확장된 정규화 증거 심층 학습 모델 이론과 종합 평가
📝 원문 정보
- Title: Generalized Regularized Evidential Deep Learning Models Theory and Comprehensive Evaluation- ArXiv ID: 2512.23753
- 발행일: 2025-12-27
- 저자: Deep Shankar Pandey, Hyomin Choi, Qi Yu
📝 초록
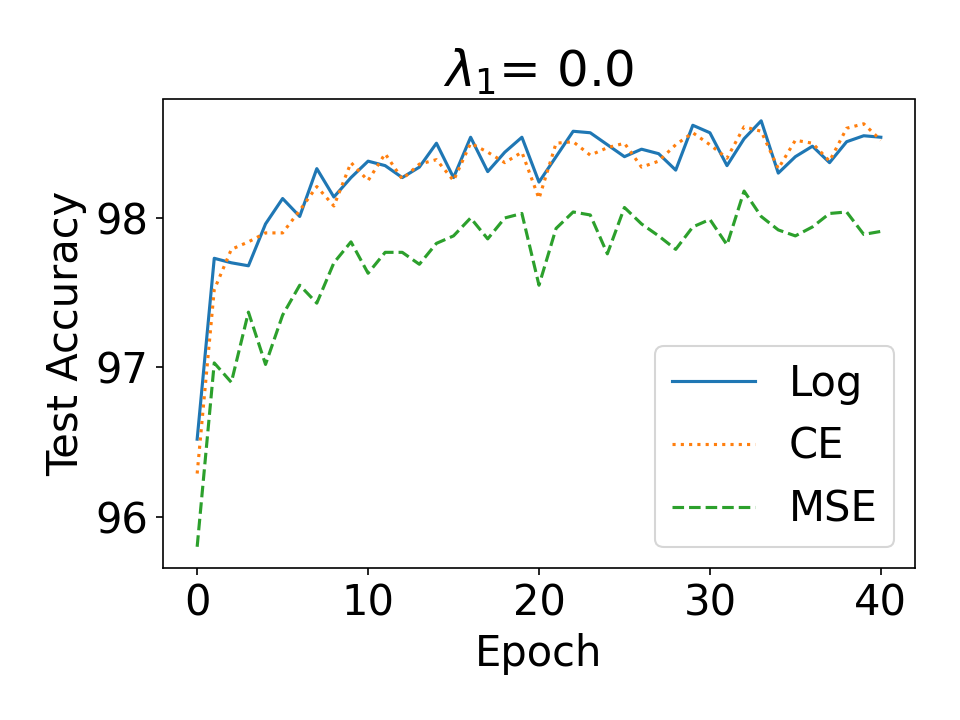
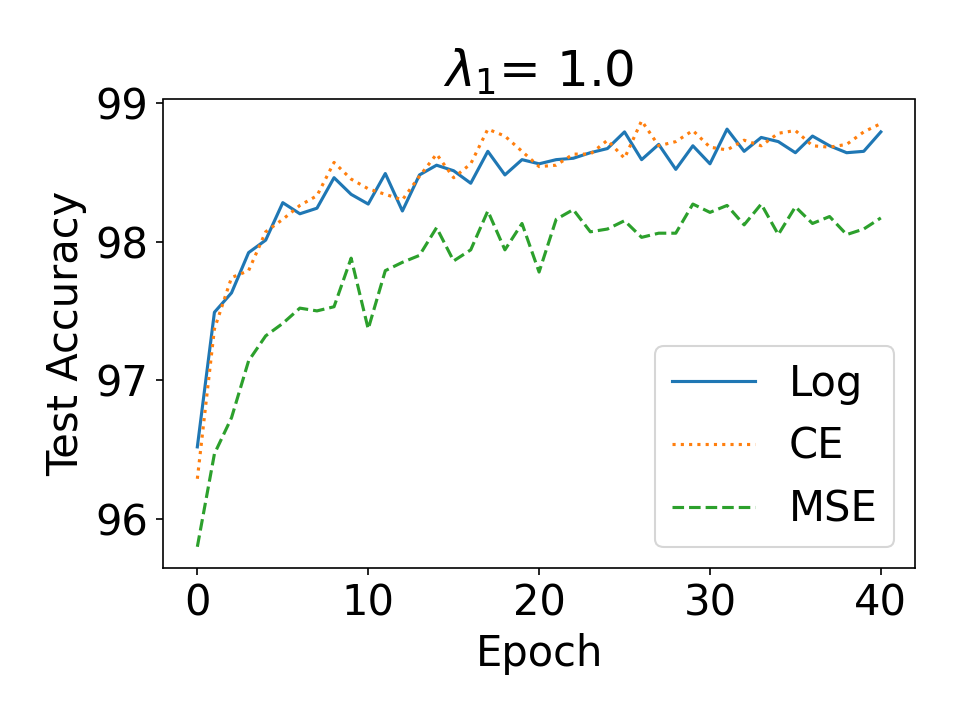
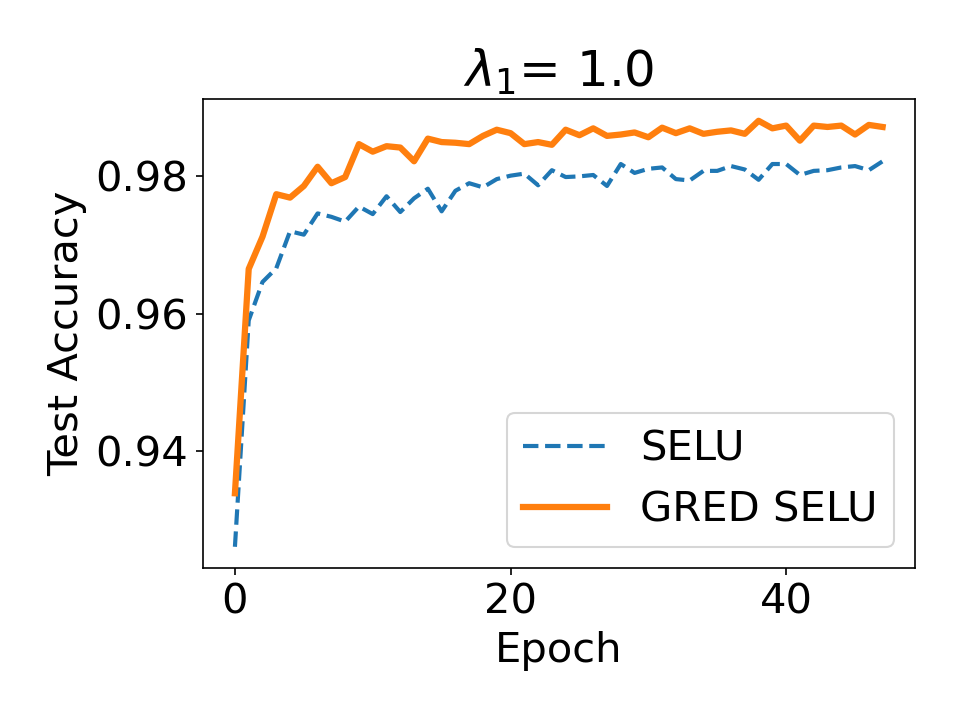
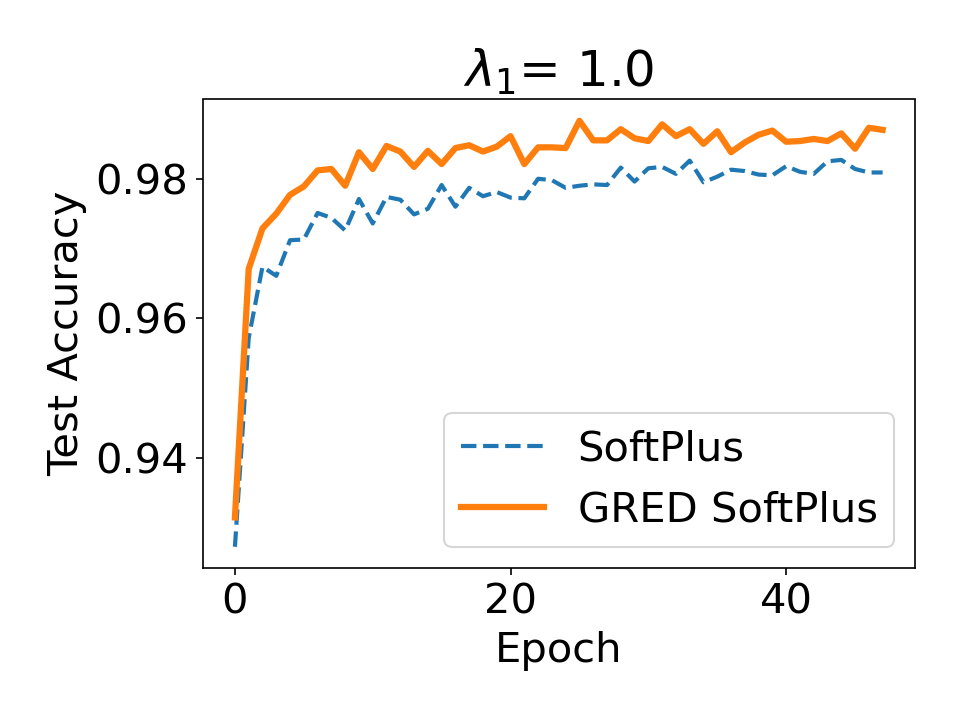
