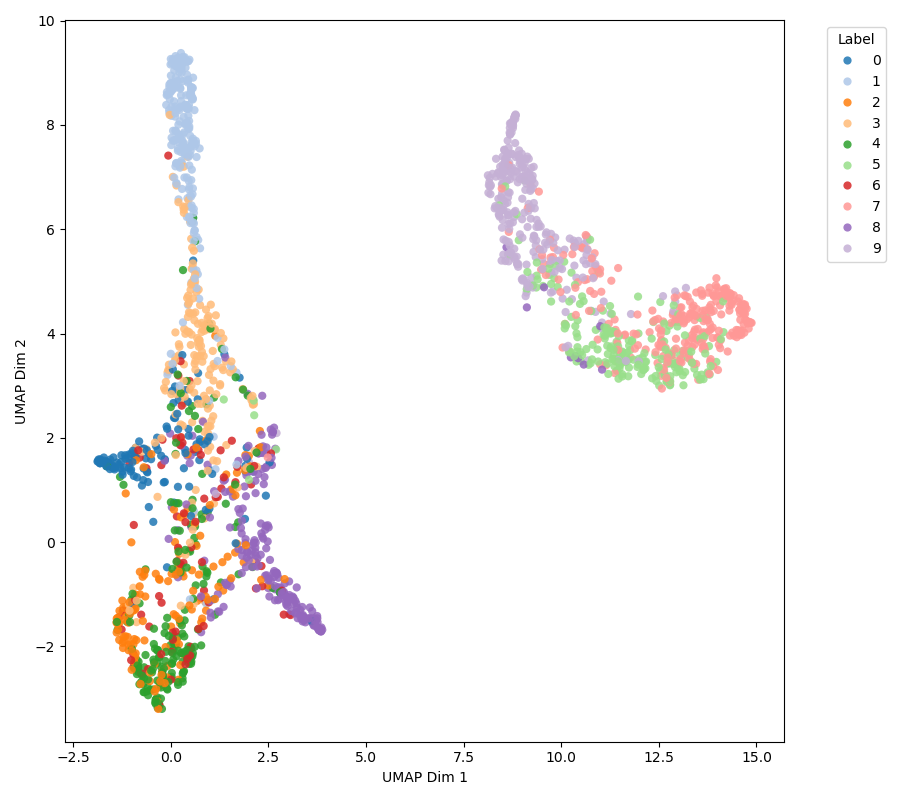
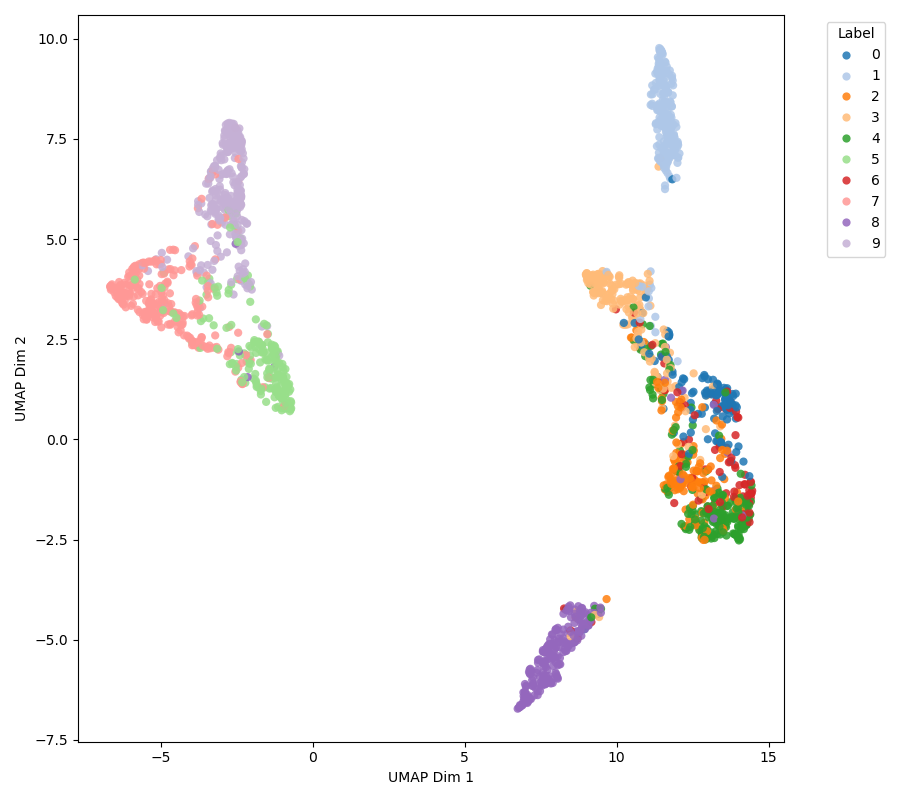
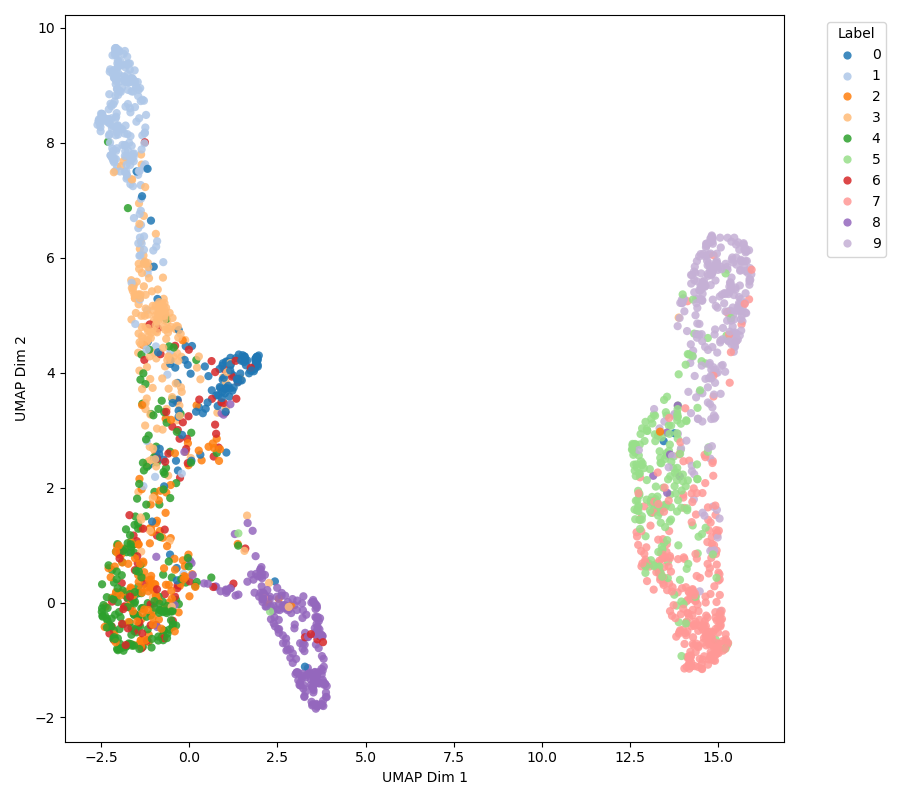
Personalized Federated Learning (PFL) faces persistent challenges, including domain heterogeneity from diverse client data, data imbalance due to skewed participation, and strict communication constraints. Traditional federated learning often lacks personalization, as a single global model cannot capture client-specific characteristics, leading to biased predictions and poor generalization, especially for clients with highly divergent data distributions.
To address these issues, we propose FedSTAR, a style-aware federated learning framework that disentangles client-specific style factors from shared content representations. FedSTAR aggregates class-wise prototypes using a Transformer-based attention mechanism, allowing the server to adaptively weight client contributions while preserving personalization.
