
A Well-Behaved Alternative to the Modularity Index
This paper reviews the modularity index and suggests an alternative index of the quality of a division of a network into subsets.
All posts under category "Computer Science / Social Networks"

This paper reviews the modularity index and suggests an alternative index of the quality of a division of a network into subsets.

We propose evolution rules of the multiagent network and determine statistical patterns in life cycle of agents - information messages. The main discussed statistical pattern is connected with the number of likes and reposts for a message. This distribution corresponds to Weibull distribution accord

Previous studies have shown that Twitter users have biases to tweet from certain locations, locational bias, and during certain hours, temporal bias. We used three years of geolocated Twitter Data to quantify these biases and test our central hypothesis that Twitter users biases are consistent acros

The paper provides a agent-based model, which describes distribution of informative messages, containing links to informational resources in the Internet. The results of modeling have been confirmed by studying a real network of Twitter microblogs. The paper describes stages of building a corporate

This is a natural generalization of the previous work by Dan, 'Modeling and Simulation of Diffusion Phenomena on Social Networks,' to appear in The proceedings of 2011 Third International Conference on Computer Modeling and Simulation. In this paper, we consider the diffusion phenomena of personal o

The suggested methodic is the way of formatting the subject areas models and co-authors networks by sounding the content networks. The paper represents the notion networks which match tags and authors of Google Scholar Citations service. Models depicted in the work were built for the physical optics

We proposed a new model, which capture the main difference between information and opinion spreading. In information spreading additional exposure to certain information has a small effect. Contrary, when an actor is exposed to 2 opinioned actors the probability to adopt the opinion is significant h

In this letter, we study some evolution networks that grow with linear preferential attachment. Based upon some recent results on the quotient Gamma function, we give a rigorous proof of the asymptotic Mandelbrot law for the degree distribution $p_k propto (k + c)^{-gamma}$ in certain conditions. We
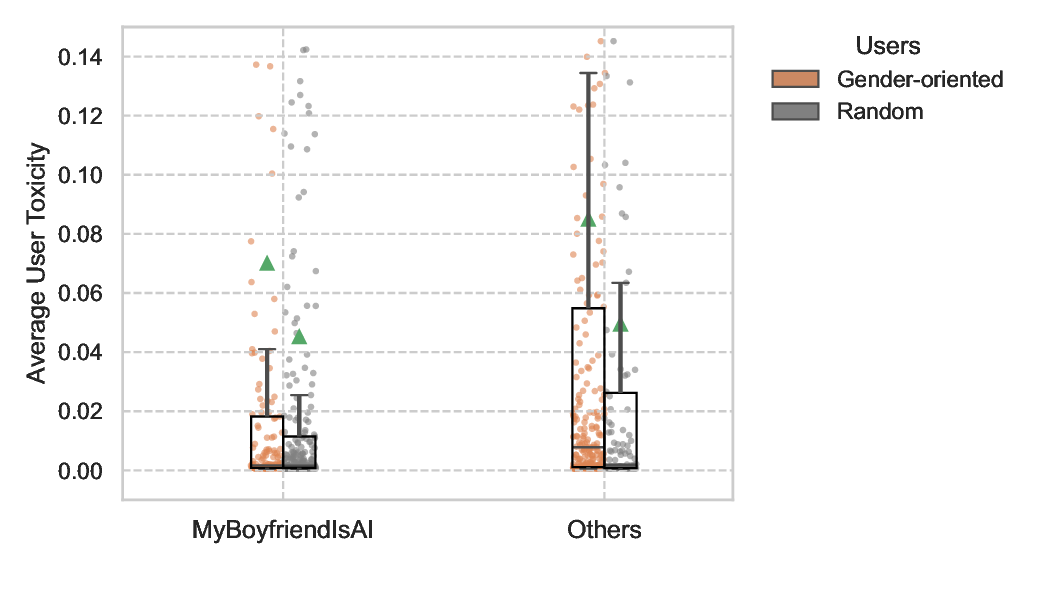
AI-companionship platforms are rapidly reshaping how people form emotional, romantic, and parasocial bonds with nonhuman agents, raising new questions about how these relationships intersect with gendered online behavior and exposure to harmful content. Focusing on the MyBoyfriendIsAI (MBIA) subredd

A comment on 'Neurophysiological dynamics of phrase-structure building during sentence processing' by Nelson et al (2017), Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 114(18), E3669-E3678.

