An Incremental Non-Linear Manifold Approximation Method
📝 Original Info
- Title: An Incremental Non-Linear Manifold Approximation Method
- ArXiv ID: 2504.09068
- Date: 2025-04-12
- Authors: Praveen T. W. Hettige, Benjamin W. Ong
📝 Abstract
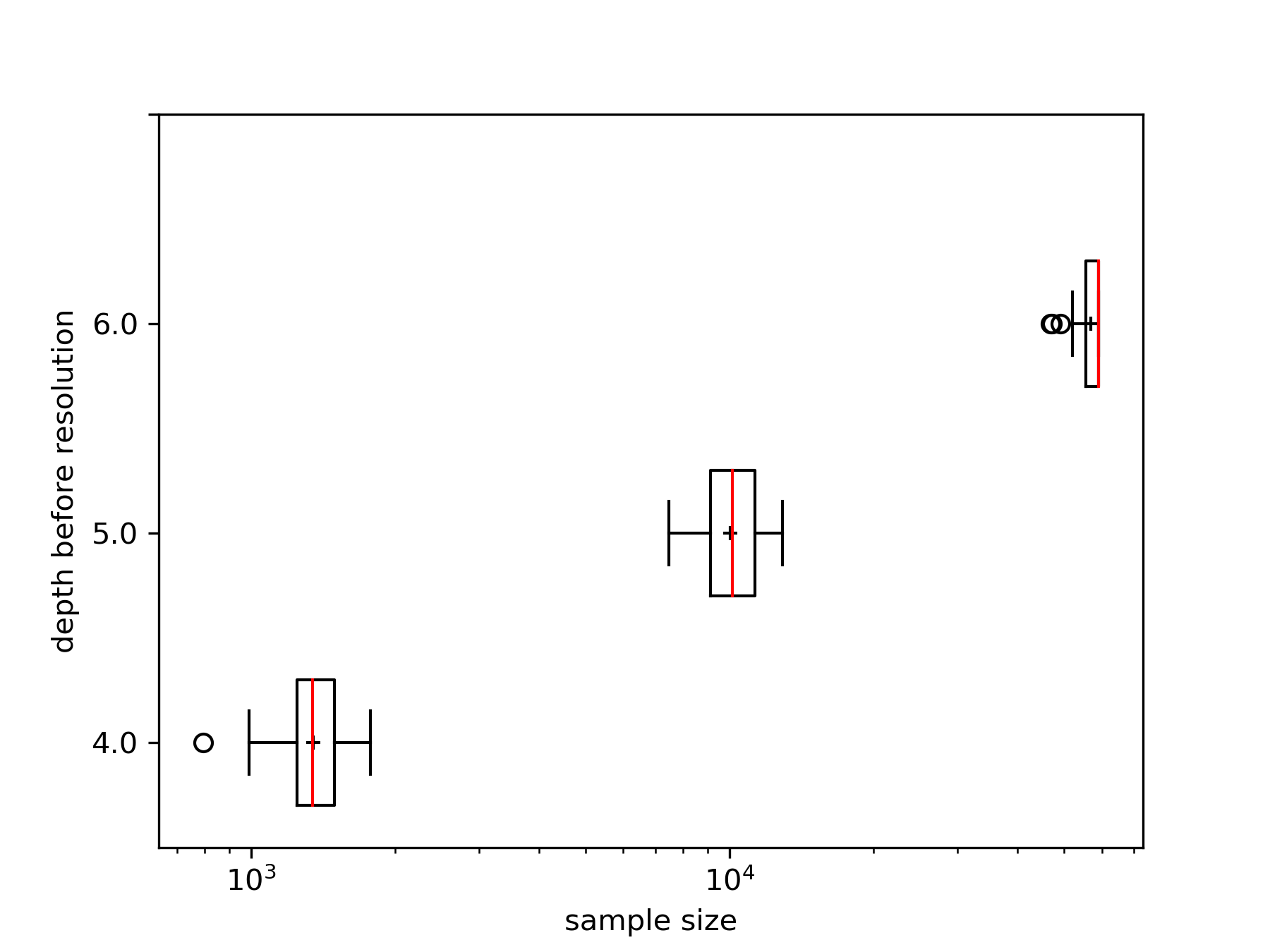
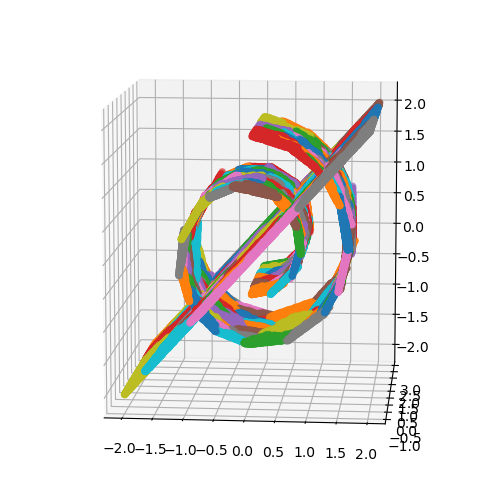
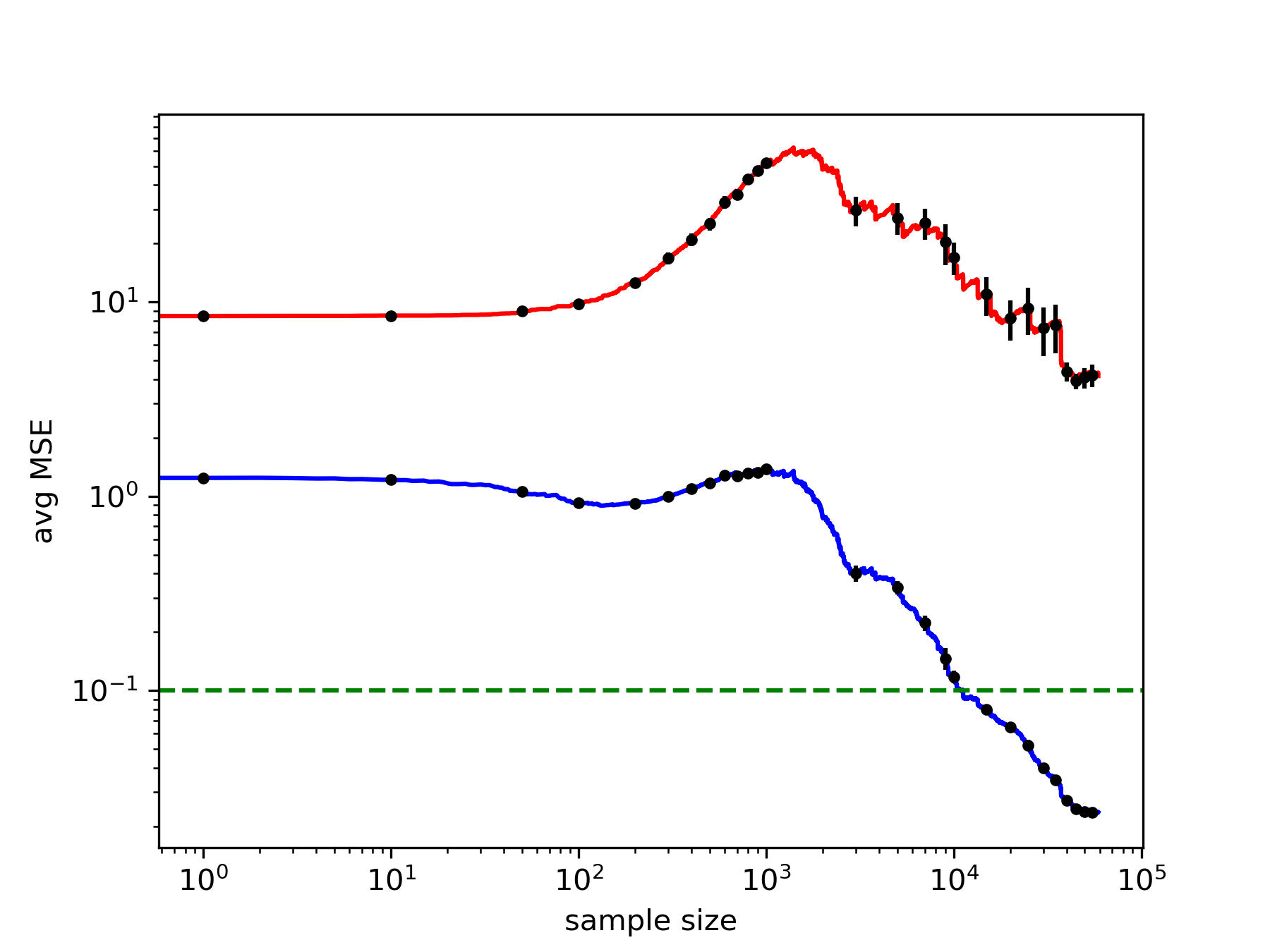
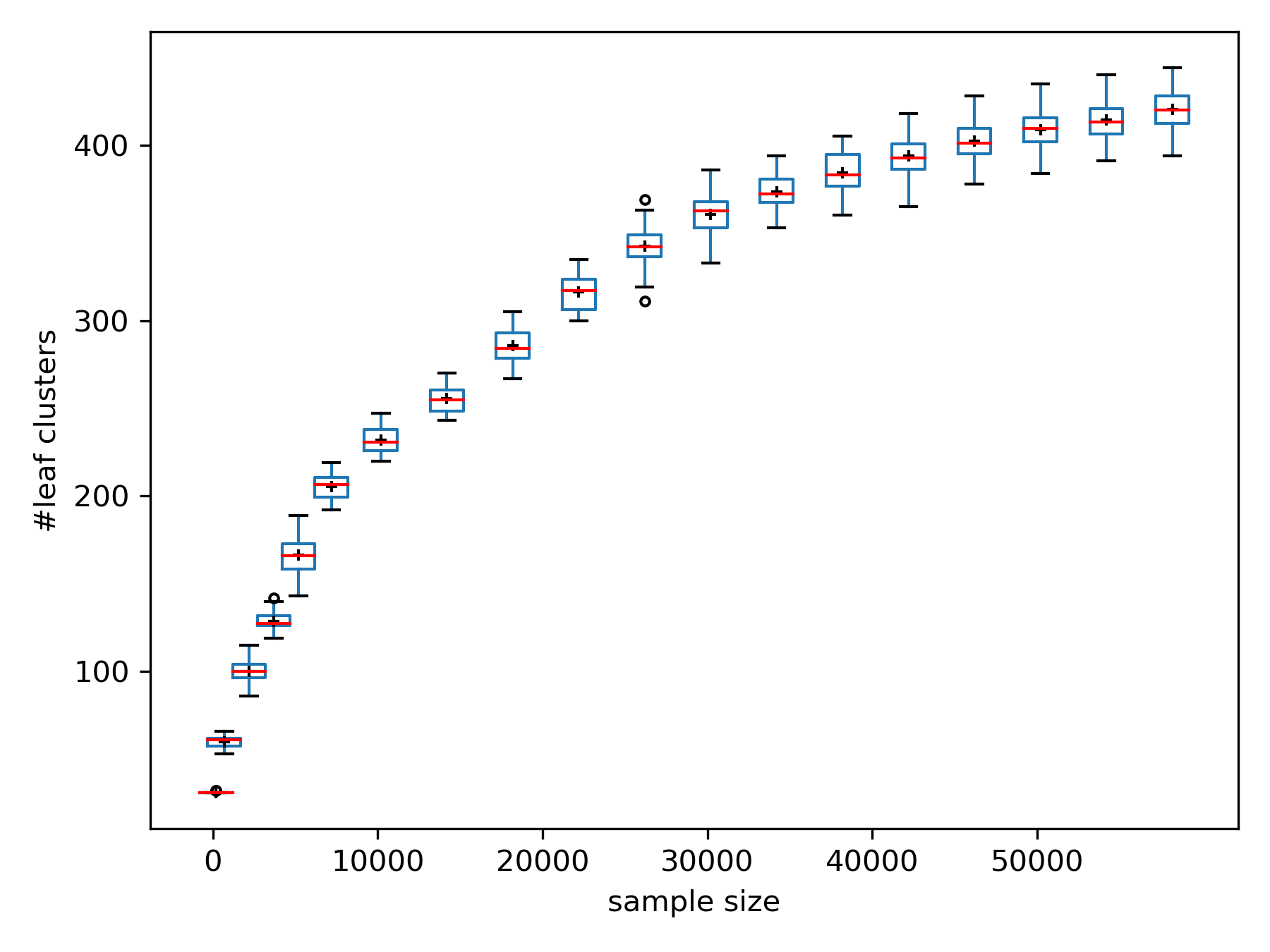
