Communication-Efficient Federated Deep Learning with Asynchronous Model Updates and Temporally Weighted Aggregation
📝 Original Paper Info
- Title: Communication-Efficient Federated Deep Learning with Asynchronous Model Update and Temporally Weighted Aggregation- ArXiv ID: 1903.07424
- Date: 2020-08-31
- Authors: Yang Chen, Xiaoyan Sun, Yaochu Jin
📝 Abstract
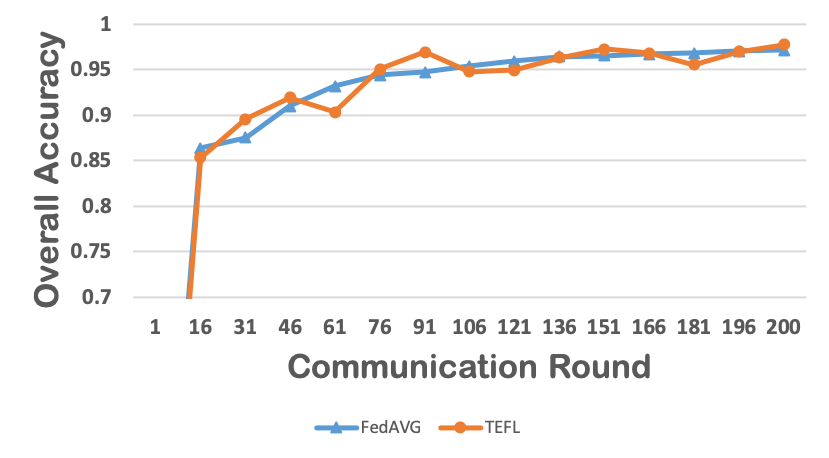
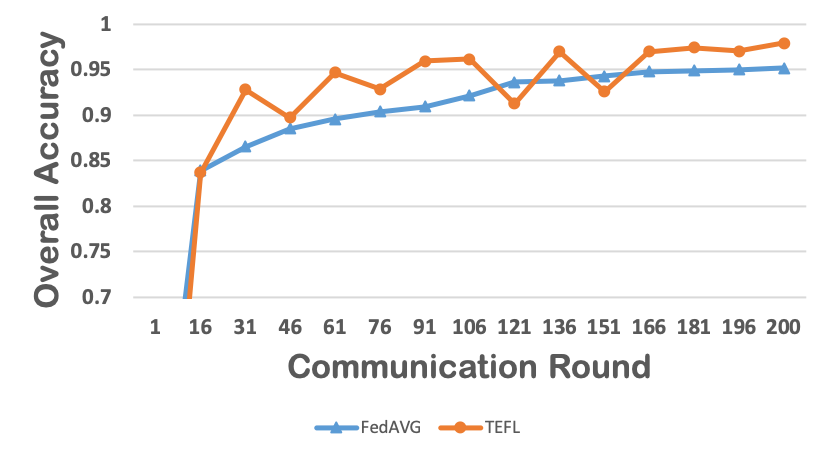
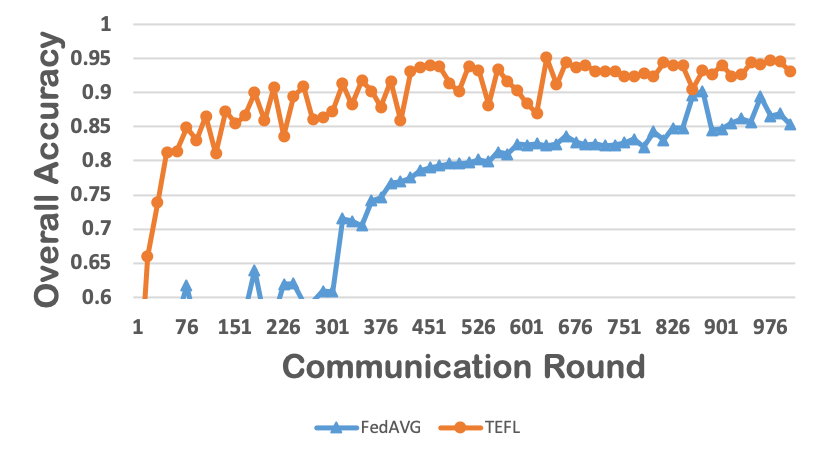
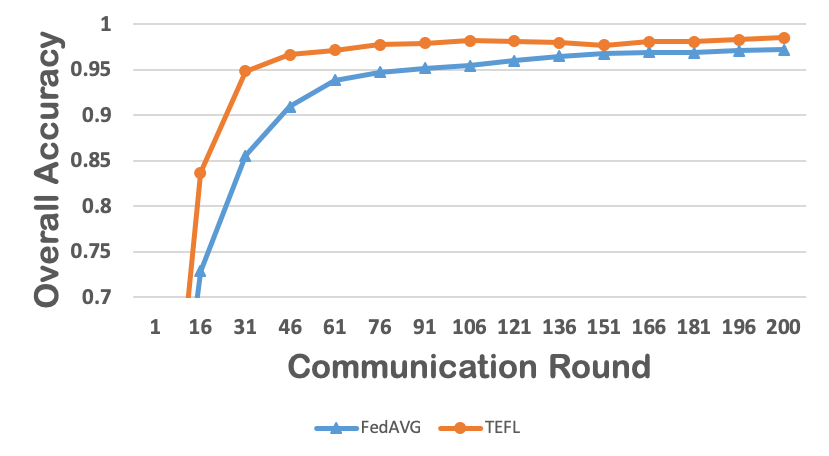
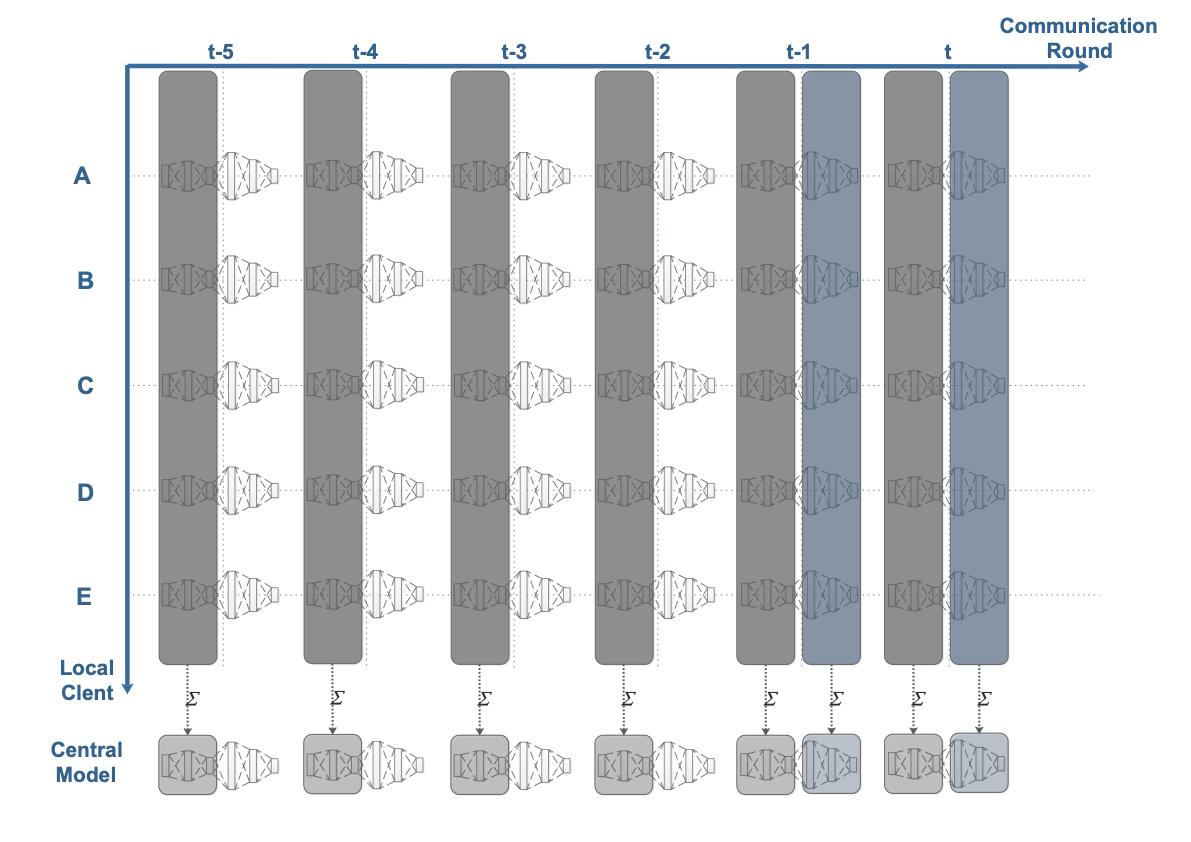