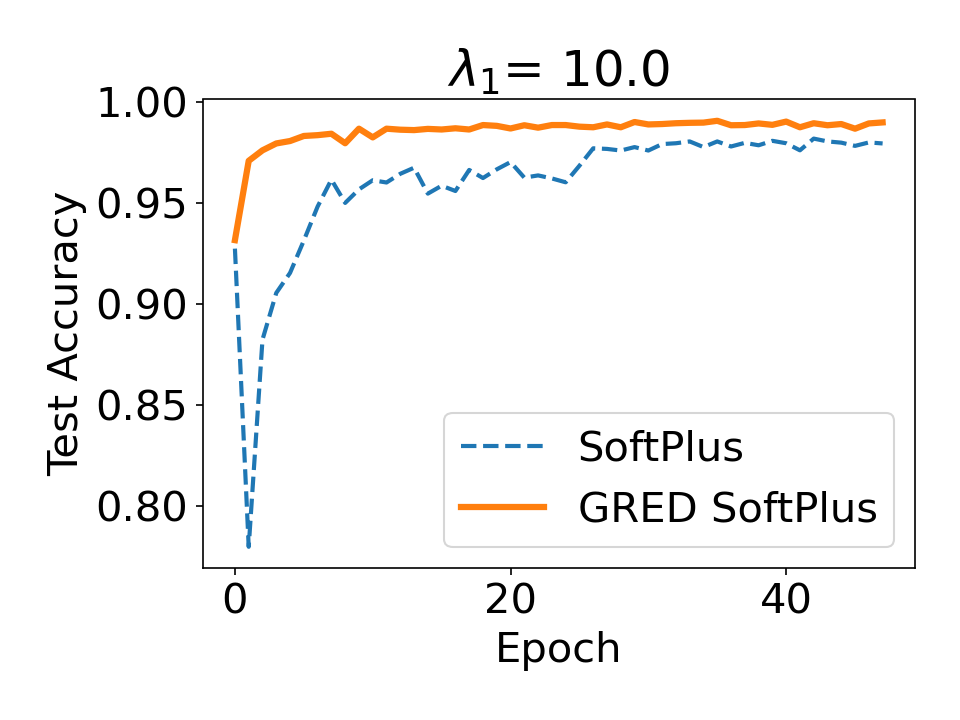
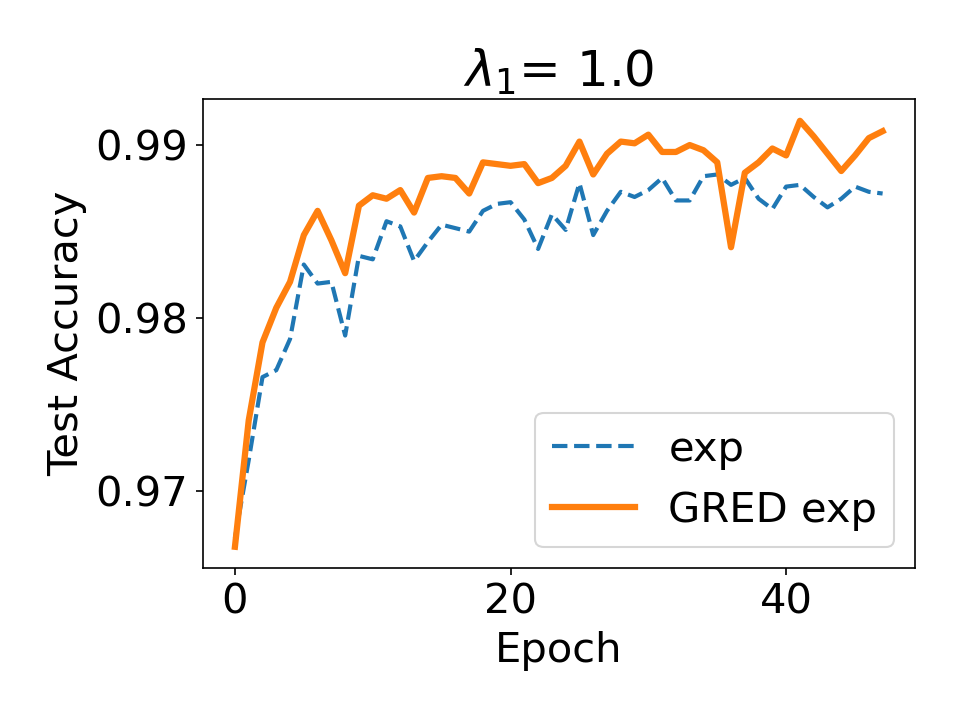
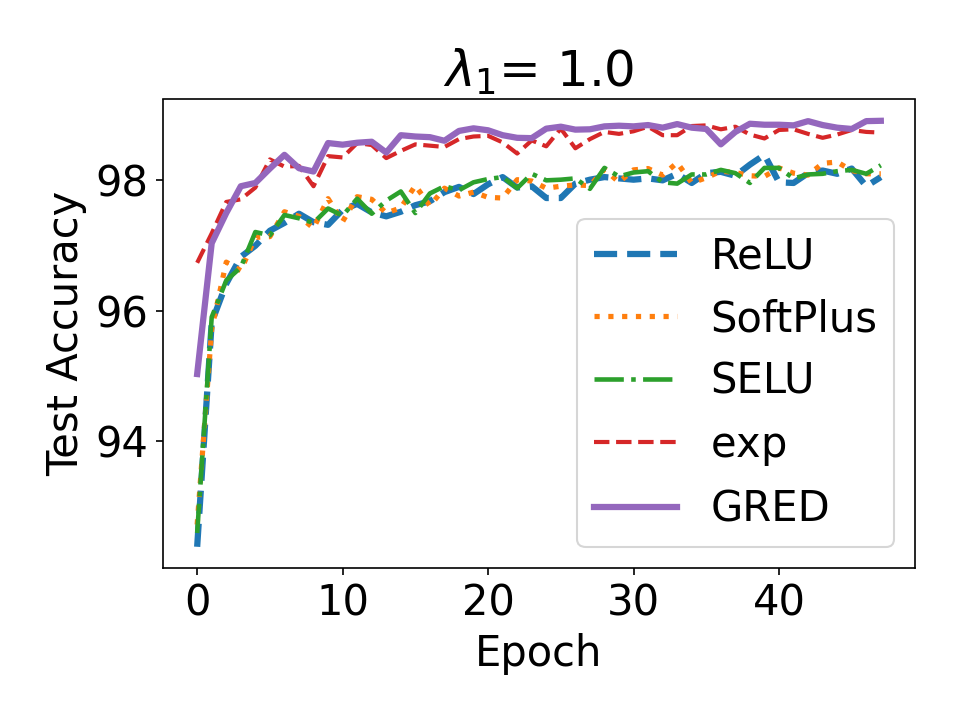
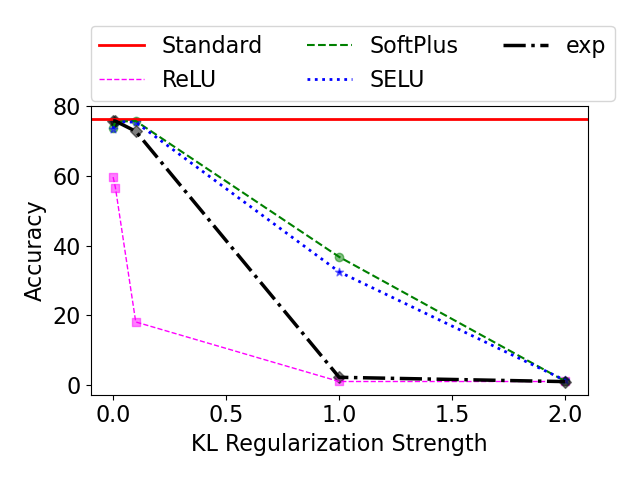
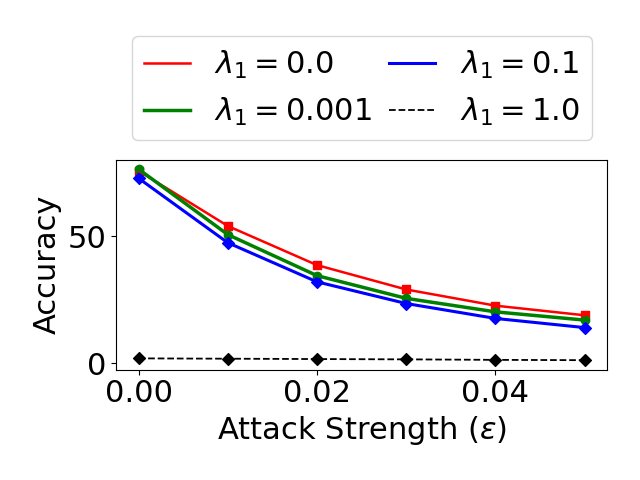
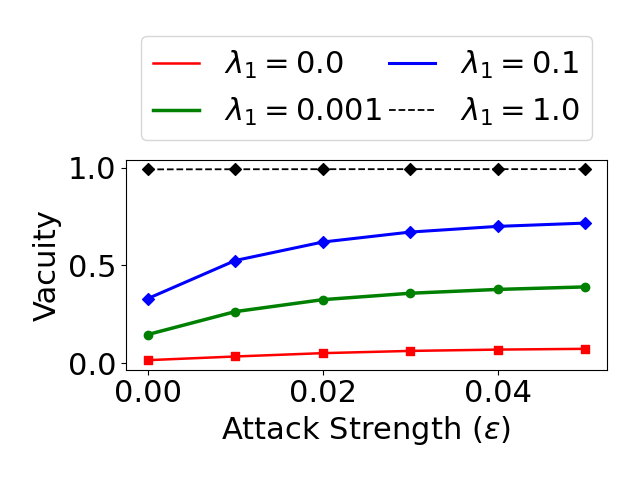
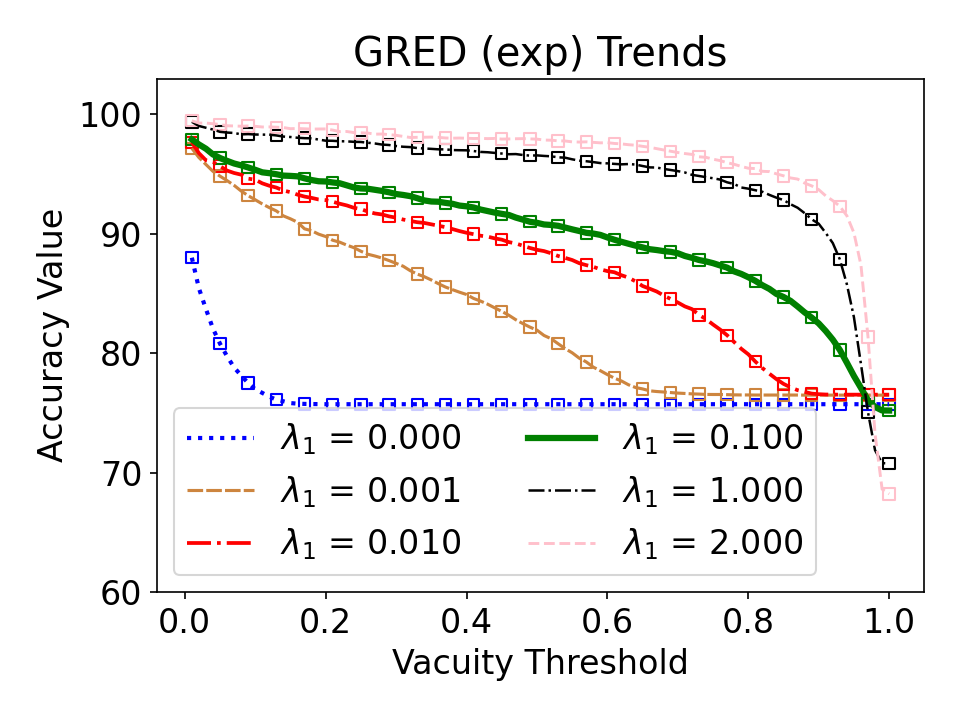
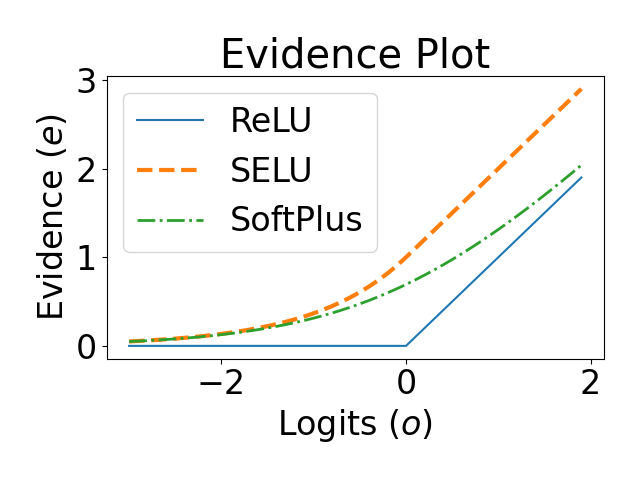
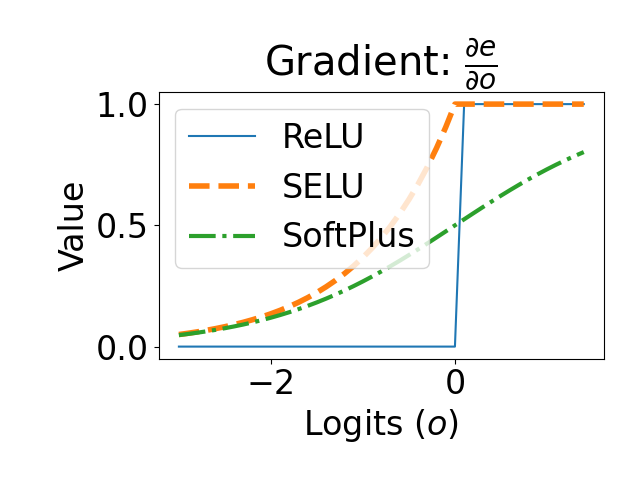
