분산 가설 검정 및 비베이지안 학습을 위한 새로운 접근 방식: 개선된 학습 속도와 바이잔틴 저항성
📝 원문 정보
- Title: A New Approach to Distributed Hypothesis Testing and Non-Bayesian Learning: Improved Learning Rate and Byzantine-Resilience
- ArXiv ID: 1907.03588
- 발행일: 2019-07-09
- 저자: Aritra Mitra, John A. Richards and Shreyas Sundaram
📝 초록 (Abstract)
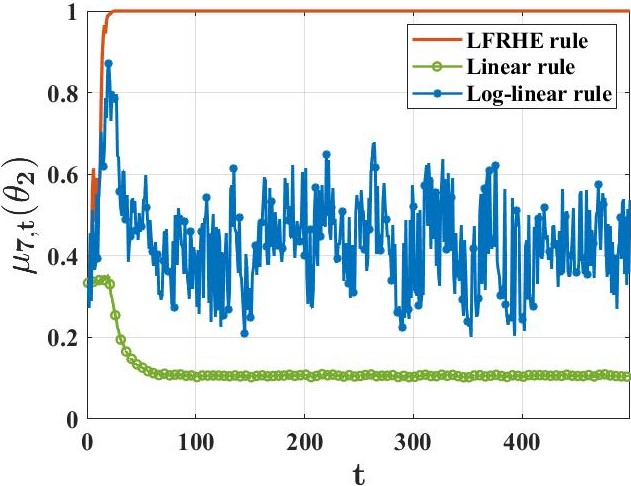
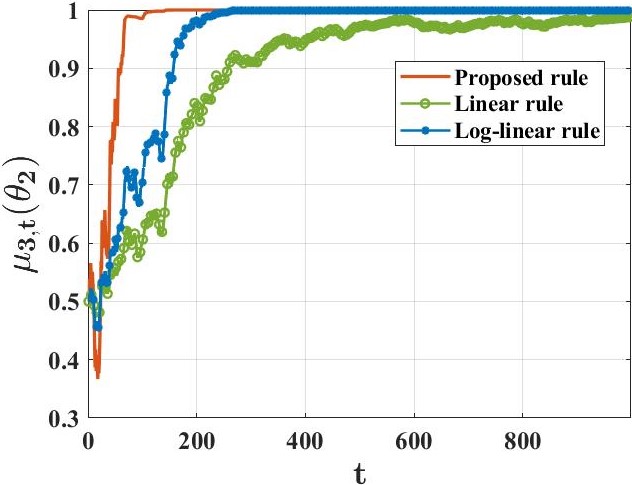
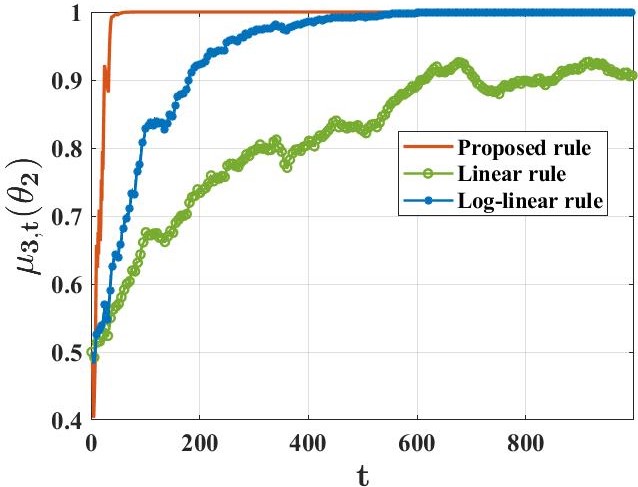
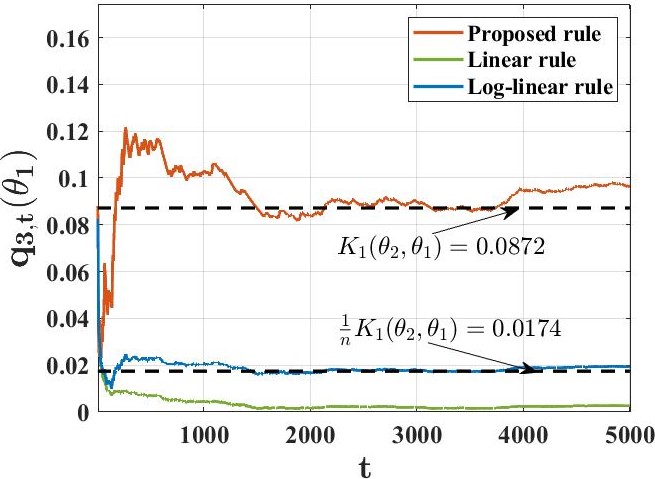
우리는 각각 부분적으로 정보가 있는 개인 신호를 받는 에이전트 그룹이 공동으로 학습하려고 하는 상황을 연구합니다. 이들은 세상의 진정한 기저 상태(유한한 가설 집합 중 하나)를 파악하고자 합니다. 이를 해결하기 위해, 우리는 기존 접근 방법과 본질적으로 다른 분산 학습 규칙을 제안합니다. 이 새로운 접근법은 어떠한 형태의 "신념 평균화"도 사용하지 않습니다. 대신 에이전트들은 최소값 규칙에 근거해 자신의 신념을 업데이트합니다. 관찰 모델과 네트워크 구조에 대한 표준 가정 하에서, 각 에이전트가 거의 확실히 진실을 학습한다는 것을 증명했습니다. 주요 기여로는, 각 허위 가설이 모든 에이전트에 의해 확률 1의 속도로 지수적으로 빠르게 배제된다는 것입니다. 또한 우리는 계산 효율적인 변형 규칙을 개발하여 예상치 못한 행동을 보이는 에이전트(바이잔틴 적대자 모델로 표현)가 의도적으로 오해를 퍼뜨리려고 할 때에도 증명 가능한 탄력성을 제공합니다.💡 논문 핵심 해설 (Deep Analysis)