Federated learning obtains a central model on the server by aggregating models trained locally on clients. As a result, federated learning does not require clients to upload their data to the server, thereby preserving the data privacy of the clients. One challenge in federated learning is to reduce the client-server communication since the end devices typically have very limited communication bandwidth. This paper presents an enhanced federated learning technique by proposing a synchronous learning strategy on the clients and a temporally weighted aggregation of the local models on the server. In the asynchronous learning strategy, different layers of the deep neural networks are categorized into shallow and deeps layers and the parameters of the deep layers are updated less frequently than those of the shallow layers. Furthermore, a temporally weighted aggregation strategy is introduced on the server to make use of the previously trained local models, thereby enhancing the accuracy and convergence of the central model. The proposed algorithm is empirically on two datasets with different deep neural networks. Our results demonstrate that the proposed asynchronous federated deep learning outperforms the baseline algorithm both in terms of communication cost and model accuracy.💡 Summary & Analysis
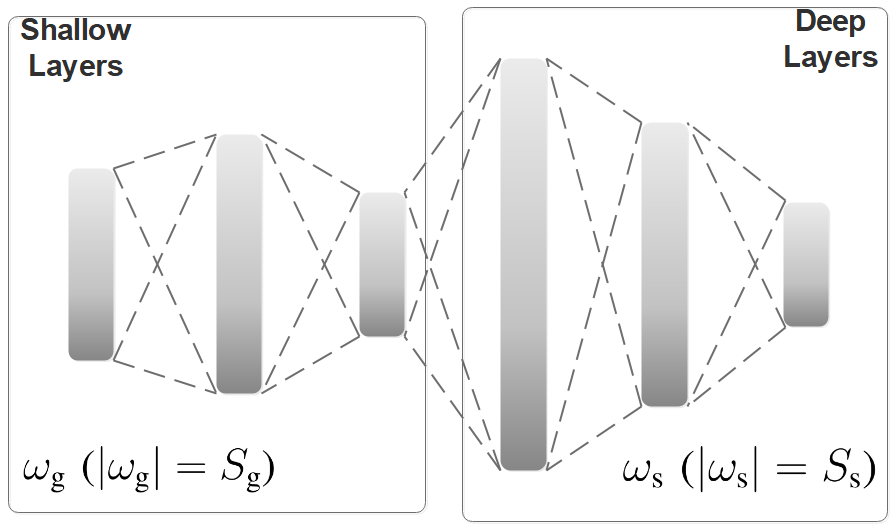
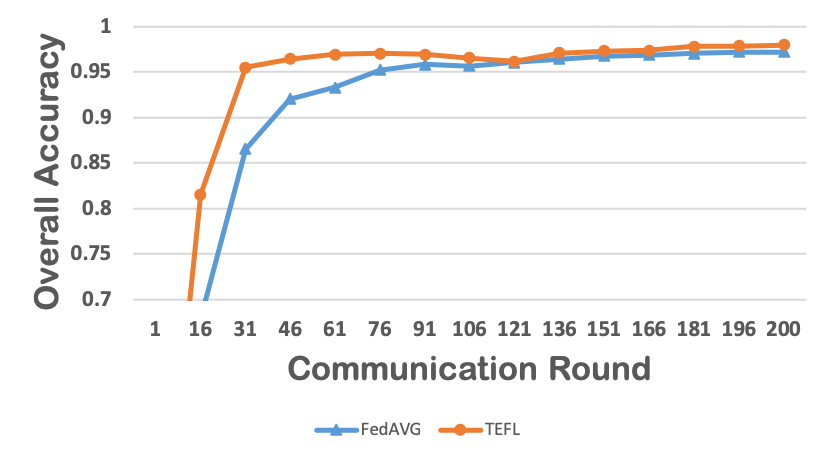
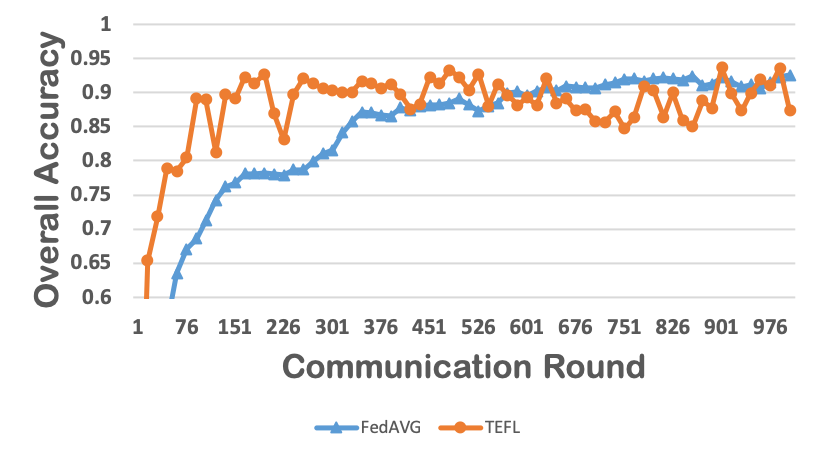
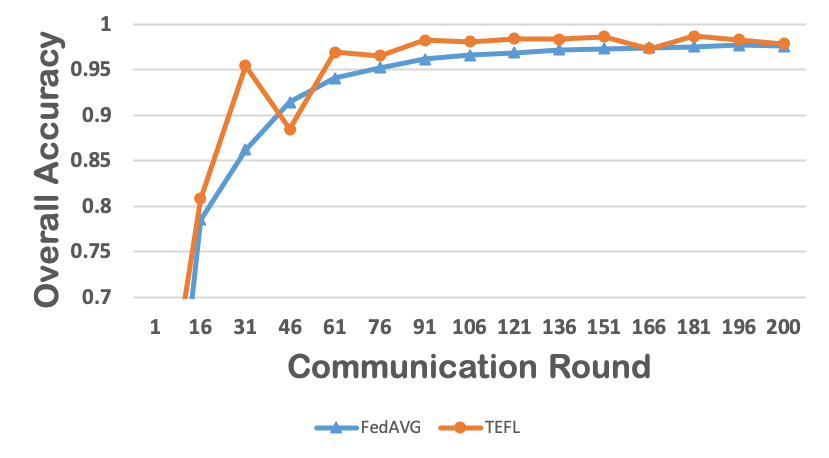
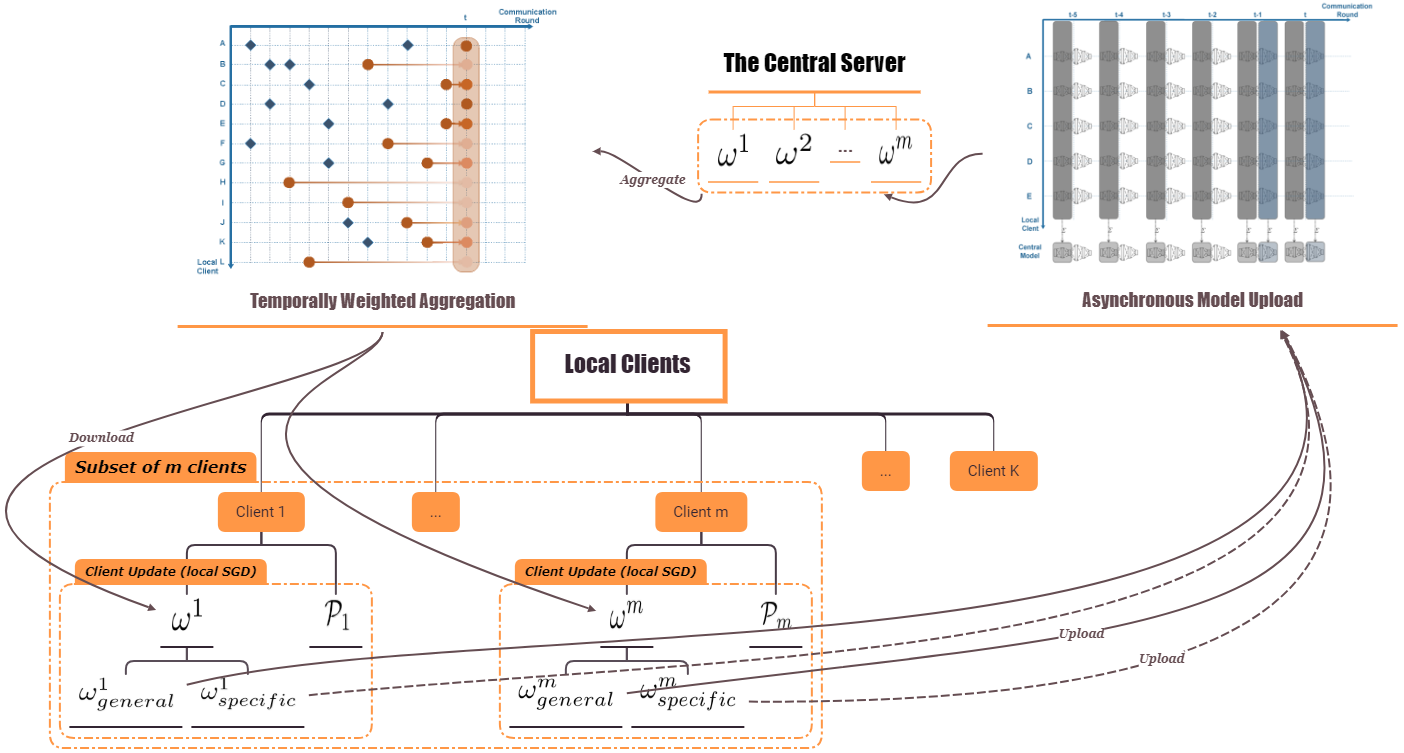
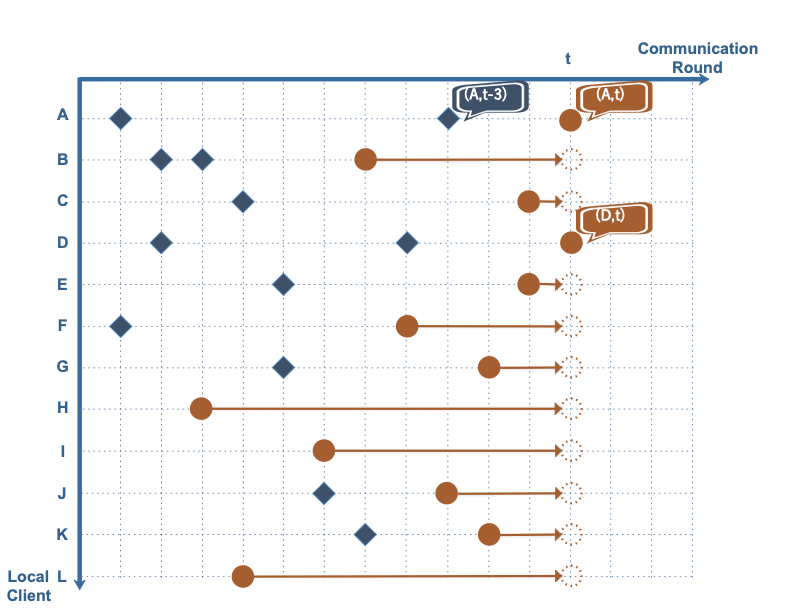
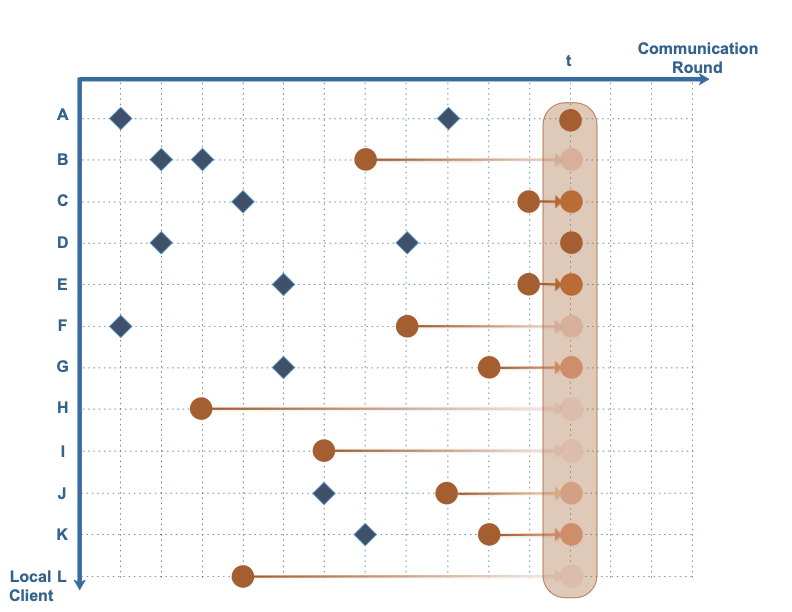
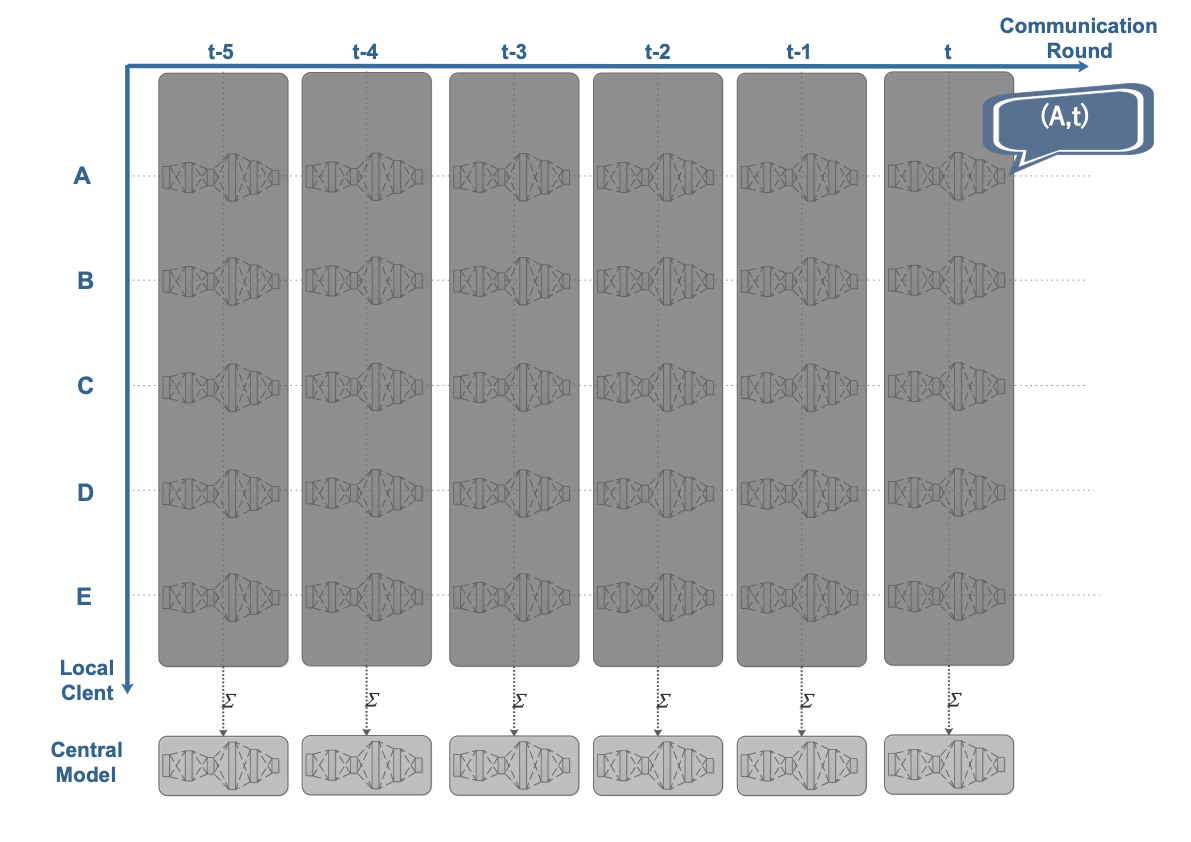
This paper focuses on reducing the communication cost between clients and servers while training deep neural networks, proposing an asynchronous learning strategy for clients and temporally weighted aggregation for model updates at the server. The central challenge addressed is that mobile or IoT devices often have limited bandwidth, making traditional centralized training methods inefficient and costly in terms of communication.The proposed solution involves categorizing layers in a neural network into shallow and deep layers; parameters of deeper layers are updated less frequently than those of shallower layers, reducing the number of updates required. On the server side, models trained locally on clients are aggregated using temporally weighted aggregation to improve model accuracy and convergence without requiring frequent communication.
The experimental results show significant improvements in both communication cost and model accuracy compared to baseline algorithms. This work is particularly important for applications involving mobile or IoT devices where bandwidth constraints are a major issue. It provides an effective way to train deep learning models while preserving data privacy on the client side, making it highly relevant for real-world scenarios.
📄 Full Paper Content (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)