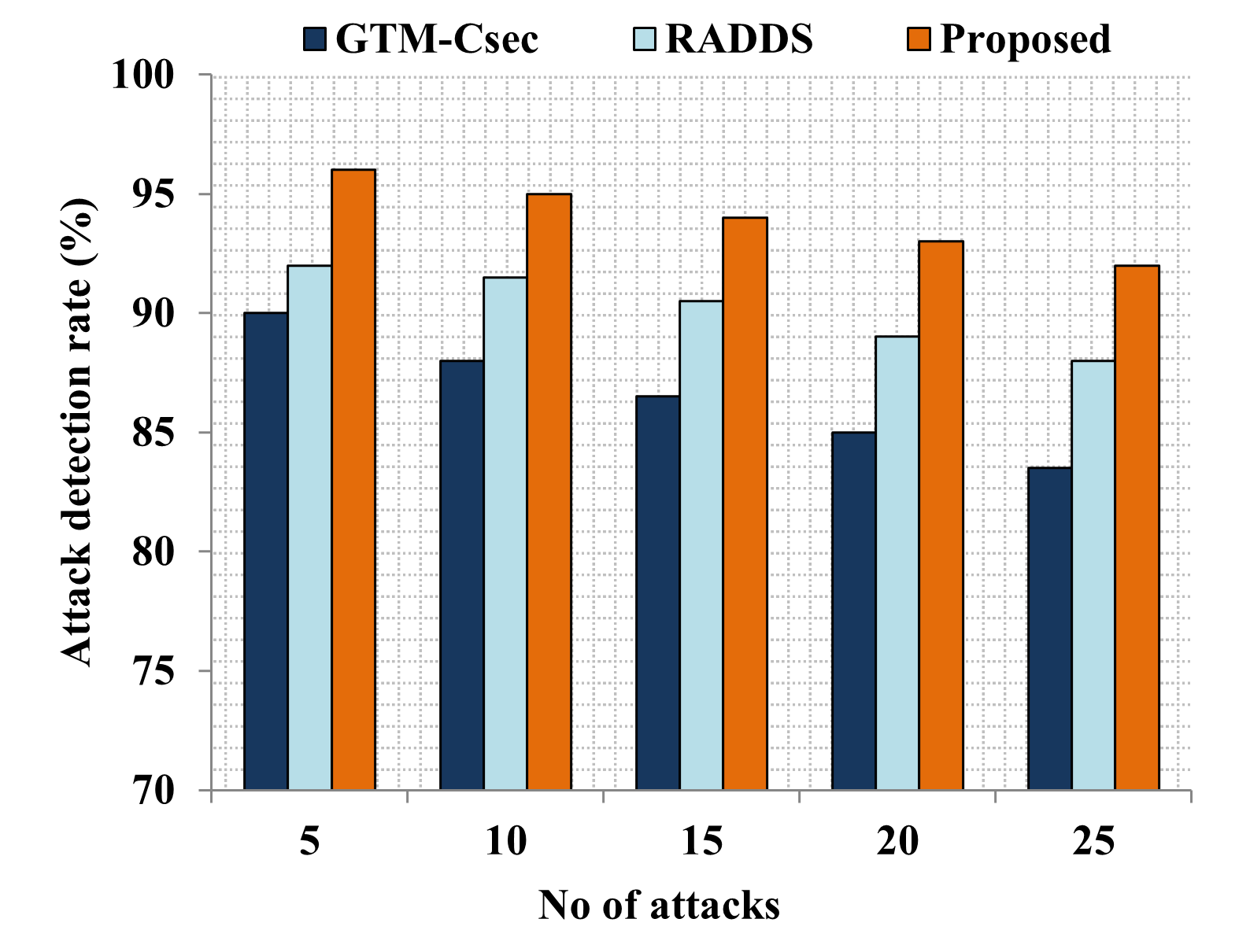
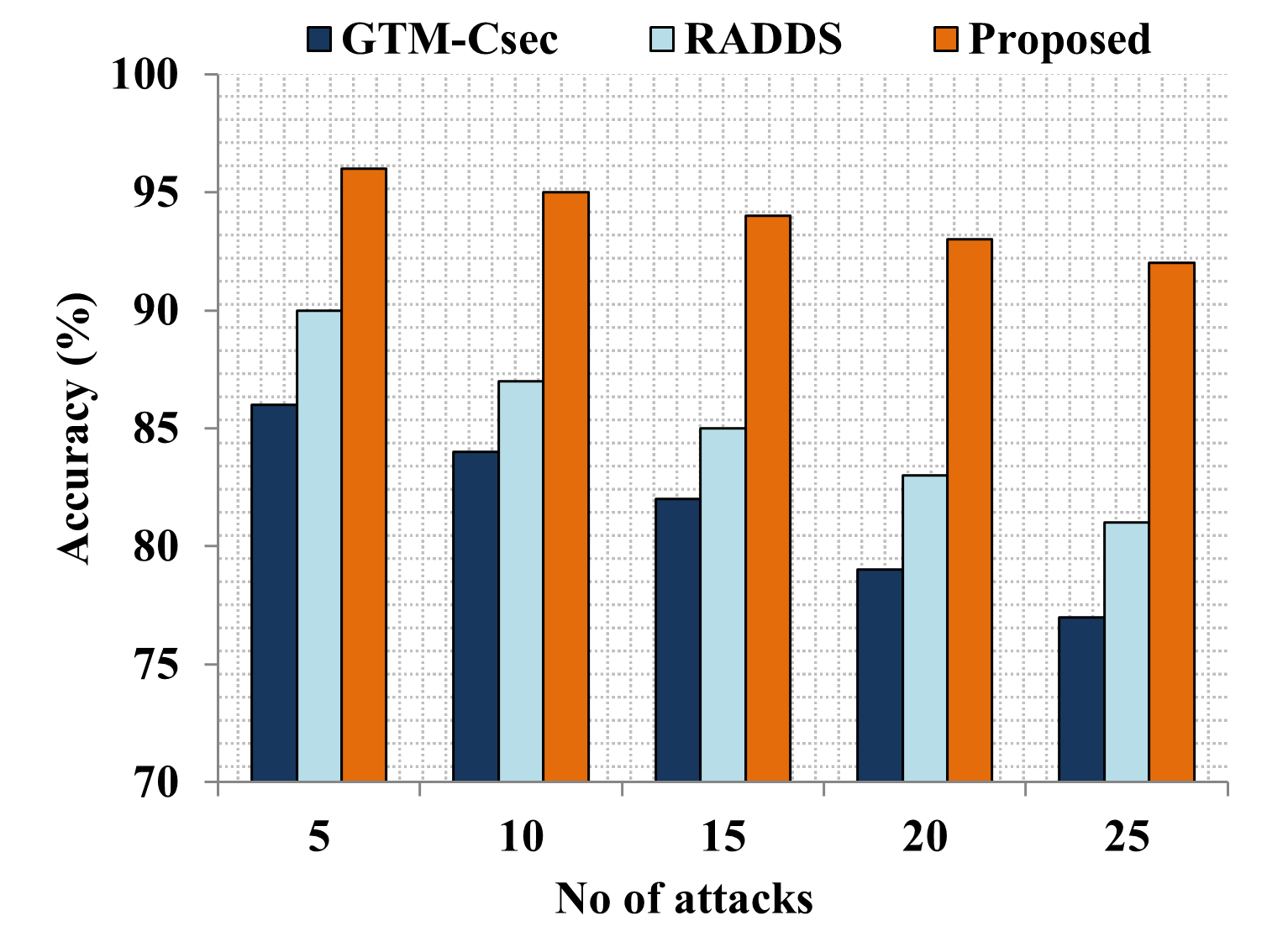
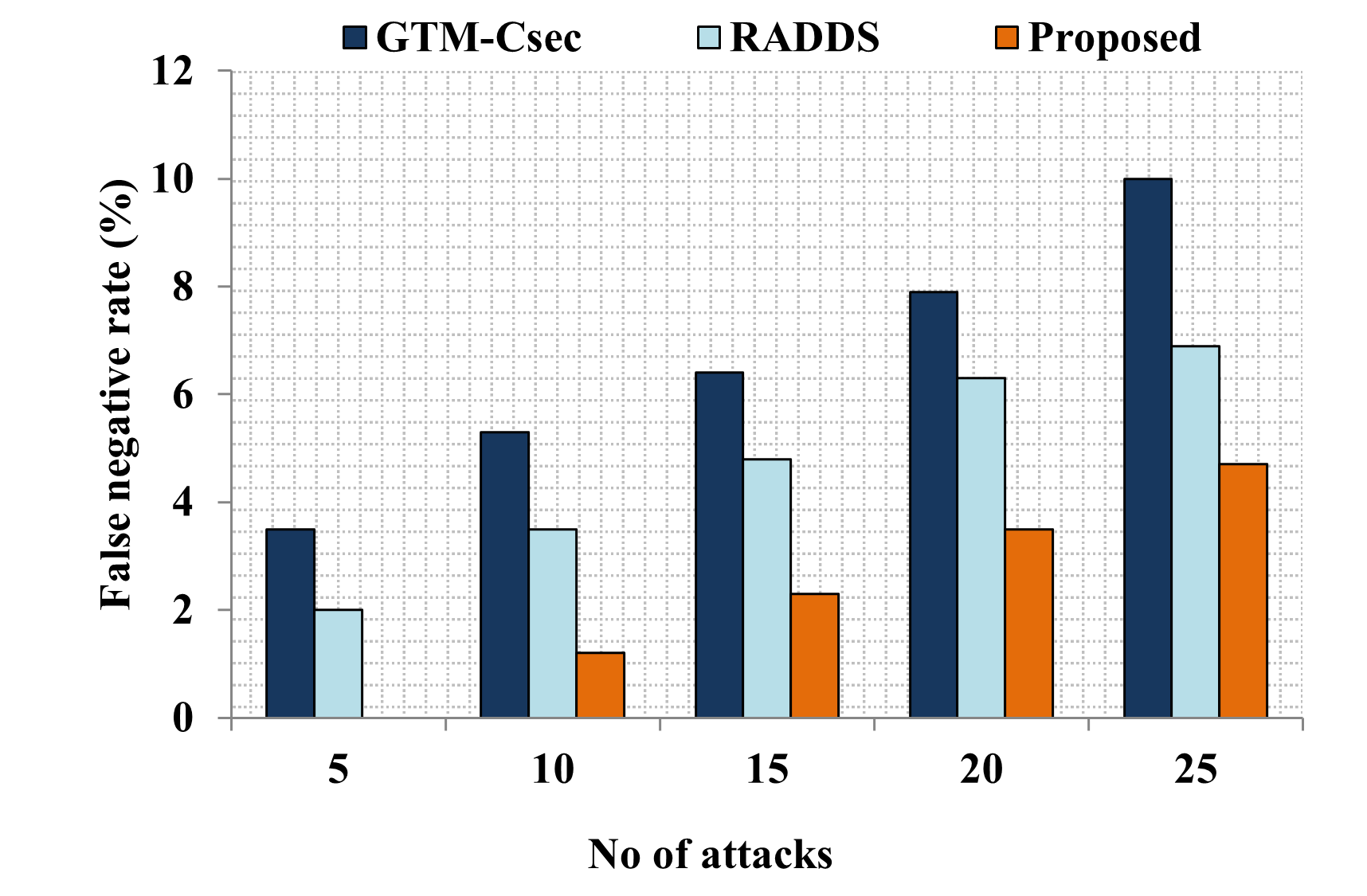
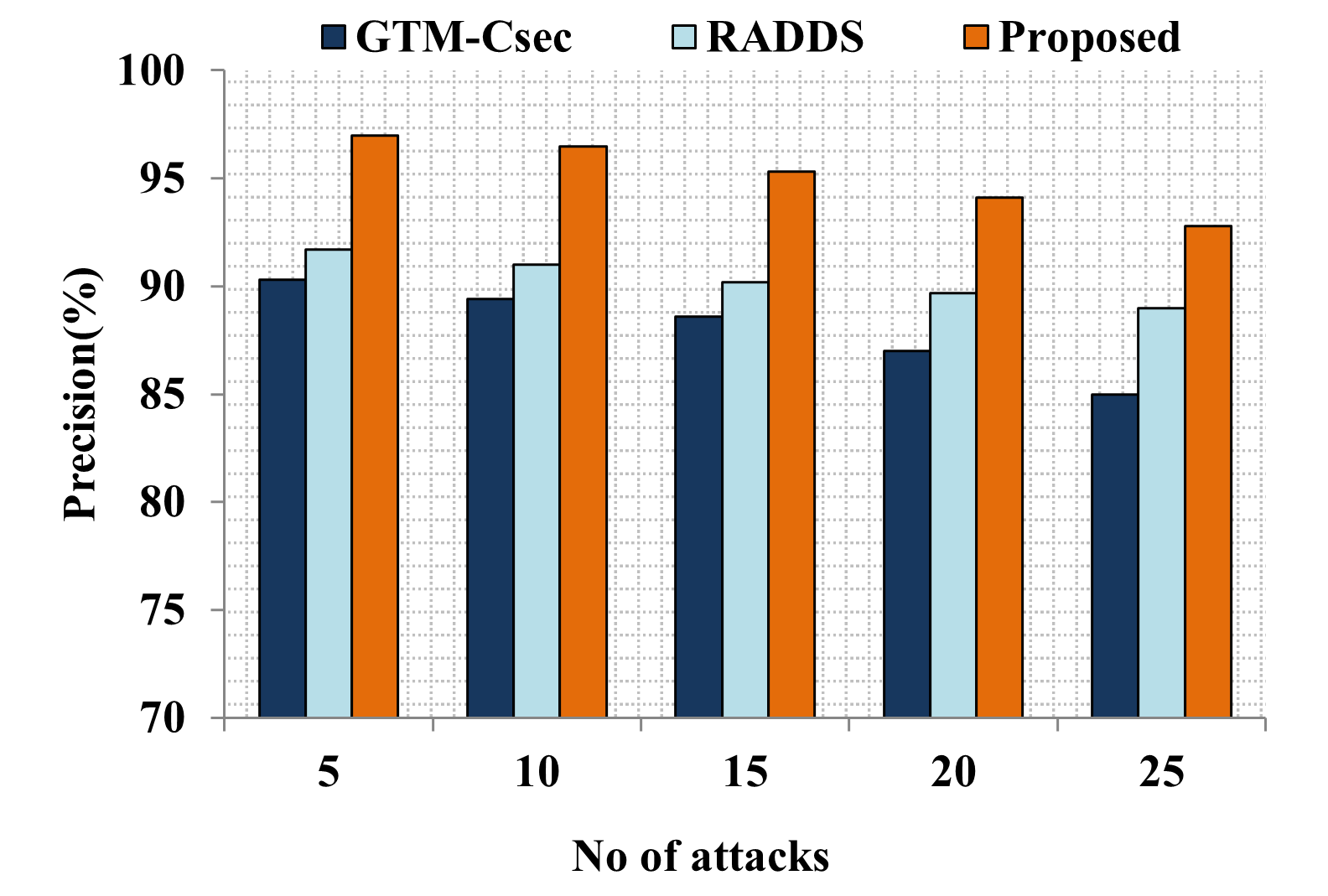
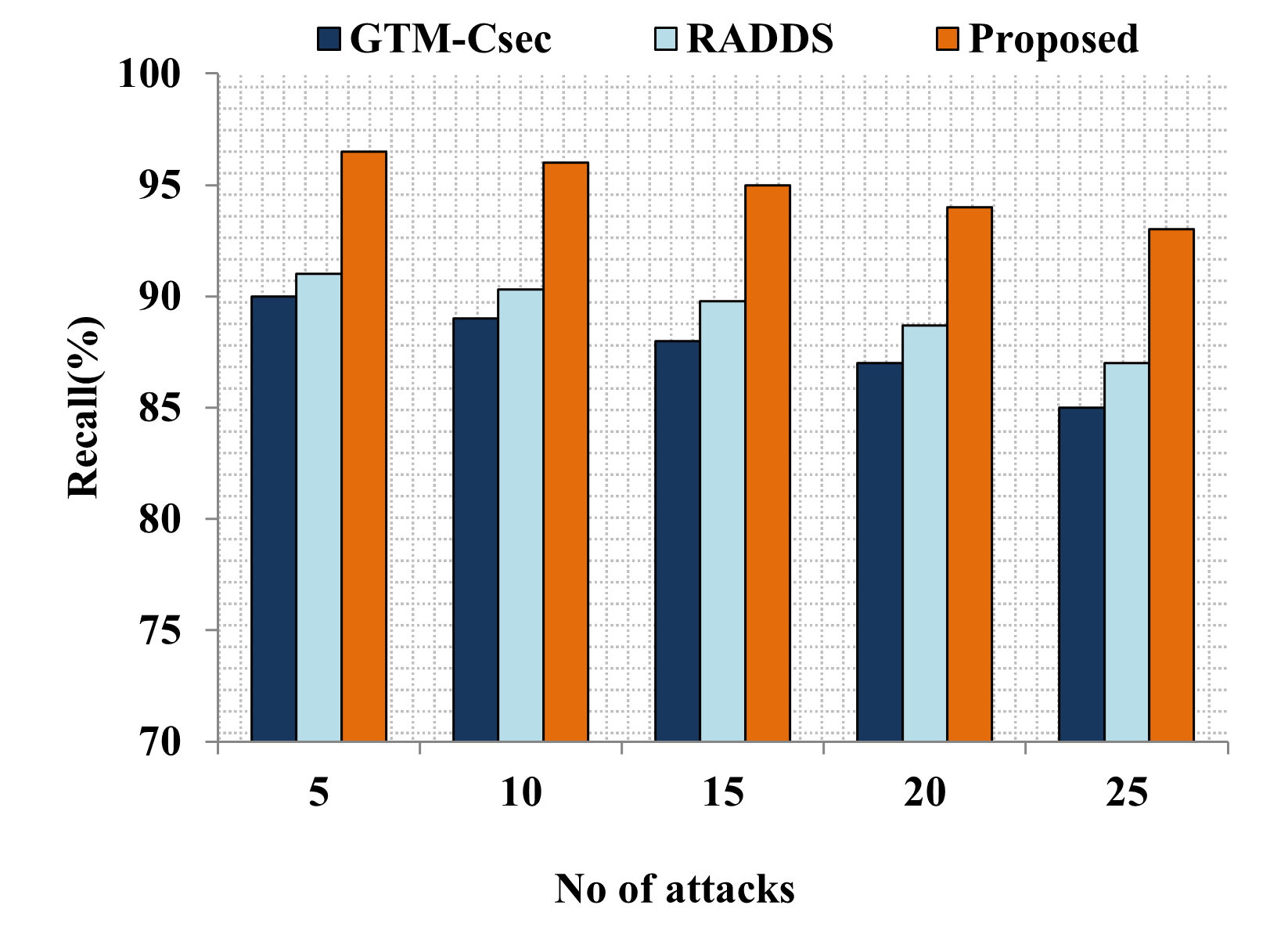
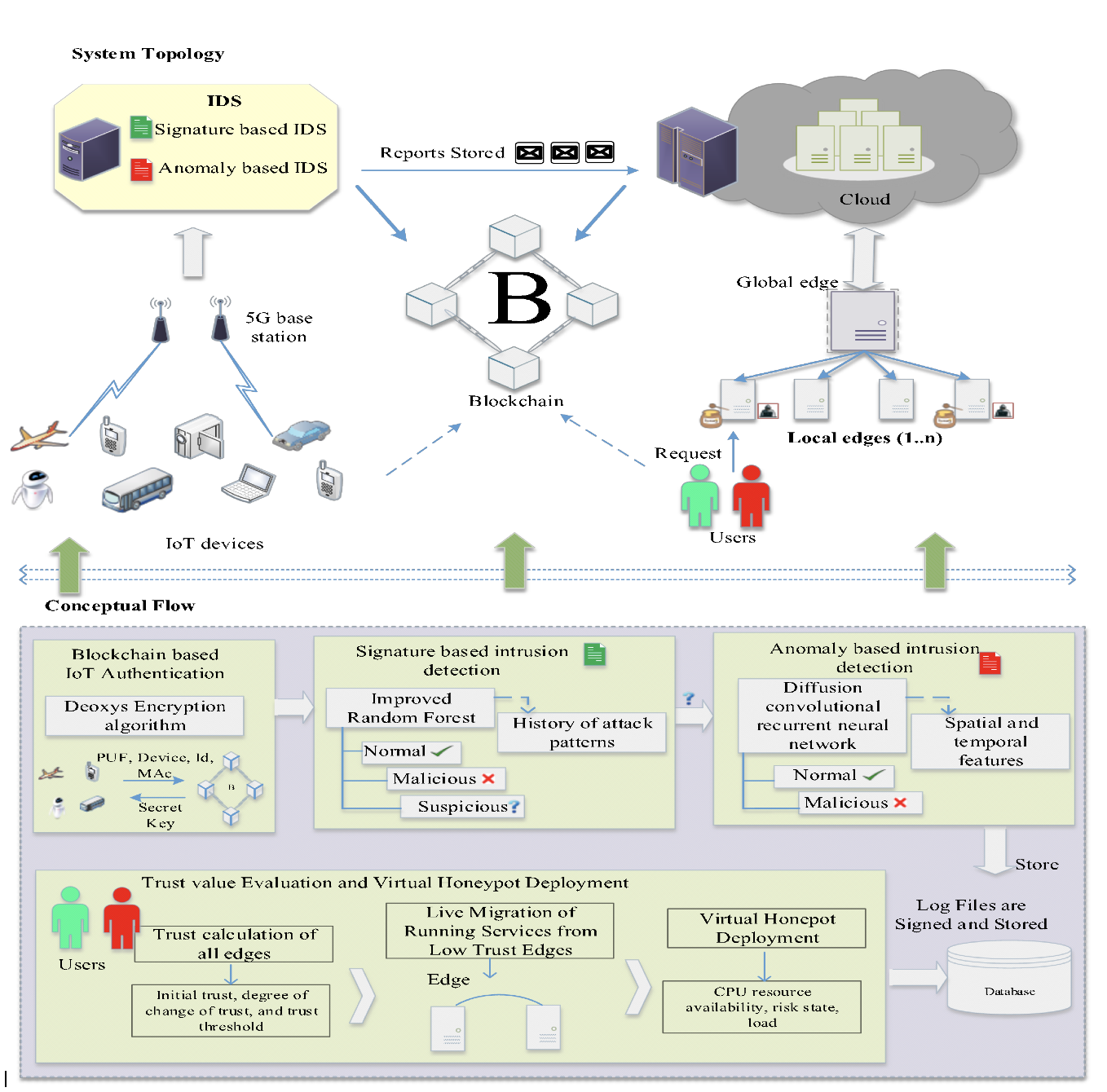
Edge computing-based Next-Generation Wireless Networks (NGWN)-IoT offer enhanced bandwidth capacity for