Mobile malware has increased rapidly last 10 years. This rapid increase is due to the rapid enhancement of mobile technology and their power to do most work for their users. Since mobile devices are personal devices, then a special action must be taken towards preserving privacy and security of the mobile data. Malware refers to all types of software applications with malicious behavior. In this paper, we propose a malware detection technique called Personal Mobile Malware Guard ? PMMG- that classifies malwares based on the mobile user feedback. PMMG controls permissions of different applications and their behavior according to the user needs. These preferences are built incrementally on a personal basis according to the feedback of the user. Performance analysis showed that it is theoretically feasible to build PMMG tool and use it on mobile devices.
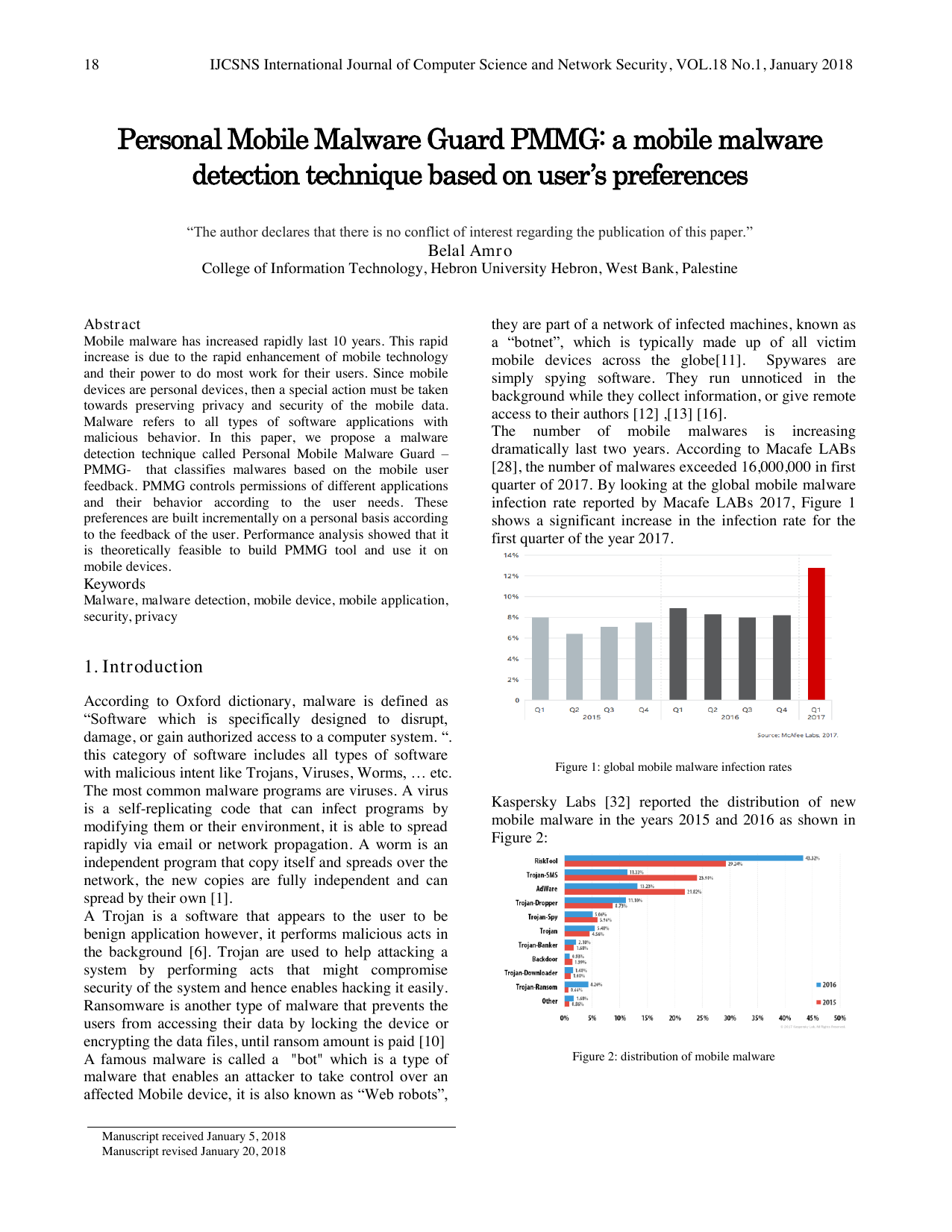
According to Oxford dictionary, malware is defined as "Software which is specifically designed to disrupt, damage, or gain authorized access to a computer system. ". this category of software includes all types of software with malicious intent like Trojans, Viruses, Worms, … etc. The most common malware programs are viruses. A virus is a self-replicating code that can infect programs by modifying them or their environment, it is able to spread rapidly via email or network propagation. A worm is an independent program that copy itself and spreads over the network, the new copies are fully independent and can spread by their own [1]. A Trojan is a software that appears to the user to be benign application however, it performs malicious acts in the background [6]. Trojan are used to help attacking a system by performing acts that might compromise security of the system and hence enables hacking it easily. Ransomware is another type of malware that prevents the users from accessing their data by locking the device or encrypting the data files, until ransom amount is paid [10] A famous malware is called a "bot" which is a type of malware that enables an attacker to take control over an affected Mobile device, it is also known as "Web robots", they are part of a network of infected machines, known as a "botnet", which is typically made up of all victim mobile devices across the globe [11]. Spywares are simply spying software. They run unnoticed in the background while they collect information, or give remote access to their authors [12] , [13] [16]. The number of mobile malwares is increasing dramatically last two years. According to Macafe LABs [28], the number of malwares exceeded 16,000,000 in first quarter of 2017. By looking at the global mobile malware infection rate reported by Macafe LABs 2017, Figure 1 shows a significant increase in the infection rate for the first quarter of the year 2017. These types of malware are harmful to systems and hence must be detected and removed to make sure that the system functions well. The rest of the paper is organized as follows: A literature review of current malware detection techniques is proposed. A description of how PMMG technique works is then provided. Analysis of the technique is carried out. And at last a summary is provided.