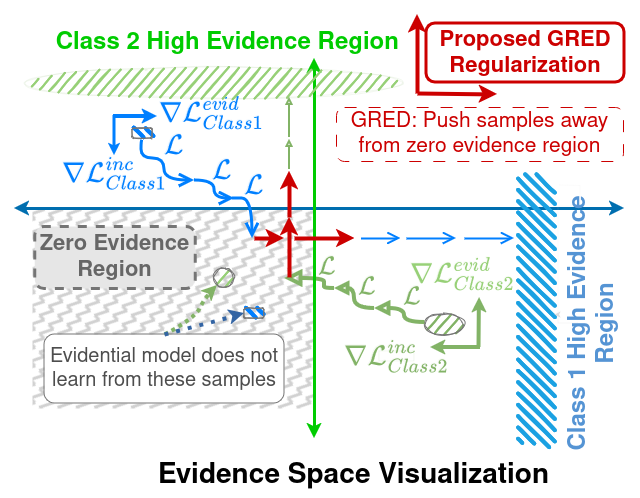
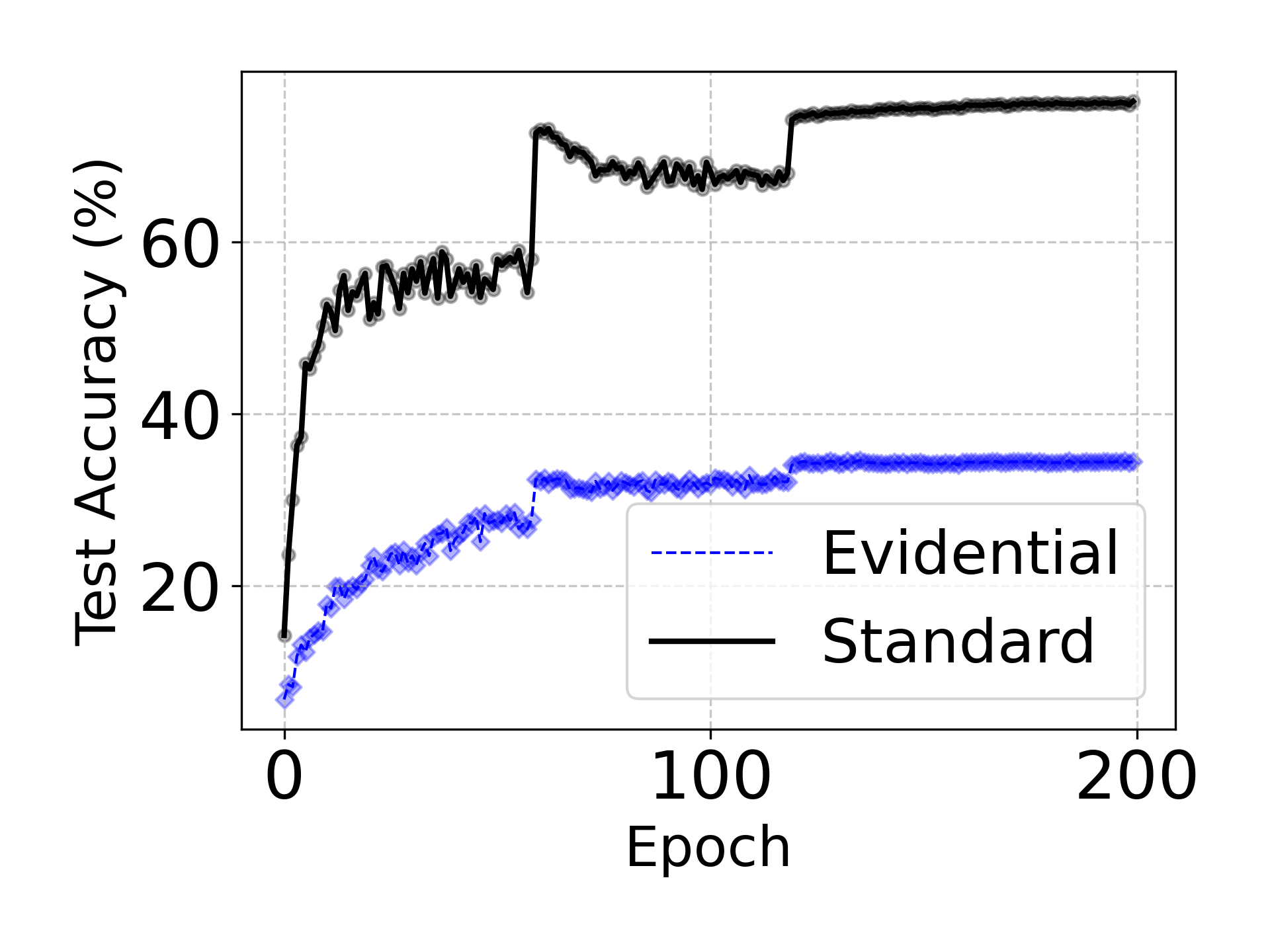
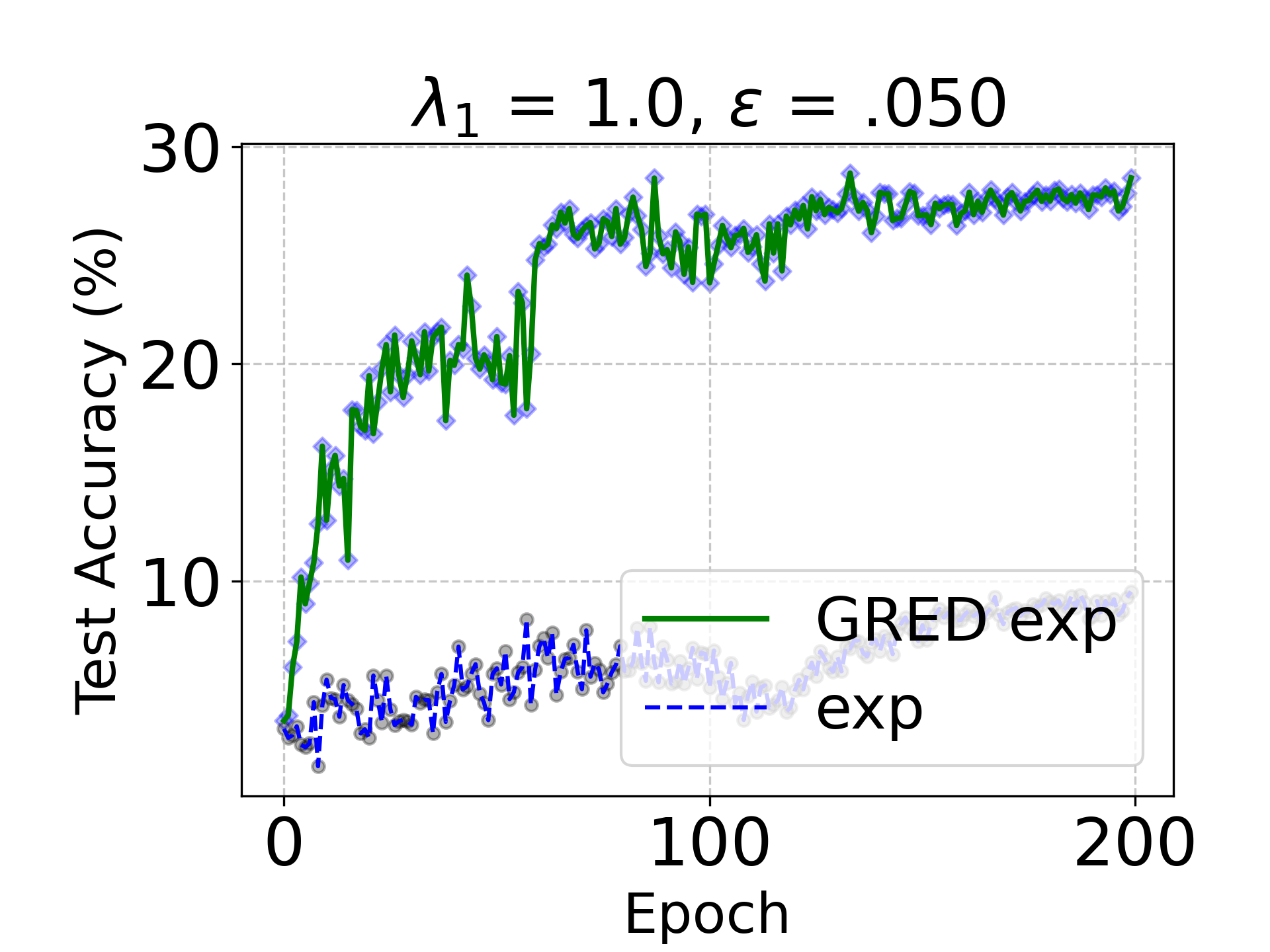
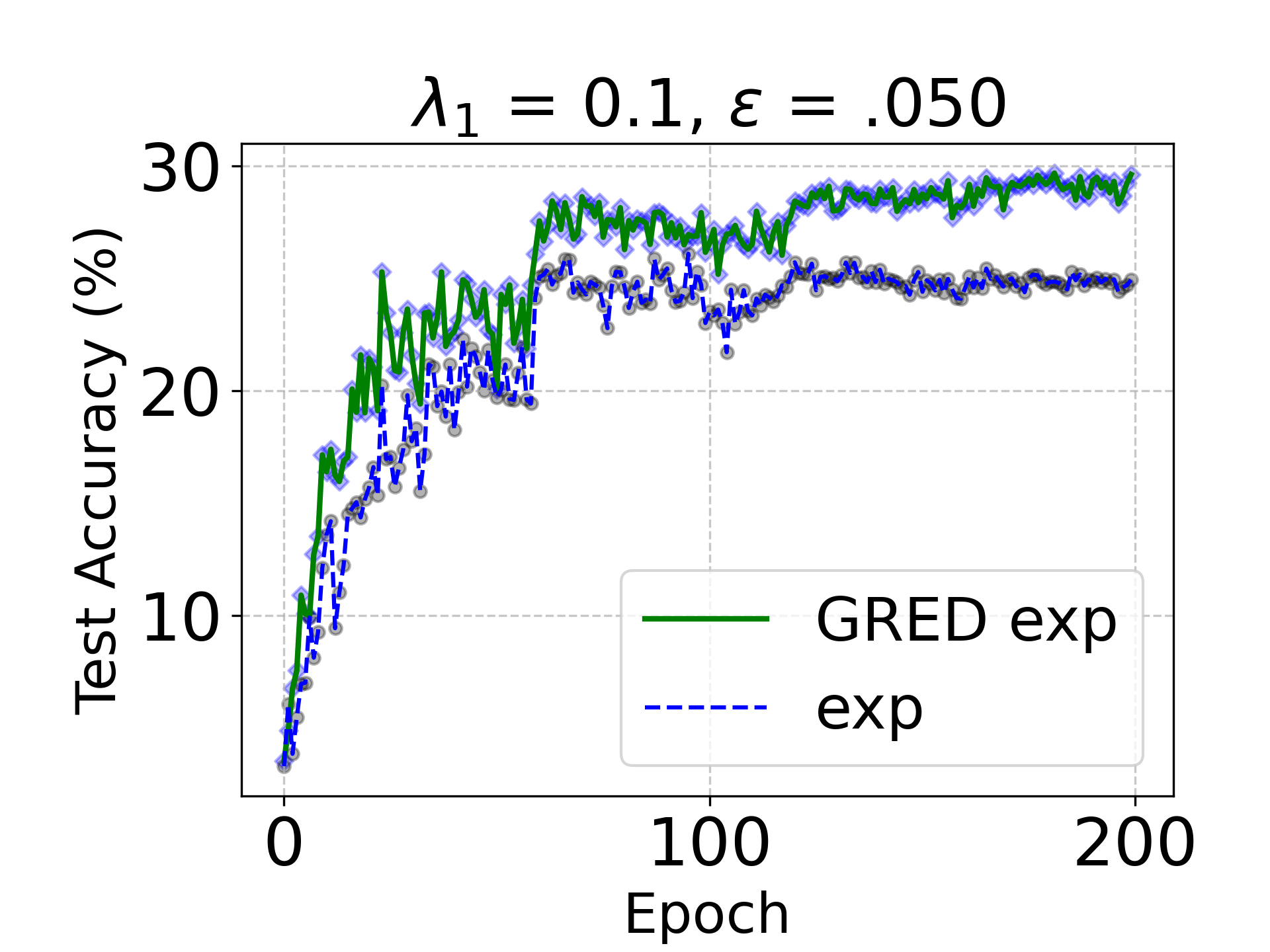
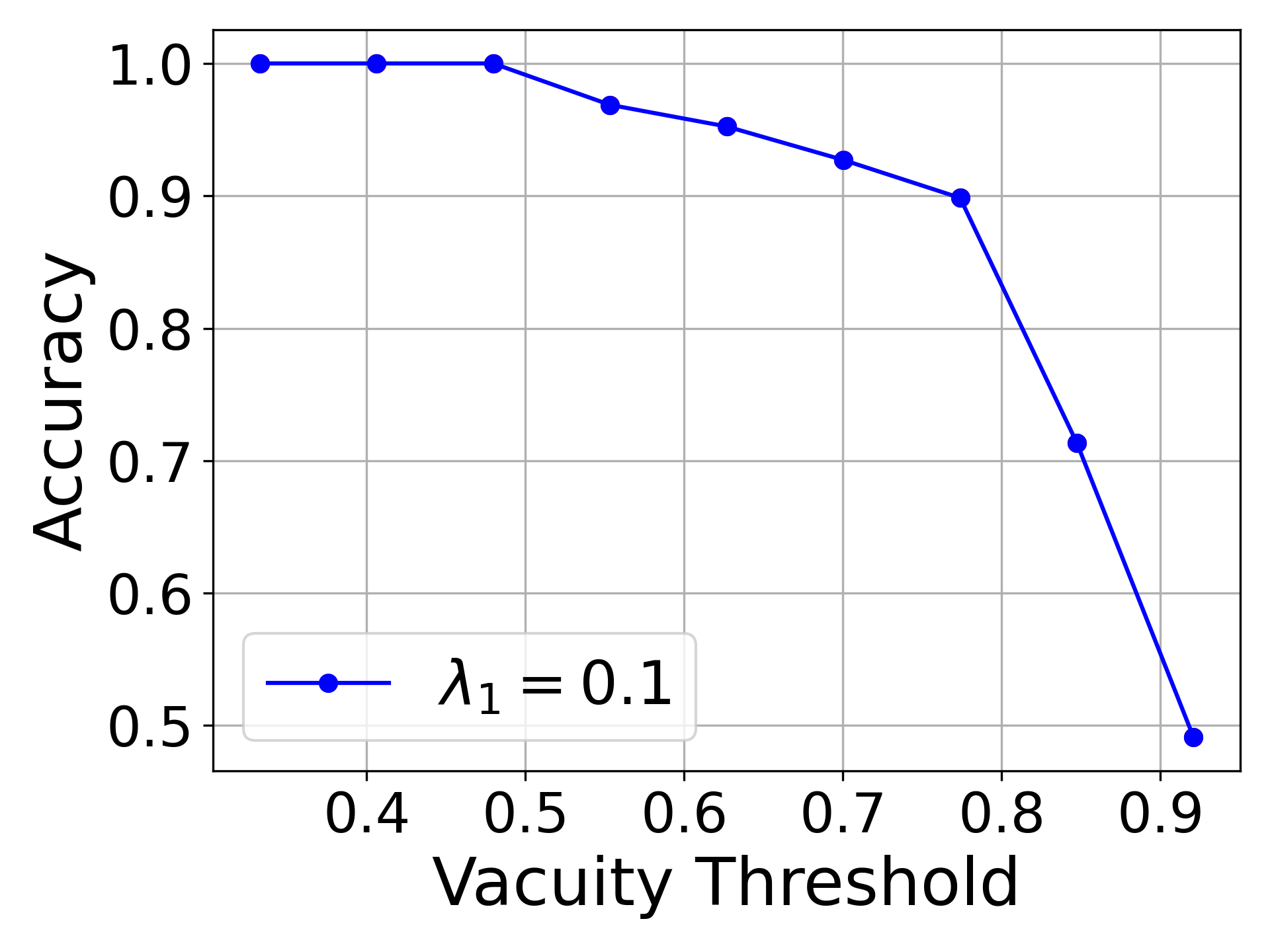
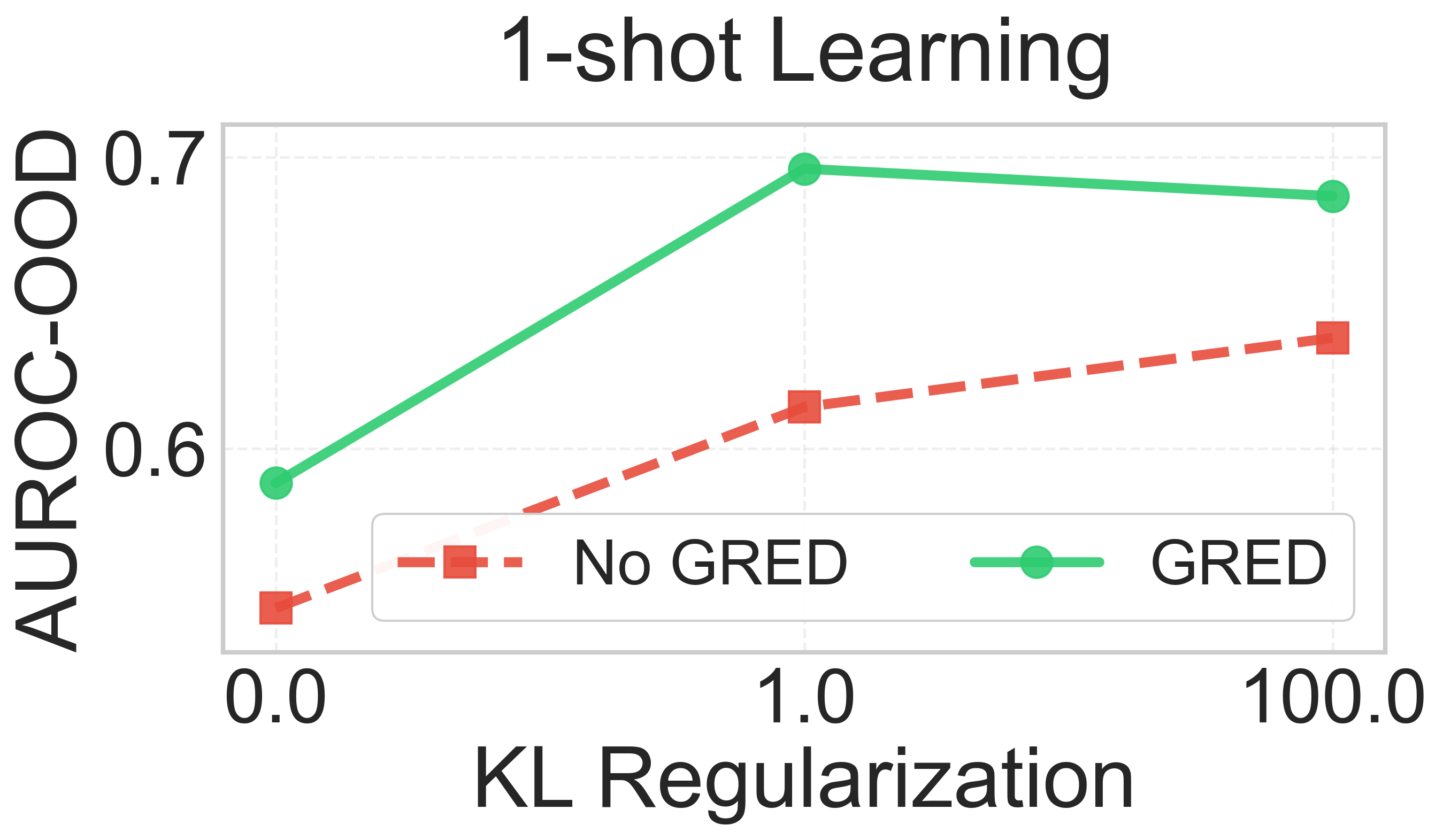
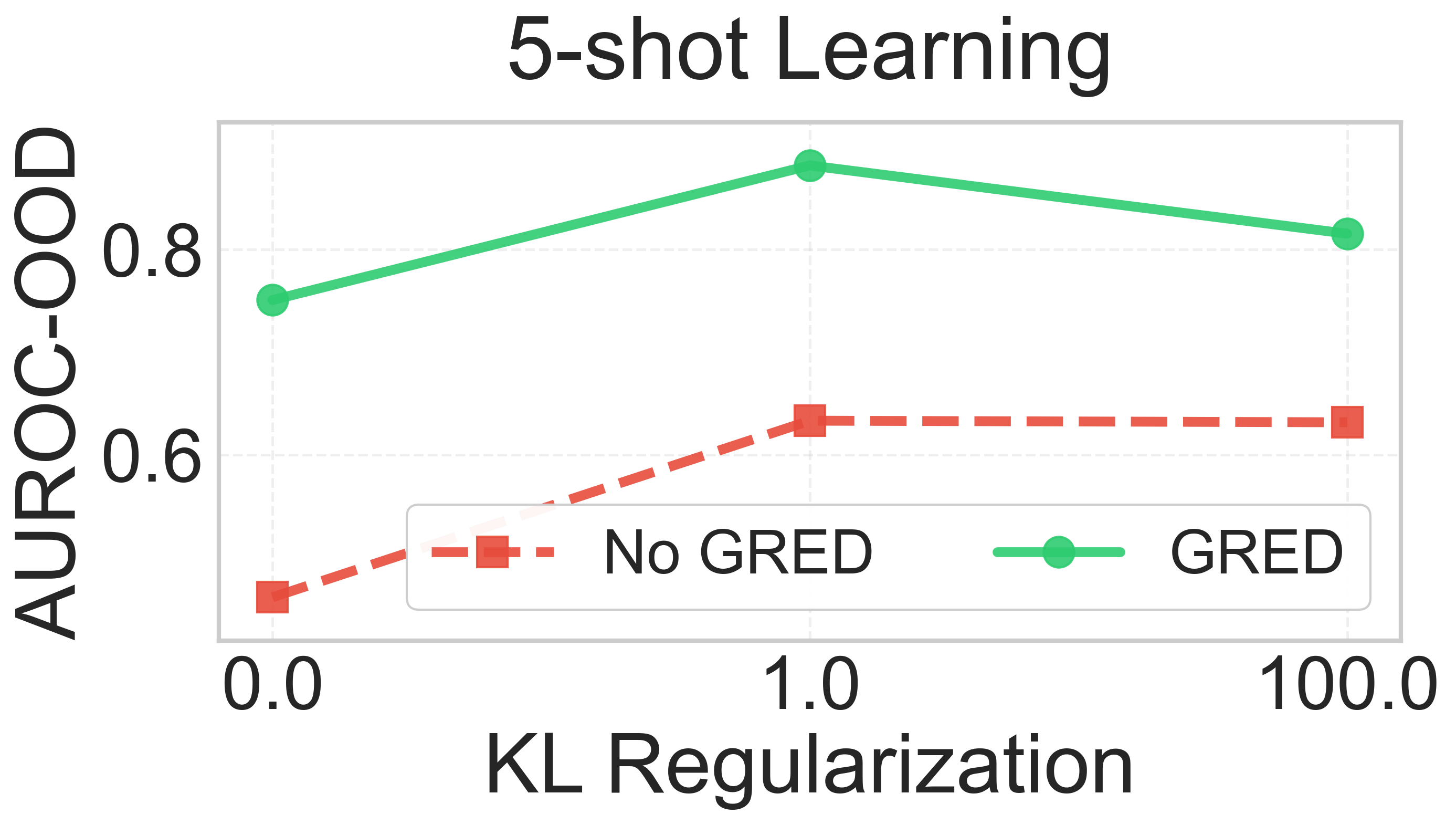
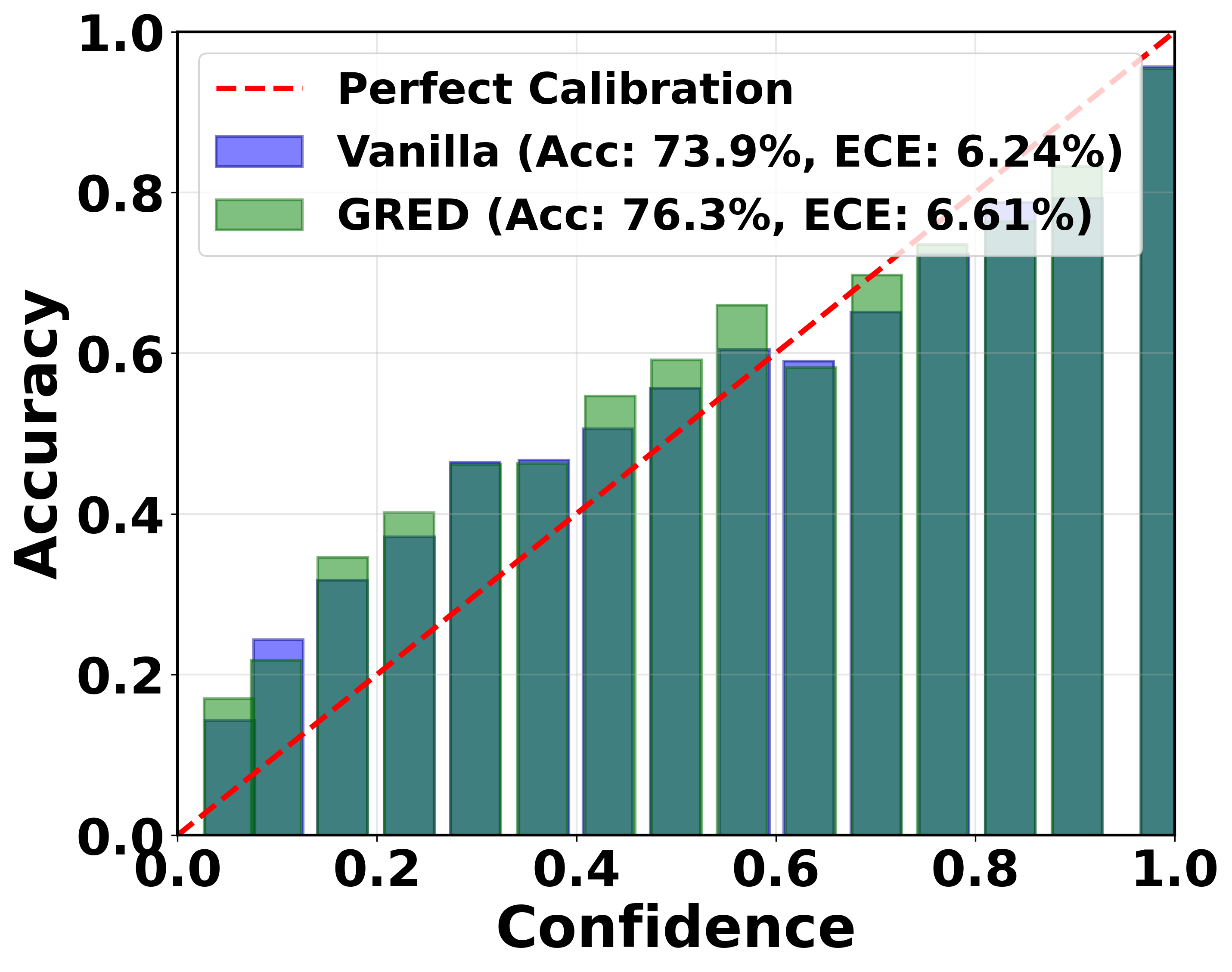
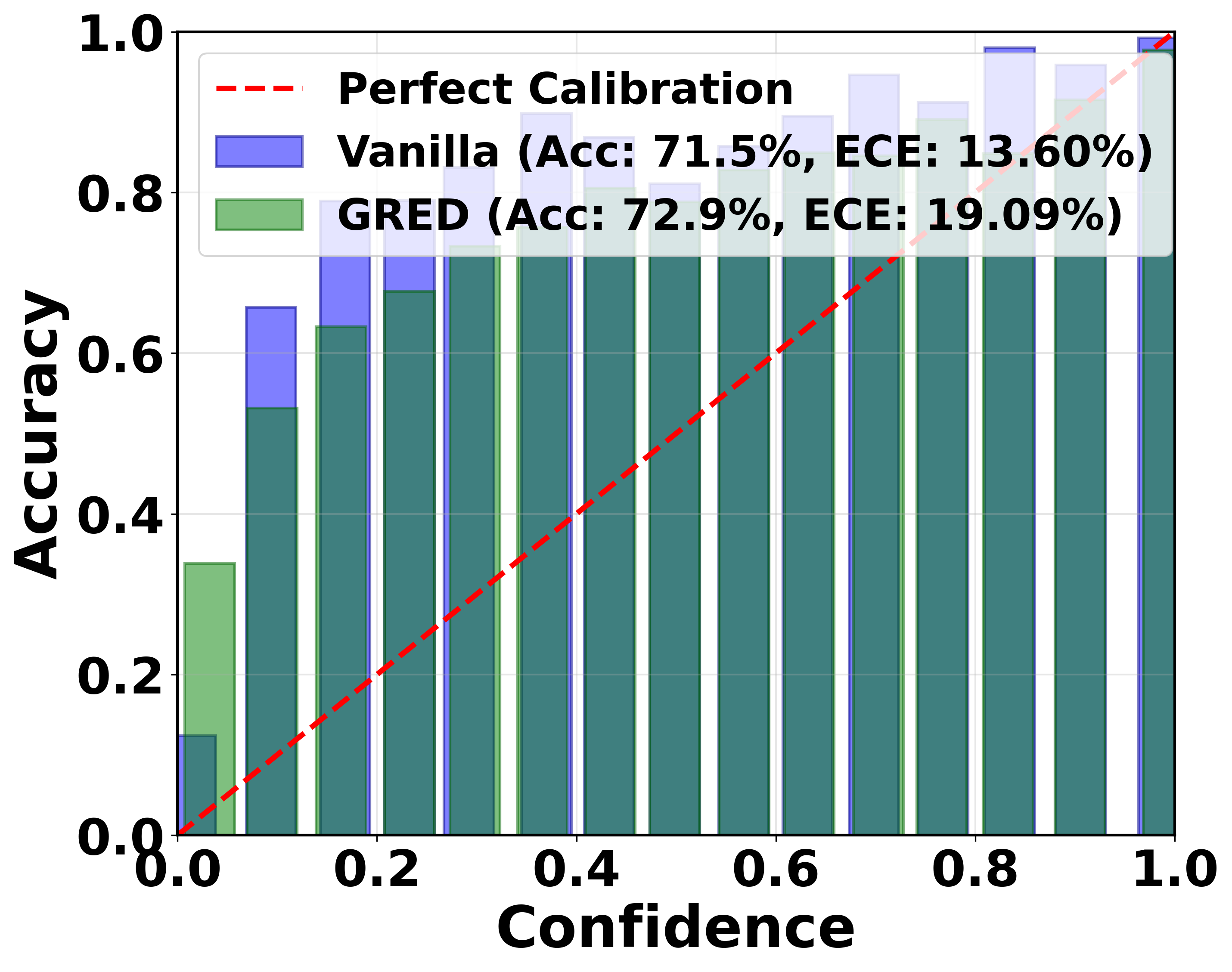