Furthermore, by exchanging compact prototypes and style vectors instead of full model parameters, FedSTAR significantly reduces communication overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that combining content-style disentanglement with attention-driven prototype aggregation improves personalization and robustness in heterogeneous environments without increasing communication cost.
Federated Learning (FL) has become a widely used paradigm for collaboratively training models across decentralized, privacy-sensitive environments [1,2]. However, most classical FL approaches assume that a single global model can adequately serve all clients. In practical deployments, clients often exhibit substantial domain heterogeneity, driven by differences in user behavior, sensing hardware, environmental conditions, and collection biases [3,4]. Without adequate personalization, these variations lead to biased global parameters, poor local generalization, and significant performance degradation, especially for clients whose data distributions differ sharply from the global average [5]. These challenges highlight the necessity of Personalized Federated Learning (PFL), where global knowledge must be shared while still accommodating client-specific characteristics [5,6].
A fundamental difficulty in PFL lies in the personalized features present in local representations. Clients may observe the same semantic categories but express them through distinctive “styles” due to lighting conditions, background textures, sensor noise, or temporal distortions [7,8]. When content and style remain entangled, the server aggregates heterogeneous representations, contaminating global prototypes and hindering effective personalization at the client side.
While style decomposition has been explored in centralized learning and domain generalization [9], its integration within federated learning-particularly under prototype-based communication-remains largely unexplored. Indeed, to the best of our knowledge, FedSTAR is the first approach to apply explicit content-style decomposition within a prototype-based personalized federated learning framework. Existing prototype-based FL methods treat prototypes as unified embeddings, mixing task-relevant content with client-specific style and limiting the expressiveness of aggregated prototypes [10,11].
Another major limitation of prior prototype-based FL methods is their reliance on simple averaging for server-side aggregation. Although averaging provides computational simplicity, it implicitly assumes that all client prototypes are equally informative and equally reliable-an assumption that rarely holds under non-IID or imbalanced settings [12,5]. In heterogeneous environments, naïve averaging can suppress minority-client information, amplify noisy or stylistic deviations, and ultimately degrade global prototype quality. Motivated by this limitations, we propose replacing uniform averaging with attention-based aggregation, enabling the server to learn the relative importance of each client’s prototype and adaptively weight contributions in a data-driven manner [13,14].
Building on these insights, we now introduce FedSTAR, our proposed framework to tackle these challenges more effectively. FedSTAR decomposes each client’s prototype into a content component aligned with global semantics and a style component representing local variability. Clients transmit only the content prototypes, while style vectors remain local and modulate representations using a lightweight StyleFiLM module, thereby enhancing personalization without additional communication cost.
At the server, FedSTAR employs a Transformer-based aggregator that integrates class embeddings, client identity embeddings, and class-wise content prototypes. Through multi-head attention, the server learns nuanced inter-client relationships and dynamically reweights prototype contributions, overcoming the limitations of uniform averaging and improving robustness to non-IID data, label imbalance, and inconsistent client participation.
Importantly, FedSTAR maintains the communication efficiency of prototype-based FL: clients exchange only compact class-level prototypes rather than full model parameters. By combining content-style disentanglement and attentionbased prototype aggregation, FedSTAR improves the quality of learned representations while offering more consistent personalization across clients.
In summary, FedSTAR provides a new perspective on personalized federated learning by integrating style-aware representation modeling, explicit content-style decomposition, and Transformer-based attention aggregation. This represents, to our knowledge, the first prototype-based PFL framework that leverages content-style separation and attention-driven prototype aggregation, enabling a principled and communication-efficient solution for heterogeneous real-world federated environments.
In summary, the main contributions of this work are as follows:
• Content-style decomposition within prototype-based personalized federated learning. This is the first framework to incorporate content-style separation in a prototype-based PFL setting. FedSTAR transmits only content-aligned prototypes while keeping style information local, preventing style noise from contaminating global representations and enabling style-aware personalization via a l
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.