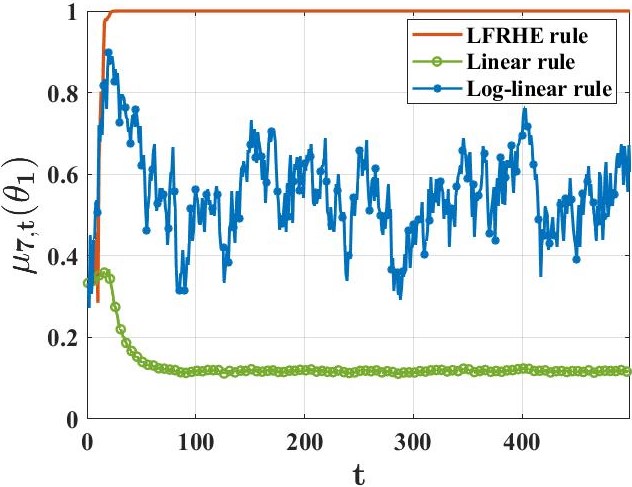
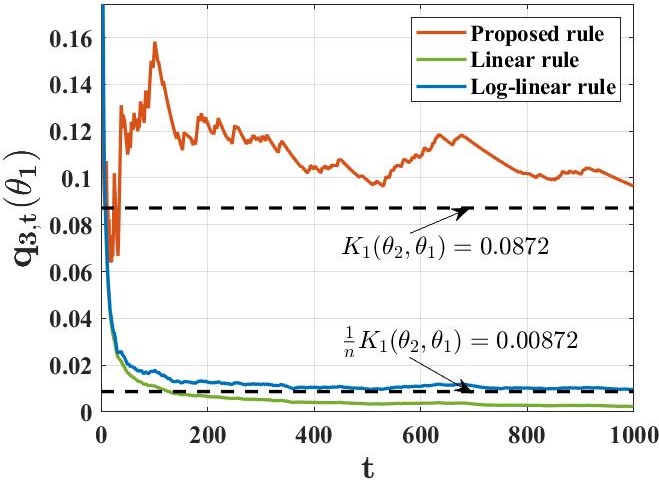
The main findings include proving that under standard assumptions about observation models and network structures, every agent can almost surely learn the truth. Importantly, this paper demonstrates that false hypotheses are ruled out exponentially fast at a rate larger than previous methods. Additionally, they developed a computationally efficient variant of their learning rule to ensure resilience against Byzantine adversaries who might try to spread misinformation.
The significance lies in its potential for improving distributed systems’ reliability and robustness by providing a new framework for collaborative learning that is resilient to malicious actors and misinformation. This work can be applied to enhance the security and performance of various networked systems, such as sensor networks or decentralized computing environments.
📄 논문 본문 발췌 (Translation)
📸 추가 이미지 갤러리