Online Social Networks (OSN) during last years acquired a huge and increasing popularity as one of the most important emerging Web phenomena, deeply modifying the behavior of users and contributing to build a solid substrate of connections and relationships among people using the Web. In this prelim

Real-world creative processes ranging from art to science rely on social feedback-loops between selection and creation. Yet, the effects of popularity feedback on collective creativity remain poorly understood. We investigate how popularity ratings influence cultural dynamics in a large-scale online

This article investigates the causal antecedents of conflictual language and the geometry of interaction in online threaded conversations related to climate change. We employ three annotation dimensions, inferred through LLM prompting and averaging, to capture complementary aspects of discursive con

In this paper we explore a connection between two seemingly different problems from two different domains: the small-set expansion problem studied in unique games conjecture, and a popular community finding approach for social networks known as the modularity clustering approach. We show that a sub-

The entities of real-world networks are connected via different types of connections (i.e. layers). The task of link prediction in multiplex networks is about finding missing connections based on both intra-layer and inter-layer correlations. Our observations confirm that that in a wide range of rea

The methodology of automatic detection of the event basis of information operations, reflected in thematic information flows, is described. The presented methodology is based on the technologies for identifying information operations, the formation of the terminological basis of the subject area, th

With a view towards understanding why undesirable outcomes often arise in ICT projects, we draw attention to three aspects in this essay. First, we present several examples to show that incorporating an ethical framework in the design of an ICT system is not sufficient in itself, and that ethics nee

Breakthrough discoveries and inventions involve unexpected combinations of contents including problems, methods, and natural entities, and also diverse contexts such as journals, subfields, and conferences. Drawing on data from tens of millions of research papers, patents, and researchers, we constr

We analyse the large-scale structure of the journal citation network built from information contained in the Thomson-Reuters Journal Citation Reports. To this end, we take advantage of the network science paraphernalia and explore network properties like density, percolation robustness, average and

State-sponsored 'bad actors' increasingly weaponize social media platforms to launch cyberattacks and disinformation campaigns during elections. Social media companies, due to their rapid growth and scale, struggle to prevent the weaponization of their platforms. This study conducts an automated spe

Social networks are not static but rather constantly evolve in time. One of the elements thought to drive the evolution of social network structure is homophily - the need for individuals to connect with others who are similar to them. In this paper, we study how the spread of a new opinion, idea, o

The purpose of this paper is investigating behaviors of Ad Hoc protocols in Agent-based simulation environments. First we bring brief introduction about agents and Ad Hoc networks. We introduce some agent-based simulation tools like NS-2. Then we focus on two protocols, which are Ad Hoc On-demand Mu

Community detection is one of the most important and interesting issues in social network analysis. In recent years, simultaneous considering of nodes' attributes and topological structures of social networks in the process of community detection has attracted the attentions of many scholars, and th

This article examines the evolution of routing protocols for intermittently connected ad hoc networks and discusses the trend toward social-based routing protocols. A survey of current routing solutions is presented, where routing protocols for opportunistic networks are classified based on the netw

Despite its importance for rumors or innovations propagation, peer-to-peer collaboration, social networking or Marketing, the dynamics of information spreading is not well understood. Since the diffusion depends on the heterogeneous patterns of human behavior and is driven by the participants' decis

Previous work has shown that species interacting in an ecosystem and actors transacting in an economic context may have notable similarities in behavior. However, the specific mechanism that may underlie similarities in nature and human systems has not been analyzed. Building on stochastic food-web

In this paper, we present a novel system named DeepVisInterests that performs the users interests prediction task from social visual data based on a deep neural approach for the ontology construction. A comprehensive statistical study have been made to validate our DeepVisInterests system. The propo

The evolutionary dynamics of the Public Goods game addresses the emergence of cooperation within groups of individuals. However, the Public Goods game on large populations of interconnected individuals has been usually modeled without any knowledge about their group structure. In this paper, by focu

Frigyes Karinthy, in his 1929 short story 'L'aancszemek' ('Chains') suggested that any two persons are distanced by at most six friendship links. (The exact wording of the story is slightly ambiguous: 'He bet us that, using no more than five individuals, one of whom is a personal acquaintance, he co

Social groups are fundamental building blocks of human societies. While our social interactions have always been constrained by geography, it has been impossible, due to practical difficulties, to evaluate the nature of this restriction on social group structure. We construct a social network of ind