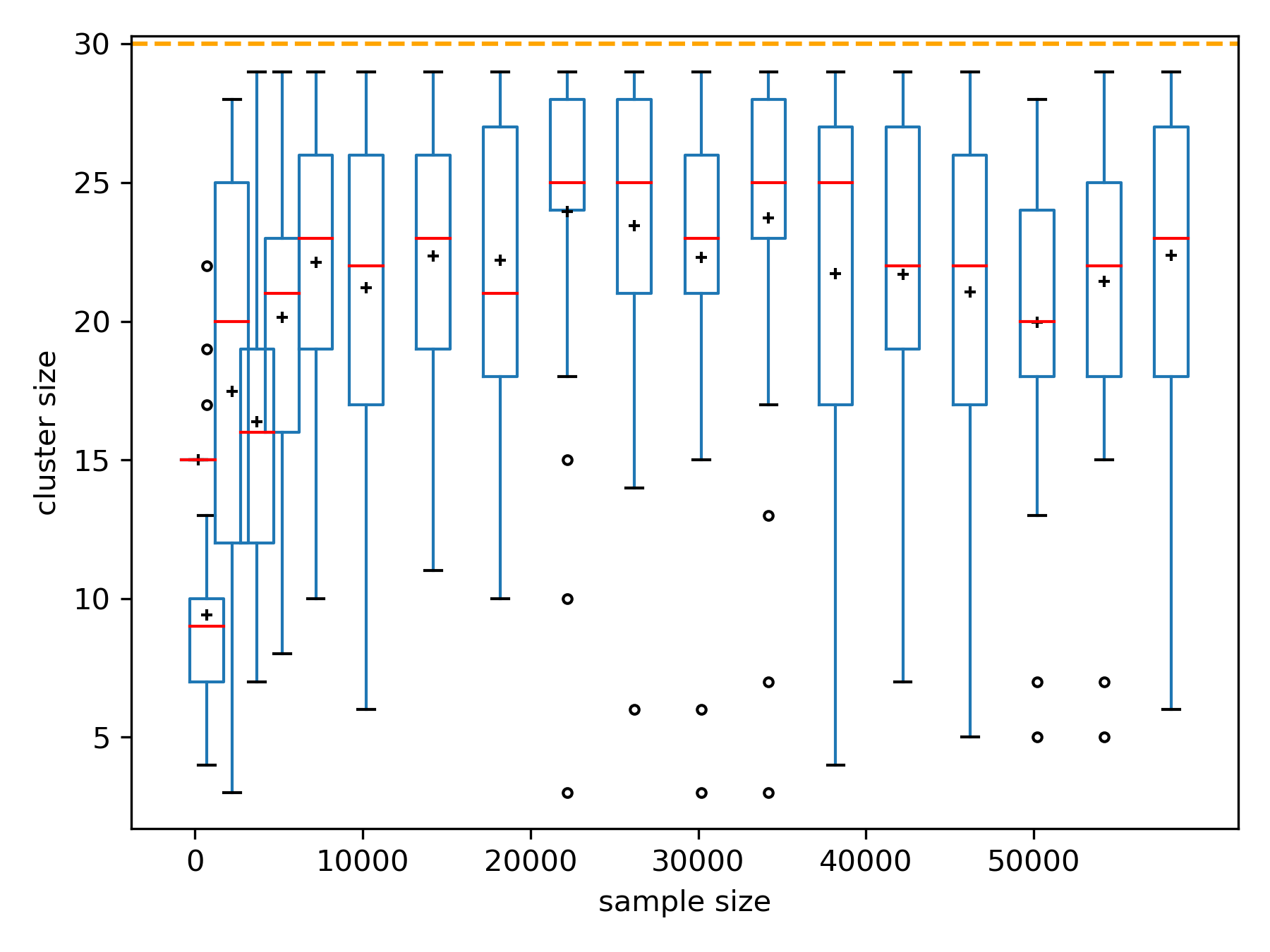
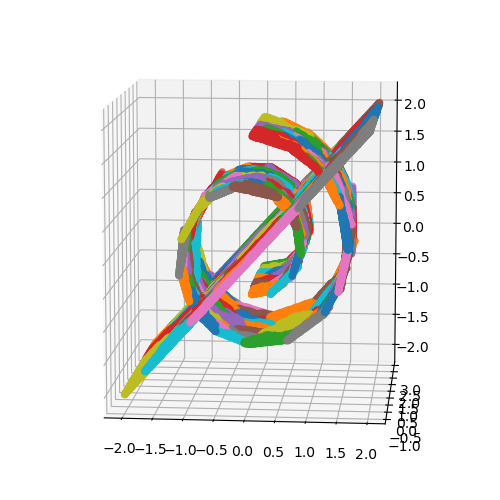
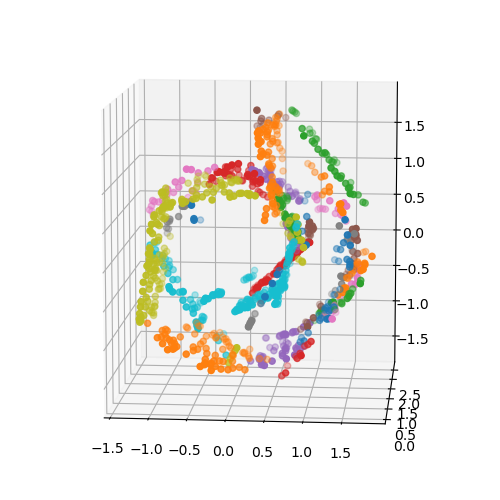
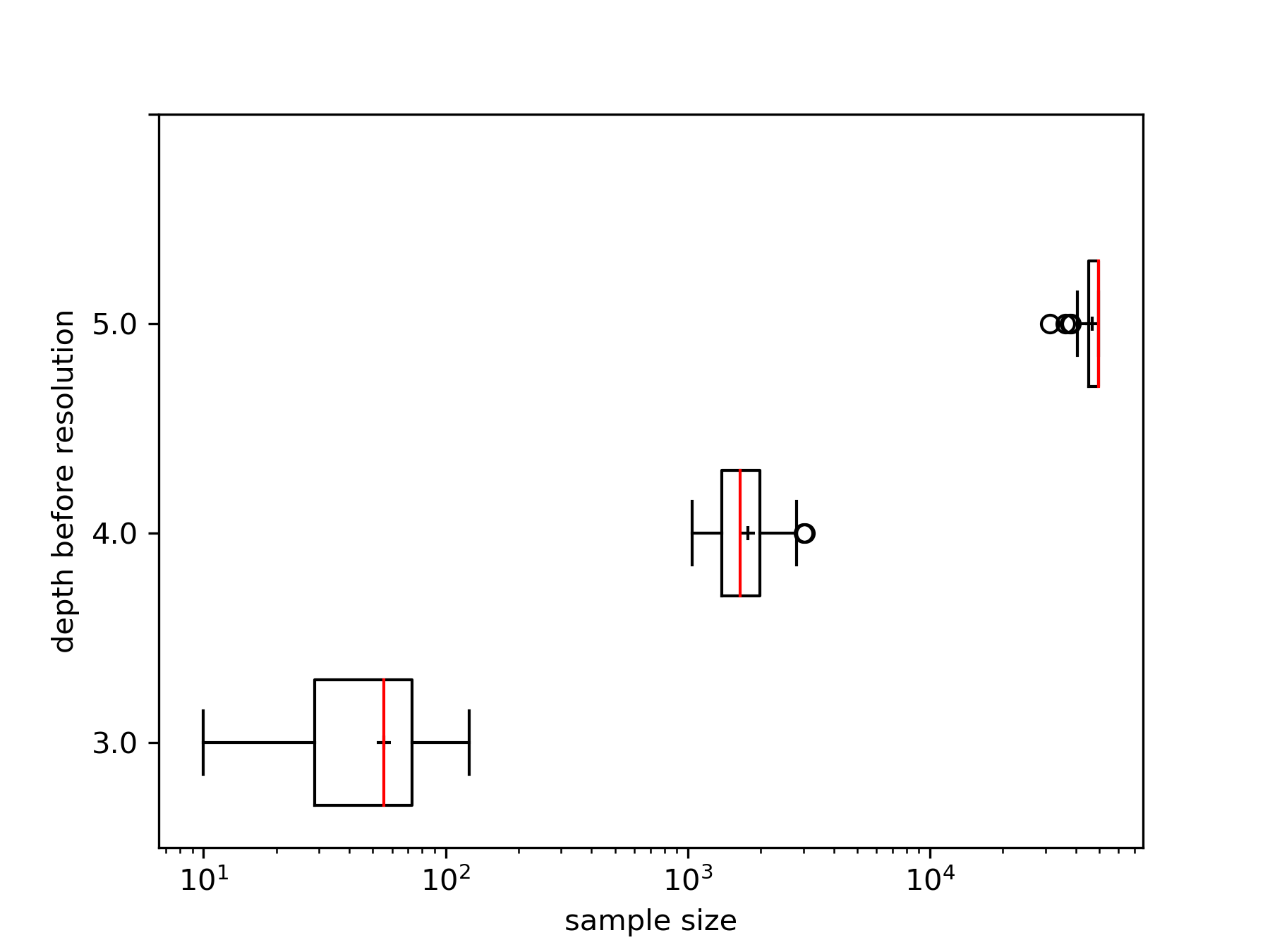
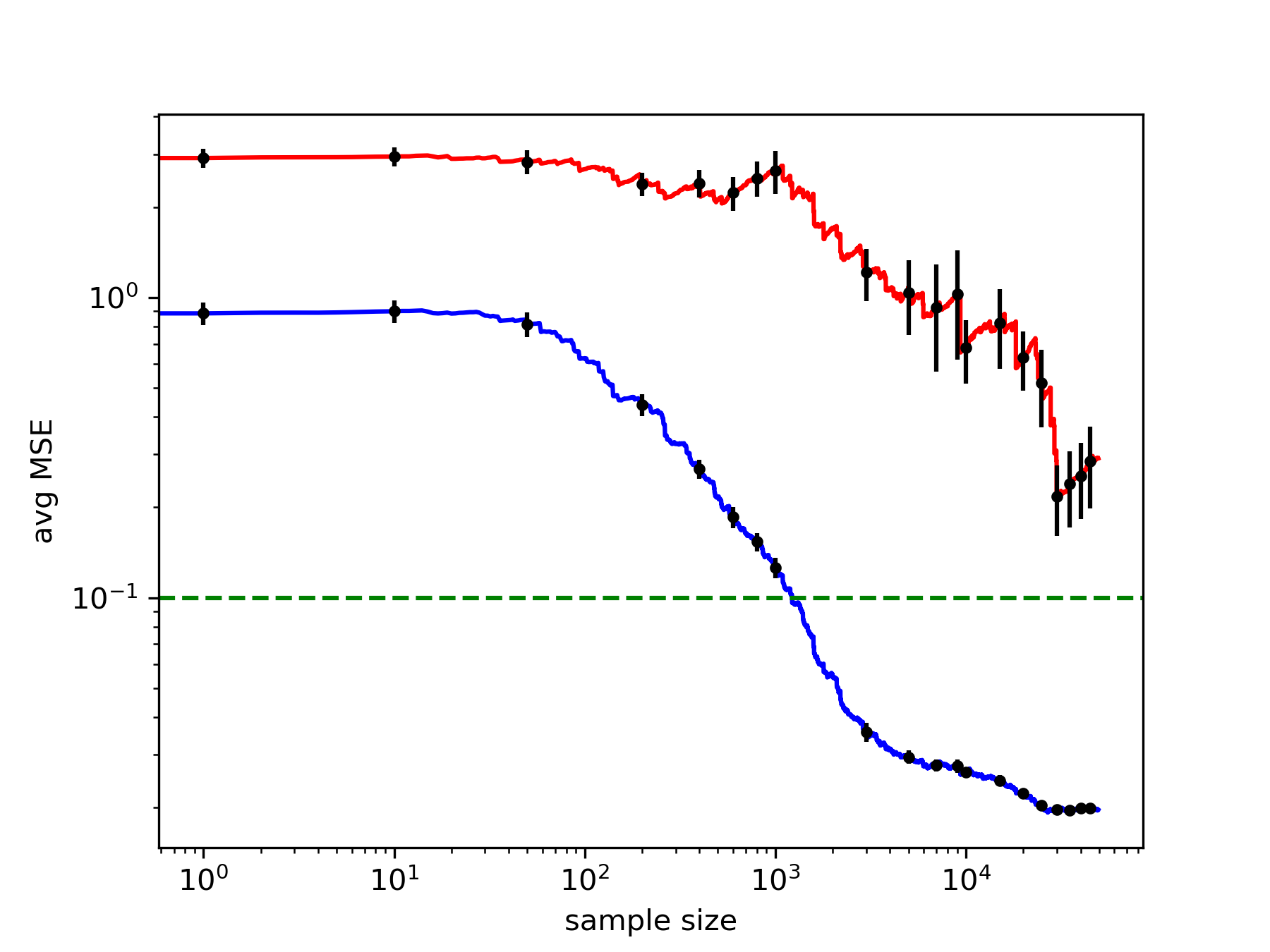
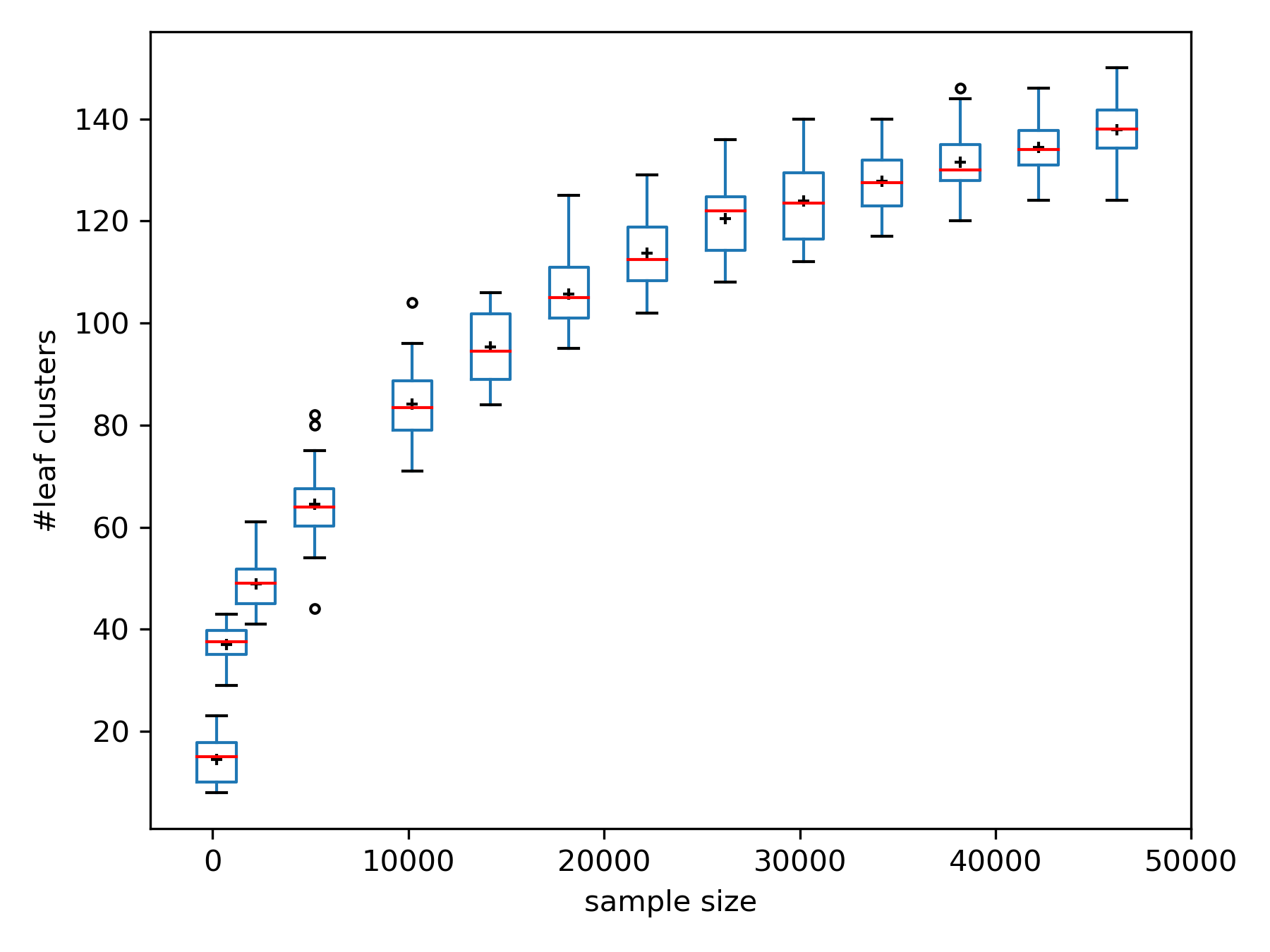
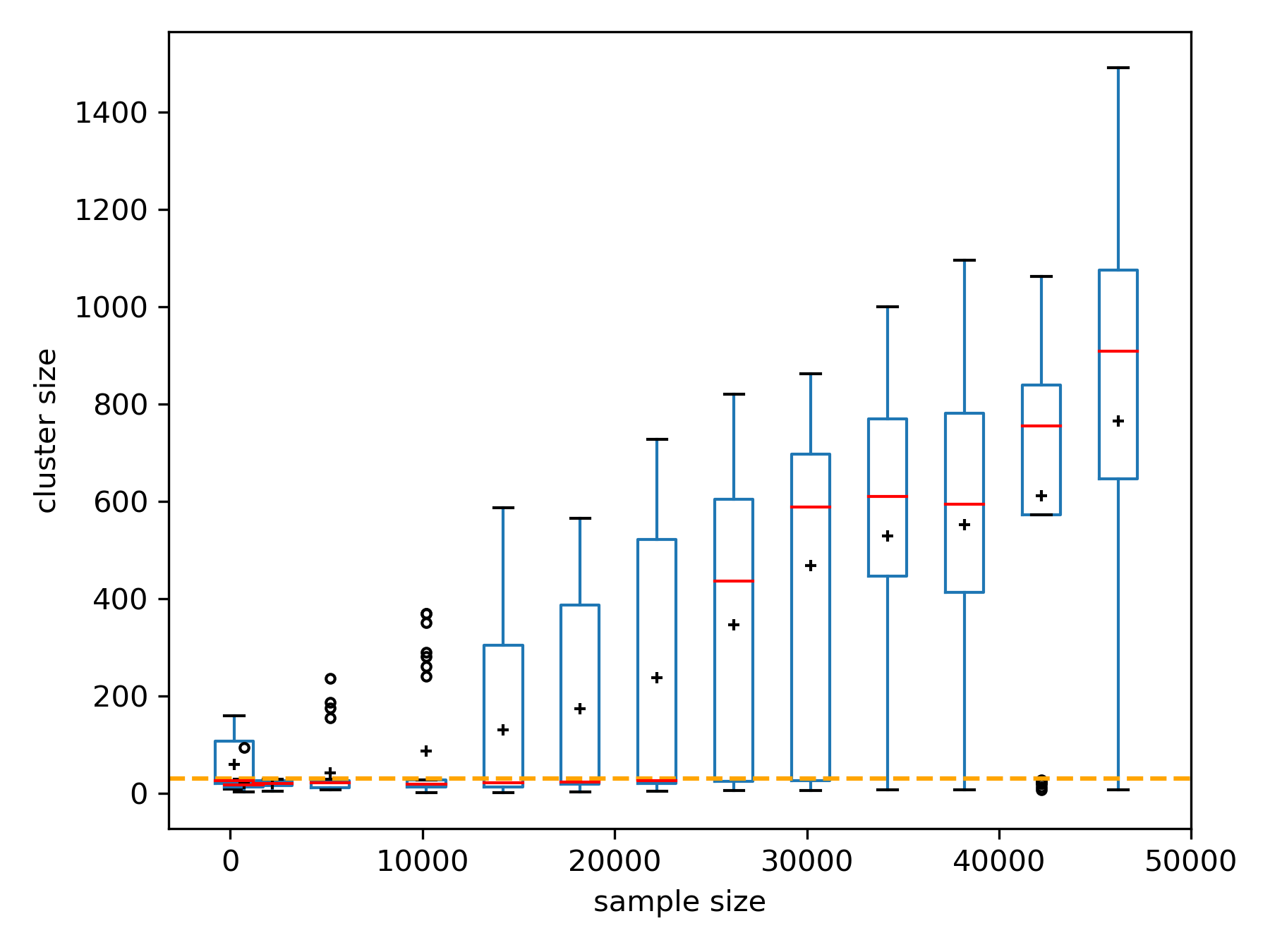
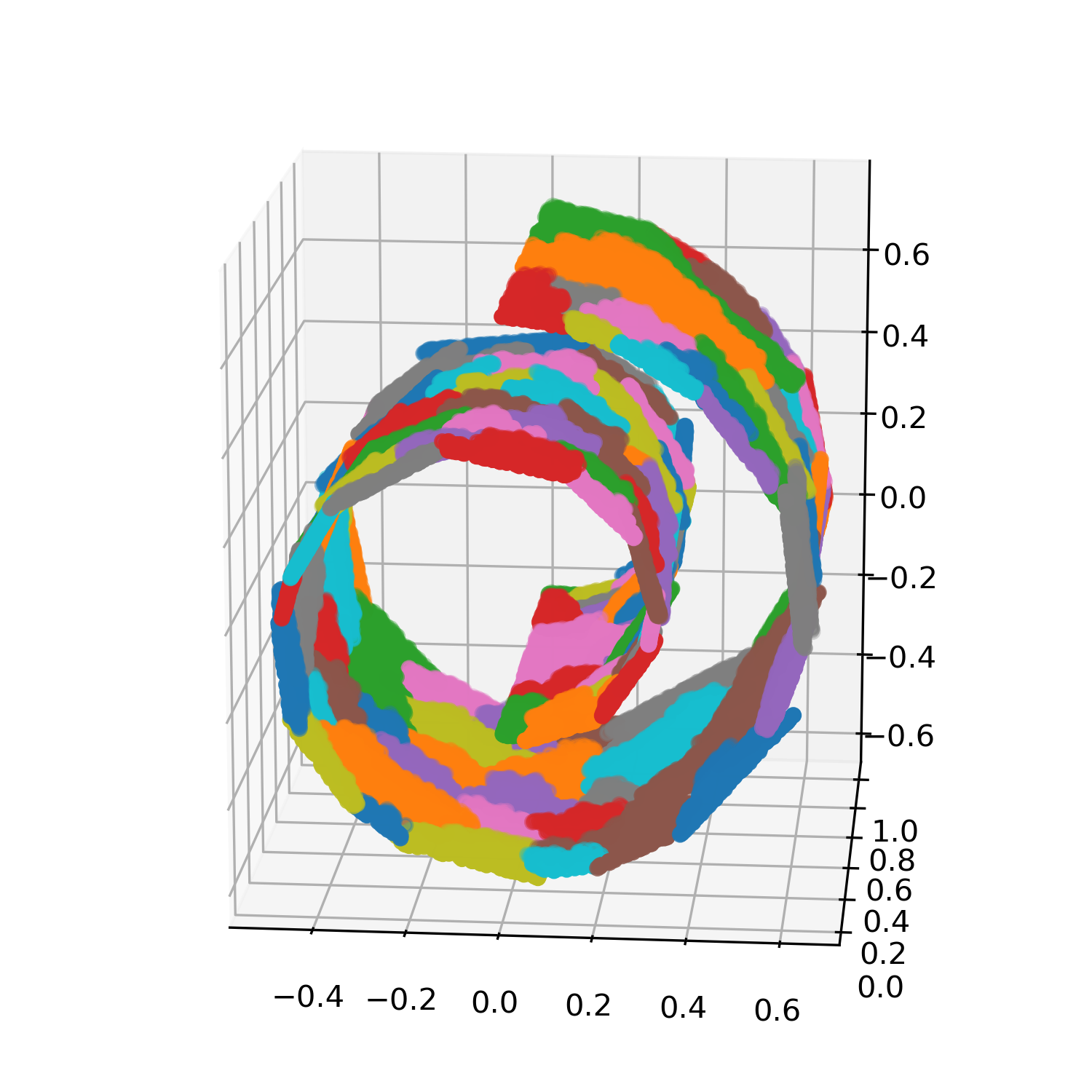
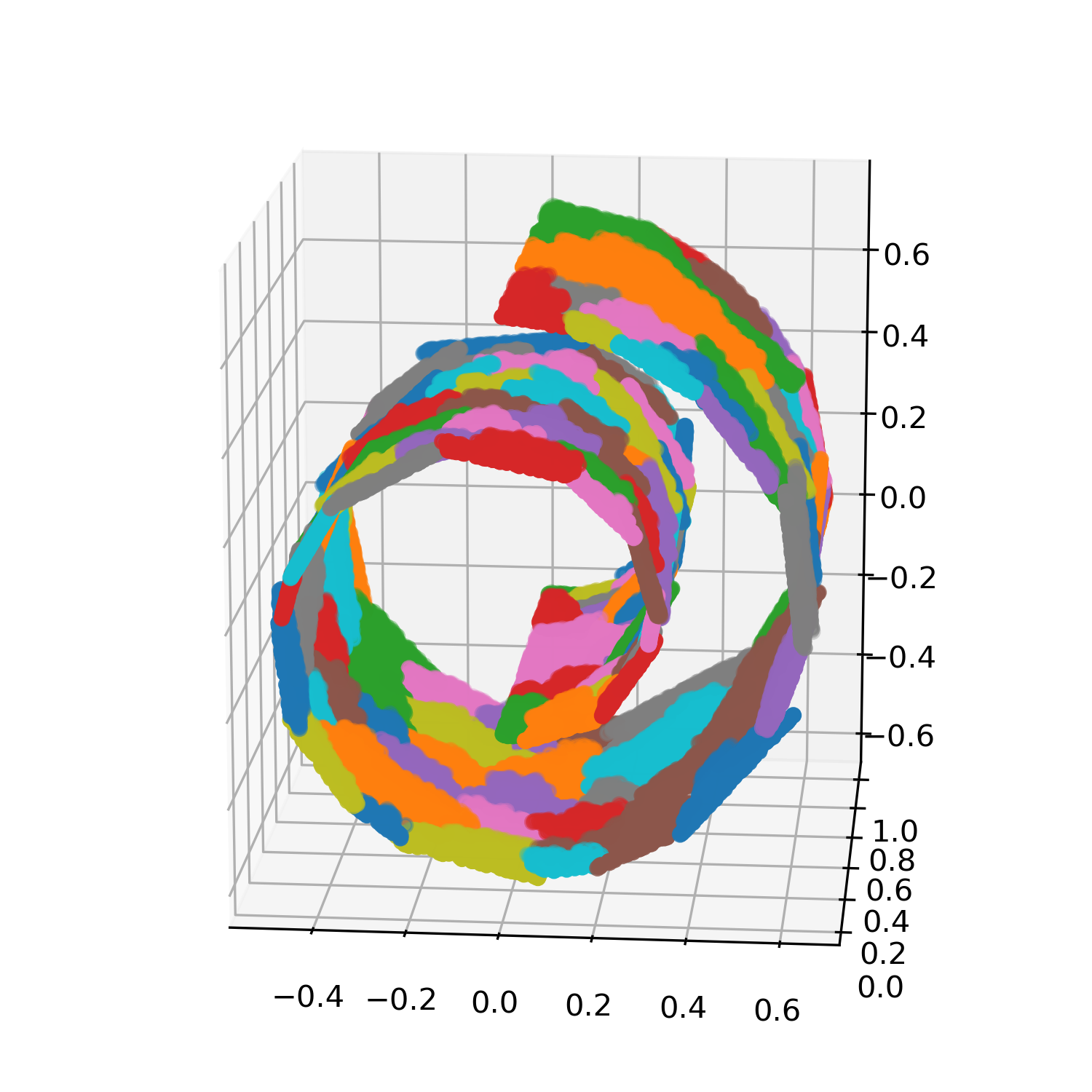
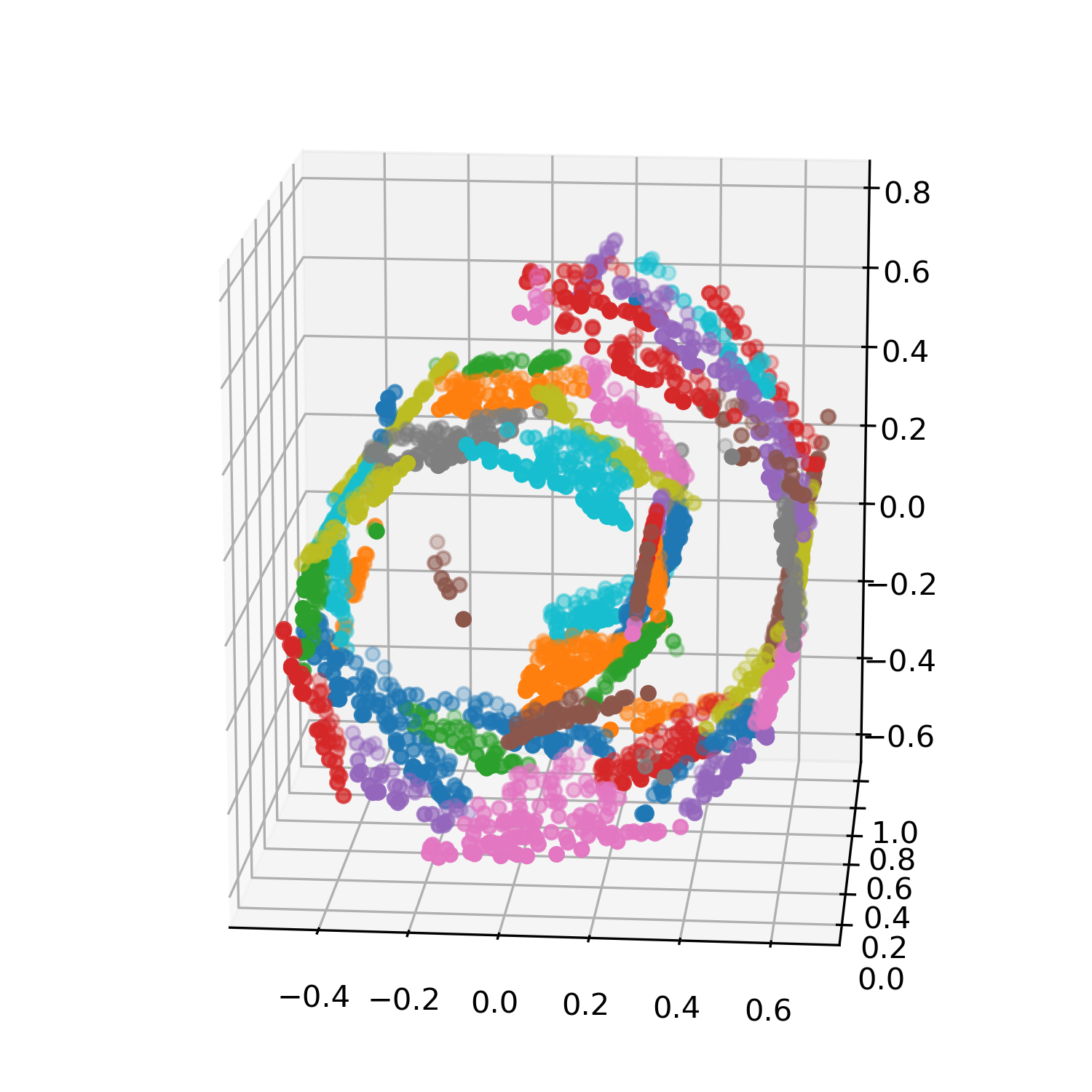