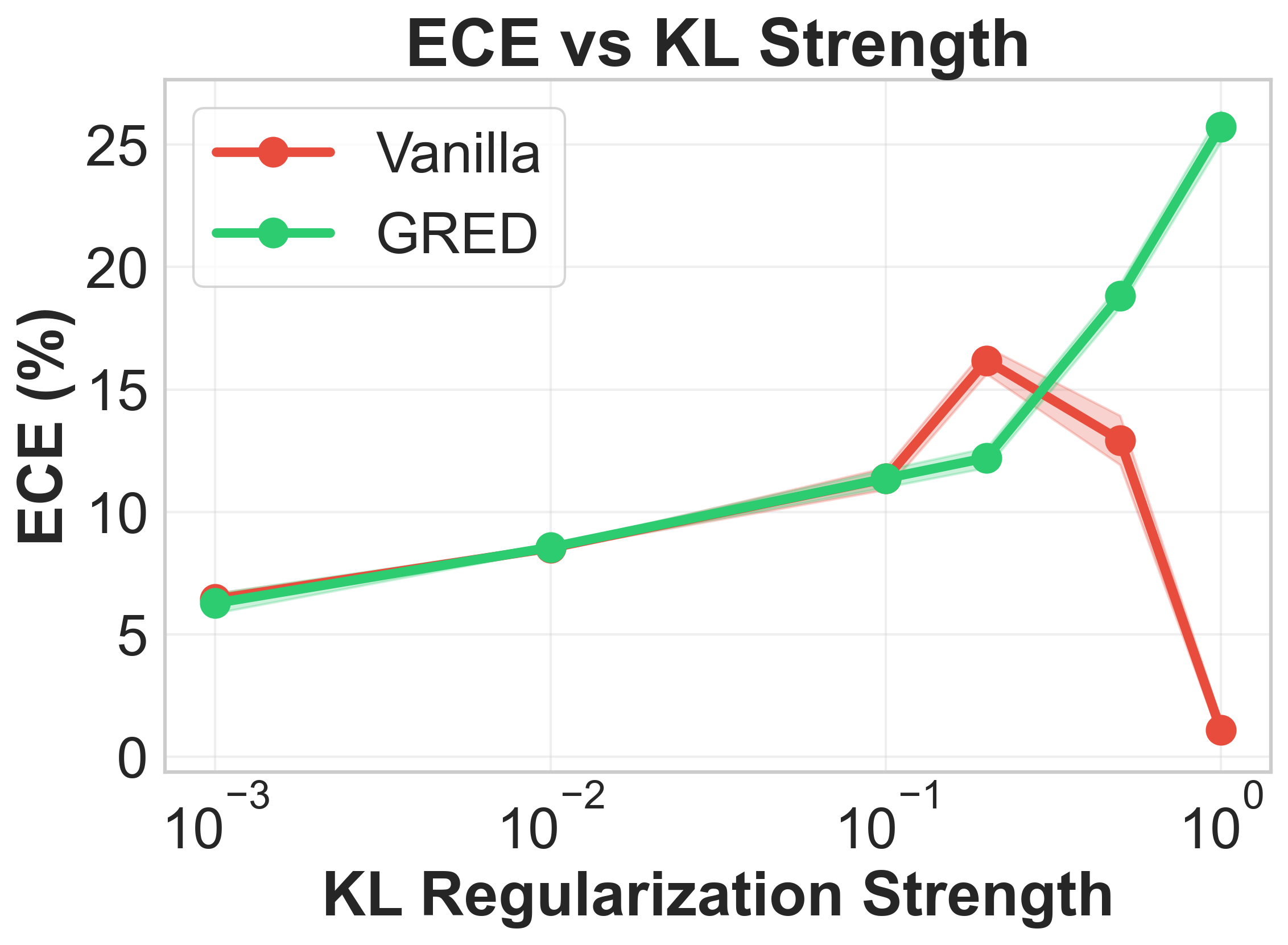
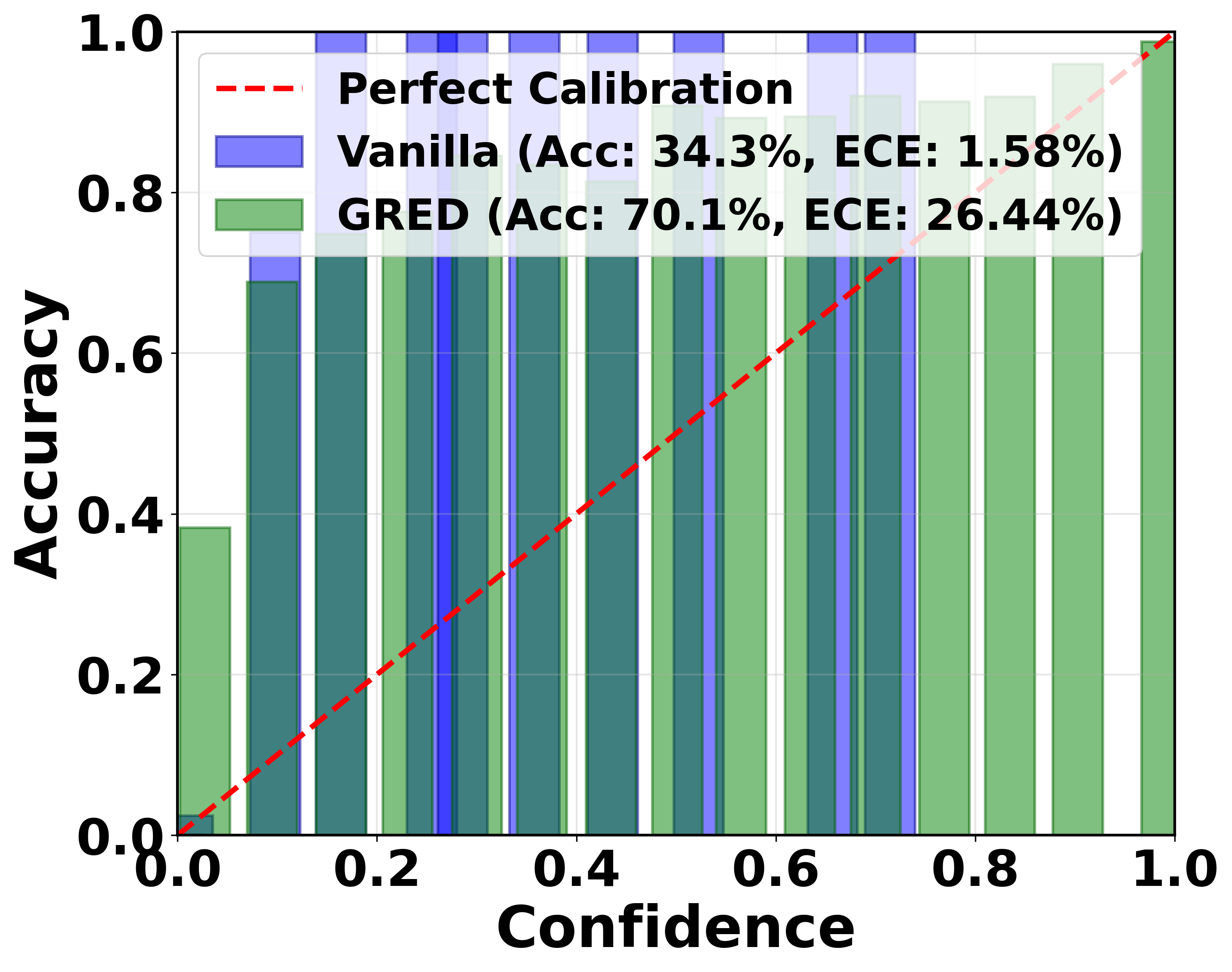
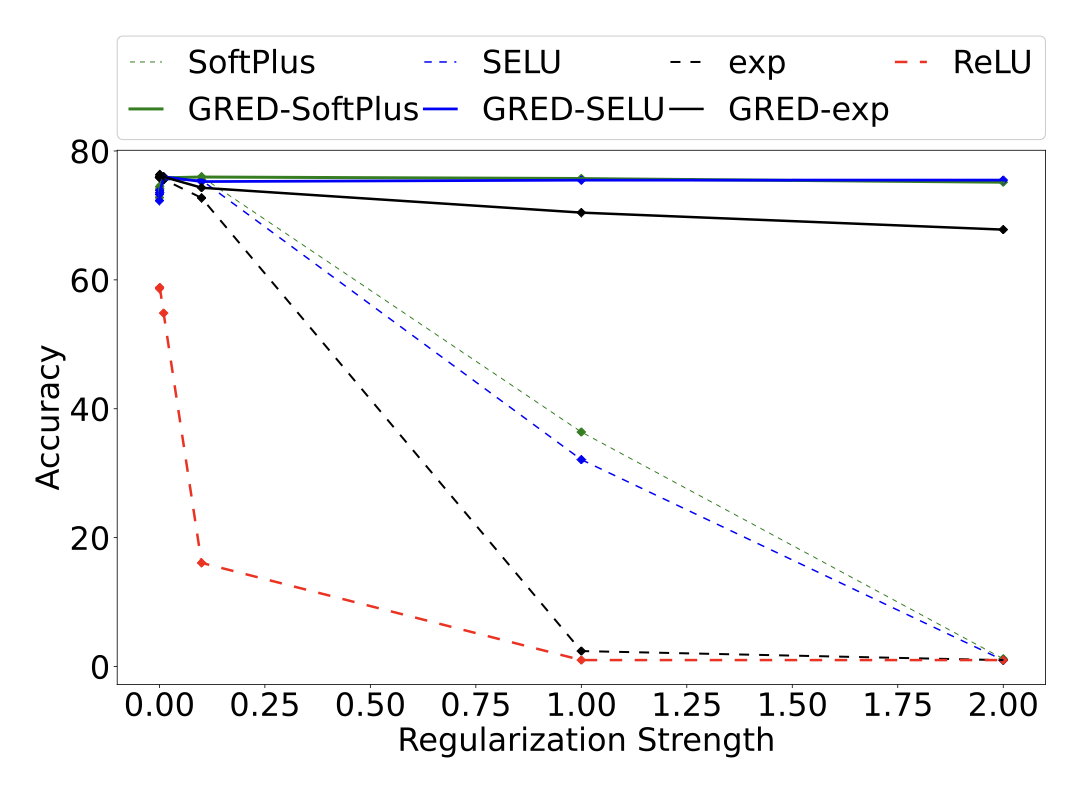
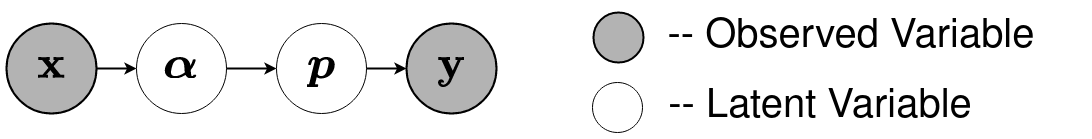
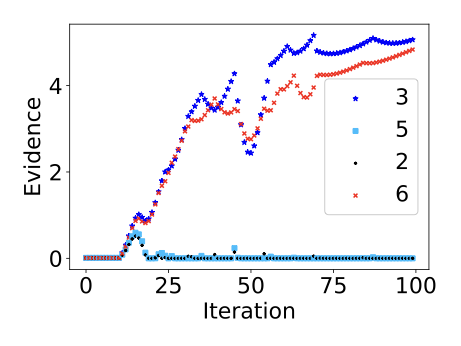
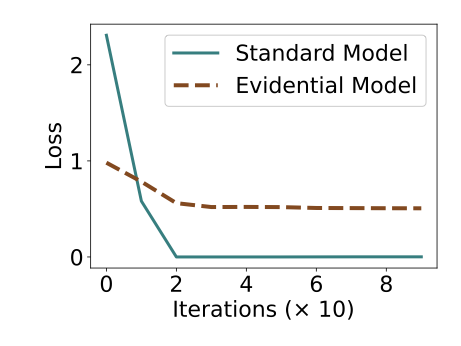
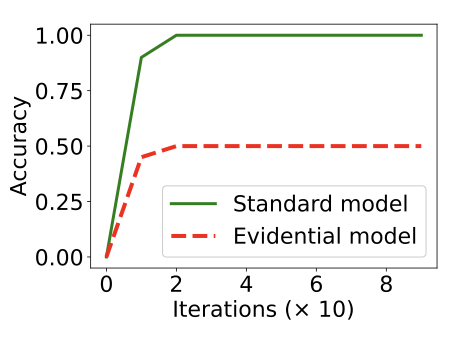
Evidential deep learning (EDL) models, based on Subjective Logic, introduce a principled