large-scale service provisioning but remain vulnerable to evolving cyber threats. Existing intrusion detection and prevention methods provide limited security as adversaries continually adapt their attack strategies. We propose a dynamic attack detection and prevention approach to address this challenge. First, blockchain-based authentication uses the Deoxys Authentication Algorithm (DAA) to verify IoT device legitimacy before data transmission. Next, a bi-stage intrusion detection system is introduced: the first stage uses signature-based detection via an Improved Random Forest (IRF) algorithm. In contrast, the second stage applies feature-based anomaly detection using a Diffusion Convolution Recurrent Neural Network (DCRNN). To ensure Quality of Service (QoS) and maintain Service Level Agreements (SLA), trust-aware service migration is performed using Heap-Based Optimization (HBO). Additionally, on-demand virtual High-Interaction honeypots deceive attackers and extract attack patterns, which are securely stored using the Bimodal Lattice Signature Scheme (BLISS) to enhance signature-based Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). The proposed framework is implemented in the NS3 simulation environment and evaluated against existing methods across multiple performance metrics, including accuracy, attack detection rate, false negative rate, precision, recall, ROC curve, memory usage, CPU usage, and execution time. Experimental results demonstrate that the framework significantly outperforms existing approaches, reinforcing the security of NGWN-enabled IoT ecosystems💡 Deep Analysis
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery

Reference
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.