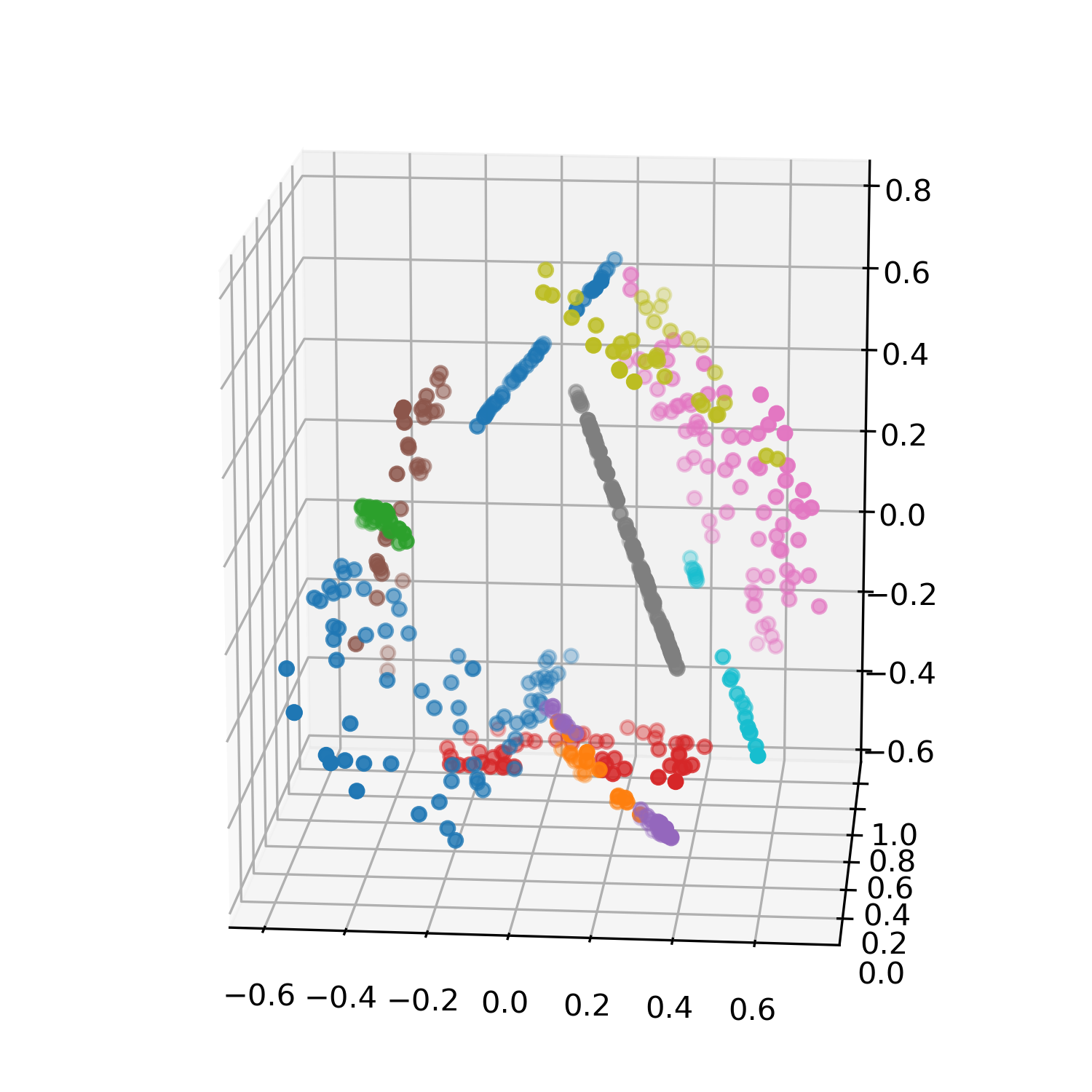
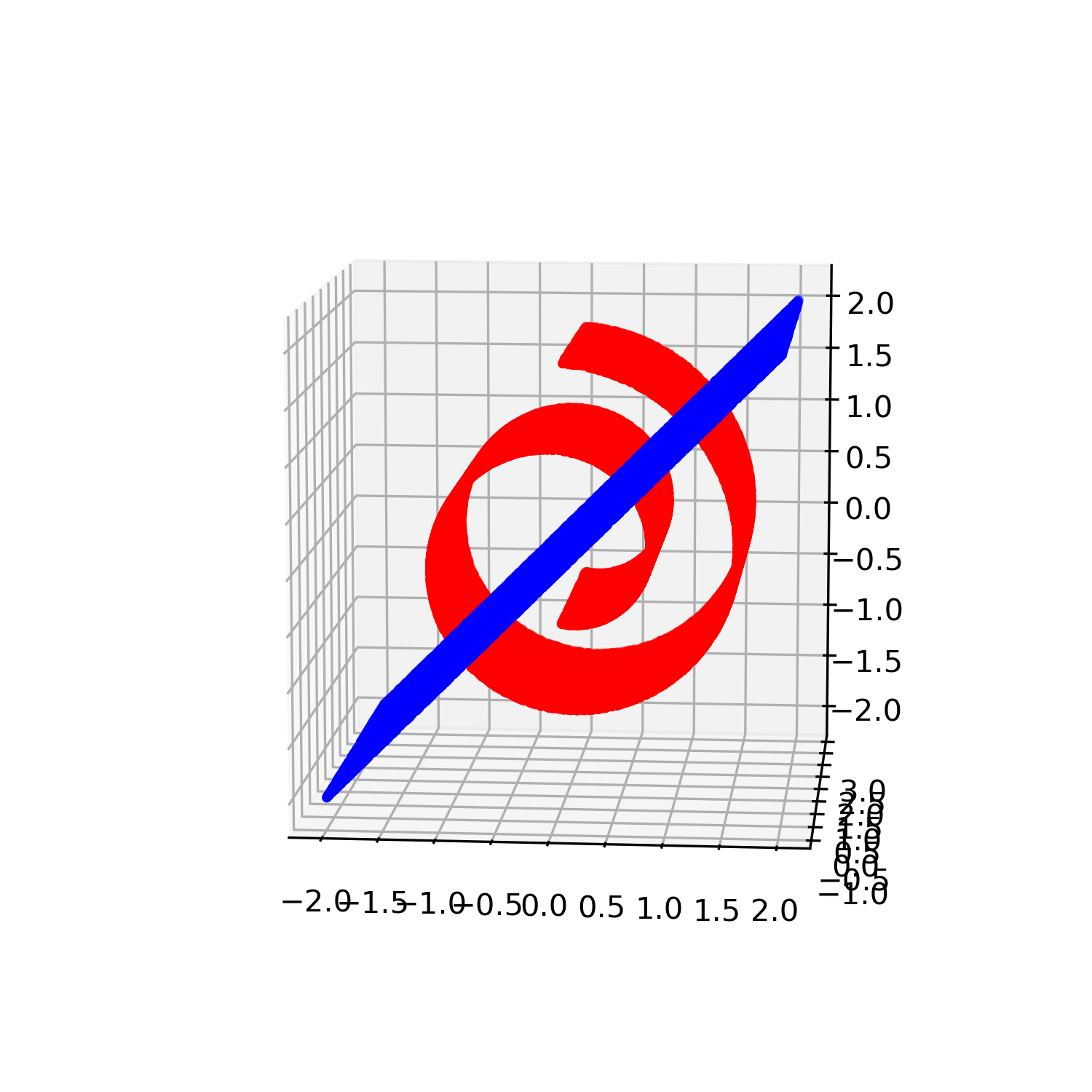
Analyzing high-dimensional data presents challenges due to the "curse of dimensionality'', making computations intensive. Dimension reduction techniques, categorized as linear or non-linear, simplify such data. Non-linear methods are particularly essential for efficiently visualizing and processing