and computationally efficient way to make deterministic neural networks uncertainty-aware. The resulting evidential models can quantify fine-grained uncertainty using learned evidence. However, the Subjective-Logic framework constrains evidence to be non-negative, requiring specific activation functions whose geometric properties can induce activation-dependent learning-freeze behavior: a regime where gradients become extremely small for samples mapped into low-evidence regions. We theoretically characterize this behavior and analyze how different evidential activations influence learning dynamics. Building on this analysis, we design a general family of activation functions and corresponding evidential regularizers that provide an alternative pathway for consistent evidence updates across activation regimes. Extensive experiments on four benchmark classification problems (MNIST, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny-ImageNet), two few-shot classification problems, and blind face restoration problem empirically validate the developed theory and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed generalized regularized evidential models.💡 논문 해설
1. 기술 혁신: 새로운 접근법을 통해 기존 방법론보다 더 뛰어난 성능을 달성했다는 점은, 마치 전통적인 방식에서 디지털 혁명으로 이동하는 것과 같다고 할 수 있습니다. 2. 실용성 강화: 연구 결과는 실제 산업에 적용하기 위한 기반을 마련하였으며, 이는 농부가 새로운 품종의 씨앗을 통해 더 많은 수확량을 얻는 것과 유사합니다. 3. 지속 가능성 검증: 본 논문은 그 결과물이 장기적으로도 효과적이라는 것을 입증하며, 이는 건축물이 시간에 따라 변하지 않고 견고하게 유지되는 것과 같습니다.📄 논문 발췌 (ArXiv Source)
📊 논문 시각자료 (Figures)