To better detect malwares, we have to both understand their behavior and how do they spread, in this section, we provide a brief summary of how do malwares spread. We also provide the state-of-the-art mobile malware detection technique.
To mitigate malware attacks, we should be aware of malware spreading techniques. In this section, we categorize malware spreading techniques as follows:
Malware authors repackage popular mobile applications in official market, and distribute them on other less monitored third party markets. Repackaging includes the disassembling of the popular benign apps, and appending the malicious content and reassembling. This is done by reverse-engineering tools. TrendMicro report have shown that 77% of the top 50 free apps available in Google Play are repackaged [14].
Drive by Download refers to an unintentional download of malware in the background. It Occurs when a user visit a website that contains malicious content and downloads malware into the device. Android/NotCompatible [15] is the most popular mobile malware of this category.
Uses dynamic payload to download an embedded encrypted source in an application. After installation, the app decrypts the encrypted malicious payload and executes the malicious code [16].
Stealth Malware Technique refers to an exploit of hardware vulnerabilities to obfuscate the malicious code to easily bypass the antimalware. Different stealth techniques such as key permutation, dynamic loading, native code execution, code encryption, and java reflection are used to attack the victim’s device [16].
In this section, we analyze the state-of-the-art malware detection techniques for mobile devices. According to [30], mobile malware detection techniques are categorized into two categories according to the basis they rely on when detecting for malwares. The categories are statics techniques and dynamic techniques
Static techniques rely on the source code of an application to classify it accordingly without having the application executed. These techniques are classified into one of the following classes according to the basis they rely on for analyzing the source code. Table 1 Virtual machine analysis [20].
tests the app behavior and analyses control and data flow which in sake of detecting dangerous functionalities
Analysis is performed at instruction level and consumes more power and storage space.
How does it work Advantages Disadvantages Anomaly based [21], [22], [23], [24] based on watching the behavior of the device by keeping track of different parameters and the status of the components of the device
The larger the parameters engaged the more the calculation require
This content is AI-processed based on open access ArXiv data.