complex data structures in interactive and graphical applications. This research develops an incremental non-linear dimension reduction method using the Geometric Multi-Resolution Analysis (GMRA) framework for streaming data. The proposed method enables real-time data analysis and visualization by incrementally updating the cluster map, PCA basis vectors, and wavelet coefficients. Numerical experiments show that the incremental GMRA accurately represents non-linear manifolds even with small initial samples and aligns closely with batch GMRA, demonstrating efficient updates and maintaining the multiscale structure. The findings highlight the potential of Incremental GMRA for real-time visualization and interactive graphics applications that require adaptive high-dimensional data representations.💡 Deep Analysis
This research explores the key findings and methodology presented in the paper: An Incremental Non-Linear Manifold Approximation Method.Analyzing high-dimensional data presents challenges due to the “curse of dimensionality’’, making computations intensive. Dimension reduction techniques, categorized as linear or non-linear, simplify such data. Non-linear methods are particularly essential for efficiently visualizing and processing complex data structures in interactive and graphical applications. This research develops an incremental non-linear dimension reduction method using the Geometric Multi-Resolution Analysis (GMRA) framework for streaming data. The proposed method enables real-time data analysis and visualization by incrementally updating the cluster map, PCA basis vectors, and wavelet coefficients. Numerical experiments show that the incremental GMRA accurately represents non-linear manifolds even with small initial samples and aligns closely with batch GMRA, demonstrating efficient updates and maintaining the multiscale structure. The findings highlight the potential of Incremental GMRA for real-time visuali
📄 Full Content
📸 Image Gallery