Graph based entropy, an index of the diversity of events in their distribution to parts of a co-occurrence graph, is proposed for detecting signs of structural changes in the data that are informative in explaining latent dynamics of consumers behavior. For obtaining graph-based entropy, connected s

The architecture of bipartite networks linking two classes of constituents is affected by the interactions within each class. For the bipartite networks representing the mutualistic relationship between pollinating animals and plants, it has been known that their degree distributions are broad but o

We analyze 26.2 million comments published in Arabic language on Twitter, from July 2014 to January 2015, when ISIS' strength reached its peak and the group was prominently expanding the territorial area under its control. By doing that, we are able to measure the share of support and aversion towar

The heterogeneous structure implies that a very few nodes may play the critical role in maintaining structural and functional properties of a large-scale network. Identifying these vital nodes is one of the most important tasks in network science, which allow us to better conduct successful social a

We analyze the structure and evolution of discussion cascades in four popular websites: Slashdot, Barrapunto, Meneame and Wikipedia. Despite the big heterogeneities between these sites, a preferential attachment (PA) model with bias to the root can capture the temporal evolution of the observed tree

Resolving major societal challenges, such as stagnated economic growth or wasted resources, heavily relies on successful project delivery. However, projects are notoriously hard to deliver successfully, partly due to their interconnected nature which makes them prone to cascading failures. We deploy

Due to the increasingly complex and interconnected nature of global supply chain networks (SCNs), a recent strand of research has applied network science methods to model SCN growth and subsequently analyse various topological features, such as robustness. This paper provides: (1) a comprehensive re

This paper replicates, extends, and refutes conclusions made in a study published in PLoS ONE ('Even Good Bots Fight'), which claimed to identify substantial levels of conflict between automated software agents (or bots) in Wikipedia using purely quantitative methods. By applying an integrative mixe

Background: We study mechanisms underlying the collective emotional behavior of Bloggers by using the agent-based modeling and the parameters inferred from the related empirical data. Methodology/Principal Findings: A bipartite network of emotional agents and posts evolves through the addition of

Understanding the principles of consensus in communities and finding ways to optimal solutions beneficial for entire community becomes crucial as the speeds and scales of interaction in modern distributed systems increase. Such systems can be both social and information computer networks that unite

We consider the problem of diffusing information in networks that contain malicious nodes. We assume that each normal node in the network has no knowledge of the network topology other than an upper bound on the number of malicious nodes in its neighborhood. We introduce a topological property known

Massive content about user's social, personal and professional life stored on Online Social Networks (OSNs) has attracted not only the attention of researchers and social analysts but also the cyber criminals. These cyber criminals penetrate illegally into an OSN by establishing fake profiles or by

Predicting the occurrence of links is a fundamental problem in networks. In the link prediction problem we are given a snapshot of a network and would like to infer which interactions among existing members are likely to occur in the near future or which existing interactions are we missing. Althoug

Recent studies have shown strong correlation between social networking data and national influenza rates. We expanded upon this success to develop an automated text mining system that classifies Twitter messages in real time into six syndromic categories based on key terms from a public health ontol

What is the state of the research on crowdsourcing for policy making? This article begins to answer this question by collecting, categorizing, and situating an extensive body of the extant research investigating policy crowdsourcing, within a new framework built on fundamental typologies from each f

In this research, we investigate the impact of delegating decision making to information technology (IT) on an important human decision bias - the sunk cost effect. To address our research question, we use a unique and very rich dataset containing actual market transaction data for approximately 7,0

We propose an adaptive diffusion mechanism to optimize a global cost function in a distributed manner over a network of nodes. The cost function is assumed to consist of a collection of individual components. Diffusion adaptation allows the nodes to cooperate and diffuse information in real-time; it

In many real-world situations, different and often opposite opinions, innovations, or products are competing with one another for their social influence in a networked society. In this paper, we study competitive influence propagation in social networks under the competitive linear threshold (CLT) m

We analyze properties of apportionment functions in context of the problem of allocating seats in the European Parliament. Necessary and sufficient conditions for apportionment functions are investigated. Some exemplary families of apportionment functions are specified and the corresponding partitio

Besides the need for a better understanding of networks, there is a need for prescriptive models and tools to specify requirements concerning networks and their associated graph representations. We propose class-based graphs as a means to specify requirements concerning object-based graphs. Various
Enter keywords to search articles